Configuring MS SQL Server as the Backend Database
By default, the Key Manager Plus application is bundled and pre-configured with PostgreSQL database, allowing for immediate deployment without additional database setup. However, if you prefer to use MS SQL Server as the backend database, you can do so by following the configuration steps outlined below.
Caution: Please note that if you have already started using Key Manager Plus with the bundled PostgreSQL database and want to switch to MS SQL Server as your backend database, the configuration process will not transfer any existing data from the bundled PostgreSQL database.
- SSL Certificate for Encrypted SQL Connection
- Enabling SSL Encryption in SQL Server
- Configuring MS SQL as the Backend Database
1. SSL Certificate for Encrypted SQL Connection
Note: To ensure a high level of security, Key Manager Plus has been configured to connect to the SQL server only through SSL.
Before connecting Key Manager Plus to the SQL Server, SSL encryption must be enabled on the SQL Server. This requires creating an SSL certificate for the SQL Server, deploying it on the SQL server, and adding the same certificate to the Key Manager Plus keystore. You can generate either a Certificate Authority (CA)-signed certificate or a self-signed certificate - both options are available directly from the Key Manager Plus interface.
1.1 Generating an SSL Certificate for the SQL Server
Key Manager Plus offers two convenient methods for generating an SSL certificate for your SQL Server:
- Creating a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) and getting it signed by a trusted third-party Certificate Authority (CA).
- Creating a self-signed certificate directly from the Key Manager Plus interface.
Both options can be initiated from within the product. For detailed instructions, refer to the relevant help documentation links provided.
To generate a CA-signed SSL certificate, follow these steps:
- Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) from the Key Manager Plus interface.
- Use the generated CSR to order a certificate from a recognized third-party Certificate Authority (CA).
- Once the request is processed, the CA will issue the signed server SSL certificate along with the CA’s root certificate, typically in `.cer` format. The same can be retrieved from the relevant CA order from the Key Manager Plus interface.
Key Manager Plus also provides the ability to create a self-signed SSL certificate without requiring a third-party CA. Refer to this help documentation to learn how to create and manage self-signed certificates using Key Manager Plus.
Note: While creating a self-signed certificate specify the FQDN of the SQL server in the Certificate Name field.
After obtaining the signed SSL certificate (either CA-signed or self-signed), install it on the SQL Server using the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) by following these steps:
- Click Start and select Run. In the Run dialog box, type MMC and press enter. This opens the Microsoft Management Console (MMC).
- From the Console menu, select Add/Remove Snap-in.
- Click Add, then select Certificates and click Add again.
- When prompted, choose to manage certificates for the Computer Account.
- Navigate to Manage User Certificates (Local Computer) >> Personal >> Certificates.
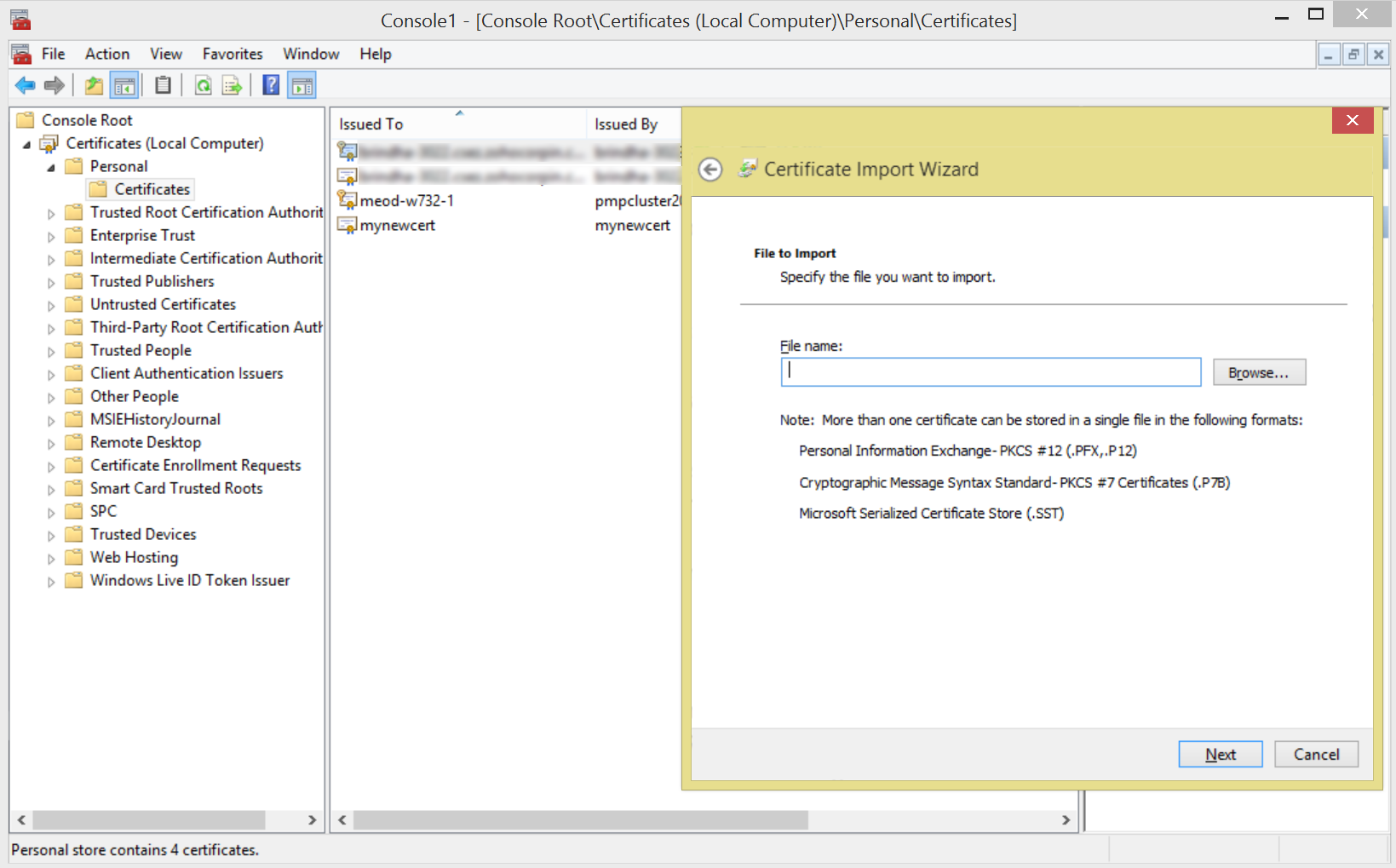
- Right-click on Certificates, select All Tasks, and then click Import.
- Browse to the location of your signed server certificate, select it, and complete the import process.
If you have created the server certificate using the third-party CA, install the CA root certificate in Key Manager Plus by following these steps:
- Copy the CA's root certificate to the <Key-Manager-Plus-Installation-Folder>\bin directory.
- From the same directory, execute the following command:
importCert.bat <Absolute-Path-of-the-Certificate>
Replace <Absolute-Path-of-the-Certificate> with the actual path of the root certificate file you copied. This command adds the root certificate to the Key Manager Plus certificate store.
Once installed, proceed to import the same certificate into the Key Manager Plus keystore to complete the trust setup for a secured connection via SSL.
1.2 Importing the SQL Server Certificate to Key Manager Plus
Upon completing with the certificate installation on the SQL server, follow the below steps to import the server certificate to the Key Manager Plus certificate store:
- Copy the server certificate and paste it under the <Key-Manager-Plus-Installation-Folder>\bin directory.
- Execute the following command to add the certificate to the store:
importCert.bat <Absolute-Path-of-the-Certificate>
Replace <Absolute-Path-of-the-Certificate> with the actual path of the server certificate file you copied.
2. Enabling SSL Encryption in SQL Server
- On the machine where the SQL server is running, click Start and open the SQL Server Configuration Manager.
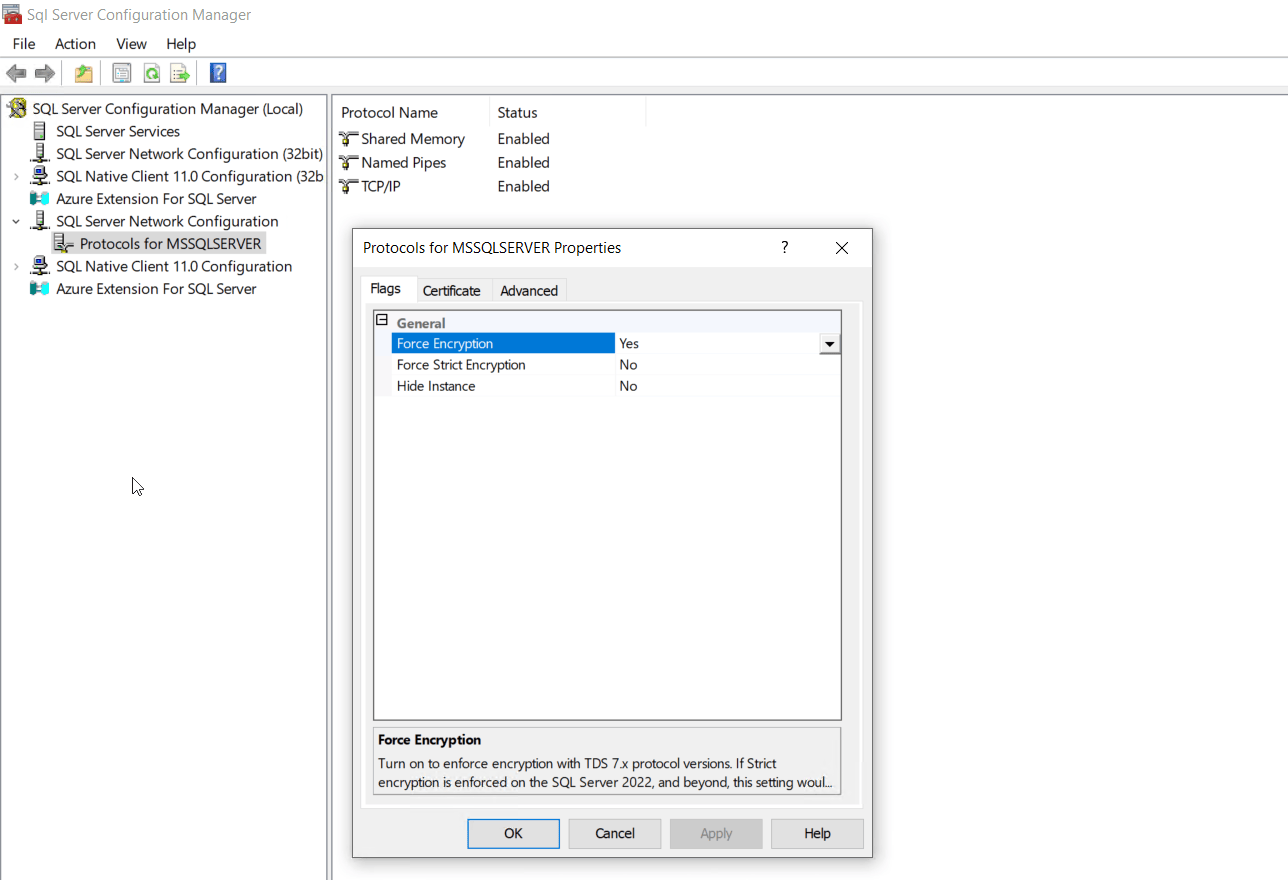
- Expand the SQL Server Network Configuration in the left pane, right-click the Protocols for the server you want to configure, and click Properties.
- Go to the Certificate tab and configure the database engine to use the server certificate.
- Set Force Encryption to Yes to ensure all client/server communications are encrypted. This setting will deny access to clients that cannot support encryption, which is the recommended configuration for security. Alternatively, you can set Force Encryption to No if you prefer the encryption to be requested by the client application. This is not recommended as it can lead to unencrypted communications.
- Restart the SQL Server.
For more details, refer to the section Configuring SSL for SQL Server in Microsoft's knowledge base article.
3. Configuring MS SQL Server as the Backend Database
Provide the details about the SQL server to Key Manager Plus by executing the file ChangeDB.bat (Windows) or ChangeDB.sh (Linux). Follow the below steps:
- Navigate to <Key-Manager-Plus-Installation-Folder>\bin folder and execute the file ChangeDB.bat (Windows) or ChangeDB.sh(Linux).
- In the pop-up that opens up, read the Best Practices Guide first by clicking the 'Open the best practices document' button. Click the 'Continue with setup' button to proceed with the DB change configuration.
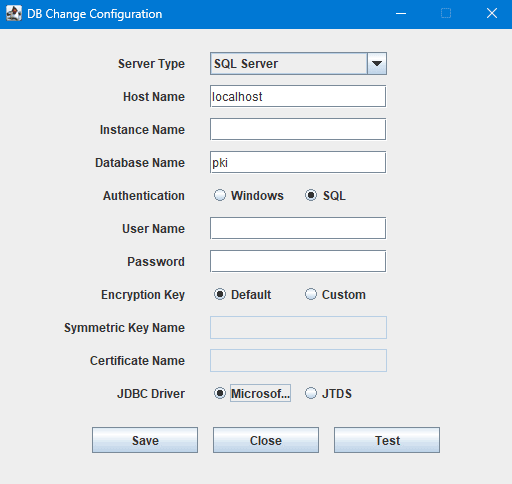
- In the window displayed, enter the below details:
- Select the Server Type as SQL Server.
- Host Name: The name or the IP address of the machine where the MS SQL server is installed.
- Instance Name: Specify the named instance of the SQL server, to be used for Key Manager Plus. If the instance name is not specified, Key Manager Plus will try establishing connection with the default instance on port 1433.
Note: Since Key Manager Plus connects to MS SQL only in SSL mode, it is recommended that you create a dedicated database instance running in a specific port for Key Manager Plus. If you want to specify a port number other than 1433, you can specify it in the Host Name parameter above as <hostname>:<port>.
- Database Name: Name of the Key Manager Plus database. Default is pki. If you want to have a different database name, specify it here. Key Manager Plus will take care of creating the Master Key, Symmetric Key, etc.
- Authentication: The way by which you wish to connect to the SQL server. Choose Windows if you are connecting to the SQL server from Windows. Make use of the Windows Single Sign On facility, provided the Key Manager Plus service is running with a service account, which has the privilege to connect to the SQL server. Otherwise, select the option SQL.
Note: It is recommended to choose the option Windows, as the Username and Password used for authentication are not stored anywhere.
- User Name and Password: If you have selected the option SQL in the above step, specify the user name and password with which Key Manager Plus can connect to the database.
Notes: The User Name and Password entered here will be stored in the database_params.conf file in Key Manager Plus. So, take care of hardening the host. You can use even your Windows login credentials if you are connecting to the database from Windows. In this case, you need to enter the User Name as <domain-name>\<username>.
- Encryption Key: The key to encrypt your data and store it in the SQL server. You may either leave it Default allowing Key Manager Plus to generate a key. If you want to have your custom key, select the option Custom.
- If you have selected the option Custom, do the following:
- Create Database - For details, refer to https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/databases/create-a-database?view=sql-server-ver16
- Create Master Key - For details, refer to https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/security/encryption/create-a-database-master-key?view=sql-server-ver16
- Create Certificate - For details, refer to https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/security/encryption/create-a-certificate?view=sql-server-ver16
- Create Symmetric Key - For details, refer to https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/statements/create-symmetric-key-transact-sql?view=sql-server-ver16
- Provide the Certificate Name and Symmetric Key Name in the GUI.
- JDBC Driver: The driver works seamlessly with the MS SQL server database. Microsoft (Recommended) is the default driver selected in the field and is recommended for most installations because it is compatible with the latest SQL server versions and features. The alternative JDBC driver available for selection is 'JTDS', which supports specific compatibility features.
Note: From build 7040 onwards, Key Manager Plus no longer supports the jTDS driver. Instead, the JDBC driver will act as the default driver for database connections.
- Finally, click Test to ensure that the connection settings are proper, and then click Save.
Caution: After performing the above steps, navigate to the <Key-Manager-Plus-Installation-Folder>/conf directory and move the masterkey.key file to a secure location. The SQL Server encrypts the data with a hierarchical encryption and key management infrastructure. Each layer encrypts the layer below it by using a combination of certificates, asymmetric keys, and symmetric keys. One among them is the Database Master Key, which in turn is created by the Service Master Key and a Password. This password is stored in Key Manager Plus under the <Key-Manager-Plus-Installation-Directory>/conf directory in a file named masterkey.key. It is highly recommended that you move the masterkey.key file to a secure location. This is to ensure data security. Take care to keep this key safe. You will require it while performing High Availability and Disaster Recovery. If you lose this key, you will have to configure MS SQL server setup all over again.
For more details on encryption and key management in MS SQL, refer to this MSDN document.
You have now successfully configured MS SQL server as the backend database for the Key Manager Plus server.