Playbook management overview
Last updated on:
In this page
Overview
Playbooks are automated response workflows designed to help mitigate security incidents as soon as alerts are triggered. Whether it’s disabling compromised user accounts, blocking IPs, or enforcing USB policies, playbooks reduce response time and manual intervention through intelligent recommendations and predefined actions. This document explains how playbooks work, how to execute them, and how they align with real-world use cases mapped to the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
What is playbook?
You can mitigate security incidents in your network before they result in a breach by automating response workflows when alerts are triggered. The product allows you to create such workflows to automatically perform actions such as disabling USB ports, shutting down systems, and changing firewall rules when security incidents are detected. This automated capability that provides remediation suggestions is called Playbook.
Playbook recommendations
Playbook recommendations are intelligent, context-aware response suggestions provided for every alert raised in the system. As soon as the product is launched, the playbook recommendation engine is initialized in the background. These recommendations are based on predefined logic that links specific alert types to optimal mitigation or investigation workflows, such as disabling a user account for suspicious login activity, or blocking an IP after detecting port scanning. This system ensures faster, guided incident response and minimizes manual decision-making during critical security events.
When you click on an alert, the engine processes the alert’s event data and metadata including parameters like event type, source device, user behavior, and historical response patterns. Based on this context, it evaluates and maps the alert to the most relevant response workflows in the form of playbooks.
Each applicable playbook is assigned a relevance score that reflects how well it matches the characteristics of the alert. The top five scoring playbooks are then displayed under the Run Playbook section.
Workflow architecture
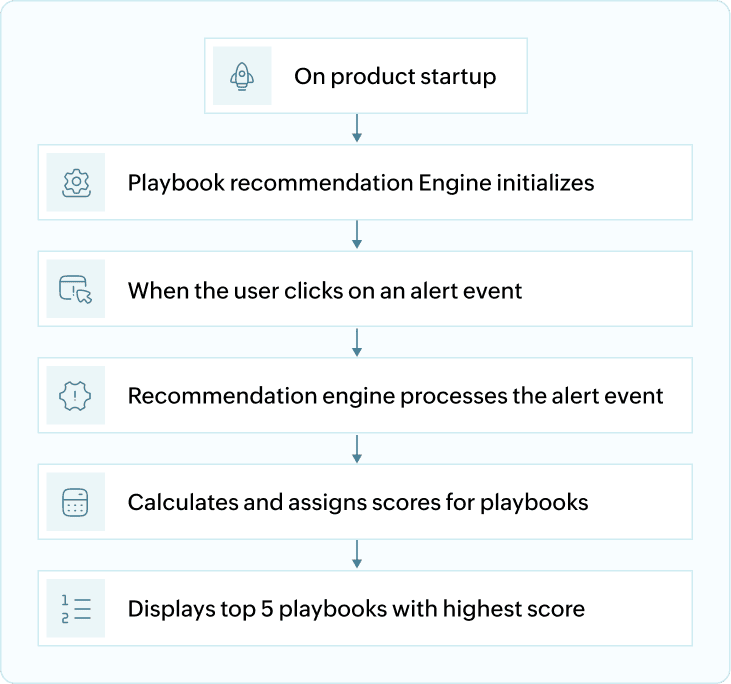
How is a playbook executed?
There are two ways in which a playbook can be executed:
A. When a playbook is associated to an alert profile
When an event triggers an alert, and the alert profile has a playbook linked to it, the playbook runs automatically. In short, the event causes an alert, and the alert triggers the assigned playbook.
Refer to this document to learn how to associate a playbook to an alert profile.
B. On-Demand playbook execution
When an event occurrence is identified, you can manually execute a playbook- either from the list of Recommended Playbooks or Other Playbooks provided in the product console via the Alerts tab.
Below is the step-by-step guide on how to execute a playbook manually.
- In the product console, navigate to the Alerts tab. The Run Playbook option is provided for each of the alerts generated. Click on the Run Playbook option associated with the alert you wish to execute the playbook for.
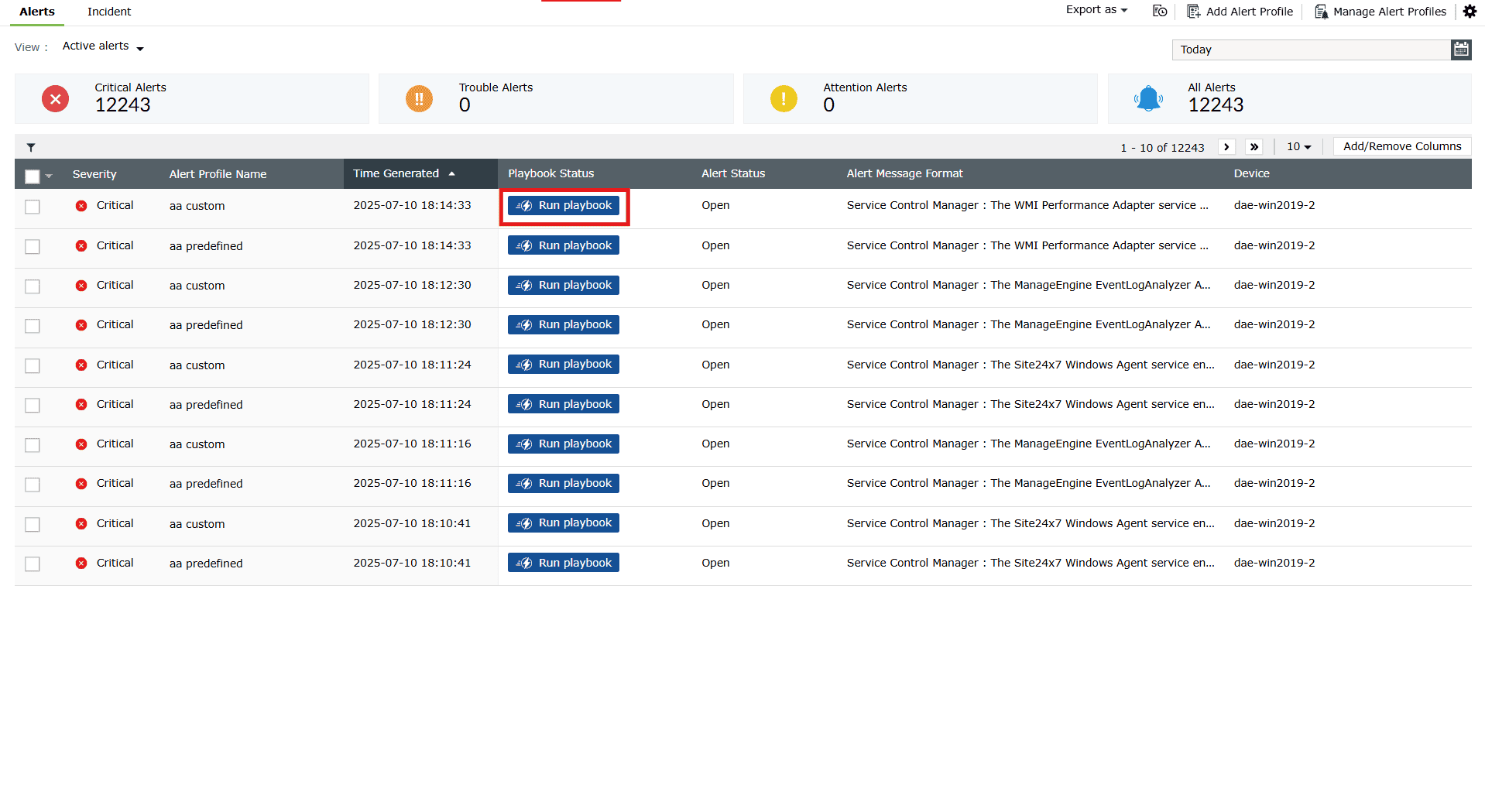
Image 1: Run playbook option for alerts in the alert profile - The Run playbook box with the available recommendations for that alert slides in. Click on the Run playbook button of any recommendation option you wish to execute as shown below.
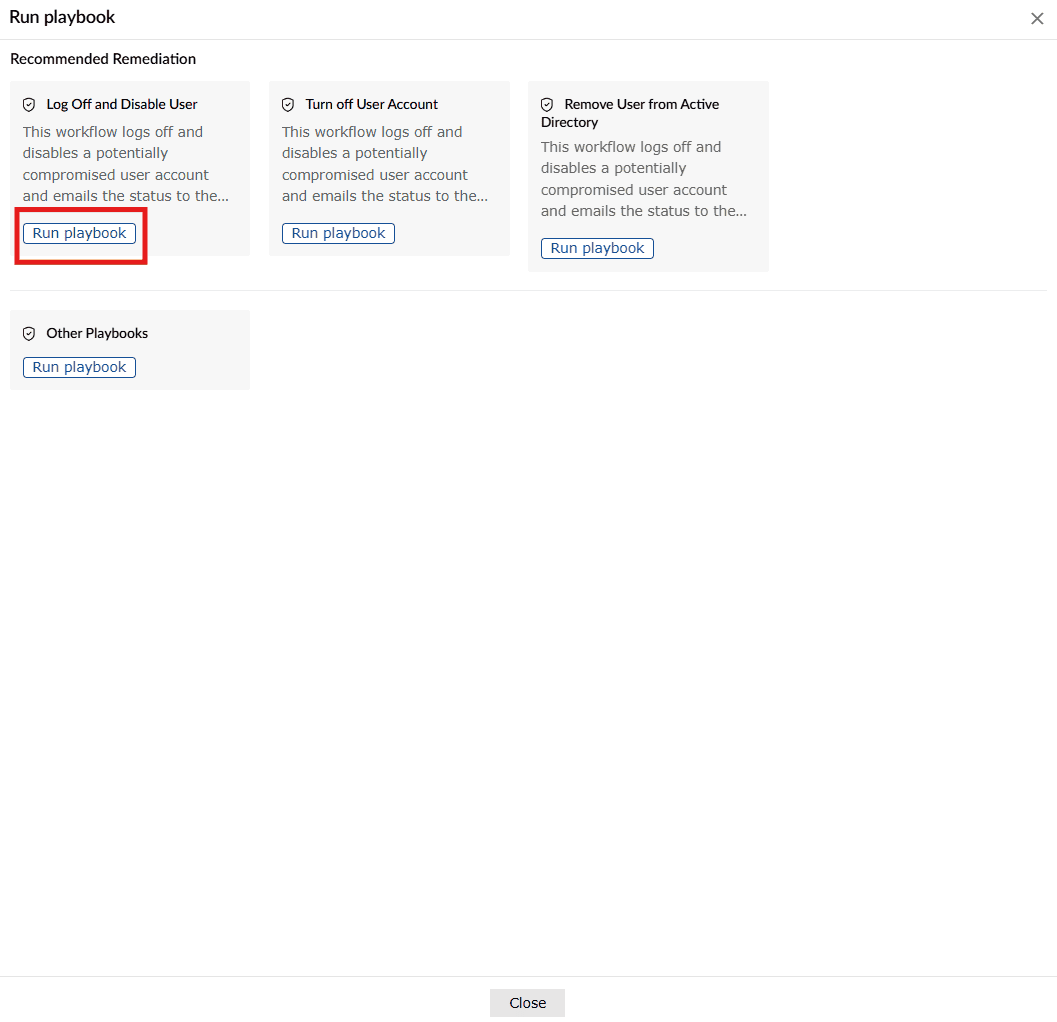
- The recommendations expand into fields as shown below.
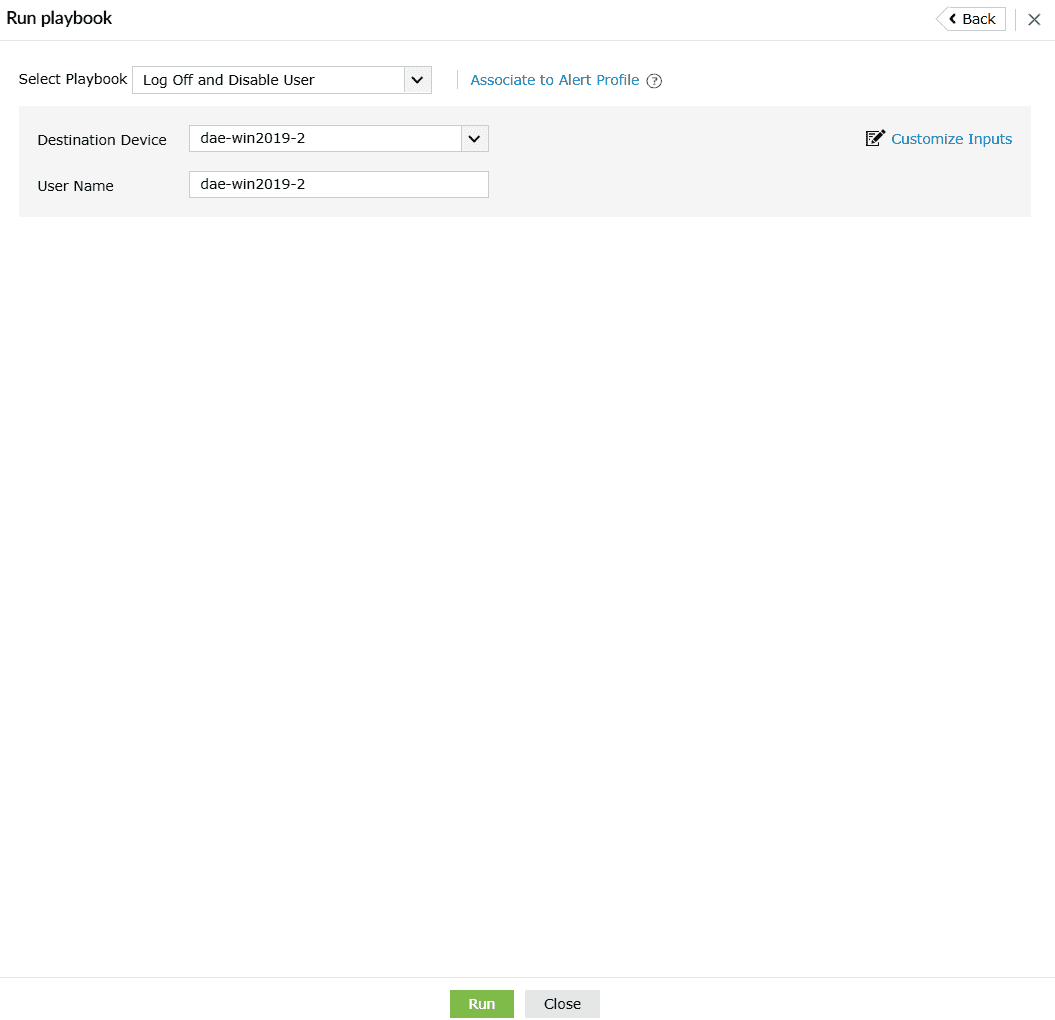
- The fields in each playbook recommendation vary from playbook to playbook. Click on Run after providing all the necessary inputs. The playbook is executed, and the below pop-up appears.
Playbook history
You can access and view the list of playbooks used until now from the playbook history as explained below:
- Click anywhere on the row of the required alert profile in the Alerts tab.
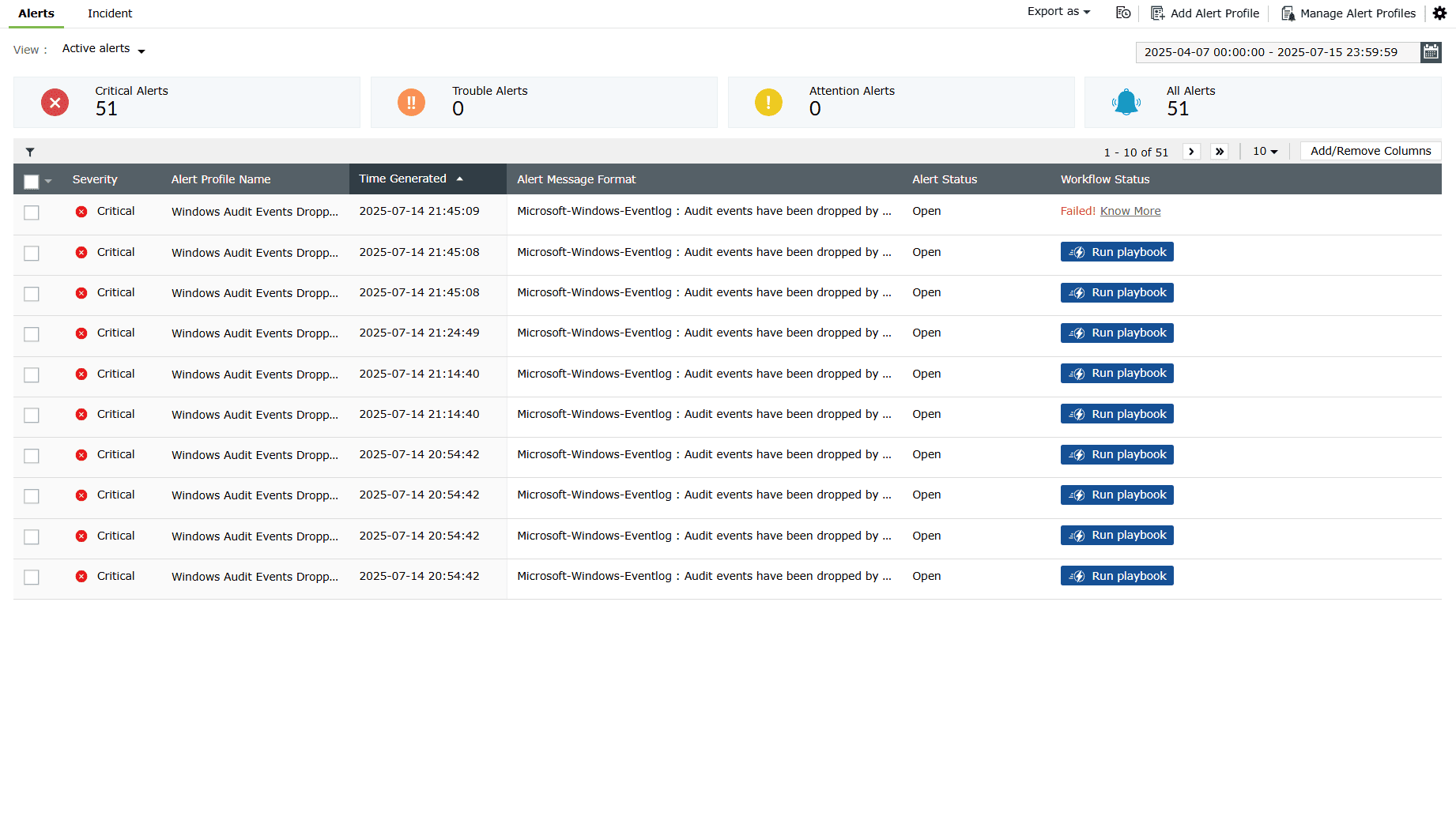
Image 2: Playbook remediations for alerts via the Alerts tab - When you click on an alert name, the details of the alert and the related playbooks appear. Under Remediation, you can see the history of the playbooks used for the same alert up until now.
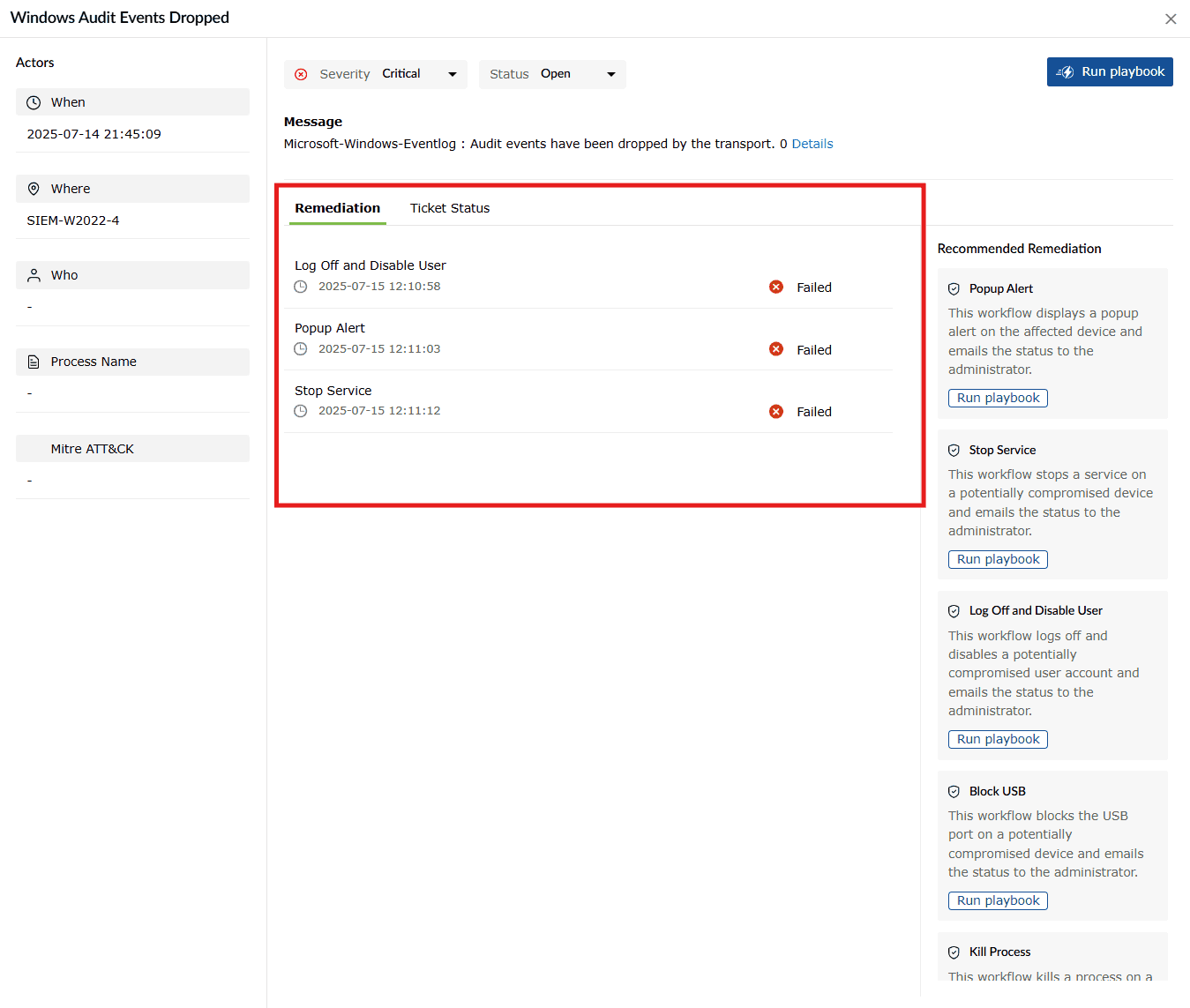
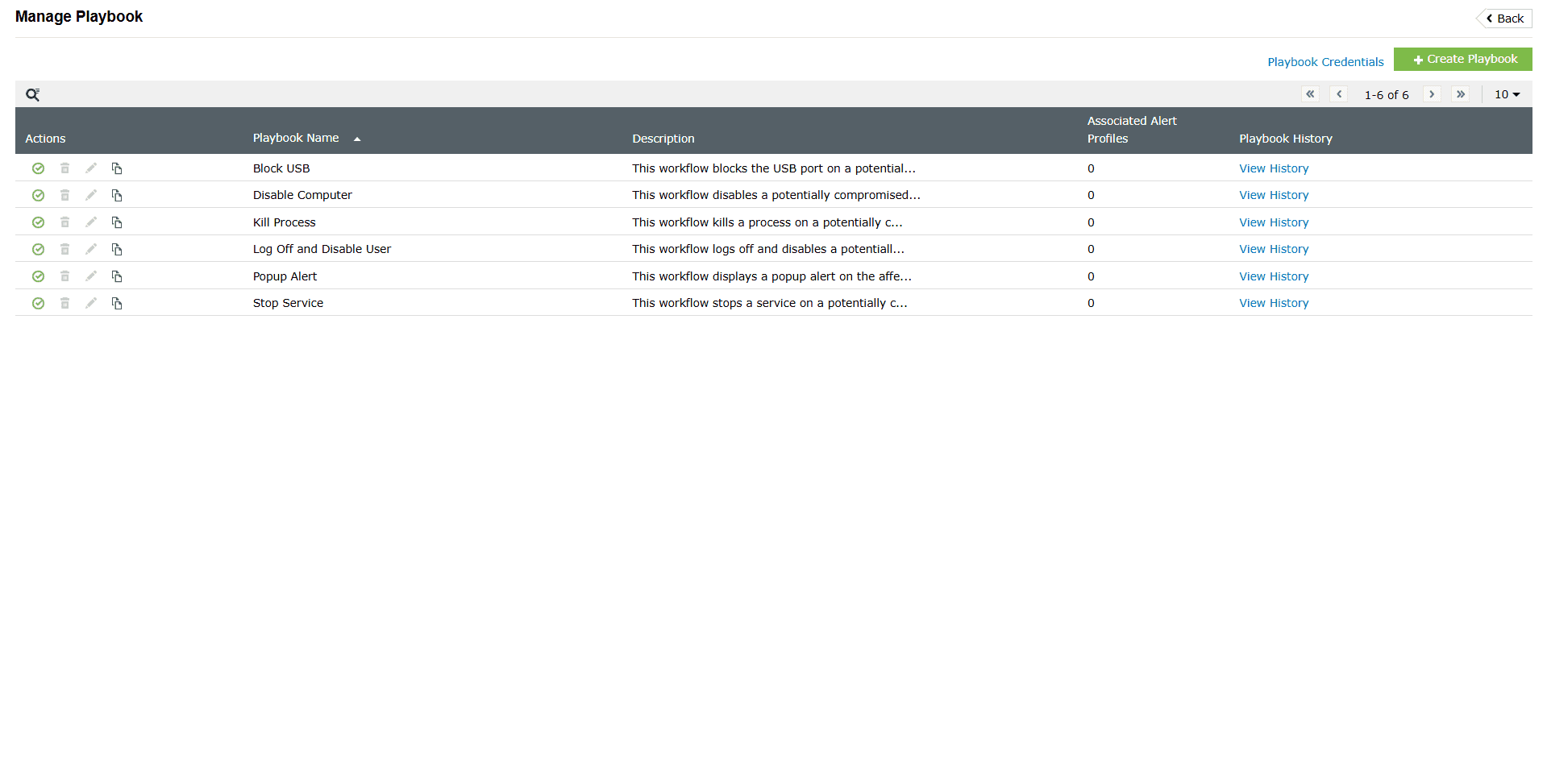
Image 3: Viewing playbooks history from the remediations
Pre-defined playbooks
The product offers 6 predefined playbooks for quick response to common security incidents. These ready-to-use playbooks perform actions like blocking USB ports, disabling computers, killing processes, or logging off users. Though they can’t be edited or deleted, you can run them on demand, link them to alert profiles, or use them as templates when creating custom playbooks. Below is the list of all 6 predefined playbooks and their description.
| Playbook name | Description |
|---|---|
| Block USB | This playbook blocks the USB port on a potentially compromised device and emails the status to the administrator. |
| Disable Computer | This playbook disables a potentially compromised computer and emails the status to the administrator. |
| Kill Process | This playbook kills a process on a potentially compromised device and emails the status to the administrator. |
| Log Off and Disable User | This playbook logs off and disables a potentially compromised user account and emails the status to the administrator. |
| Popup Alert | This playbook displays a popup alert on the affected device and emails the status to the administrator. |
| Stop Service | This playbook stops a service on a potentially compromised device and emails the status to the administrator. |
Use cases
1. Real-time ransomware containment in endpoint environments
Use case
Ransomware attacks usually begin with suspicious file activity or an unauthorized encryption process on the endpoints.
With Playbooks
Playbooks aid in effective remediation strategies when a potential ransomware attack attempt is detected. You can auto-trigger a playbook to disable USB ports, shut down infected systems, block lateral movement via firewall rules, and also notify SOC teams—all within seconds of detection. This helps in reducing the attack blast radius while ensuring business continuity.
Tactic: Impact (TA0040), Execution (TA0002)
Technique: Data Encrypted for Impact (T1486), Command and Scripting Interpreter (T1059)
2. Adaptive firewall rule automation against emerging threats
Use case
A swift response is crucial after detection of Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) like malicious IPs or domains identified in threat intelligence feeds.
With Playbooks
The matching of alerts can trigger instant automated updates to firewall configurations like deny inbound/outbound rules for Cisco ASA, FortiGate, PaloAlto, SophosXG; etc and effectively blacklist malicious endpoints without the need for any manual rule entry thus, ensuring a rapid response across perimeter devices.
Tactic: Defense Evasion (TA0005), Command and Control (TA0011)
Technique: Ingress Tool Transfer (T1105), Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols (T1071.001)
3. Automatic user account lockdown during Brute-force attacks
Use case
User accounts are targeted during malicious attempts like brute force login attempts and password spraying.
With Playbooks
When an alert for multiple failed login attempts is triggered, a well configured playbook can instantly disable the associated account, block the source IP in the firewall and also notify the admins via alert notifications. This ensures instantaneous mitigation before the attacker(s) successfully authenticate
Tactic: Credential Access (TA0006)
Technique: Brute Force (T1110), Password Spraying (T1110.003)
4. Smart patching of vulnerabilities through Endpoint Central
Use case
Unpatched systems are highly advantageous as entry points for attackers. In large organizations, coordination with IT teams for patching is often delayed/time-consuming.
With Playbooks
When a vulnerability is detected, a playbook can approve the patch and also initiate its deployment via Endpoint Central without requiring any human intervention. This closes critical vulnerabilities faster than any of the manual processes.
Tactic: Initial Access (TA0001), Persistence (TA0003)
Technique: Exploit Public-Facing Application (T1190), Exploitation for Privilege Escalation (T1068)
5. Rogue device detection and network quarantine
Use case
Unknown devices can suddenly appear on the network, often behaving anomalously or bypassing the critical asset inventories.
With Playbooks
When an alert is triggered for such suspicious device activities, a traceroute can be run along with a ping test to assess network path, then disable that device account in AD and create deny access rules in firewalls. This ensures that suspicious assets are isolated immediately while preserving evidence for forensics simultaneously.
Tactic: Discovery (TA0007), Lateral Movement (TA0008)
Technique: Remote System Discovery (T1018), Exploitation of Remote Services (T1210)
6. Centralized enforcement of USB security policies
Use case
Unmanaged USB ports on high-risk systems can act as entry points for attacks pertaining to data leaks
With Playbooks
Optimized configurations could be made in the playbooks to automatically disable USB ports on systems detected for anomalous behavior or based on policy violation alerts. This also ensures zero-trust enforcement even in distributed endpoint environments.
Tactic: Collection (TA0009), Exfiltration (TA0010)
Technique: Data Staged (T1074), Exfiltration Over Physical Medium (T1052)
Read also
This document covered Playbook functionality, execution methods, and use cases. For related capabilities that enhance security orchestration and response, refer to