Endpoint management and compliance:
The duo that can save you millions
April 03 · 8 min read

That's how much your organization could stand to lose with a single weak endpoint. With that kind of money, you could buy over 2,000 MacBooks—each with a one-year subscription to
an antivirus solution.
Let's not forget, the painfully high price of a cyberattack does not include the reputational damage and customer trust you might lose. A study by the Ponemon Institute reveals that 68% of organizations have faced endpoint attacks resulting in compromised data or IT infrastructure. These big figures demand a proactive approach to endpoint management and compliance. This article explores the evolution of our endpoint management practices at Zoho Corporation, highlighting how we've adapted to the changing compliance landscape and regulatory requirements for data privacy.
The evolution of endpoint management in compliance
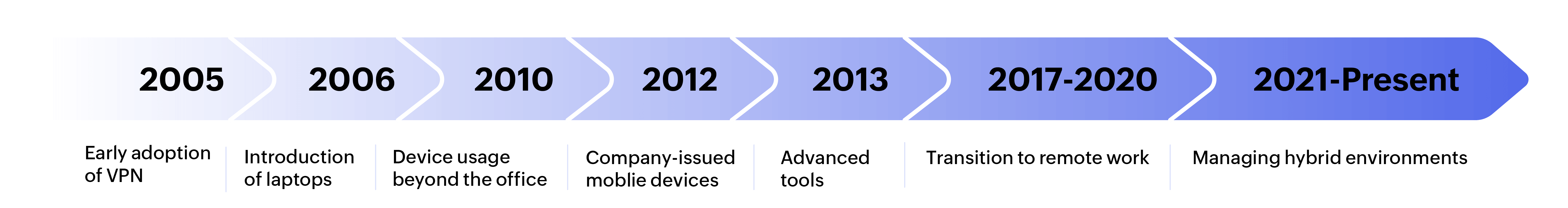
At Zoho Corp., endpoint management practices have evolved over time to address changing regulatory requirements. Here's how our approach has developed:
Year |
Technology landscape |
Our endpoint management
|
| 2005: Early adoption of VPN | Remote access enabled through VPN, with most employees using office-based desktop setups. | Focused on securing on-premises devices with VPN configurations. Limited attention to remote device management or compliance. |
| 2006: Introduction of laptops | Laptops become more common, but desktops still dominate workplace setups. | Implemented policies like "device encryption policy" to secure both desktops and laptops, marking the start of managing endpoint diversity. |
| 2010: Device usage beyond the office | Portable devices make remote work more feasible, with increased laptop usage outside the office. | Introduced remote monitoring to track devices in diverse environments and implemented basic compliance tracking. |
| 2012: Company-issued mobile devices | Rise of 3G networks enables mobile connectivity; employees receive company-owned smartphones and tablets. | Expanded management to include mobile device management (MDM) solutions, ensuring security across a wider range of endpoints. |
| 2013: Advanced tools | The workplace becomes more complex with multiple device types, remote work, and regulatory scrutiny. | Endpoint management tools evolved to centralize control, deploy patches, and ensure compliance across diverse device types. |
| 2017–2020: Transition to remote work | Cloud services adoption accelerates, and the pandemic drives full-scale remote work across all teams. | Integrated advanced compliance tools, automated patching, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) to support widespread remote work securely. |
| 2021–Present Managing hybrid environments | Complex work environments with remote, hybrid, and global teams; increasing regulatory requirements like the GDPR, HIPAA, and the PCI DSS. | Enhanced endpoint management tools with real-time compliance monitoring, proactive threat detection, and adaptive security policies for modern workplaces. |
A key factor in our transformation was the shift to cloud-based endpoint management. It started with a simple need: managing the growing number of devices accessing our network. Traditional on-premises methods fell short as the workforce became more mobile and distributed. The shift to a cloud-based system, powered by the endpoint management agent, closed process gaps and enabled proactive protection. For example, updates and patches previously depended on VPN connections, but employees often connected to the VPN only for specific tasks, creating security vulnerabilities. With the cloud-based system, updates, patches, and compliance policies were automatically pushed to all devices connected to the internet. This eliminated the dependency on VPNs, ensuring that devices—whether in the office or remote—stayed compliant without requiring manual intervention.
However, with this convenience came a new challenge: ensuring secure network connections. If a device connected to an unsecured network, it risked compromising compliance and security. This realization led to policies that mandated secure connections, further safeguarding sensitive data and regulatory adherence.
Zoho Corp.'s efforts
Zoho Corp. has adopted a range of measures to strengthen endpoint management and ensure compliance, addressing the unique challenges of today’s dynamic workplace. Let's explore these initiatives in detail.
1. User privileges and policy changes
The level of control that companies apply depends on their security policies and the degree of freedom they grant employees. At Zoho Corp., employees have a default restricted access level but can request temporary elevated access through a self-service portal.
During privileged access, however, there is an increased risk of weak points being unintentionally exposed. To mitigate this, endpoint management tools must monitor activity and provide real-time visibility into the network. This helps our IT teams ensure that all operations align with compliance requirements while quickly identifying and addressing any potential vulnerabilities.
When introducing new policies—like when we increased the minimum password length from 10 to 12 characters—we begin by assessing their impact. The security, compliance, and endpoint management teams work together to evaluate the necessity of the change. Once the security, compliance, and endpoint management teams conclude that the change is needed, we proceeded with implementing it. The new policy is communicated clearly to employees, and enforcement is done through the endpoint management system. Now, the endpoint management system ensures compliance by preventing users from bypassing the new requirement.
By integrating security with endpoint management, we ensure that policy changes are not only compliant but also effectively communicated and enforced. This approach minimizes risks and ensures that all compliance requirements are met.
2. Audit management
For organizations looking to offer products or services internationally, meeting compliance standards is mandatory. During a recent audit, Zoho Corp. was required to report all installed software versions across the entire network. This level of visibility is straightforward in a tightly controlled environment where users cannot install software independently. However, since Zoho Corp. allows employees to install authorized software, we use an endpoint management tool to track software versions and installations, ensuring vulnerabilities are quickly
identified and patched.
3. BYOD management
Bring your own device (BYOD) has become the norm, and it continues to pose challenges for endpoint management teams. While BYOD allows employees to use their personal devices for work, it also increases the risk of non-compliance, as personal devices may not meet the stringent security and compliance standards required by many regulatory frameworks.
Organizations must carefully control the access of personal devices to corporate data and resources, ensuring that only compliant devices can access sensitive information. Here are some of our best practices for compliance:
- BYOD enrollment: Zoho Corp. supports BYOD policies with a structured approach that balances security and privacy. Through BYOD enrollment, admins can register employees' personal devices while ensuring a clear separation between personal and work data. This process creates a dedicated work profile on personal devices, protecting personal information while granting organizations control over work-related data. Enrollment can be done by sharing an enrollment link with employees for remote registration or by generating and using a link directly when admins handle the devices.
- Access control: Implement certificate-based authentication to ensure only authorized devices have access to corporate resources. For example:
- Mail access: Employees may be able to read emails but may be restricted from sending or forwarding them if their device is not compliant.
- Intranet access: Employees may access the intranet, but access to more sensitive systems, such as data centers, can be restricted.
- Conditional access: Provide limited access to non-compliant devices, ensuring they cannot access sensitive systems or corporate data.
- Security policies: Enforce strong security policies on BYOD devices, such as mandatory encryption and remote wipe functionality for lost or stolen devices.
For organizations seeking a streamlined solution, there is a growing shift towards providing company-issued devices, which offer better control over security and compliance. This shift simplifies endpoint management by ensuring that all devices are subject to
uniform compliance standards.
4. Compliance scoring
Endpoint management tools provide real-time metrics that contribute to compliance scores, offering a clear snapshot of organizational security health. For example, ManageEngine Endpoint Central offers a compliance score based on patching, configuration, and vulnerability management. The system tracks the deployment of critical patches, the number of devices online, and how many devices are out of sync with the system. A higher score reflects stronger compliance, serving as a measure of how well our organization is managing risks and meeting its compliance obligations.
Devices are assigned a compliance score based on factors such as:
- EDR
- Firewall status
- Patch management
- Password strength

Additionally, Zoho Corp. sets annual goals for compliance. For example, we aimed for 95% of critical patches to be deployed within a week of release. With the automation in place, we were able to achieve this target year after year, steadily improving our compliance score. This focus on continuous improvement has helped us stay ahead of potential security risks and regulatory requirements, ensuring that our security posture is always aligned with the latest standards.
5. Automation in endpoint management
Our endpoint management system is automated to handle tasks such as patch deployment and updates. However, we do not push updates automatically without thorough testing. When we receive updates from vendors like Microsoft or Apple, we first test them to ensure compatibility with our systems to avoid causing issues. Once the updates are tested, we release them to the affected devices in batches, ensuring that any potential issues are detected early.
The patching process is automated, but we use a structured approach where devices are grouped, and patches are deployed incrementally. For instance, a patch may be deployed to a group of 100 devices first. If it is successful, it is then pushed to larger groups. This method reduces the risk of widespread issues and ensures better control over the update process.
Accurate asset management for complete visibility
and control
Asset management underpins endpoint management by maintaining a comprehensive inventory of all devices. Without an accurate record, it becomes challenging to keep the network secure. Ensuring that devices are regularly updated with security patches and are running compliant software versions is a key requirement in many regulatory frameworks, such as the GDPR, HIPAA, and the PCI DSS.
Device visibility and monitoring
Consider the challenge of managing 20,000 laptops. Endpoint management tools enable IT teams to monitor which devices are offline, enforce patch compliance, and ensure all configurations meet security standards. If a device’s endpoint agent crashes or undergoes unauthorized uninstallation, IT teams can immediately detect the lapse and reconnect it to the network, ensuring consistent compliance.
Real-time visibility into endpoint activity is a non-negotiable for compliance. IT teams routinely monitor relevant parameters, like:
- Device status: Online or offline activity.
- Software versions: Compliance with approved versions (e.g., specific browser versions).
- Connectivity: Ensuring devices report to the endpoint management portal regularly.
Daily monitoring ensures every device is accounted for in the endpoint management portal. Setting a cut-off timeframe (e.g., four days or one week) is a standard practice for tracking device connectivity based on company policies. Devices that remain disconnected from the endpoint tool, whether due to technical issues or intentional absence, are flagged for immediate follow-up and the user's status is verified with the organization's HR team.
Accurate asset tracking supports endpoint management by maintaining an up-to-date inventory, allowing asset management teams to report device statuses confidently and enabling IT teams to prioritize connected, compliant devices for security updates, patches, and compliance checks. Only devices actively reporting into the system receive security updates, patches, and compliance checks, ensuring critical safeguards are applied without delay.
Efficient patch deployment and regulatory adherence
Compliance authorities, like the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) in the United States or the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) in the European Union, expect that organizations not only address vulnerabilities but also adhere to defined timelines for critical updates. For example, if a high-risk vulnerability is identified in a widely-used browser, endpoint management tools enable IT teams to apply patches within a designated timeframe, typically 24 hours, to demonstrate compliance. Ensuring this rapid response builds trust with customers by showing a proactive approach to securing their data.
Because organizations must ensure timely deployment of patches to mitigate security risks and comply with regulatory deadlines, delays in patch deployment can lead to vulnerabilities, putting compliance and security at risk. As a best practice, it’s essential that organizations not only monitor the patch status but also establish a clear system for patching devices efficiently.
Aspect |
Function |
Compliance advantage |
| Patch management | Deploy security updates within required timelines. | Reduces risks and ensures regulatory adherence. |
| Asset management | Maintain an up-to-date inventory of devices. | Guarantees no device is overlooked in compliance efforts. |
| Endpoint visibility | Monitor device configurations, status, and connectivity daily. | Enables rapid issue detection and resolution. |
Managing vulnerabilities through endpoint oversight
Our approach to handling vulnerabilities and reporting breaches has evolved as well. When a security breach or vulnerability is identified, we don’t simply react—we take immediate action.
When a potential vulnerability or breach arises, our first step is to determine its validity. Is it a genuine threat or a false alarm? Using our endpoint management solutions, we monitor all devices in real time, identifying affected endpoints and assessing the scale of the incident. This allows us to respond quickly by isolating infected devices and applying necessary patches or updates.
A detailed mitigation report is a crucial part of our process, documenting:
IP addresses involved in the incident.
Detection and resolution timelines to measure response efficiency.
Impacted devices and the remedial actions taken.
Preventative strategies implemented to mitigate future risks.
At Zoho Corp., if customer data were to be involved in a security incident, the legal team would step in to ensure the appropriate notifications were sent to everyone involved. This level of scrutiny means that we must be diligent in our actions, ensuring that we're not only securing our data but also complying with global data protection standards.
Integration with advanced cybersecurity practices
EDR
EDR is increasingly integrated with endpoint management to enhance security. Recently, Zoho Corp. enabled an EDR backup solution during a blue screen incident, demonstrating the importance of having readily available data for quick response. When the primary EDR fails, endpoint management allows rapid deployment of a backup, ensuring no lapses in security monitoring.
Implementing Zero Trust security policies
The Zero Trust security model, which assumes that no device or user is inherently trustworthy, is a key component of modern compliance strategies. Endpoint management is critical to implementing Zero Trust by ensuring that access is granted only when a device meets specific security requirements.
Two ways endpoint management enforces Zero Trust security include: -
Device compliance scoring: Devices are continuously evaluated based on factors like patch status, firewall status, and antivirus software.
Granular access controls: Access to applications and resources is granted based on device compliance scores, ensuring only secure devices are allowed to access sensitive data.
Endpoint management for the future
At Zoho Corp., our endpoint management system is now an integral part of our security and compliance strategy, with the transition to the cloud reducing server-related challenges and enhancing scalability. Automation has streamlined patch management and compliance tracking, enabling us to improve our compliance scores consistently. As endpoint management evolves alongside regulations, our ability to adapt and securely manage devices will remain critical to ensuring compliance and driving our success as a security-conscious enterprise.
