Identity stands at the forefront of modern IT security. It serves as the gateway to our online engagements, from simple interactions to complex transactions. However, as the digital realm advances, so does the complexity of protecting our identities. The current identity security approach relies on a centralized system, where users provide their personally identifiable information (PII) to a central authority. These centralized repositories are like gold mines for cybercriminals, and a single breach can lead to widespread identity theft. The rising tide of data breaches and mounting privacy concerns are pushing cybersecurity leaders to explore alternatives to traditional identity management, and decentralized identity is emerging as a promising approach.
Decentralized identity is a concept of representing and managing digital identities without relying on a central authority. Central to this concept are decentralized identifiers (DIDs), which serve as unique identifiers that individuals can create and manage independently. Unlike traditional systems where a single entity holds and verifies an identity, DIDs relies on blockchain technology, ensuring that the individual has full control over their personal data.
Also read: How to decentralize digital identities using blockchain technology
When a user creates a DID, it gets stored on a blockchain or another decentralized ledger. This DID comes paired with two cryptographic keys: a public key, visible on the blockchain for identity verification, and a private key, held confidentially by the user for transaction signatures and authentication. Rather than juggling multiple usernames and passwords, users store their DIDs, keys, and credentials in a digital wallet. When accessing services, they simply present their DID alongside a cryptographic proof, typically a signature from their private key. The service cross-references the signature with the blockchain's public key to ensure authenticity. Users have the autonomy to decide which parts of their identity data to share and with whom. It is up to each user to decide whether to grant or revoke access to their data.
The same DID can be used for authentication across various online platforms, removing the need for multiple usernames and passwords. All transactions related to DIDs and verifiable credentials are recorded on the blockchain. This ensures transparency and helps build trust, as users can verify the source and integrity of their identity data. This type of identity and access management approach is called decentralized identity management, which places the control squarely in the hands of the individual, unlike traditional systems, where an identity is verified by a central authority.
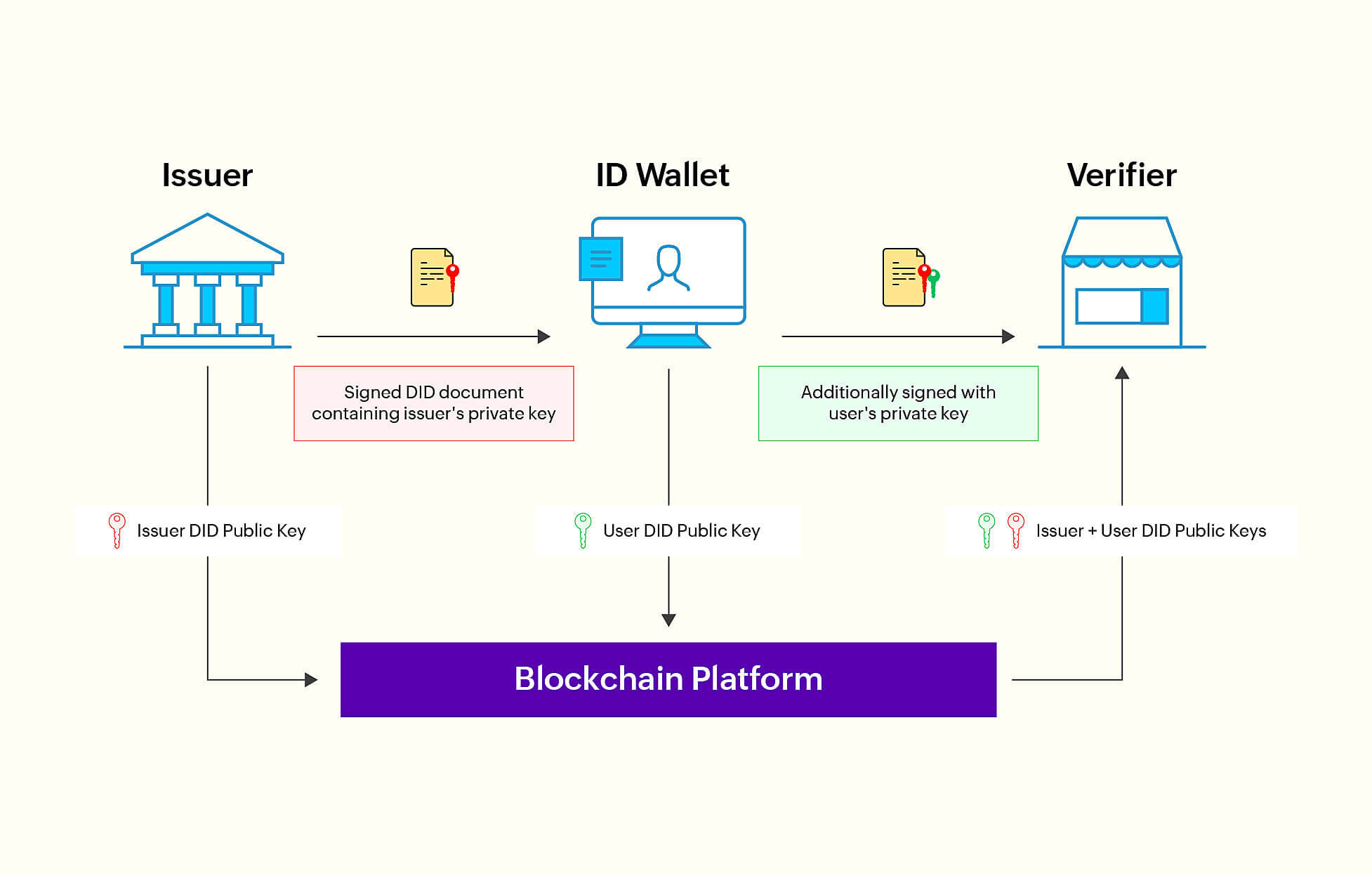
Decentralized identity management workflow
As the gatekeepers of data and access, IAM systems have long been the bedrock of organizational security. By blending IAM with the concept of decentralized identity, organizations can forge an even stronger shield for their networks. Imagine an IAM system where, instead of using usernames and passwords, users authenticate themselves using cryptographic keys linked to their unique DIDs. Blockchain technology ensures the integrity of DIDs and, consequently, can safeguard network security against identity theft. This approach empowers organizations to enhance identity security, thereby reducing data breach risks. Moreover, when individuals have the power to dictate how their information is handled, organizations demonstrate their commitment to privacy, transparency, and accountability, fostering trust with their users. Decentralized identity systems offer a range of compliance benefits for industries prioritizing data protection and regulatory adherence. By leveraging blockchain technology, these systems can ensure immutable audit trails to promote data integrity and simplify compliance audits.
While the buzz around decentralized identity grows each day, the truth is, many of today's software and platforms offer limited DID integration. In other words, decentralized identity has great potential, but it's still in the early stages of being widely implemented. Pioneering organizations and tech providers are leading the charge, experimenting with use cases and refining the technology. But for DIDs to become the norm, it will require a broader ecosystem shift, including adoption by major platforms, standardization of protocols, and user education. The journey might be long, but the destination—a world where digital identities are secure, user-centric, and decentralized—holds immense promise.