What is Phishing? Phishing defined, dissected, and explored.
- What is phishing?
- Phishing types and techniques
- Important phishing incidents
- Phishing in an enterprise scenario
- Best practices
- How can ManageEngine Log360 help?
What is phishing?
Phishing is a well-established cybercrime that has been around since the nascent stages of the internet. It can be thought of as the "con-artist of the cyberworld," as it works by combining deceptive tactics and cyber exploitation techniques.
Though phishing is usually associated with bogus emails, threat actors and scammers have kept in step with the digital revolution by using text messages, phone calls, and social media. There are now more ways than ever for scammers to deceive and collect personally identifiable information (PII), harvest credentials, steal financial data, distribute malware, and cause considerable damage through phishing.
How did phishing get its name?
It's often thought phishing got its name from the word fishing. After all, with it's use of bait and traps on unsuspecting victims, the parallels are there. Also, phishing draws inspiration from the terms like "phreaking," used by hackers to describe their hacking of telecom systems. "Phishing" was officially first used in the mid-1990s to address one of the major scamming incidents - the America Online (AOL) scam where fake credit cards were used to create AOL accounts to scam users.
Stats and facts to ponder upon: Impacts of phishing
- Ninety-one percent of successful data breaches start with a phishing email.
- Google reports that it blocks around 100 million phishing emails every day.
- According to the FBI's Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), business email compromise, one of the prominent phishing techniques, has caused monetary losses that amount to USD 26 billion.
- The AI revolution has made it easier for phishers to mimic writing styles, clone voices, and create deepfake videos for deception.
- Social media-based phishing attacks have exponentially increased in recent years, making up 12% of all the phishing scams.
Phishing types and techniques
1. Based on scale
- Casting Casting attacks are untargeted, mass campaigns aimed to throw a broad net with generic lure messages to quickly gain monetary benefits, collect PII, or distribute malicious attachments. Though they lack sophistication and personalization, and are highly likely to end up in spam folders, they can have an effective ROI if even a small percentage of people respond.
- Spear phishing Spear phishing involves targeting specific individuals, after researching their activities through multiple mediums, and crafting messages that are seemingly legitimate and relevant to the individual. The targets can range from regular employees to high-level executives across different industries. These attacks enjoy a much higher success ratio compared to generic phishing campaigns.
- Whaling Whaling is a subcategory of spear phishing that aims for the biggest 'phishies' in the sea like C-level executives, board directors, and officials from federal agencies. Business email compromise or CEO fraud is a common technique used in whaling attacks, where the threat actors compromises the email account of higher executives or spoofs the mail address to send internal phishing emails to employees. Another prevalent technique is impersonating third-party vendors and establishing trust through identity theft or spoofing.
2. Based on purpose
- Reconnaissance Phishing for information is a reconnaissance technique, as described in the MITRE ATT&CK® framework. Threat actors may send survey links, try to strike a conversation through different mediums to gather details that can be used to create a more personalized phishing attack.
- Credential harvesting This type of attack focuses on collecting user credentials. An attacker usually shares a link to a fake login page of a legitimate website to capture a user's credentials. A more sophisticated version, known as pharming, involves sharing malware that can manipulate the DNS settings locally or even poison the DNS servers to redirect users to malicious sites, even when they enter the correct URLs. Other types of malware like keylogger malware or password stealing malware can directly record keystrokes and steal locally stored passwords.
- Consent harvesting
Consent harvesting involves tricking users to grant permissions to third-party applications that pose to be from legitimate and familiar sources. Using this technique, attackers get access tokens that allow them permissions to make API calls, gain access to sensitive files, and make changes to account settings without having to steal credentials.
Phishing attacks that target many mid-to-large-sized organizations aim to launch APTs. These are highly targeted, complex attacks that may use multiple techniques of phishing in the initial access stage to gain a strong foothold in the network. The malware shared initially conducts reconnaissance activities and establishes a command and control channel to receive further payloads to gain persistence, install backdoors, and exfiltrate data.
3. Based on medium
- Website Apart from creating fake domains and clone websites, phishers actively manipulate website content to include malicious links. This is known as the waterholing technique, carried out after researching the websites their targets visit regularly. The injected content can appear in the form of pop-ups, hyperlinks in the content, CTAs, or can also download malware automatically once the user visits the page.
- Email Email is used for official communications, and yet, people give their email addresses away freely. This has helped emails to be the most effective phishing platform for decades. Attackers can use emails to initiate a conversation and establish trust, send malicious links, attachments, executables, docs with embedded macros, and more. Email offers versatile options to phish, and multiple aspects that can be spoofed like the sender name, domain, URLs, content, and attachments.
- Vishing Voice phishing, also known as vishing, is the use of direct voice calls to trick targets into performing the desired actions. Scammers pretend to be authority figures from banks, federal agencies, and organizations calling for interviews. They may use pre-recorded messages, spoof caller IDs, and even create AI-generated voices to appear authentic.
- Social media Social media like Facebook, LinkedIn, X, and Instagram have become treasure troves for scammers looking to collect personal and professional information on their targets. Apart from gathering information, phishers may set up fake profiles, send direct messages, and run deceptive ads known as malvertising. The use of AI-generated deepfake videos, fake QR codes, and adding malware links to digital ads have become increasingly prevalent.
Important phishing incidents - Attack profiling
Google and Facebook scam
- Type of attack Third-party impersonation leading to wire transfer
- Medium Email
- Impact Over $100 million
Incident: This scam was carried out by a single person from Lithuania in 2013. He impersonated a Taiwan-based, third-party associate and sent spear phishing emails with forged invoices to Google and Facebook personnel, which led to wire transfers of millions of dollars. It took two years for the tech giants to detect the scam and sue the phisher.
Operation Ghost Click
- Type of attack Pharming
- Medium Website
- Impact Four million computers affected worldwide and $14 million loss
Incident: In 2010, hackers from Estonia and Russia spread a malware called DNSChanger, which manipulated DNS settings of infected systems. This led to clicks on ads without user awareness, redirection to phishing sites, and malware distribution from the user's systems. Apart from the monetary loss, this attack exposed the personal data of millions.
Advance fee scams
- Type of attack Widespread phishing campaigns
- Medium Email / Social media / Vishing
Advance fee scams are a type of mass phishing campaign where targets are lured to pay an advance for the promise of a business opportunity, lottery win, or other attractive returns. A common example of this scam is the "Nigerian prince" email scam, where the sender requests help smuggling wealth out of a foreign country and promises to pay the victim for their assistance. This scam tricks victims into sending their bank details and paying a processing fee.
Operation Ghost Click
- Type of attack Advanced persistent threat through spearphishing
- Medium Email
- Impact Infrastructure damage
Incident: In 2010, phishing emails sent to Iranian nuclear scientists infiltrated the nuclear enrichment facility's internal network with malware and took control of the Windows Siemens Step7 software to sabotage the functioning of centrifuges. This incident is said to be a successful demonstration of a complex and undetectable malware spread through phishing for the use of cyber warfare. Though speculations exist, the perpetrators of this attack are still officially unknown.
Phishing in an enterprise scenario: How can organizations build their defenses?
Here are a few answers to important questions and best practices to help you better understand phishing in an enterprise scenario and build your defenses.
How do attackers acquire business emails?
The following are some of the common ways scammers can acquire business emails:
- Using the dark web to buy and sell email addresses. They can also be purchased legally from mailing list providers.
- Digging through company websites and social media profiles. Attackers also use harvesting bots to capture hundreds and thousands of email addresses publically available online.
- Hacking high-ranking landing pages, or creating fake landing pages and advertising them, to capture emails in bulk through forms.
How do phishing emails bypass network security?
Most organizations have at least a basic level of perimeter security with firewalls, email scanners, and anti-virus software. And email service providers have strong anti-spam filters that use authentication protocols like DKIM, DMARC, and SPF and flag mails based on IP and domain reputation scores, email sharing rates, and history of interactions. Here's how phishers bypass them:
- Hacking trusted domains and sending mails from them, or creating legitimate domains, improving their reputation score over the years, and then leveraging them for attacks.
- Hosting phishing content on trusted cloud-based applications and sharing the links.
- Sharing encrypted and password-protected files.
- Using a conversational and professional tone to improve open rates and response to emails initially, to escape being flagged as spam.
- Sharing HTML attachments, which when run locally on browsers, lead to malware payloads and spoof websites.
Social engineering scenarios
Social engineering tactics employ a combination of psychological triggers to persuade an individual to take an action. Here are some common cases of social engineering in an enterprise scenario:
| Triggers | Examples |
|---|---|
| Use of familiarity |
|
| Use of curiosity |
|
| Use of emergency |
|
| Use of panic |
|
Best practices and defensive measures for organizations
It's common knowledge that phishing attacks are expensive and can impact an organization's operations and reputation. Another serious consequence is falling out of compliance with major IT regulatory standards.
Failing to prevent phishing attacks due to poor security measures or the inability to detect, contain, and report early on attacks will lead to serious penalties. Here are some of the best practices to defend against phishing:
- Define anti-phishing policies with multiple scenarios of social engineering techniques, knowledge of identifying phishing mails, and reporting procedures.
- Conduct periodic awareness training and phishing drills relevant to employees, SOCs, and executives. The entire organization should be aware of how to react to phishing attempts.
- Deploy email scanning tools that can analyze email content, headers, domains, and URLs to flag, block, or quarantine emails. Use advanced mechanisms like sandboxing and URL detonation to securely test emails before they reach the inbox.
- Enforce the use of strong passwords, regular password updates, MFA, and VPNs.
- Perform regular system and software audits and patch management to avoid the exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities through malware infiltration from phishing emails.
- Analyze network traffic flow to help identify anomalies in outbound traffic and detect pharming attacks.
- Use information from global threat intelligence repositories to identify malicious sources and correlate network events with attack patterns.
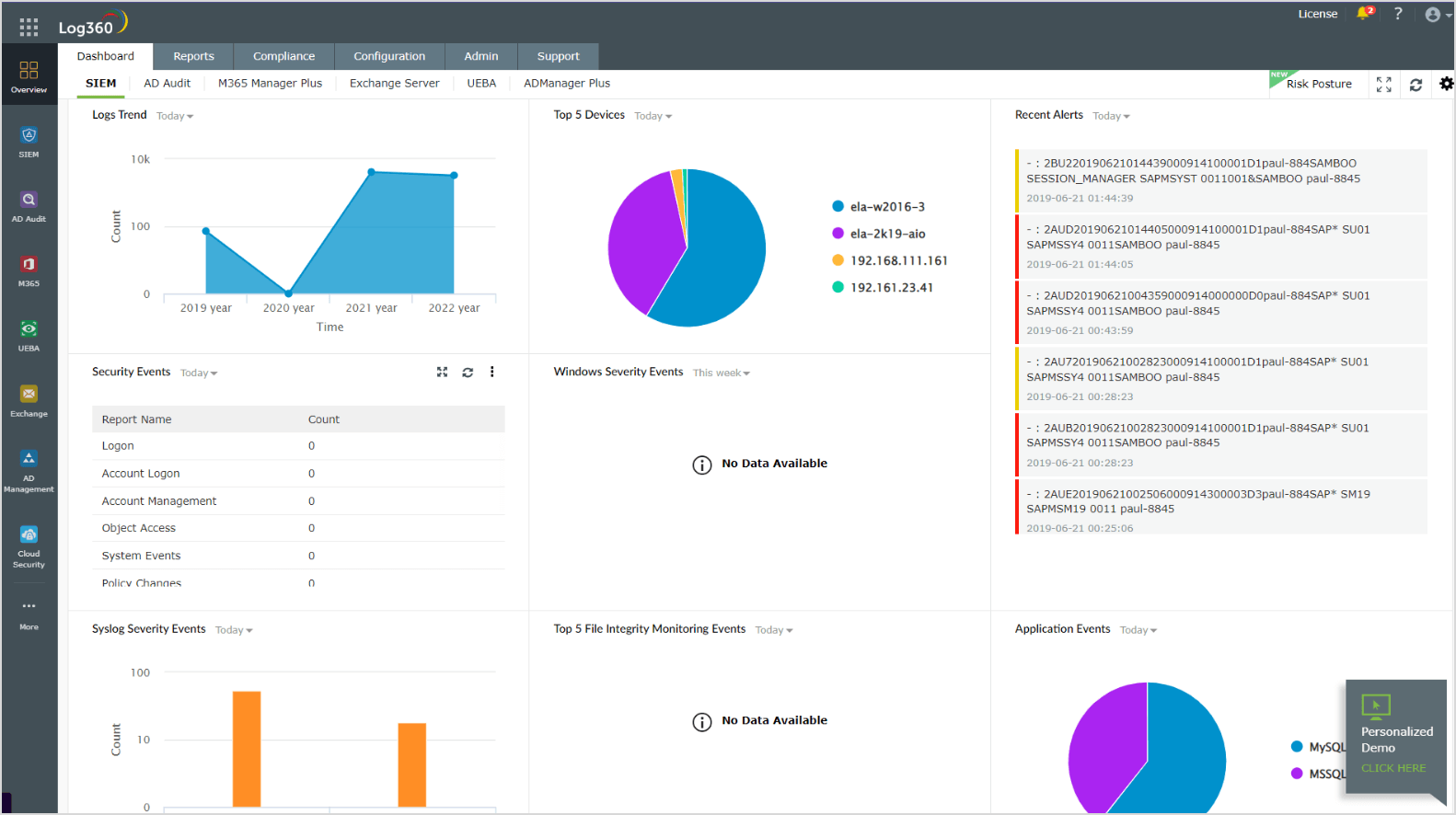
- Implement additional layers of security with tools like SIEM and UEBA to continuously monitor network entities and events. This measure will greatly help with detecting indicators of compromise, remediating threats early on with incident response workflows, and staying audit ready with automated reports.
Arming up with defensive strategies and tools will greatly reduce the success of phishing attempts on your organization, but it just takes one employee to click a malicious link and open the floodgates. Remember, Google and Facebook took years to identify a phishing scam, so it's important to be prepared for what happens after an attacker executes a successful phishing attack on your organization.
How can ManageEngine Log360 help?
ManageEngine Log360 is a SIEM tool developed to provide comprehensive protection against cyberattacks with the following threat detection and incident response capabilities:
- A central monitoring` entity for your layers of defense. Log360 helps monitor network events and anomalies by collecting logs from perimeter devices, firewalls, antivirus software, servers and database applications, Active Directory, and cloud sources.
- The rule-based correlation engine can draw the connections between activities across your network to identify attack patterns.
- Microsoft 365 and Exchange Server auditing features help monitor the inbound and outbound email traffic and analyze email content to identify malicious attachments.
- Real-time notifications of attack detection sent through the alerting system allow SOCs to immediately activate remedial measures through the predefined incident response workflows.
- Advanced threat intelligence, offered through integrated global threat feeds, helps cut off any interaction with millions of globally blocklisted URLs and IPs.
Enhance your security posture by leveraging the capabilities of Log360
Let our experts evaluate your security requirements and demonstrate how Log360 can help satisfy them.