Automated Machine Learning in Analytics Plus
Automated machine learning in Analytics Plus provides a code-free experience to train, verify, and build custom machine learning models with high efficiency. The simple and user-friendly design makes it possible for people with a minimal level of expertise to create ML models easily and make smart business choices.
Users can use their own historical data from various segments of IT, such as network operations data, to build a model that will help predict the next downtime or cluster problematic devices together based on recent activity, or data from help desk tickets to build a model that will predict the probability of escalation of a ticket.
- Best practices
- Steps involved in building and launching an Auto ML Model
- Machine learning models in Analytics Plus
- What If Analysis in Auto ML
Best practices
Clearly define the business problem for which you intend to build an ML model. Ensure you select the relevant fields and columns that have a direct correlation with the expected results. While AutoML can be a powerful tool, its accuracy depends on the information made available to build the model.
Building a ML model in Analytics Plus comprises of two high-level steps,
- Select the input dataset for training and pick the model that fits your use case. Please note that you require sample or historical data available with you in order to build an ML model. For example, if you wish to build a model that predicts the next downtime, you should have historical performance data and outages that happened in the past for the model to learn from.
- Assess the model performance and deploy the model to a new dataset.
Steps involved in building and launching an Auto ML Model
Select the data for training
Access the workspace which has the training table or dataset.
To invoke the AutoML environment, click the Create icon on the side navigation panel.
Click Create New Analysis.
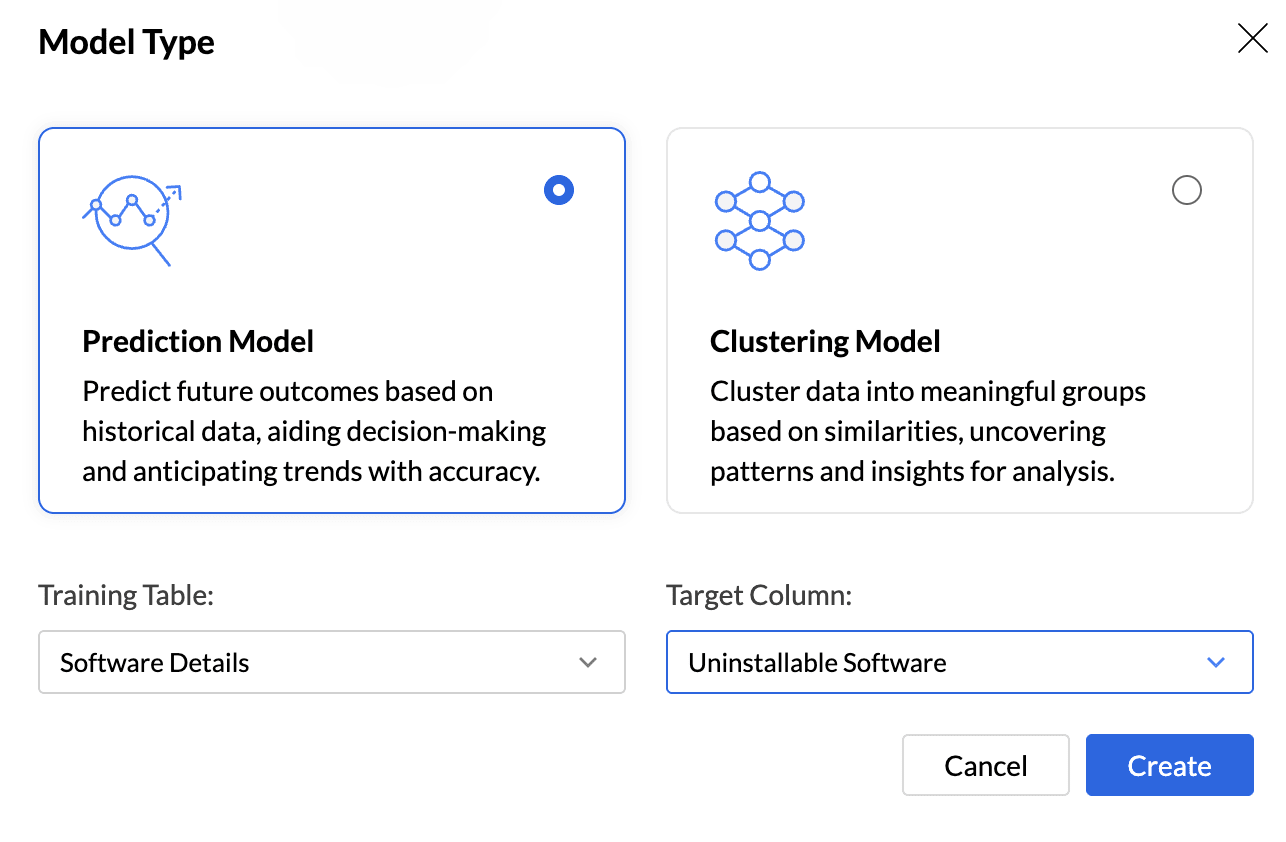
Select the Model Type that should be used for training based on your goal. Analytics Plus supports two models, Prediction and Clustering.
The Training Table is the dataset used to train the machine learning model. Select the appropriate Training Table.
The Target column (or target variable) is the specific column in the dataset that you aim to predict. It contains the outcomes or labels that the model is trained to forecast based on the input features.
Click Create.
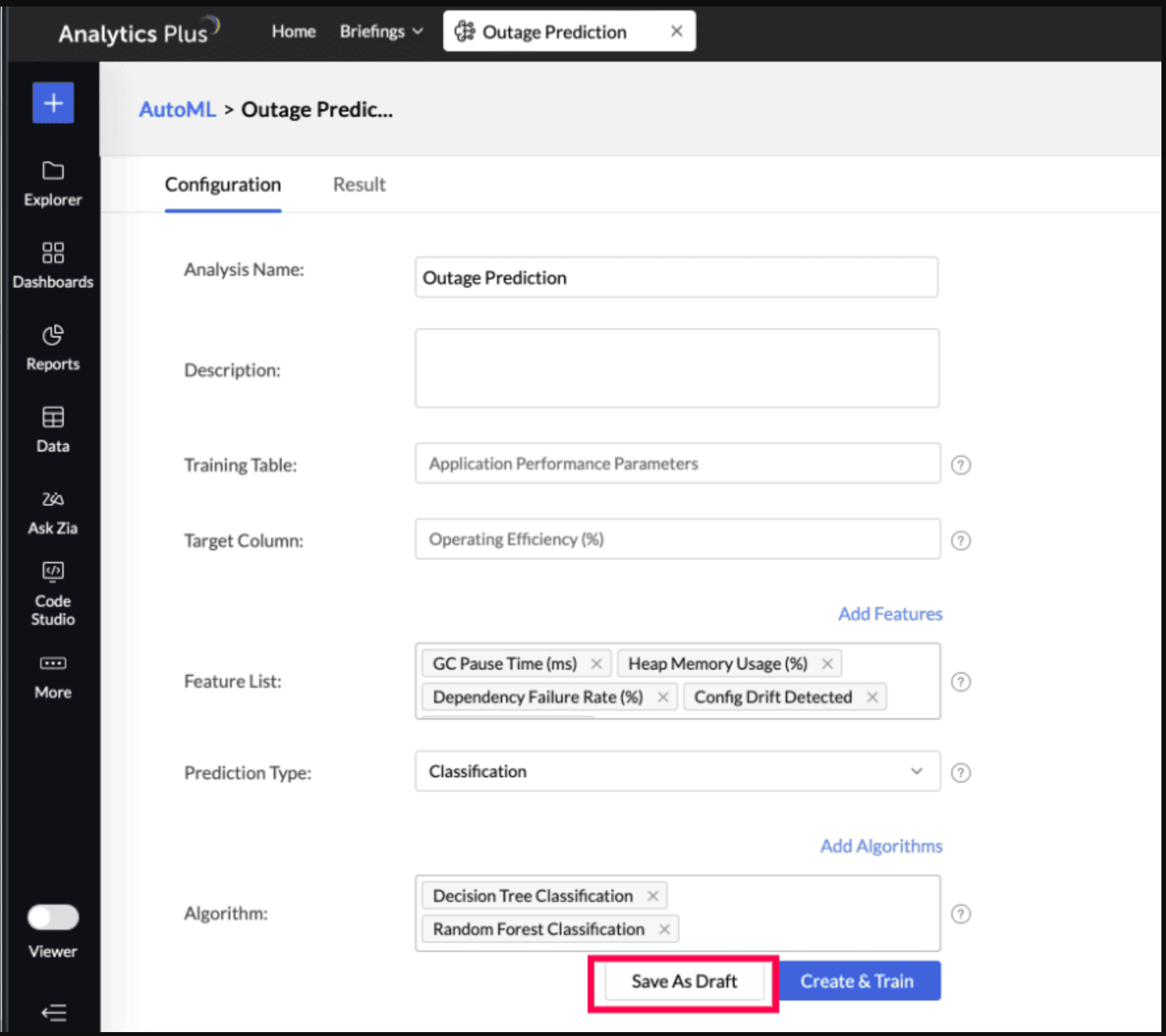
In the AutoML configuration page, Specify a suitable Analysis Name and add a Description about the training model.
The selected Training Table and Target Column will be displayed.
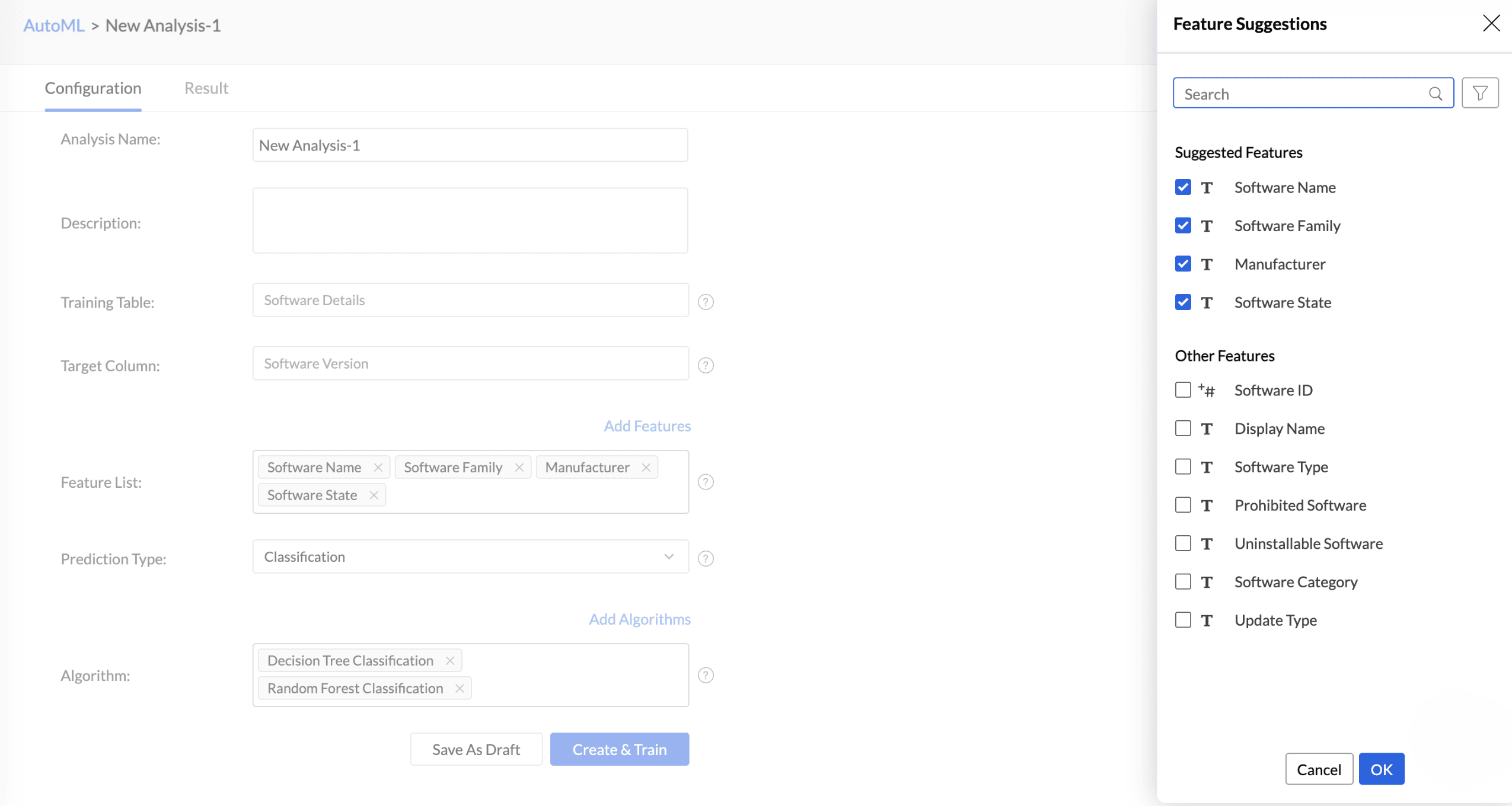
Features are the factors that influence the column being predicted. Click Add Features to include additional influencing columns. Analytics Plus will automatically suggest features that influence the column in the Suggested Features field. You can also select other features that may have an impact.
Choose the Prediction Type.
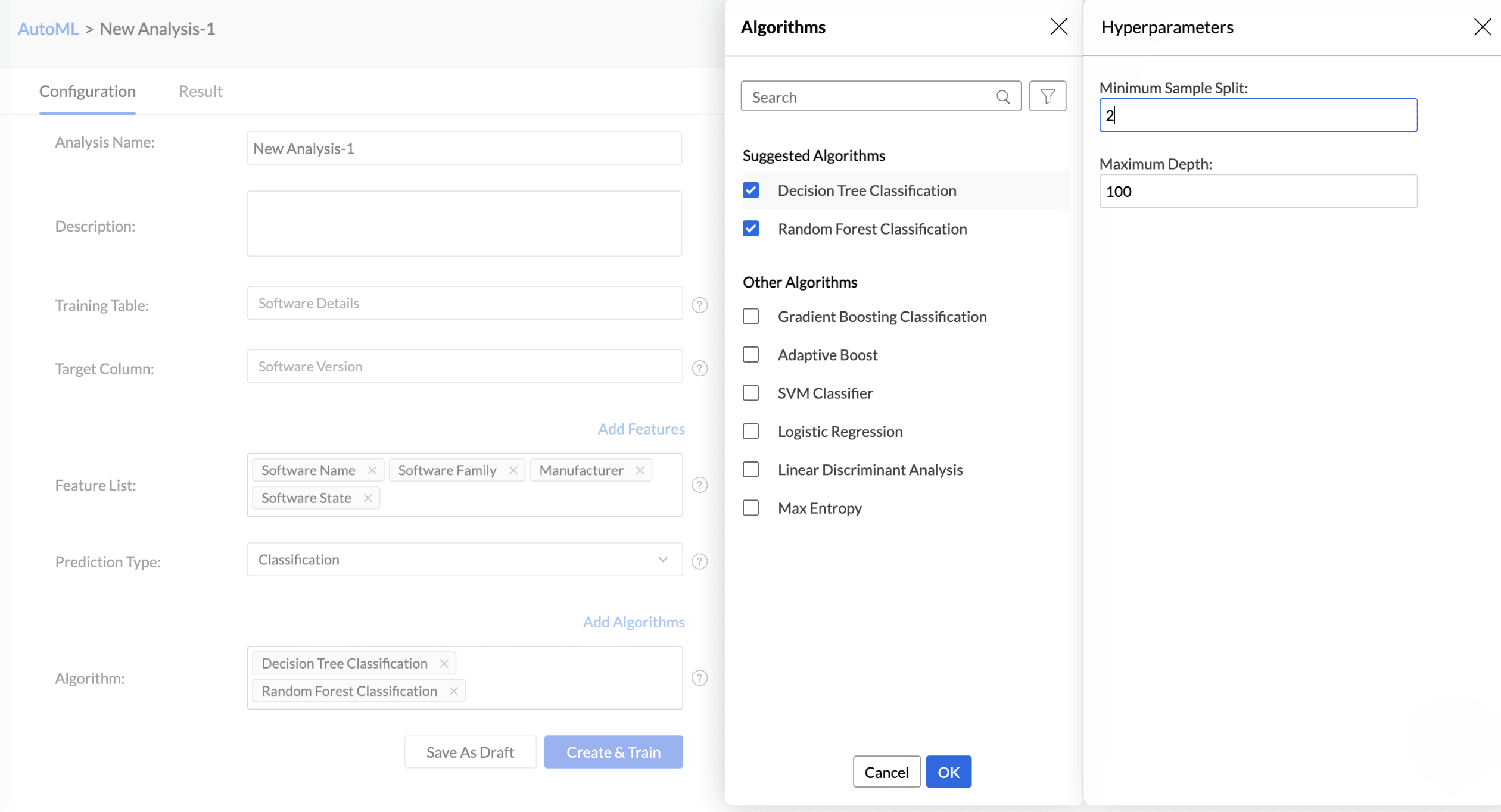
Analytics Plus automatically selects the most suitable algorithm for training. However, you can also choose specific algorithms for model training. Click Add Algorithm to select the algorithms you want to use for training the model.
Click the Settings icon to modify the parameter settings.
The Save as Draft option lets you preserve the model configuration, including algorithm selection and feature settings, so that you can initiate model training later at your convenience.
Click Create and Train to initiate the model training.
Choose the Server options and click Save and Train.
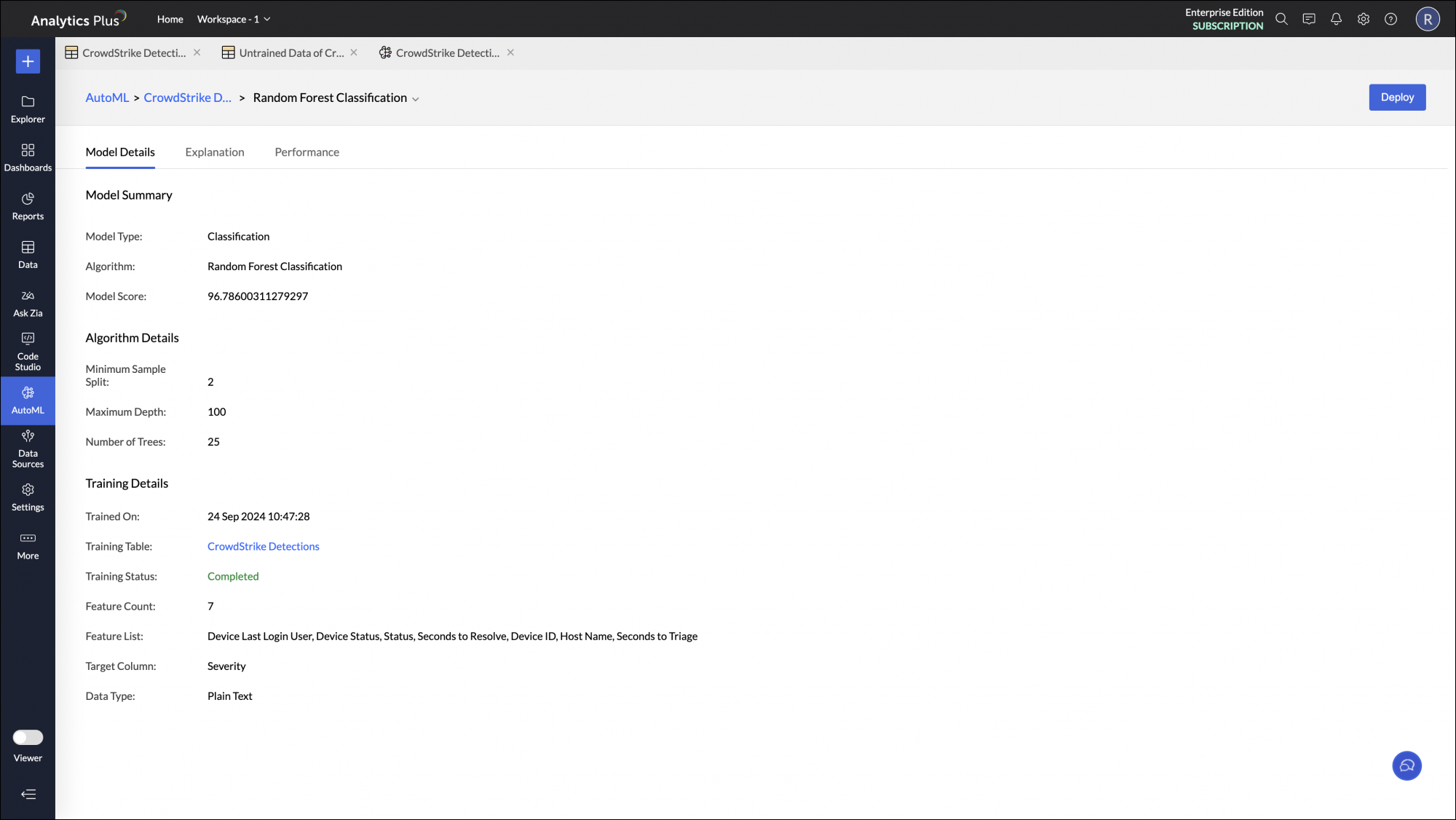
Model information
Once the training is completed, the model will be saved and will be listed in the Analysis tab. Click the model name to get additional details such as the Algorithm Name, Accuracy and Training Time of the model.
Deploy the ML model
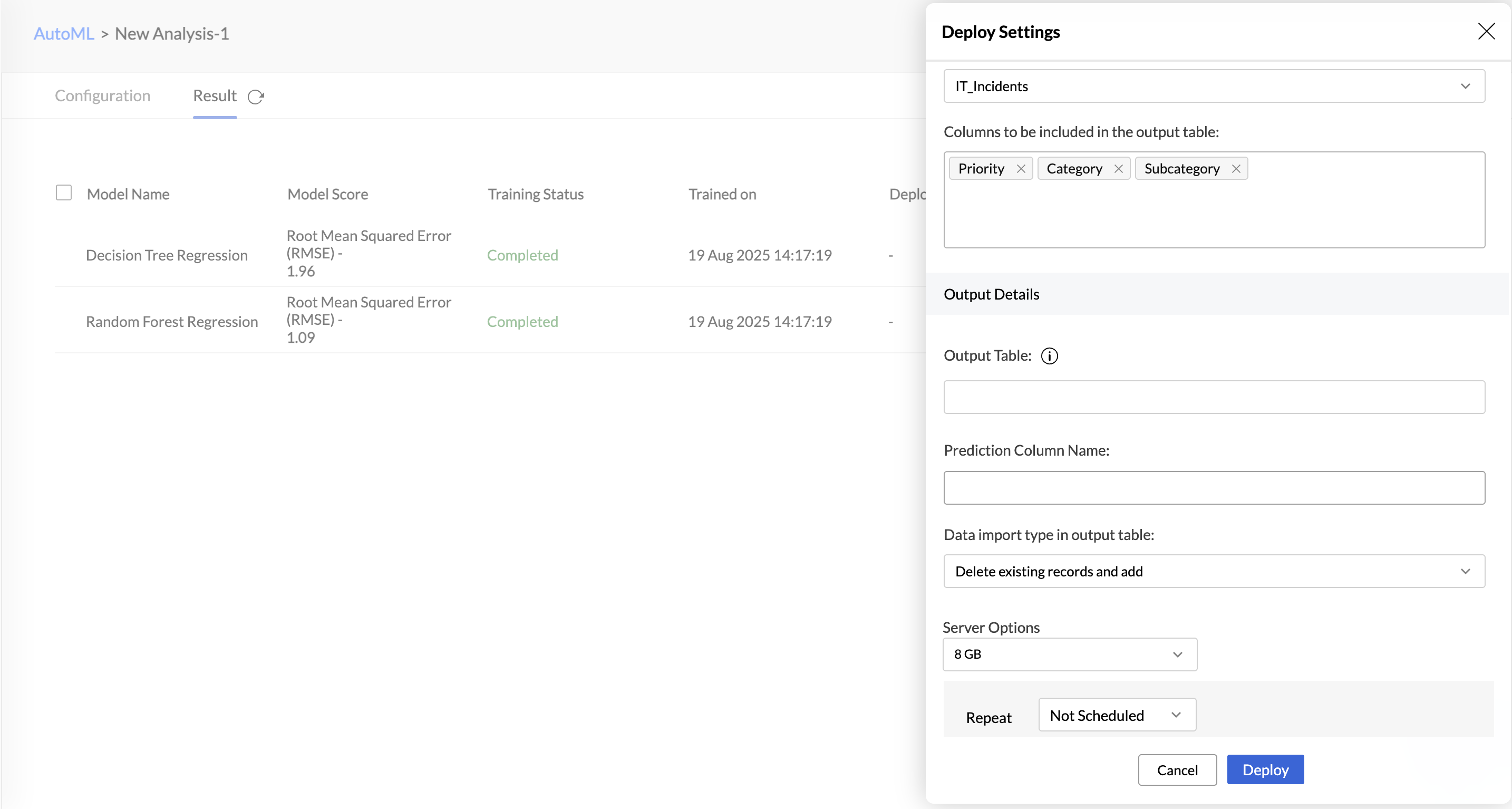
Once you have assessed the quality of the ML model, you can deploy it on a production dataset to get results.
- Click the Deploy Now button on the top.
- Select the Input table for which the prediction model should be applied.
- Select the Output table - this is the table where the result of the model will be stored.
- Choose the import type in output table -
- Delete existing records and add - Deletes all existing rows in the table and adds the imported data as new entry.
- Add records at the end - Choosing this will append the new records to the end of the table.
- Add records and replace if already exists - Updates the existing records in the table and appends the new records at the end of the table.
- Select the Schedule Time.
- Click Deploy Now.
A new table will be created; you can then create visualizations on top of it.
Retrain the ML Model
Data patterns and operational insights evolve, requiring constant model adaptation. Machine learning models trained on old data lead to inaccurate insights and poor decisions. Periodically training ML models helps adapt to current trends, reduce errors, eliminate data drift, improve model performance, and make them suitable for current business objectives.
Analytics Plus allows you to retrain an ML model in any of the following three ways:
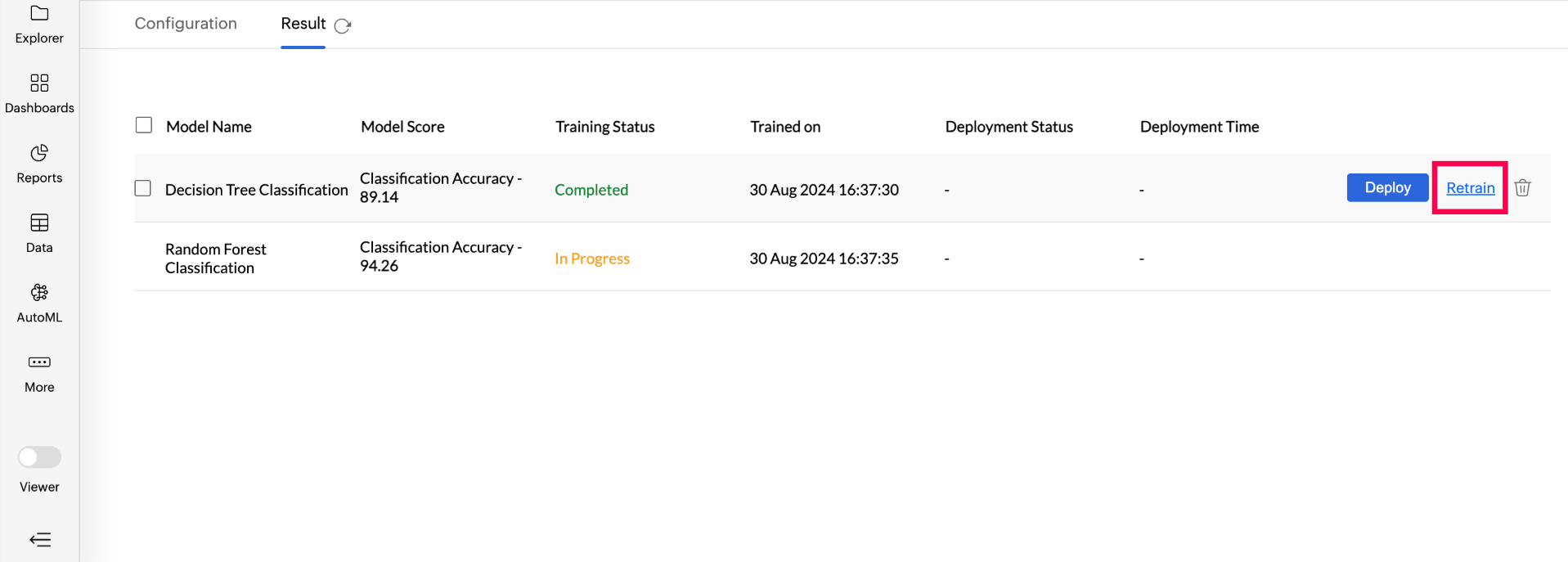
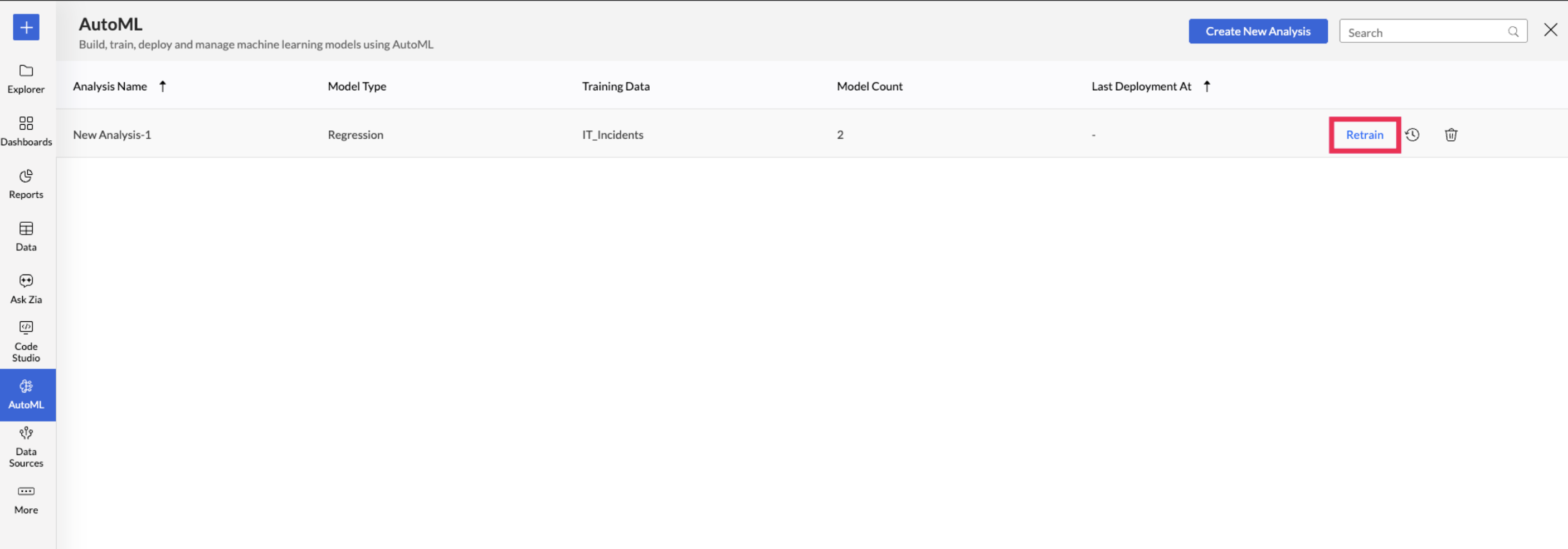
Retraining a specific ML model: Access the AutoML tab and choose the Model you want to retrain. Hover on the model and click Retrain.
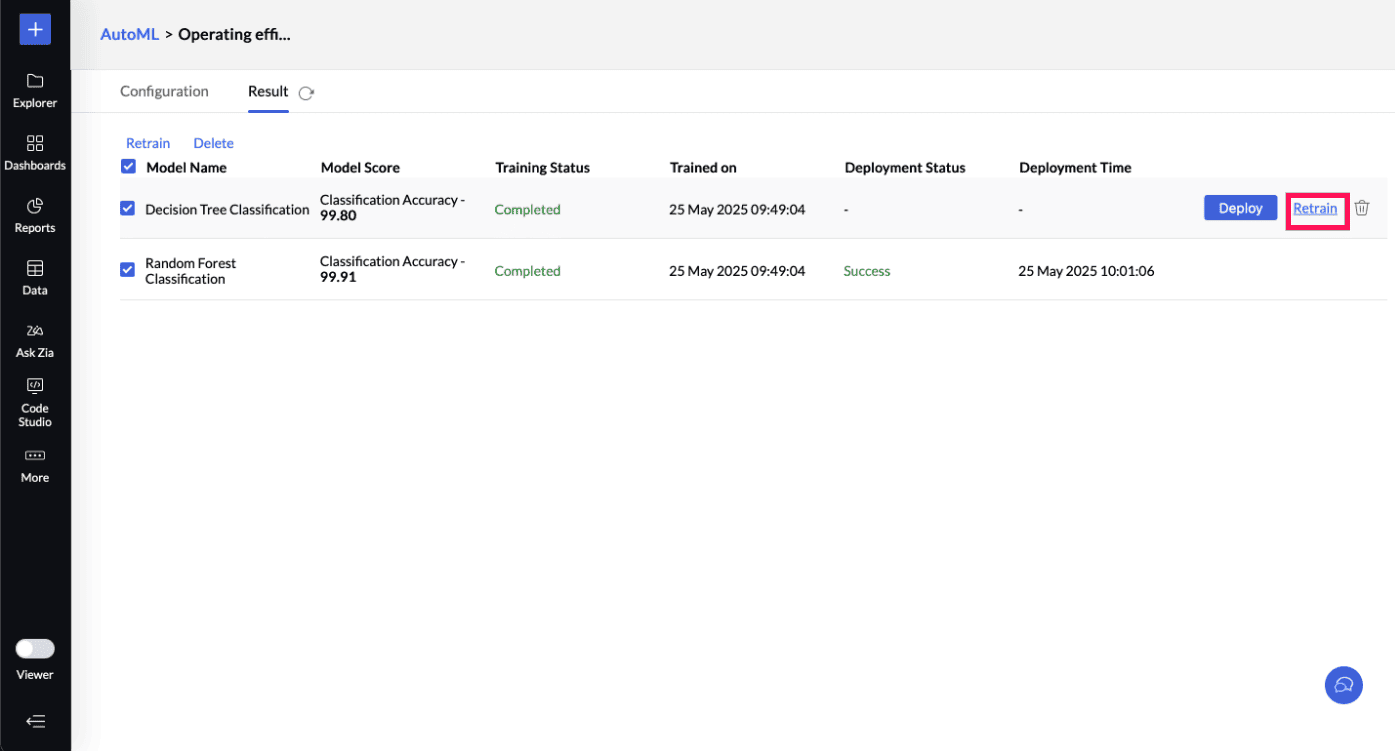
Retraining Multiple ML Models: You can also multi-select the ML models you want to train and click the Retrain option on the toolbar.
Retraining an Analysis: Access the AutoML tab and hover over the Analysis to be retrained, and click Retrain. This will retrain all the models in the selected analysis.
Deleting the ML model
Deleting a machine learning model permanently removes the trained model and its associated metadata from the system. This is usually done to free up storage, remove obsolete models, or eliminate those misaligned with current data or business goals.
Machine learning models in Analytics Plus
The quality of the output generated by AutoML framework will depend on choosing the right machine learning model from the available list of options. Ensure you select the model that is most appropriate to the dataset at hand and the result that is expected.
Regression Model
Regression is a supervised learning method used to determine the relationship between the dependent and independent variables. The regression model is primarily used for predictive analysis.
Random Forest Regression
Random forest regression is a supervised machine learning algorithm that uses a combination (ensemble) of decision trees for prediction. Random subsets of the training data are chosen while constructing each decision tree. Each decision tree is combined to output a single prediction value.
The random forest model is best suited for predicting continuous values, like time series forecasting and price predictions. Since the algorithm involves constructing multiple decision trees, the predictions are always of high accuracy.
Classification Model
Classification is a supervised machine learning method that predicts the category or type to which an observation or data point belongs. For instance, the classification of emails as spam, social, or primary.
Random Forest Classification
The random forest classification is a supervised machine learning method that combines multiple decision trees to arrive at a conclusion. This method is best suited for discrete variables.
Clustering Model
Clustering is an unsupervised learning technique. This model identifies patterns and relationships within the data that are not immediately apparent and groups similar data points into clusters.
K - means
The K-means algorithm segregates a dataset into K distinct, non-overlapping clusters. This is an iterative process that assigns each data point to one of the K-clusters based on the input provided. This algorithm works effectively with quantitative data as it is based on calculating distances between data points.
K - modes
The K-modes algorithm is used for grouping categorical data, like segmentation based on demographics. Each cluster is determined by modes; the most frequent value in the cluster.
K - Prototypes
The K-Prototypes algorithm is an extension of the K-Means algorithm used for clustering datasets containing both numerical and categorical features. It combines the K-Means algorithm's clustering approach for numerical data with a mechanism to handle categorical data.
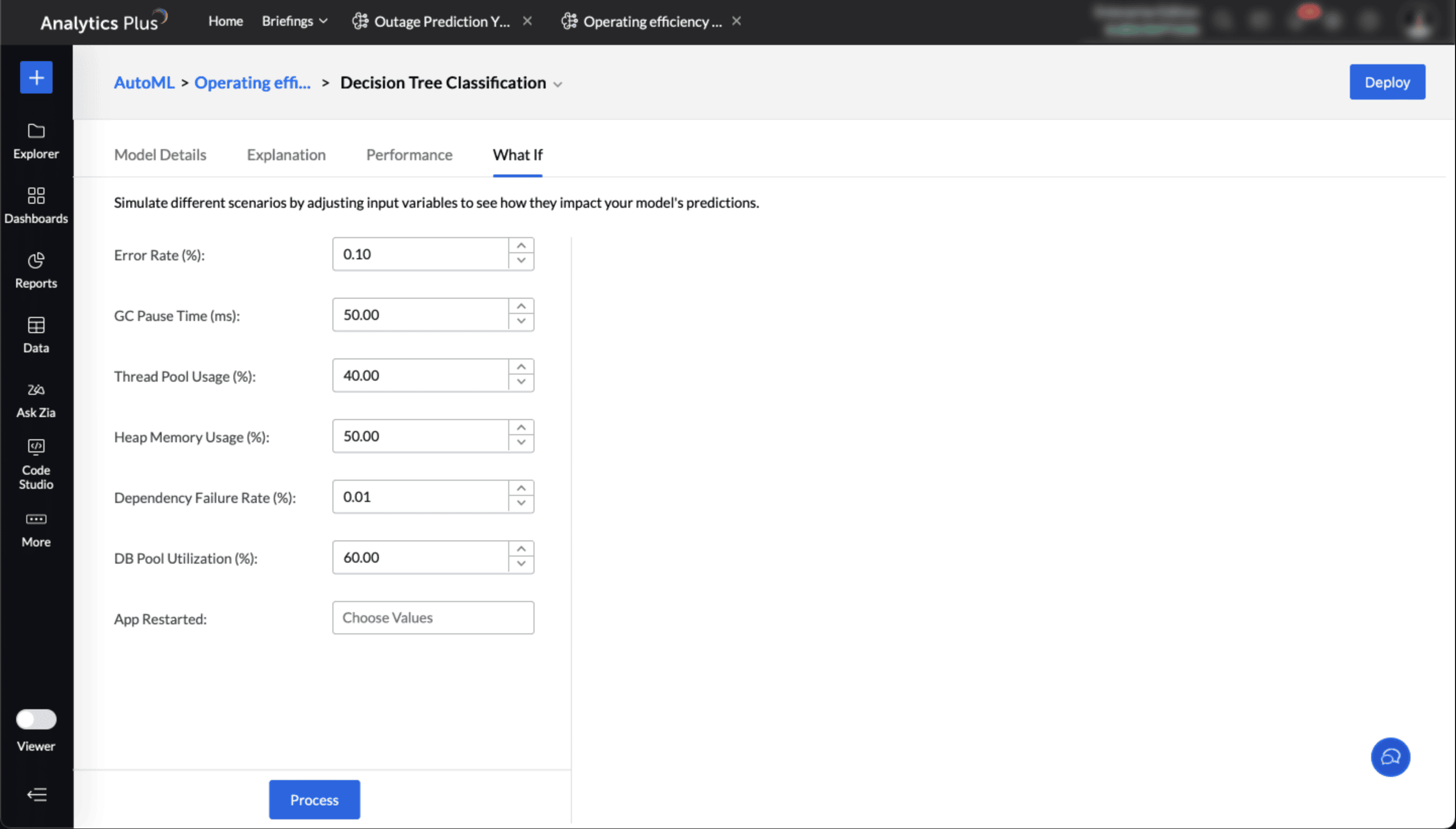
What -if analysis in AutoML
What-if analysis in AutoML enables you to explore how changes in IT metrics or operational factors affect the final outcomes predicted by the machine learning models. By simulating different scenarios, you can:
Understand feature impact: Identify which parameters, such as ticket volume, response time, or SLA compliance, most influence the outcome.
Test hypothetical situations: Evaluate the effect of changes—for example, hiring additional support agents, modifying shift schedules, or adjusting incident prioritization.
Support IT planning: Predict future outcomes by modelling best case, worst case, or most likely scenarios.
Save as draft:
The Save as Draft option lets you preserve the model configuration, including algorithm selection and feature settings, so that you can initiate model training later at your convenience.