Sensors
Overview
Sensors in DEX Manager Plus allow IT administrators to define and collect custom device metrics that go beyond standard performance indicators. These script-based data collector enable organizations to capture real-time, environment-specific data—such as registry values, hardware compatibility, event information, application specific additional information (Antivirus details,etc) to enhance visibility and drive automated decision-making.
Sensors are highly flexible and can be used to power workflows, generate reports, and surface meaningful insights tailored to your unique endpoint environment.
Why Use Sensors?
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom Intelligence | Monitor any system state that matters to your organization and gain visibility |
| Data-Driven Automation | Use sensor outputs as dynamic triggers in workflows. |
| Flexible Reporting | Track and export custom data via dashboards and reports. |
| Scalable Management | Deploy sensors across device groups with centralized control. |
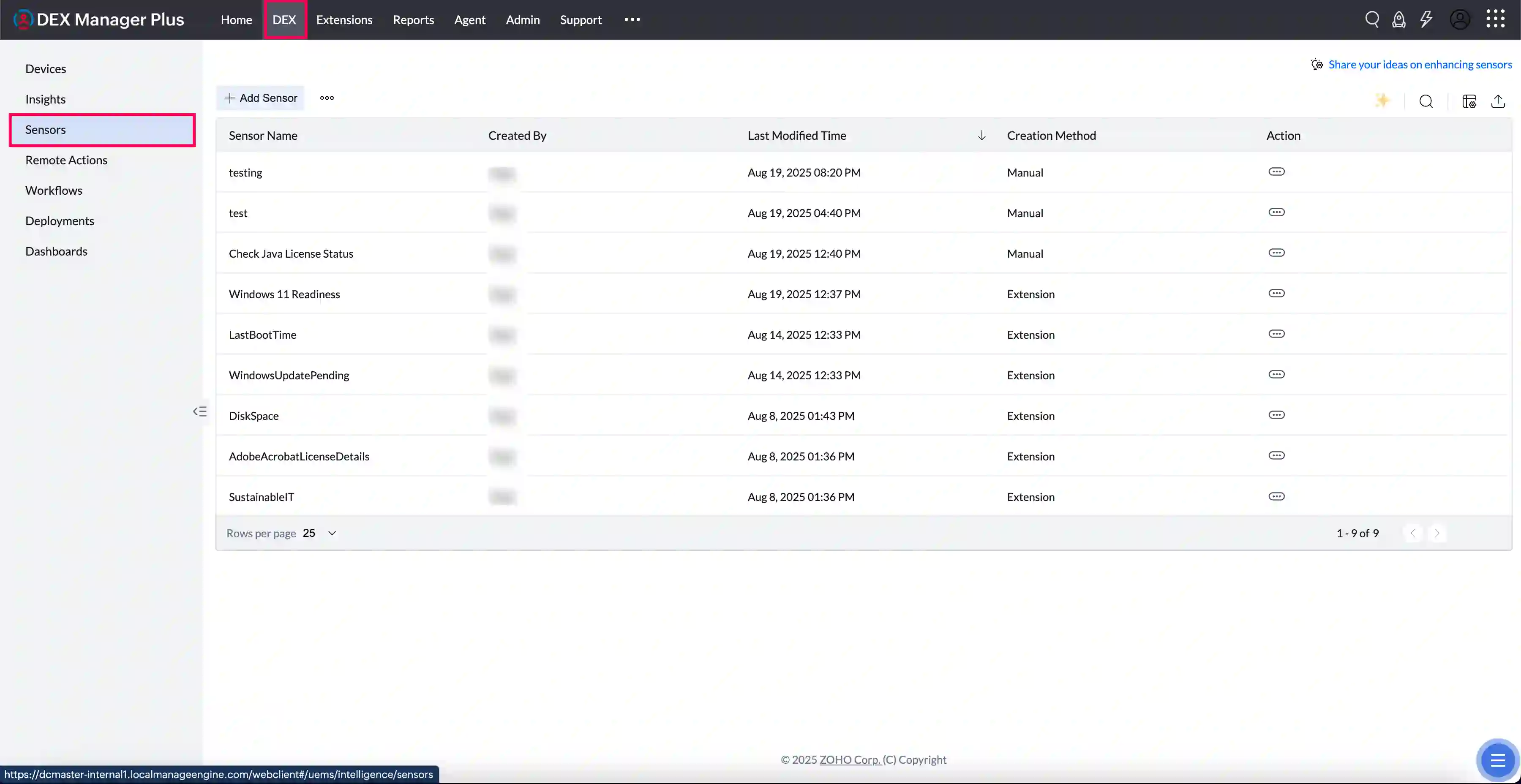
Accessing the Sensors Module
Navigate to Sensors from the left-hand pane of DEX tab. The main view lists all created sensors with their names, types, and usage status. Use the Add Sensor button to create new ones.
Creating and Deploying a Sensor
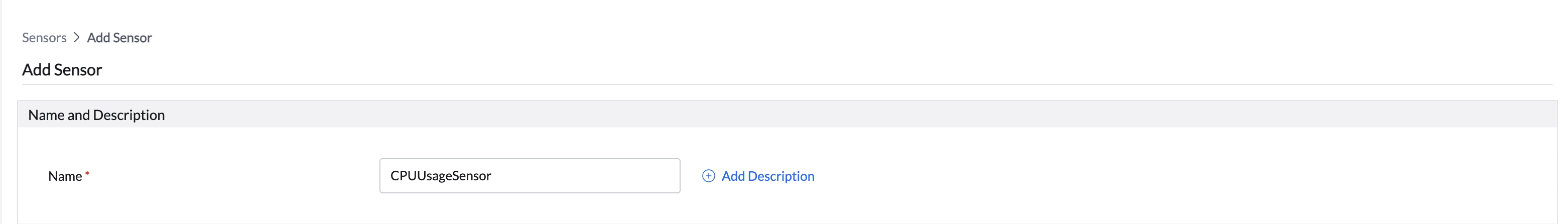
Step 1: Define Sensor Details
- Sensor Name: Enter a unique, descriptive name.
- Description (optional): Summarize the sensor’s purpose or logic.
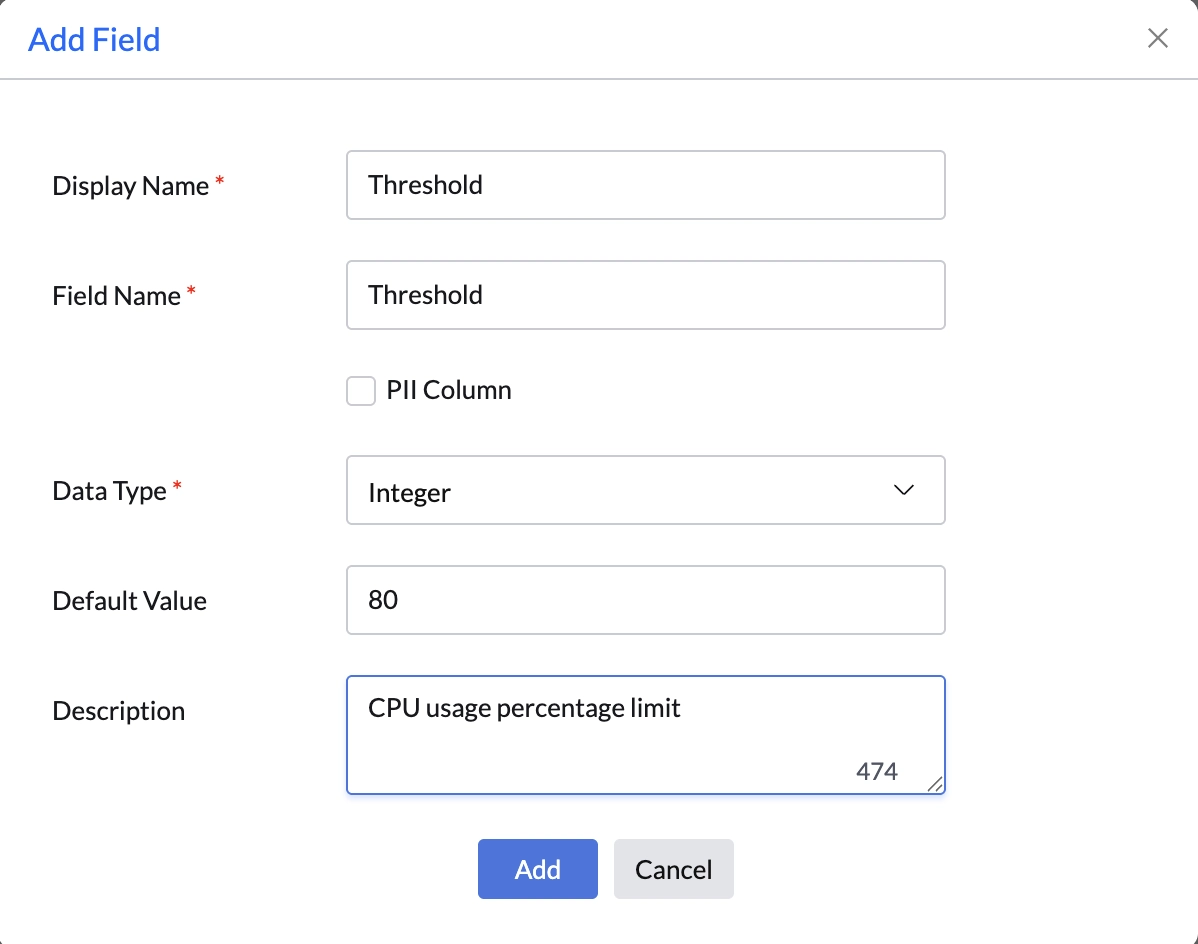
Step 2: Declare Fields
Use Add Field to define input/output variables. These fields act as data carriers between the sensor and the script. You can define field type (string, number, etc.) and optionally flag fields as PII for compliance.
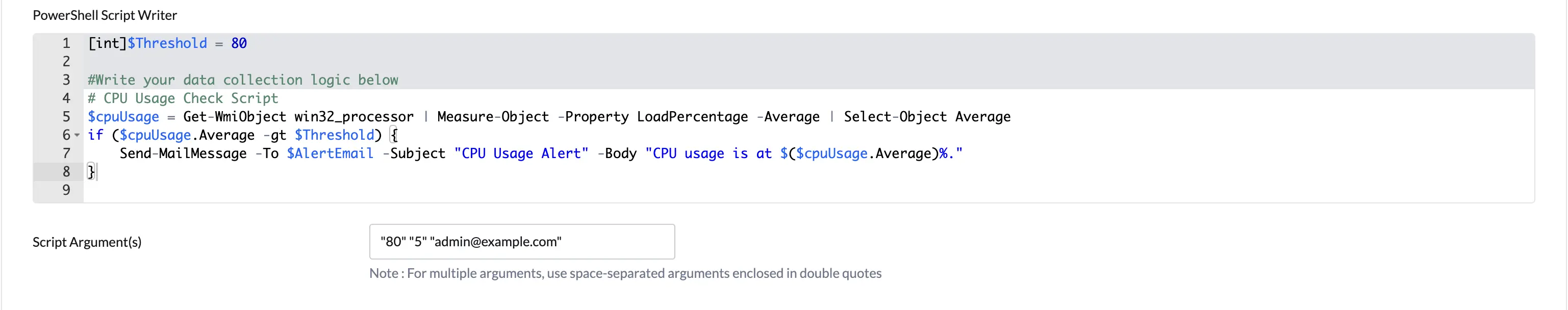
Step 3: Write the Script
Use the built-in Script Writer to compose your PowerShell script. Fields defined above are available as variables. The script must output structured values that match the declared fields.
Step 4: Set Run History Retention
Define how many execution records should be stored per execution of deployment. Minimum: 1 and Maximum: 5. This helps track trends over time and enables post-event analysis.
Step 5: Save
Click Save to add the sensor to your repository. The sensor will now available for data collection in targetted endpoints.
Deploying Sensor
- Navigate to DEX > Deployments from the left-hand pane. The Deployments tab displays a list of all active, scheduled, and completed deployments.
- Click Create Deployment to create new sensor deployment
- Enter Deployment Details - Deployment Name and Description (if Applicable)
- Select Sensor as Resource Type and choose required sensors for deployment
- Choose one or more Custom Groups to define the scope.
- Choose Deployment Type (Immediate or Schedule) based on need . Fill schedule frequency, trigger time,etc if schedule is chosen.
- Click Deploy to trigger deployment.
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Network Strength | Monitor endpoint connectivity quality in remote setups and trigger alerts if poor. e.g Wi-Fi signal strength, speed |
| Windows 11 Readiness | Check TPM version, OS build, and hardware specs to assess upgrade compatibility. |
| POS Hardware Check | Ensure barcode scanners and printers are connected to retail systems. |
| Inactive Local Users | Detect dormant local accounts for cleanup and compliance. |
| Software Checks | Track specific software versions, edition, usage and flag outdated or unlicensed installations. |
Best Practices
| Practice | Why It Helps |
|---|---|
| Use descriptive sensor names | Improves discoverability and reduces misconfiguration |
| Flag sensitive fields as PII | Ensures privacy and regulatory compliance |
| Test sensor on a small group | Prevents execution failures or device impact |
| Avoid overlap with built-in metrics | Focus sensors on what’s unique to your environment |
| Reuse sensors in multiple workflows | Promotes modular, scalable automation |


 Yes
Yes