Using the Dashboard
The Dashboard is shown when the Home tab is clicked. It is the first page you see when you log in. You can also customize your Dashboard Views as per requirements. | Profiles (Dashboard Views) selection is available only in the Home tab. List all the custom dashboard views created by the user. 'All Devices' view is the default dashboard view. |
| Bookmarks | Allows you to set a bookmark for the current page, and manage existing bookmarks |
Once the server has started receiving records, the Dashboard dynamically changes to display the current statistics for each device whose log files are analyzed. The Firewall Analyzer dashboard shows the: The Traffic Overview graphs shows protocol-wise distribution of traffic across each device. At one glance, you can see the total traffic generated by each protocol group across each device. You can also drill down from the bars in the graph to see specific protocol usage in the Protocol Usage Report. The Security Overview graphs shows distribution of security events like attack, virus, port scans, etc.. generated across each device. Drill down from the bars in the graph to see the corresponding events generated. | Firewall Analyzer will recognize only those firewall log messages which contains the attribute denoting a port scan. Currently Firewall Analyzer recognizes the attribute denoting a port scan for Fortigate, NetScreen & CheckPoint firewall's alone. |
The Traffic Statistics table, shows the Traffic Overview graph's data in more detail, with specific percentage values of incoming and outgoing traffic per protocol group across each device. The Show bar lets you view the the top 5(default) / 10 / 15 or All protocol groups, captured in the logs across the configured devices. You can click on the Traffic IN, Traffic OUT, and Total Traffic for each protocol group of the configured device to obtain the drill-downs of the traffic. If the 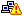 icon is displayed above the table, it indicates that intranet's have not been configured. You need to configure intranet's if you want to separate inbound and outbound firewall traffic. icon is displayed above the table, it indicates that intranet's have not been configured. You need to configure intranet's if you want to separate inbound and outbound firewall traffic. Click the Live Syslog link is provided in Home > Traffic Statistics > Device Name (besides the Firewall device). This will show the live syslogs information for the specific firewall. This will give the live syslog details i.e., Source IP, Destination IP, Port and syslog informations, provided the interfaces (i.e., eth0 etc.) should be open. In Linux the application should be started using root user. You can apply filter on Source IP and Port to get live syslogs received from particular IP/Port. If you click Live Syslog link, the Firewall Analyzer - Syslog Viewer screen pops up. In the screen, on top you will find 'Receiving Syslog Packets. _ packets received' message appears. Below that there is a Capture Filter :option with Host IP Addressand Port. This capture filter will help you to watch the live syslogs from the filtered host and port. In the case, since you clicked from a specific device, the specific Firewall device information is loaded in to it by default. The fields of the syslog packets displayed are: Source,Destination,Port, andMessage.
Click the View Syslog link is provided in Home > Traffic Statistics > Device Name (besides the Proxy device). Ensure that the device has data for the selected calendar time range. This will show the raw syslogs information for the specific proxy device. The traffic values in the table let you drill down to see traffic details for the corresponding protocol group in the Protocol Usage Report. The  Quick Reports link provides you 'quick' access to the top level details of traffic like Top Hosts, Top Destinations, Top Conversations, Top Protocol Groups, Top Firewall Rules, Top VPN Reports, and Top Attack Reports for the corresponding firewall. Quick Reports link provides you 'quick' access to the top level details of traffic like Top Hosts, Top Destinations, Top Conversations, Top Protocol Groups, Top Firewall Rules, Top VPN Reports, and Top Attack Reports for the corresponding firewall. | Quick Reports for Squid Proxies will provide only the following reports: Top Hosts, Top Destinations, and Top Conversations. |
The  icon next to the Unassigned protocol group indicates traffic details for protocols that have not been assigned to any protocol group. Click the icon, and under the View Identifiers tab, you can see the traffic details for each of these unassigned protocols. The Assign Group tab provides you with options to either associate these unknown protocols to the predefined Protocol Groups (and Protocols) or create a new Protocol Group (and Protocol). You can do this by selecting from the listed identifier and assigning it to either the pre-defined Protocol Group (and Protocol) or create a icon next to the Unassigned protocol group indicates traffic details for protocols that have not been assigned to any protocol group. Click the icon, and under the View Identifiers tab, you can see the traffic details for each of these unassigned protocols. The Assign Group tab provides you with options to either associate these unknown protocols to the predefined Protocol Groups (and Protocols) or create a new Protocol Group (and Protocol). You can do this by selecting from the listed identifier and assigning it to either the pre-defined Protocol Group (and Protocol) or create a  new protocol group (and new Protocol). new protocol group (and new Protocol). Multiple Selection enables you to assign multiple identifiers to a particular protocol group (and protocol). Single selection enables you to assign each of the individual identifier to a particular protocol group (and protocol). The Security Statistics table, shows the Security Overview graph's data in more detail, along with the distribution of the Configured Alerts. Click the View Syslogs link is provided in Home > Security Statistics > Device Name (besides the Firewall device). Ensure that the device has data for the selected calendar time range. This will show the recent security events for the specific firewall. If you click View Syslogs link, the Recent Security Events screen pops up. In that screen you can view latest Security Events received from device for the time duration <Last 15 Mins, Last 30 Mins, Last 1 Hour, Last 2 Hours, Last 3 Hours, Last 6 Hours>. In the screen, on top you will find Formatted Logs,Raw Logs tabs. You can choose the tabs to view either formatted logs or raw logs. Click  Configure Columns to select the columns to be displayed for the formatted logs The columns are: All Columns, Device, Host, User, Protocol, Destination, Date/Time, Virus/Attack, VPN, Severity, Rule Number/ID, Status, URL, Duration, Description, StartTime. Configure Columns to select the columns to be displayed for the formatted logs The columns are: All Columns, Device, Host, User, Protocol, Destination, Date/Time, Virus/Attack, VPN, Severity, Rule Number/ID, Status, URL, Duration, Description, StartTime. Below that, the number of lines of logs displayed are indicated in the Showing : _ to _ of total _ logs field. The number lines displayed per page is indicated in the View per page : 5 [10] 20 25 50 75 100 250 500 field. Default value is 10. The default columns displayed are: Host, Protocol, Destination, Date/Time, Status, Severity, and Description. You can add or remove columns using Configure Columns icon given above. The Configured Alerts are classified according to the priority as High, Medium, and Low. Clicking on the alert counts against High, Medium, Low, or All Alerts will list you complete details like Alert Profile name, the generated time, the device for which the alert was raised, the alert priority, and the status of the alert. The security statistics table provides you with the counts for Attacks, Virus, Failed Logons, Security Events, Denied Events, Config Changes and Compliance Reports. Attacks: Firewall Analyzer will recognize only those firewall log messages which contains the attribute denoting an attack. Virus: Firewall Analyzer will recognize only those firewall log messages which contains the attribute denoting a virus. | Currently Firewall Analyzer recognizes the attribute denoting a virus for almost all firewall's except Cisco Pix, whose log messages do not contain the attribute denoting a virus. |
Failed Log Ons: Firewall Analyzer will recognize only those firewall log messages which contains the attribute denoting a failed log on. | Currently Firewall Analyzer recognizes the attribute denoting a failed log on for Fortigate, NetScreen, Cisco Pix, & Identiforce firewall's Failed Log Ons are not available for CheckPoint firewall's |
Denied Events: Firewall Analyzer will recognize only those firewall log messages which contains the attribute denoting a denied request. Security Events: The Security Events in Firewall Analyzer are based on the severity attributes Emergency, Alert, Critical, and Error only. | Since Security Events are based on severity attributes, they may also include the other events like port scans, attacks, virus, failed log ons, security events, and denied events. |
Clicking on the counts against each of the above events in the security statistics table will lead you to the corresponding the quick reports for those events. Compliance Reports: The Compliance Reports related to Firewall Rules/Policies Configuration/Changes. Clicking the report opens up with the rules related events. Editing Device DetailsClick the  (for firewall) or (for firewall) or  (for squid) icon next to a device name to change the device's details. You can change the device's display name, up link speed and down link speed. The device name and the vendor type cannot be changed. (for squid) icon next to a device name to change the device's details. You can change the device's display name, up link speed and down link speed. The device name and the vendor type cannot be changed. | Up Link Speed and Down Link Speed determines the % IN Traffic and % OUT traffic. |
Click the  icon to delete the device from the database. You are asked to confirm your choice, after which the device is permanently deleted. icon to delete the device from the database. You are asked to confirm your choice, after which the device is permanently deleted.  | When a device is deleted, all existing data pertaining to that device is permanently deleted from the database. Later if logs are received from that device, the device is added as a new device, and reports are generated. To stop this from happening, you need to configure the device to stop sending logs to Firewall Analyzer. |
SearchDoing a search in Firewall Analyzer UI is easy. Firewall Analyzer offers both a Basic Search and Advanced Search in all the pages of the product. The search results can be saved as report profiles and can also be scheduled to run the search and mail the report profile on an hourly, daily, weekly, monthly or once only basis. But the reports profiles created via search cannot be edited and will not contain graphical representation of data, and drill down facility.  Basic Search, enables you to search for the following : Basic Search, enables you to search for the following :
| Search for | Description |
|---|
| Hosts | Refers to the IP Address or DNS Names which were recorded in the firewall logs
example: 192.168.0.1,web-server | | Protocol Identifiers | Refers to the list of protocols and protocol identifiers that are available in the Protocol Groups page (Settings >> Protocol Groups)
example: 6969/tcp, icmp, IPSec | | User Names | Refers to the authenticated user name required by some firewall's
example: john, kate | | Attack | Refers to the attack name.
examples: UDP Snort, Ip spoof | | Virus | Refers to the Virus name.
examples: JS/Exception, W32/Mitglieder |
|