- Free Edition
- Quick Links
- MFA
- Self-Service Password Management
- Single Sign-On
- Password Synchronizer
- Password Policy Enforcer
- Employee Self-Service
- Reporting and auditing
- Integrations
- Related Products
- ADManager Plus Active Directory Management & Reporting
- ADAudit Plus Real-time Active Directory Auditing and UBA
- Exchange Reporter Plus Exchange Server Auditing & Reporting
- EventLog Analyzer Real-time Log Analysis & Reporting
- M365 Manager Plus Microsoft 365 Management & Reporting Tool
- DataSecurity Plus File server auditing & data discovery
- RecoveryManager Plus Enterprise backup and recovery tool
- SharePoint Manager Plus SharePoint Reporting and Auditing
- AD360 Integrated Identity & Access Management
- Log360 (On-Premise | Cloud) Comprehensive SIEM and UEBA
- AD Free Tools Active Directory FREE Tools
What is offline MFA, and why do you need it?
For multi-factor authentication (MFA) to function in the users' devices, it typically must be connected to the internet or to the same network as the MFA server to communicate authentication information. But unforeseen conditions can sometimes sever the connection to the MFA server, taking the user offline. In these cases, both bypassing MFA or blocking access are unwise.
Offline MFA bridges the gap, enabling you to enforce MFA for your users even when they have no access to the MFA server. This way, your users' offline status does not have to limit your organization's cybersecurity.
Implement offline MFA for Windows and macOS logins with ADSelfService Plus
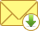
ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus supports offline MFA for Windows and macOS machine logins. Admins can configure one or more MFA factors for users to authenticate with. Users need to enroll themselves in the respective authenticators when they are online so that they can perform MFA when they are offline.
- Authenticators
- Enrollment and security
- Disenrollment
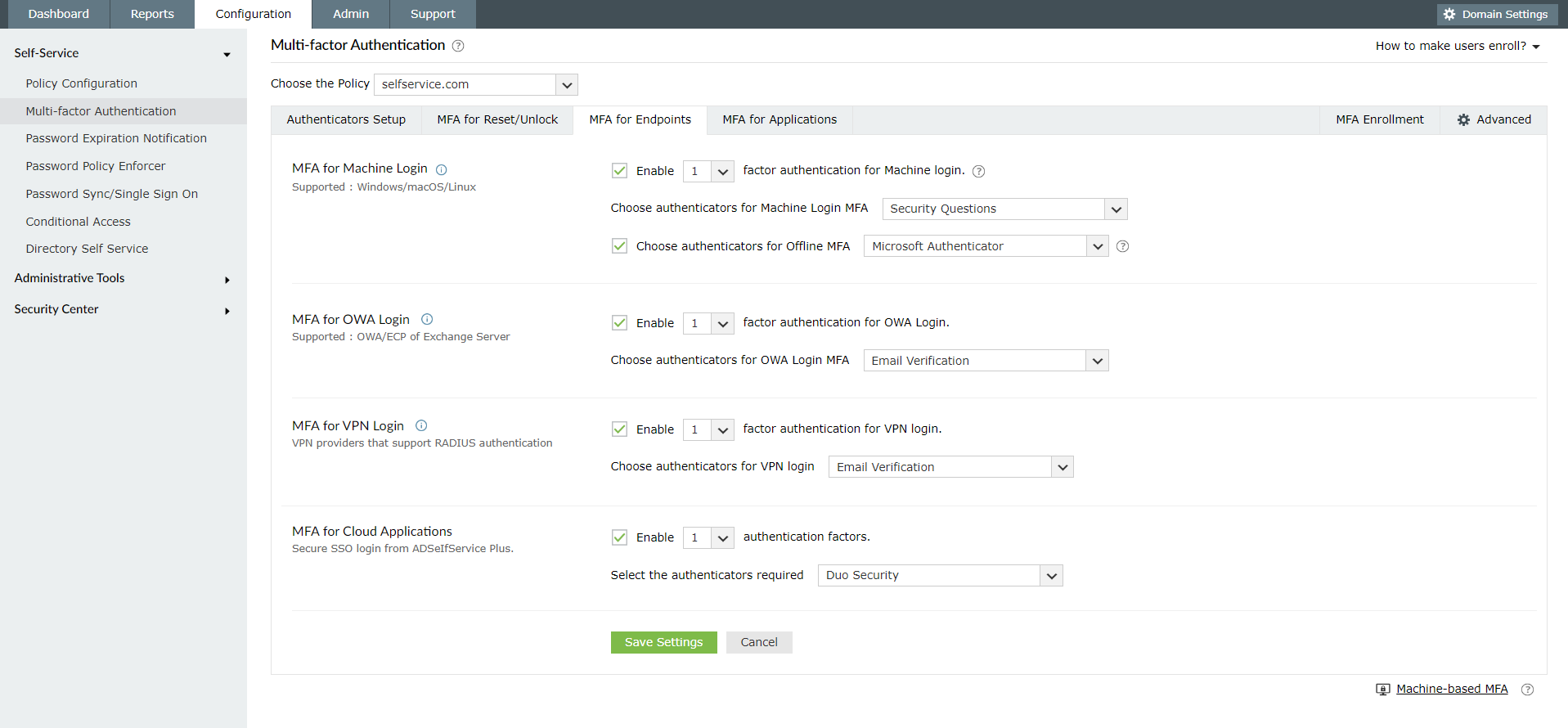
Decide whether you want to enable offline MFA in your organization and choose the authentication factors you want to use.
Choose between letting your users enroll in offline MFA themselves or automatically enrolling them in offline MFA on a particular device.
Set the number of times a user can perform offline MFA based on the number of attempts or the number of days, after which they have to perform online MFA at least once.
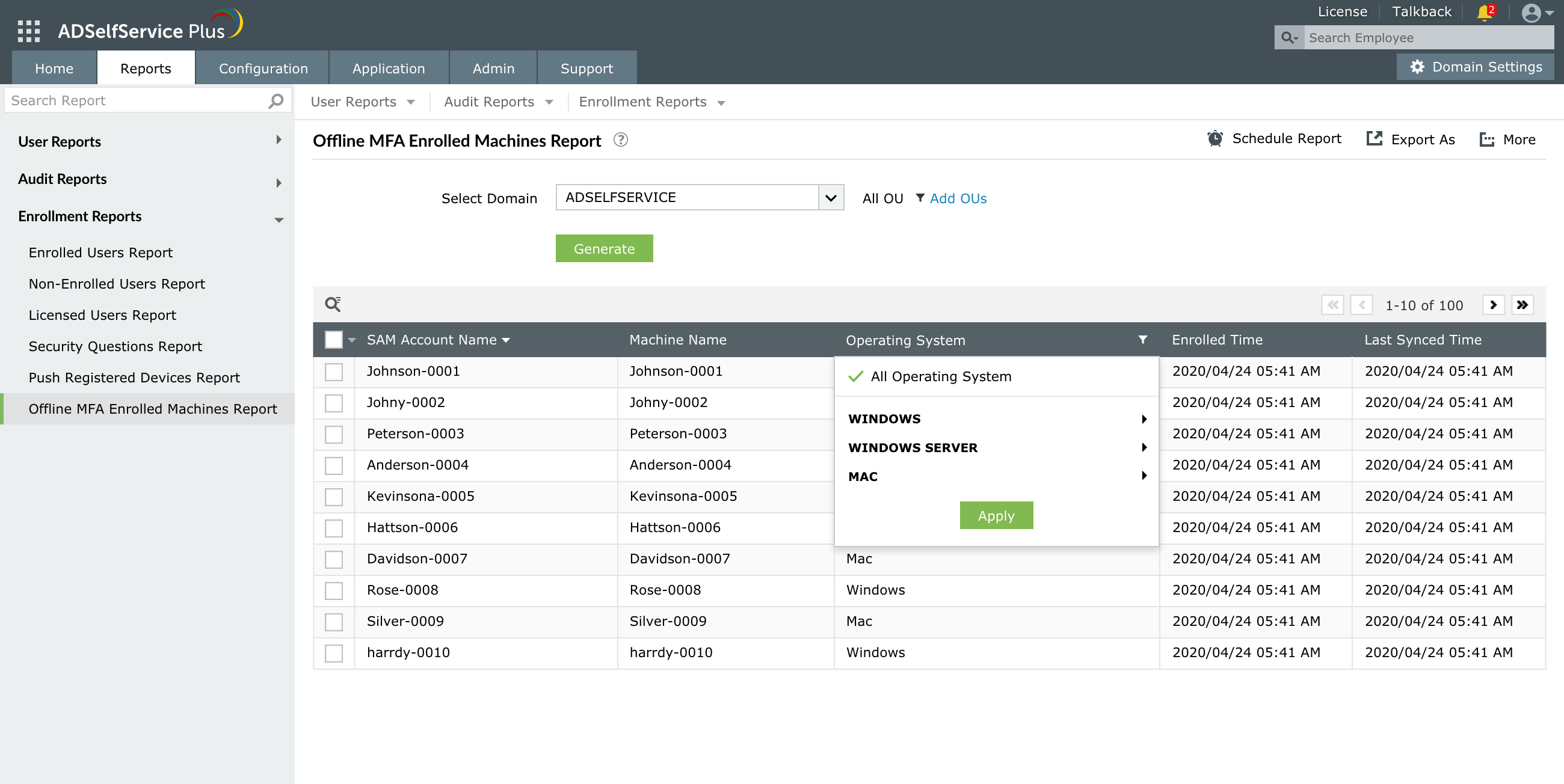
Generate a consolidated report of users who have enrolled in offline MFA, along with timestamps, and disenroll users if needed.
Offline MFA will work in both of the following scenarios:
- The user has an internet connection but is not connected to the MFA server.
- The user is not connected to either the internet or the MFA server.
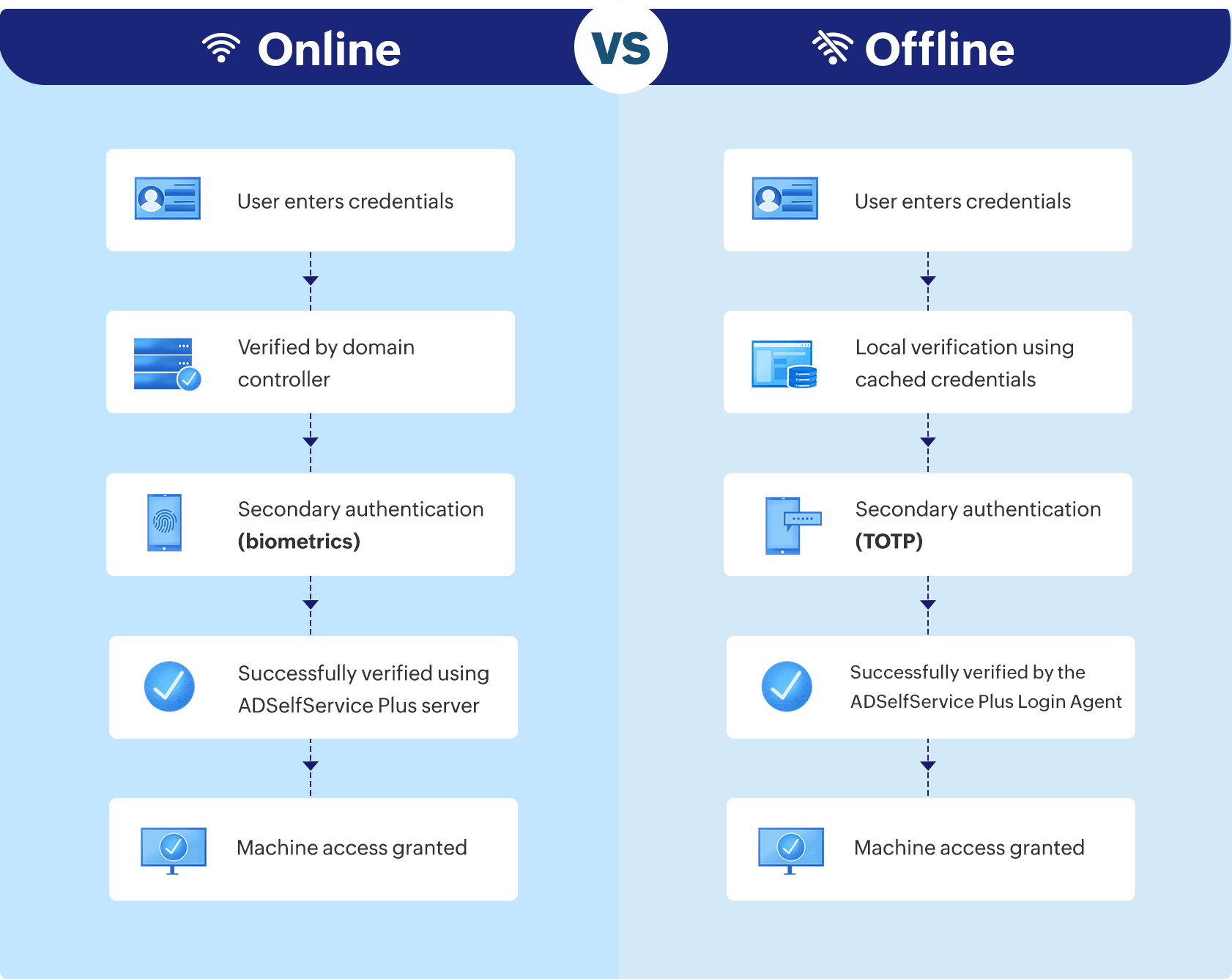
How offline MFA for Windows logins works

- Enabling offline MFA initially prompts users to enroll in the authenticator(s) configured by their admin. This happens during a machine login attempt that is carried out when the users are connected to the ADSelfService Plus server when they are online.
- Admins can give users the choice of enrolling in the offline MFA authenticators on a particular device. Alternatively, admins can make enrollment mandatory for users when they log in.
Note: Users who choose to skip MFA enrollment will not be able to prove their identities through MFA during login. Based on the admin-enabled configurations, either MFA will be bypassed for them, or they will not be able to access their machines.
- Once users have successfully enrolled in offline MFA, the authentication data needed to verify their identity is stored locally on that particular device.
- Now, when users attempt machine login when they are not connected to the ADSelfService Plus server, they will be able to verify their identity with the enrolled authenticators and access the machine.
- If you do not want users to log in through offline MFA over an extended period, you can limit the number of offline MFA attempts. Once the limit is reached, the users must connect to ADSelfService Plus and verify their identity at least once.
ADSelfService Plus supports offline MFA for both domain users and local, standalone users.
How offline MFA for macOS logins works
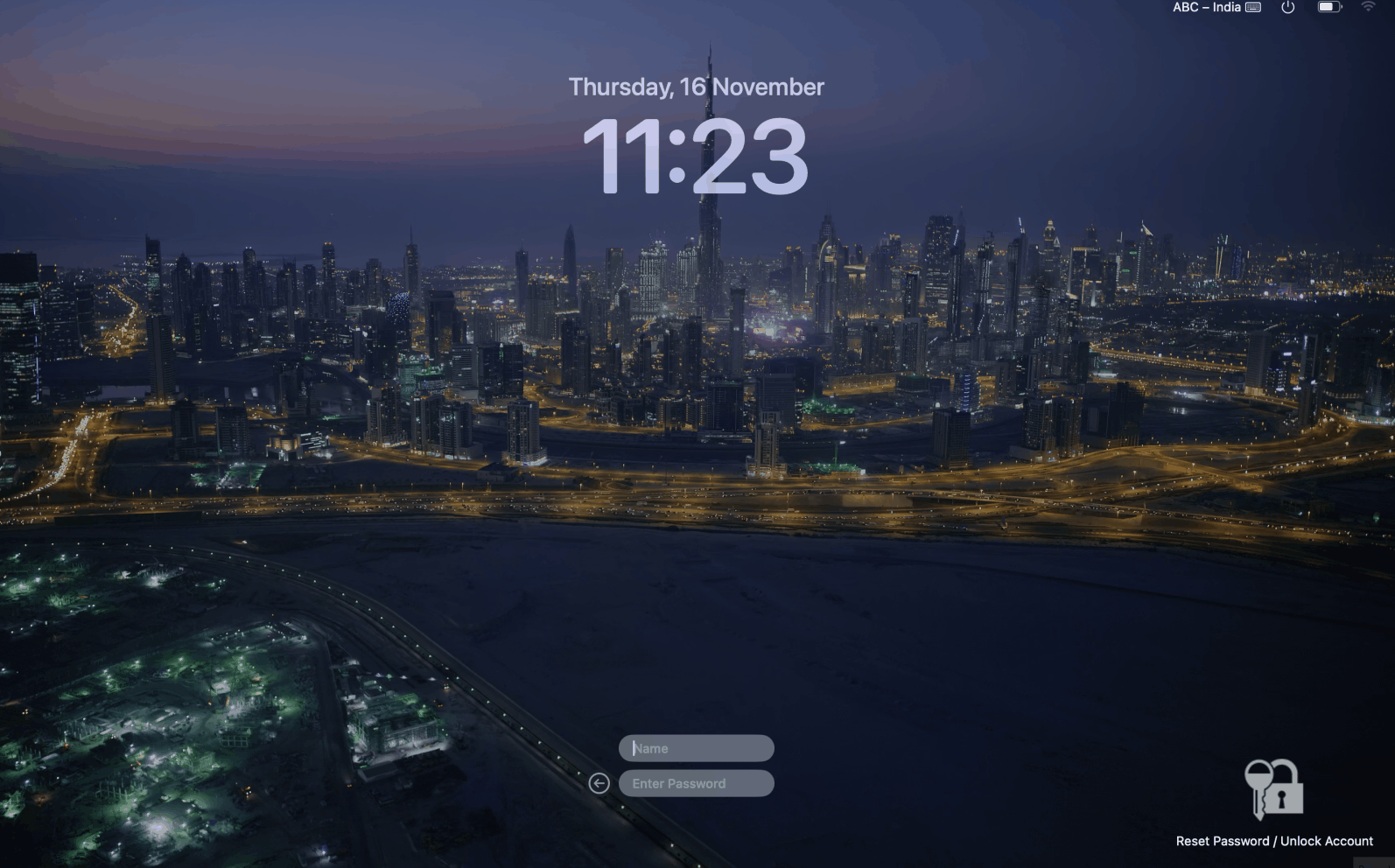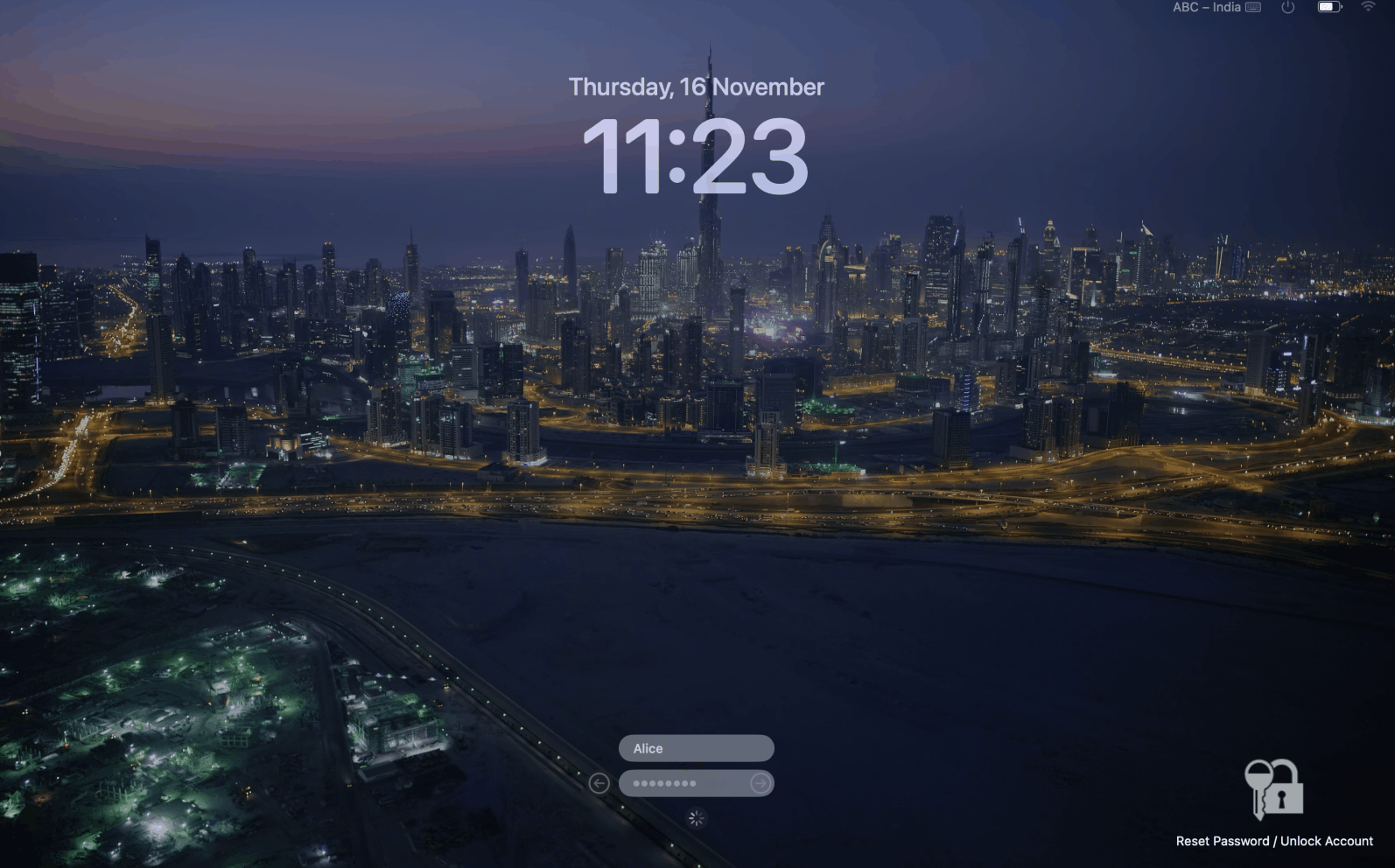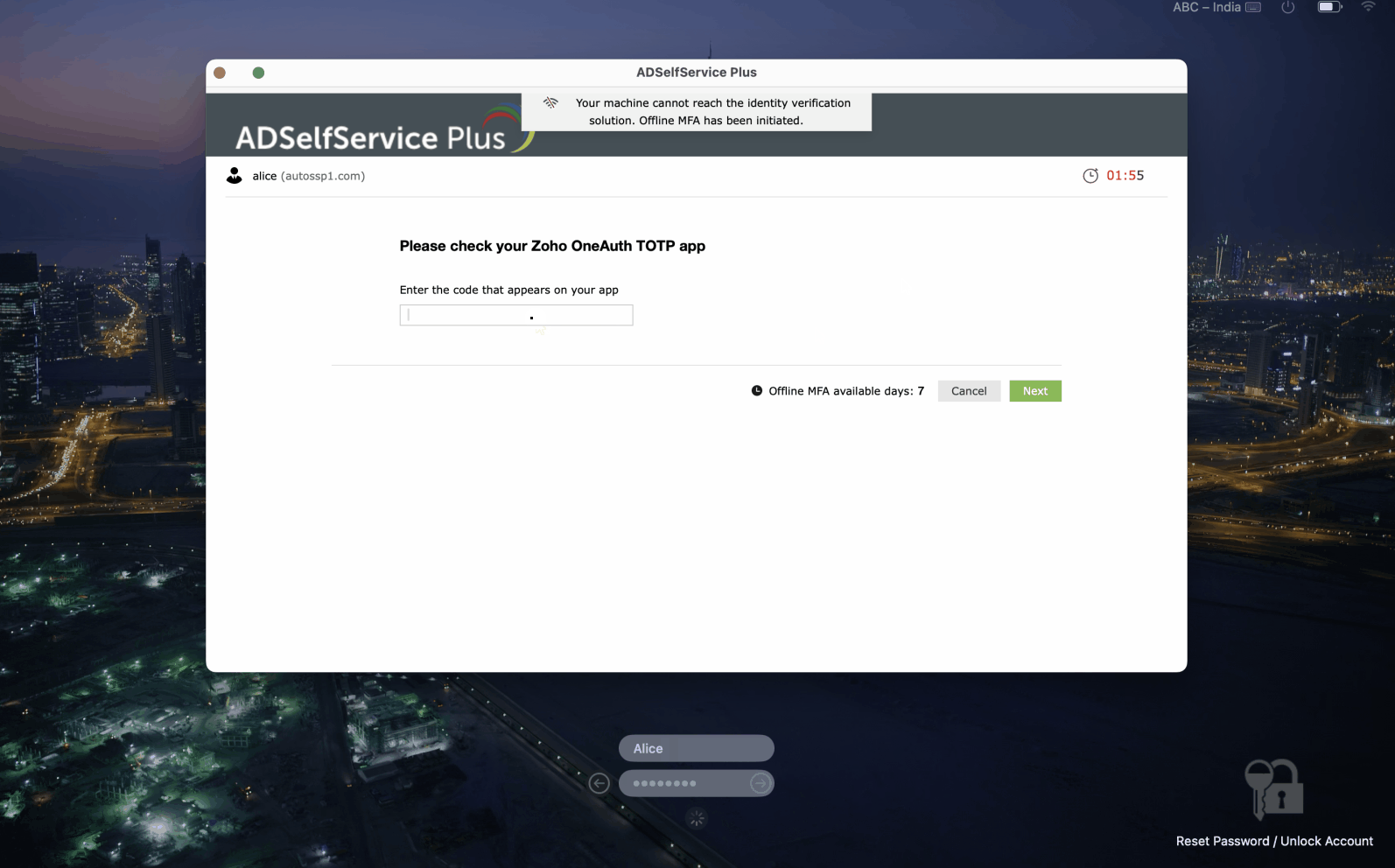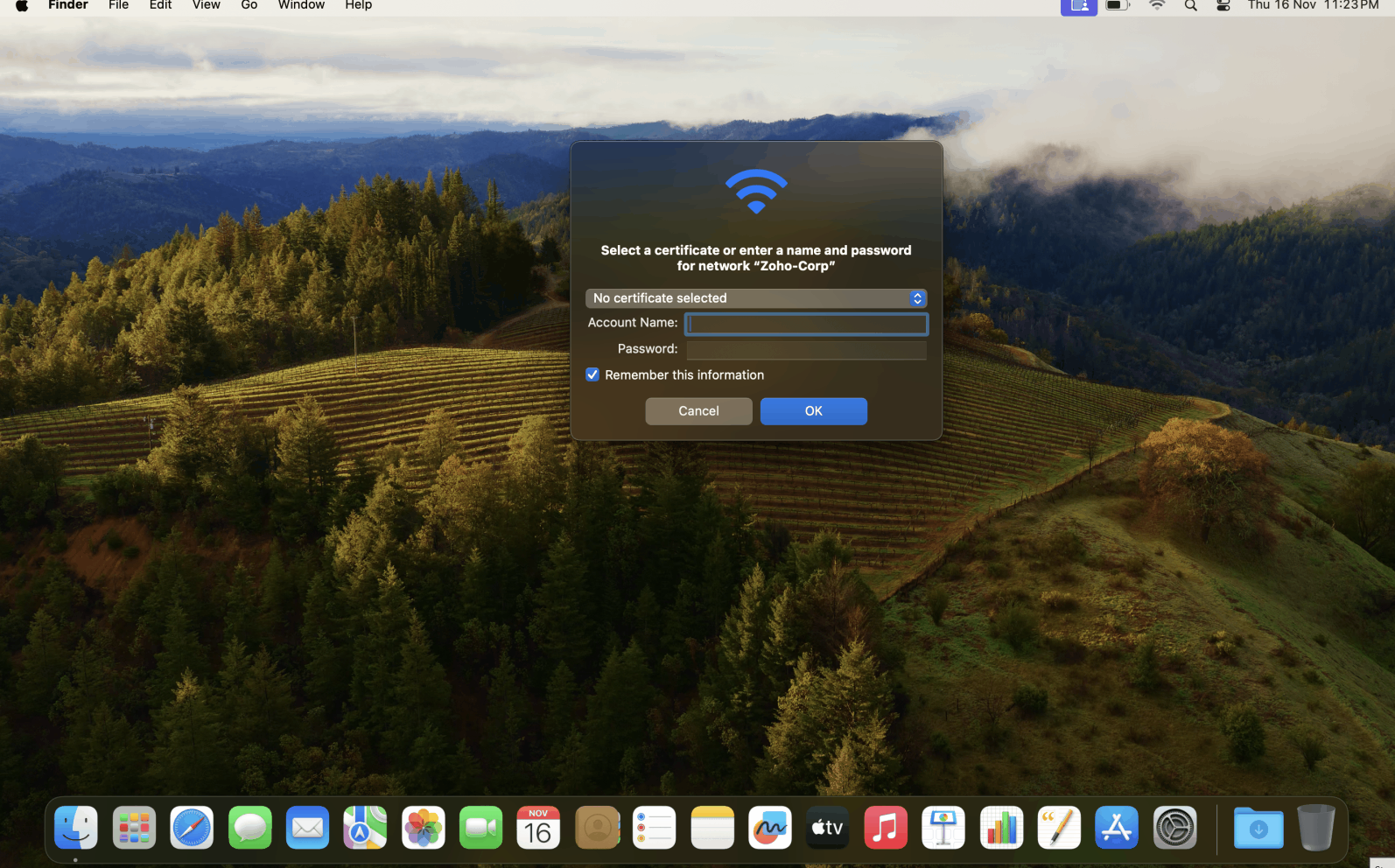
- Enabling offline MFA initially prompts users to enroll in the authenticator(s) configured by their admin. This happens during a machine login attempt that is carried out when the user is connected to the ADSelfService Plus server (i.e., when they are online).
- Admins can give users the choice of enrolling in the offline MFA authenticators on a particular device. Alternatively, admins can make enrollment mandatory for users when they log in.
Note: Users who choose to skip MFA enrollment will not be able to prove their identities through MFA during login. Based on the admin-enabled configurations, either MFA will be bypassed for them, or they will not be able to access their machines.
- Once a user has successfully enrolled in offline MFA, the authentication data needed to verify their identity is stored locally on that particular device.
- Now when the user attempts machine login when they are not connected to the ADSelfService Plus server, they will be able to verify their identity with the enrolled authenticators and access the machine.
- If you do not want users to log in through offline MFA over an extended period, you can limit the number of offline MFA attempts. Once the limit is reached, the user must connect to ADSelfService Plus and verify their identity at least once.
Supported authenticators for offline MFA
ADSelfService Plus supports the following authenticators for offline MFA:
- Google Authenticator
- Microsoft Authenticator
- Zoho OneAuth's TOTP authenticator
- Custom TOTP authenticators
Benefits of offline MFA for Windows and macOS logins using ADSelfService Plus
- Ensure the security of your remote and traveling workforce:
Rest assured that your users' machines are secured with MFA whether they are working remotely or have connectivity issues.
- Track enrollment with predefined reports:
Generate readable, consolidated reports of users who have enrolled in offline MFA, along with the timestamps, and disenroll users if necessary.
- Enroll multiple devices:
Allow users to enroll in offline MFA on multiple devices.
Highlights of ADSelfService Plus
Password self-service
Unburden Windows AD users from lengthy help desk calls by empowering them with self-service password reset and account unlock capabilities.
Multi-factor authentication
Enable context-based MFA with 20 different authentication factors for endpoint, application, VPN, OWA, and RDP logins.
One identity with single sign-on
Get seamless one-click access to more than 100 cloud applications. With enterprise single sign-on (SSO), users can access all their cloud applications using their Windows AD credentials.
Password and account expiry notifications
Notify Windows AD users of their impending password and account expiry via email and SMS notifications.
Password synchronization
Synchronize Windows AD user passwords and account changes across multiple systems automatically, including Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, IBM iSeries, and more.
Password policy enforcer
Strong passwords resist various hacking threats. Enforce Windows AD users to adhere to compliant passwords by displaying password complexity requirements.