Key takeaways
Understanding the essence of APTs: Advanced, persistent, and true threats
The acronym APT (advanced persistent threat) precisely describes the nature of these sophisticated cyberattacks.
Advanced: APT actors employ sophisticated techniques and custom-developed tools that go beyond conventional malware. They often exploit zero-day vulnerabilities, encrypted channels, and fileless malware to evade detection.
Persistent: Persistence refers to the attacker’s ability to stay hidden within a compromised environment for a prolonged period. This allows attackers to continuously monitor and extract sensitive data over months or years without triggering security alerts.
Threat: APTs represent a credible and ongoing threat because they are carried out by well-funded, highly skilled groups with strategic objectives. These campaigns are typically backed by nation-states or organized threat actors seeking to conduct espionage, or steal intellectual property for political, military, or financial gain.
What is APT?
An advanced persistent threat (APT) is a sophisticated cyberattack where threat actors use advanced, multi-stage techniques like custom malware, zero-day exploits , and social engineering, to infiltrate a network. They actively maintain prolonged, stealthy access to exfiltrate sensitive data, conduct espionage, or sabotage critical systems.The primary goal of an APT is typically data exfiltration , espionage, or sustained disruption, rather than a quick opportunistic attack. The MITRE ATT&CK ® framework tracks and documents APT groups like APT28 and APT29 by mapping their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) with unique identifiers.
Stages of an APT attack
Most APTs progress through distinct stages: initially breaching a network, then expanding their access internally, and finally achieving their objective, which often involves discreetly extracting sensitive data. The following section briefly describes the stages of an APT attack.
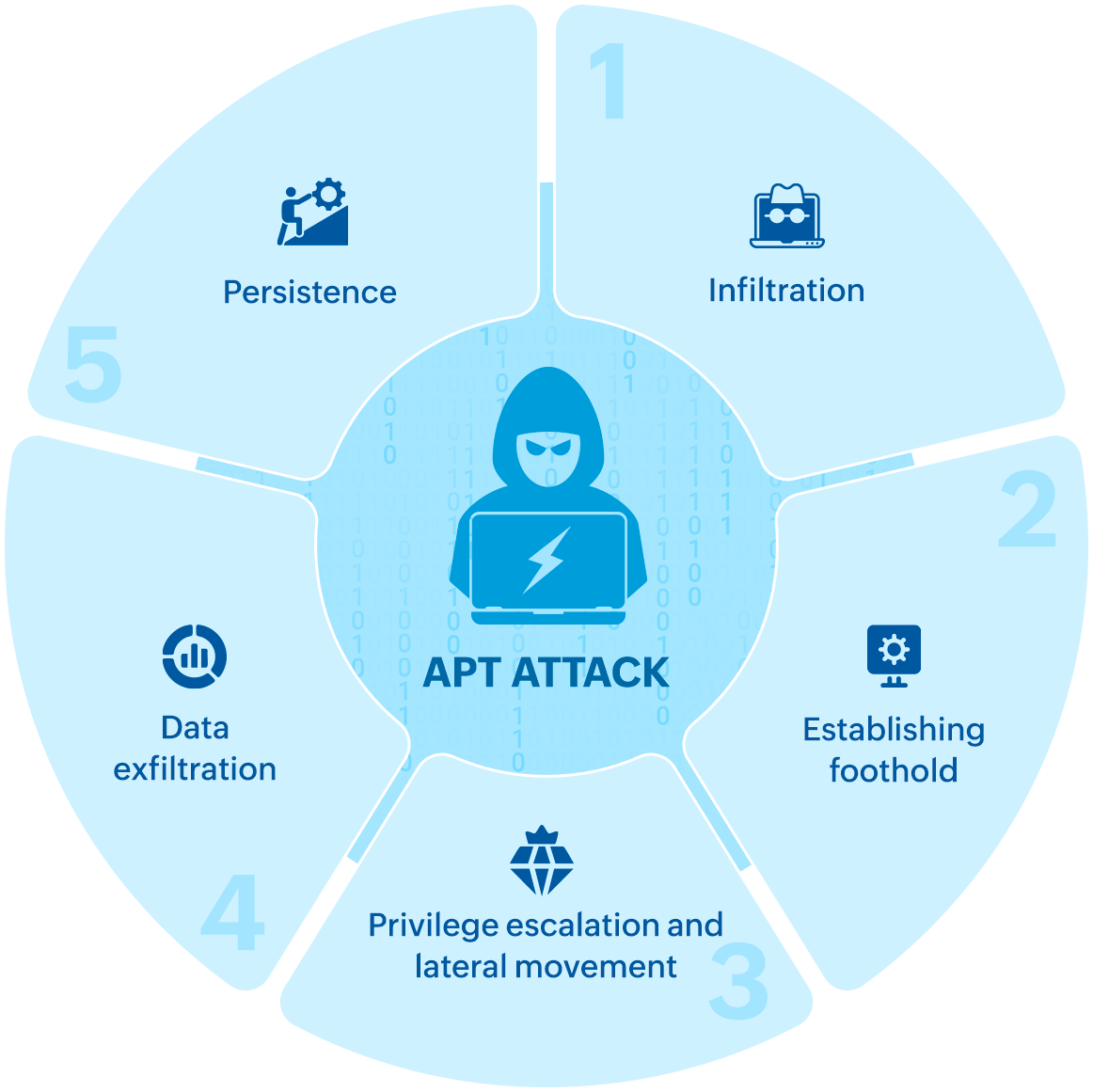
Stage 1: Infiltration
Adversaries gain entry into the target’s network using tactics such as spear-phishing, social engineering, exploiting system vulnerabilities, or leveraging malware. The attackers carefully select the initial entry points to minimize detection while establishing a long-term presence.
MITRE ATT&CK framework association
Some of the techniques and sub-techniques used at this stage of the APT attack include:
- T1566 Phishing: Using deceptive emails to lure victims into executing malicious payloads.
- T1190 Exploit public-facing application: Using known vulnerabilities to breach internet-facing services.
- T1189 Drive-by compromise: Unintentional downloads from compromised websites.
Stage 2: Establishing foothold
Once inside the network, attackers deploy additional malicious payloads like backdoor trojans, rootkits, or remote access tools to maintain ongoing access even if initial vulnerabilities are patched or credentials are changed.
MITRE ATT&CK framework association
The most common techniques and sub-techniques used at this stage of the advanced persistent threat attack include:
- T1055 Process injection: Attackers inject malicious code into legitimate processes such as svchost.exe or explorer.exe to evade detection.
- T1105 Ingress tool transfer: Downloading additional malicious tools post-infiltration.
- T1547 Boot or logon autostart execution: Configuring malware to execute on startup for persistence.
Stage 3: Privilege escalation and lateral movement
After attaining an initial foothold in the network, adversaries escalate their privileges to gain higher-level access and then move laterally across systems to identify other vulnerabilities or high-value targets. This dual approach ensures that the attack can persist even if some compromise points are discovered and remediated, allowing the threat actors to maintain control and progress toward their objectives.
MITRE ATT&CK framework association
Privilege escalation techniques:
- T1068 Exploitation for privilege escalation: Leveraging OS-level flaws to increase access.
- T1059 Command and scripting interpreter: Used to run malicious scripts or commands that might help attackers exploit privilege escalation vulnerabilities.
Lateral movement technique:
- T1021 Remote services: Using RDP, SMB, or SSH to move laterally across hosts within the network after gaining higher privileges and credentials.
Stage 4: Data exfiltration
Adversaries commonly secure stolen data within a protected network location by accumulating a sufficient amount before initiating extraction, known as " exfiltration ". Employing tactics such as a denial-of-service attack , cybercriminals divert the attention of the security team, ensuring a seamless exfiltration process. Even after exfiltration, the compromised network remains vulnerable, leaving the door open for future intrusions.
MITRE ATT&CK framework association
The major techniques and sub-techniques used at this stage of the Advanced persistent threat attack include:
- T1041 Exfiltration over C2 channel: Using command and control traffic for data theft.
- T1030 Data transfer size limits: Sending data in small, unnoticed chunks.
- T1567 Exfiltration over web service: Using cloud platforms or web services to exfiltrate data.
Stage 5: Persistence
Even after achieving their initial objective, APT attackers might leave behind hidden backdoors or create rogue accounts to regain access for future exploitation, making remediation particularly challenging.
MITRE ATT&CK framework association
The major techniques and sub-techniques used at this stage of the APT attack include:
- T1136 Create account: Adding unauthorized users to maintain access.
- T1505 Server software component: Embedding malicious modules into trusted software.
- T1027 Obfuscated files or information: Encrypting or modifying payloads to evade antivirus and EDR systems.
Advanced persistent threat examples
2020 – SolarWinds supply chain attack: Nation-state actors compromised the Orion software platform, distributing malware to over 18,000 customers, including United States federal agencies and Fortune 500 companies. This allowed widespread espionage and data theft.
2023 – Volt typhoon: A state-sponsored group linked to China targeted U.S. critical infrastructure, including communications, energy, transportation, and water sectors. The group remained undetected for months, using living-off-the-land (LOTL) techniques and compromised routers to maintain access.
2024 – Midnight Blizzard Microsoft email breach: APT29, a group linked to Russia, infiltrated Microsoft’s corporate email systems by compromising a legacy test account. The attackers accessed mailboxes belonging to senior leadership and cybersecurity staff, enabling them to steal sensitive communications and internal files. The breach highlighted the risks of unsecured legacy systems.
2025 – Snow Portal supply chain compromise: In a widespread supply-chain attack, threat actors inserted a backdoor into a widely used software dependency, later dubbed "Snow Portal." The compromised update was distributed to thousands of organizations, allowing attackers to gain initial access, create persistence mechanisms, and exfiltrate data undetected.
2025 – APT detection surge (RSA): The majority of attacks targeted U.S. telecommunications, transportation, and critical infrastructure sectors. Chinese-linked groups like APT40, Mustang Panda, and APT41 were identified as the most active threat actors, using stealthier and more evasive tactics.
Combat advanced persistent threats with Log360 - Book your free demo now!
starts at $2,130
To assist your evaluation Log360 offers:
- 30-day, fully functional free trial
- No user limits
- Free 24/5 tech support
Thanks for your interest in ManageEngine Log360
We have received your request for a personalized demo and will contact you shortly.
Fill this form to schedule a personalized web demo
Latest trends in APT attacks: Threat actors, techniques, and notable incidents
APTs have surged in both volume and sophistication throughout 2024 and in early 2025, with 136% surge in the U.S. in Q1 2025 according to the latest Trellix CyberThreat report. While these attacks are increasingly targeting a broader range of industries and geographies, certain industries faced the sharpest rise in APT incidents. The telecom sector accounted for 47% of all detected APT activity, followed by the transportation and shipping industries. Simultaneously, APT detections in the telecom industries also increased by 92% in the first quarter of 2025, compared to the previous quarter, underscoring the growing threats to critical infrastructure.
Key threat actors behind the recent APT campaigns
- APT40, Mustang Panda and APT 41: These groups have led a wave of sophisticated cyber operations, focusing on both cyber espionage and financially motivated activities. Notably, APT41 has targeted sectors such as healthcare, high-tech, telecom, and shipping and logistics, often leveraging software supply chain compromises and advanced malware. APT41 stands out for combining state-sponsored espionage with criminal operations, including ransomware and theft in video game industry, and is known for using non-public malware and compromised digital certificates.
- APT29: Midnight Blizzard, a threat group attributed to Russia's Foreign Intelligence Services (RFIS) often targets inactive user accounts and other account manipulation techniques for intrusion and persistence, intensified its focus on transportation, shipping, and telecommunications, with attacks often aligned with real-world geopolitical conflicts.
Emerging tactics and technologies in APT:
The latest trends in APT attacks highlight a surge in AI-driven attacks, cloud exploitation, and advanced evasion techniques.
- AI-powered APT attacks: APT groups are now leveraging artificial intelligence and deep learning to automate reconnaissance, craft highly convincing phishing campaigns, and dynamically adapt malware to evade detection. When AI drives an APT stage, it becomes increasingly difficult to detect and contain the attack.
- Cloud exploitation: As organizations migrate to cloud environments, APTs are exploiting cloud misconfigurations as an increasing rate.
- Supply chain attacks: With the APT actors increasingly targeting IoT devices and transportation industries, there has been a marked increase in attacks on supply chains. APTs often inject malicious code into legitimate software updates to amplify the reach and impact of their campaigns.
- LOTL and open source tools: APT actors are increasingly using legitimate system tools and open-source software to manage command and control (C2) infrastructure, making detection and attribution more challenging.
Map threats to MITRE ATT&CK TTPs and uncover APTs faster.
Indicators for detecting an APT
Determining if your organization has fallen victim to APTs is difficult given the meticulous measures cybercriminals take to evade detection. However, there are indicators that can serve as an early alert mechanism for APT occurrences.
Network-level indicators of APT activity:
- Unusual outbound traffic to unfamiliar IP addresses or domains (Moderate difficulty): This might indicate data exfiltration or communication with command-and-control (C2) servers.
ManageEngine Log360 detects this behavior by analyzing outbound traffic patterns by baselining traffic and using machine learning models to detect anomalies. It also spots suspicious traffic such as connections to low-reputation helping security teams flag potential exfiltration attempts early.
- Consistent beaconing behavior to external servers at regular intervals (High difficulty): This type of repetitive communication is a hallmark of malware calling back to its C2 server, often used to maintain remote access or receive instructions.
ManageEngine Log360 detects behavior by detecting periodic network communication patterns using anomaly detection and traffic baselining techniques. Learn more on how Log360 can help you tackle APT attacks by scheduling a call with our solution experts.
- Use of domain generation algorithms (DGAs) for dynamic domain resolution (High difficulty): Attackers use DGAs to generate numerous domain names on the fly, helping them evade traditional domain-blocking defenses and maintain resilient C2 infrastructure.
Log360 leverages threat intelligence feeds and DNS traffic analysis to detect connections to suspicious domains often associated with DGAs. Unusual DNS query patterns and rare domain requests can also be flagged through UEBA-driven anomaly detection.
- DNS tunneling to encapsulate data within DNS queries (High difficulty): This technique hides data exfiltration or C2 commands within seemingly legitimate DNS requests, bypassing firewalls and traditional DLP controls.
Log360 monitors for anomalies such as abnormally high DNS query volumes, high-entropy or suspicious domain names, and unusual DNS record types or payload sizes. These indicators, when correlated with user or host behavior, help uncover stealthy DNS tunneling attempts often used by APT actors.
Host/endpoint-level indicators for APT activity:
- Suspicious logins from privileged accounts during non-business hours (Easy to detect): Login attempts outside of normal working hours, especially from high-privilege accounts, might indicate credential compromise or malicious lateral movement.
Log360 uses UEBA to build a behavioral baseline for each user and triggers alerts when a login occurs outside the expected time window, especially from unusual IP addresses or geolocations.
- Use of legitimate administrative tools like PowerShell or PsExec for lateral movement (Moderate difficulty): Attackers often abuse built-in tools to avoid detection while moving laterally within the network. These actions might appear legitimate unless correlated with context.
Log360 detects such misuse by correlating process execution logs with user roles and context, highlighting anomalies such as a non-admin user launching remote commands or executing scripts across multiple endpoints within a short timeframe.
- Unauthorized modifications to startup scripts or registry entries for persistence (Moderate to high difficulty): Attackers might alter system configurations to ensure malware runs on every reboot, maintaining access over extended periods even after detection attempts.
Log360 monitors for unexpected changes in task scheduler entries, and registry run keys, comparing them against known baselines and alerting when deviations or tampering is detected.
- Presence of backdoor trojans or rootkits (High difficulty): These malicious programs can provide attackers with persistent, covert access to compromised systems.
Log360 leverages integrated threat intelligence, file integrity monitoring, and behavioral analytics to detect indicators of backdoors or rootkits. This includes unsigned driver loads, abnormal process behavior, hidden network activity, and unauthorized access attempts, helping security teams respond before deeper system compromise occurs.
Worried about undetected APTs lurking in your network?
How can you prevent an APT attack?
APTs pose a significant obstacle in cybersecurity. As technological progress marches forward and attacks grow increasingly refined, it is imperative that both entities and individuals embrace a preemptive and multifaceted strategy to protect against APTs. By comprehending the traits of APTs and establishing resilient security protocols, we can effectively traverse the obscurities of the digital realm and shield our digital valuables from determined foes. Here are some ways to prevent APTs threats:
- Deploy a web application firewall (WAF)
A WAF acts as the first line of defense between your web applications and the internet. It inspects incoming traffic, filters out malicious requests, and blocks known attack patterns. To stay ahead of evolving threats, it’s essential to regularly update and fine-tune your WAF rules based on the latest threat intelligence.
- Utilize threat intelligence
To stay up to date on APT groups, their TTPs, as well as emerging threats, refer to threat intelligence feeds from credible sources. Organizations can use threat alerts to restrict communications from harmful sources as well as automatically trigger a workflow to add blacklisted IPs to the firewall and permanently block them.
- Conduct threat hunting
Go beyond automated detection by proactively seeking out hidden threats within your environment. Threat hunting helps uncover attack indicators that might bypass traditional security tools, enabling you to take swift action before attackers can escalate.Configuring real-time alerts ensures your security team is notified the moment threat patterns recur in your network.
- Detect and prevent backdoors:
Backdoors are commonly used by APT attackers to maintain persistent access to a system. Detecting them early requires continuous monitoring of network traffic, user behavior, and system logs to identify signs of unauthorized remote access, privilege escalations, or covert malware activity. By implementing a unified threat monitoring strategy, you can eliminate attacker footholds before they escalate into full-blown breaches.
- Leverage SOAR capabilities for automated response
Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) capabilities help streamline threat response by automating repetitive and time-sensitive remediation tasks. From isolating compromised systems to disabling suspicious accounts and blocking malicious traffic, SOAR empowers security teams to respond faster and more consistently, minimizing attacker dwell time and reducing overall risk.
How Log360 can help detect and prevent APT attacks
APT actors often operate under the radar, using stealthy techniques to maintain long-term access to your network. ManageEngine Log360, a unified SIEM solution, is built to counter these threats through continuous monitoring, correlation-driven detection, and accelerated response workflows.
Detecting advanced threat behaviors across systems and networks
Log360 tracks real-time network traffic and system activities to detect abnormal behaviors that indicate the presence of APTs. Whether it’s unusual outbound traffic patterns, unauthorized privilege escalation, or lateral movement across systems, Log360 uses behavioral analytics and correlation rules to surface indicators that traditional solutions might miss.
Correlating events to reveal multi-stage attacks
Log360 correlates logs from firewalls, endpoints, servers, and cloud platforms to uncover hidden relationships and surface attack chains. By linking seemingly isolated events, it helps identify APT techniques like c redential misuse, data staging, and exfiltration .
Mapping APT activity to MITRE ATT&CK TTPs
Log360 maps detected malicious behaviors such as persistence (T1547), valid account usage (T1078), or command-and-control communication (T1071) to the corresponding tactics and techniques defined in the MITRE ATT&CK framework. This mapping provides security analysts with contextual insights and prescriptive countermeasures to accelerate threat detection and response.
Enhancing detection with threat intelligence
Deviations such as a user logging in from an unusual location or accessing sensitive systems outside business hours are flagged as potential signs of an APT. Combined with integrated threat intelligence feeds, Log360 helps distinguish real threats from noise.
Accelerating incident response with automated workflows
Log360’s TDIR capabilities guide analysts from detection to resolution. Playbook-based automation helps teams contain APT activity faster, limiting dwell time, and reducing the impact of data theft or disruption.
FAQs
What are APTs?
Advanced persistent threats (APTs) are prolonged and targeted cyberattacks in which threat actors gain unauthorized access to a network and remain undetected for an extended period. These attacks are often carried out by well-funded groups such as nation-states or organized cybercriminals using sophisticated tools like zero-day exploits, custom malware, and social engineering. Unlike typical cyberattacks, APTs focus on espionage, data theft, or sabotage rather than immediate financial gain, making them more dangerous and difficult to detect.
What is APT in cybersecurity?
An APT is a targeted cyberattack in which an attacker gains unauthorized access to a network and remains undetected for an extended period. These attacks are often carried out by well-funded and highly skilled threat groups aiming to steal sensitive data, conduct espionage, or disrupt operations. APTs are “advanced” due to the custom tools and stealth techniques used, and “persistent” because the attackers maintain long-term access to the target environment.
How do APT attacks work?
APT attacks unfold in multiple stages: initial compromise (often via phishing or exploiting vulnerabilities), establishing a foothold, privilege escalation, internal reconnaissance, lateral movement, data exfiltration, and maintaining persistence. Attackers use advanced techniques and evade detection by mimicking legitimate activity and using tools already present in the environment.
What is the difference between APT and other cyberattacks?
Unlike typical cyberattacks that are quick and opportunistic, APTs are long-term, targeted, and involve multiple stages. They are often conducted by nation-states or organized groups with specific strategic objectives, making them more dangerous and harder to detect.
Secure your organization's critical assets from advanced persistent threats and strengthen your cybersecurity posture against both known and emerging threats with ManageEngine Log360.
- What is APT?
- Stages of an APT attack
- Advanced persistent threat examples
- Latest trends in APT attacks: Threat actors, techniques, and notable incidents
- Indicators for detecting an APT
- How can you prevent an APT attack?
- How Log360 can help detect and prevent APT attacks
- FAQs