L’ID d’événement Windows 4769 est généré chaque fois que le Centre de distribution de clés (KDC) reçoit une demande de ticket Kerberos Ticket Granting Service (TGS).
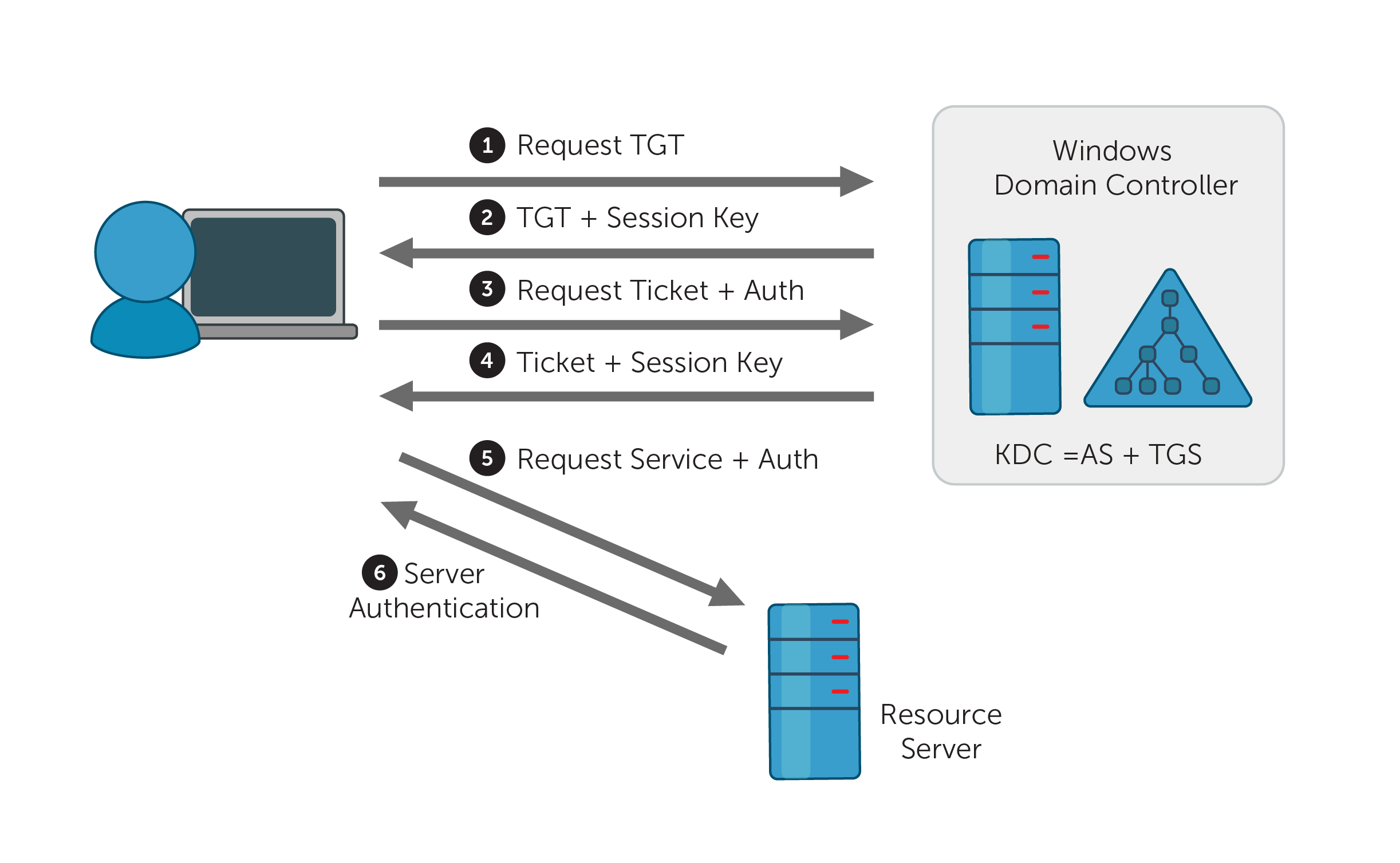
Figure 1. Kerberos authentication protocol
Une fois que le client a reçu un ticket d'attribution de ticket (TGT) du KDC, il stocke ce TGT et l'envoie au TGS avec le nom de principal de service (SPN) de la ressource à laquelle il souhaite accéder. Les TGT sont valables pendant une certaine période.
ID d'événement 4769 (S) - Une demande de service d'octroi de tickets Kerberos (TGS) a été effectuée avec succès
Le KDC vérifie le TGT de l'utilisateur avant que le TGS n'envoie au client une clé de session valide pour le service. L'ID d'événement 4769 est enregistré avec un code de résultat égal à « 0x0 » si le ticket de service et la clé de session ont été accordés.
ID d'événement 4769 (F) - Échec d'une demande de service d'attribution de tickets Kerberos (TGS)
Si la question du TGS échoue, le même ID d'événement 4769 est enregistré, mais avec un code de résultat non égal à> « 0x0 ». (Voir tous les codes de résultats)
L’ID d'événement 4768 est généré chaque fois que le KDC tente de valider les informations d'identification.
L'ID d'événement 4776 indique une tentative d'authentification utilisant l'authentification NTLM.
Nom du compte: Le nom principal de l'utilisateur (UPN) du compte qui a demandé le ticket de service.
Remarque :
Le nom du compte d'ordinateur se termine par un $ dans un UPN. Le champ Nom du compte a généralement le format suivant : user_account_name@FULL\_DOMAIN\_NAME.
Exemple de compte utilisateur : mark@ADAP.WORKSHOP.COM
Exemple de compte d'ordinateur : WIN12R2$@ADAP.WORKSHOP.COM
Domaine du compte: Le nom du domaine Kerberos auquel appartient le nom du compte.
GUID de connexion: Un identifiant unique global (GUID) est un nombre entier de 128 bits utilisé pour identifier des ressources, des activités ou des instances. Le GUID de connexion peut vous aider à corréler l’ID d’événement 4769 avec d'autres événements pouvant contenir le même GUID de connexion. Ces événements comprennent les ID 4624, 4648(S) et 4964(S).
Nom du service: Le nom du service dans le domaine Kerberos pour lequel le ticket TGS a été demandé.
ID du service: Le SID du compte de service dans le domaine Kerberos pour lequel le ticket TGS a été demandé.
Adresse du client: L'adresse IP de l'ordinateur à partir duquel la requête TGS a été reçue.
Port client: Le numéro de port source de la connexion au réseau du client (demande TGS). Le port client est « 0 » pour les demandes locales (localhost).
Options de ticket: Un ensemble de différents indicateurs de ticket au format hexadécimal.
Les valeurs les plus courantes incluent notamment :
0x40810010 — Transmissible, Renouvelable, Canonicaliser, Renouvelable-ok
0x40810000 — Transmissible, Renouvelable, Canonicaliser
0x60810010 — Transmissible, Transmis, Renouvelable, Canonicaliser, Renouvelable-ok
Services de transit: Ce champ contient une liste de SPN qui ont été demandés si la délégation Kerberos a été utilisée.
| Type | Type Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x1 | DES-CBC-CRC | Disabled by default for Windows 7 or later and Windows Server 2008 R2 or later. |
| 0x3 | DES-CBC-MD5 | Disabled by default for Windows 7 or later and Windows Server 2008 R2 or later. |
| 0x11 | AES128-CTS-HMAC-SHA1-96 | Supported for Windows Server 2008 or later and Windows Vista or later. |
| 0x12 | AES256-CTS-HMAC-SHA1-96 | Supported for Windows Server 2008 or later and Windows Vista or later. |
| 0x17 | RC4-HMAC | Default suite for operating systems before Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista. |
| 0x18 | RC4-HMAC-EXP | Default suite for operating systems before Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista. |
| 0xFFFFFFFF or 0xffffffff | - | This type shows in Audit Failure events. |
Failure Code: This is a set of different failure codes displayed in hexadecimal format. The result codes are listed in the following table:
See RFC1510 for more details.
| Code | Code name | Description | Possible causes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0 | KDC_ERR_NONE | No error | No errors were found. |
| 0x1 | KDC_ERR_NAME_EXP | Client's entry in KDC database has expired | No information. |
| 0x2 | KDC_ERR_SERVICE_EXP | Server's entry in KDC database has expired | No information. |
| 0x3 | KDC_ERR_BAD_PVNO | Requested Kerberos version number not supported | No information. |
| 0x4 | KDC_ERR_C_OLD_MAST_KVNO | Client's key encrypted in old master key | No information. |
| 0x5 | KDC_ERR_S_OLD_MAST_KVNO | Server's key encrypted in old master key | No information. |
| 0x6 | KDC_ERR_C_PRINCIPAL_UNKNOWN | Client not found in Kerberos database | The username doesn’t exist. |
| 0x7 | KDC_ERR_S_PRINCIPAL_UNKNOWN | Server not found in Kerberos database | The domain controller can’t find the server’s name in Active Directory. |
| 0x8 | KDC_ERR_PRINCIPAL_NOT_UNIQUE | Multiple principal entries in KDC database |
Duplicate principal names exist. Unique principal names are crucial for ensuring mutual authentication; duplicate principal names are strictly forbidden, even across multiple realms. Without unique principal names, the client has no way of ensuring that the server it's communicating with is the correct one |
| 0x9 | KDC_ERR_NULL_KEY | The client or server has a null key (master key) | No master key was found for the client or server. This usually means that the administrator should reset the password on the account. |
| 0xA | KDC_ERR_CANNOT_POSTDATE | Ticket (TGT) not eligible for postdating | A client has requested postdating of a Kerberos ticket (setting the ticket’s start time to a future date/time), or there is a time difference between the client and the KDC. |
| 0xB | KDC_ERR_NEVER_VALID | Requested start time is later than the end time | There is a time difference between the KDC and the client. |
| 0xC | KDC_ERR_POLICY | Requested start time is later than the end time | There are logon restrictions on the user’s account, like a workstation restriction, smart card authentication requirement, or logon time restriction. |
| 0xD | KDC_ERR_BADOPTION | KDC cannot accommodate requested option | The TGT is about to expire, or the client is attempting to delegate credentials to an SPN that’s not in its allowed-to-delegate-to list. |
| 0xE | KDC_ERR_ETYPE_NOTSUPP | KDC has no support for encryption type | The KDC or client received a packet that it can’t decrypt. |
| 0xF | KDC_ERR_SUMTYPE_NOSUPP | KDC has no support for checksum type | The KDC, server, or client received a packet that it doesn’t have an appropriate encryption key for, so it can’t decrypt the ticket. |
| 0x10 | KDC_ERR_PADATA_TYPE_NOSUPP | KDC has no support for PADATA type (pre-authentication data) |
This error code can’t occur in event 4768, but it can occur in event 4771. |
| 0x11 | KDC_ERR_TRTYPE_NO_SUPP | KDC has no support for transited type | No information. |
| 0x12 | KDC_ERR_CLIENT_REVOKED | Client’s credentials have been revoked | There may be explicit restrictions on the account; the account could also be disabled, expired, or locked out. |
| 0x13 | KDC_ERR_SERVICE_REVOKED | Credentials for server have been revoked | No information. |
| 0x14 | KDC_ERR_TGT_REVOKED | TGT has been revoked |
Since the remote KDC may change its PKCROSS key while there are PKCROSS tickets still active, it should cache the old PKCROSS keys until the last issued PKCROSS ticket expires. Otherwise, the remote KDC will respond to a client with this error code. See RFC1510 for more details. |
| 0x15 | KDC_ERR_CLIENT_NOTYET | Client not yet valid—try again later | No information. |
| 0x16 | KDC_ERR_SERVICE_NOTYET | Server not yet valid—try again later | No information. |
| 0x17 | KDC_ERR_KEY_EXPIRED | Password has expired—change password to reset |
The user’s password has expired. This error code can’t occur in event 4768, but it does occur in event 4771. |
| 0x18 | KDC_ERR_PREAUTH_FAILED | Pre-authentication information was invalid |
The wrong password was provided. This error code can’t occur in event 4768, but it does occur in event 4771. |
| 0x19 | KDC_ERR_PREAUTH_REQUIRED | Additional pre-authentication required |
Often occurs in UNIX interoperability scenarios. MIT-Kerberos clients do not request pre-authentication when they send a KRB_AS_REQ message. If pre-authentication is required (the default setting), Windows systems will send this error. Most MIT-Kerberos clients will respond to this error by giving preauthentication, in which case the error can be ignored |
| 0x1A | KDC_ERR_SERVER_NOMATCH | KDC does not know about the requested server | No information. |
| 0x1B | KDC_ERR_SVC_UNAVAILABLE | KDC is unavailable | No information. |
| 0x1F | KRB_AP_ERR_BAD_INTEGRITY | Integrity check on decrypted field failed |
The authenticator was encrypted with something other than the session key, so the client can’t decrypt the resulting message. The modification of the message could be the result of an attack or network noise. |
| 0x20 | KRB_AP_ERR_TKT_EXPIRED | The ticket has expired |
The smaller the value for the Kerberos policy setting Maximum lifetime for user ticket, the more likely it is that this error will occur. Because ticket renewal is automatic, you shouldn’t have to do anything if you get this message. |
| 0x21 | KRB_AP_ERR_TKT_NYV | The ticket is not yet valid |
The clocks on the KDC and the client aren’t synchronized. If cross-realm Kerberos authentication is being attempted, then you should verify time synchronization between the KDC in the target realm and the KDC in the client realm. |
| 0x22 | KRB_AP_ERR_REPEAT | The request is a replay | A specific authenticator showed up twice; in other words, the KDC detected that this session ticket duplicates one that it has already received. |
| 0x23 | KRB_AP_ERR_NOT_US | The ticket is not for us | The server has received a ticket that was meant for a different realm. |
| 0x24 | KRB_AP_ERR_BADMATCH | The ticket and authenticator do not match |
|
| 0x25 | KRB_AP_ERR_SKEW | The clock skew is too great | A client computer sent a timestamp whose value differs from that of the server’s timestamp by more than the Maximum tolerance for computer clock synchronization setting in the Kerberos policy. |
| 0x26 | KRB_AP_ERR_BADADDR | Network address in network layer header doesn't match address inside ticket |
|
| 0x28 | KRB_AP_ERR_BADVERSION | Protocol version numbers don't match (PVNO) | An application checks the KRB_SAFE message to verify that the protocol version and type fields match the current version and KRB_SAFE, respectively. A mismatch generates this error code. |
| 0x28 | KRB_AP_ERR_MSG_TYPE | Message type is unsupported |
|
| 0x29 | KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED | Message stream modified and checksum didn't match |
|
| 0x2A | KRB_AP_ERR_BADORDER | Message out of order (possible tampering) |
This event generates for KRB_SAFE and KRB_PRIV messages if an incorrect sequence number is included or if a sequence number is expected but not present. See RFC4120 for more details. |
| 0x2C | KRB_AP_ERR_BADKEYVER | Specified version of key is not available | The server can’t use the key version indicated by the ticket in the KRB_AP_REQ (e.g. it indicates an old key that the server doesn’t have a copy of). |
| 0x2D | KRB_AP_ERR_NOKEY | Service key not available |
The server doesn’t have the right key to decipher the ticket. Because it's possible for the server to be registered in multiple realms with different keys in each realm, the realm field in the unencrypted portion of the ticket in the KRB_AP_REQ is used to specify which secret key the server should use to decrypt that ticket |
| 0x2E | KRB_AP_ERR_MUT_FAIL | Mutual authentication failed | No information. |
| 0x2F | KRB_AP_ERR_BADDIRECTION | Incorrect message direction | No information. |
| 0x30 | KRB_AP_ERR_METHOD | Alternative authentication method required | According to RFC4120, this error message is obsolete. |
| 0x31 | KRB_AP_ERR_BADSEQ | Incorrect sequence number in message | No information. |
| 0x32 | KRB_AP_ERR_INAPP_CKSUM | Inappropriate type of checksum in message (checksum may be unsupported) | When the KDC receives a KRB_TGS_REQ message, it decrypts it. Afterwards, the user-supplied checksum in the Authenticator must be verified against the contents of the request, and the message must be rejected if the checksums don't match (with an error code of KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED) or if the checksum is not collision-proof (with an error code of KRB_AP_ERR_INAPP_CKSUM). |
| 0x33 | KRB_AP_PATH_NOT_ACCEPTED | Desired path is unreachable | No information. |
| 0x34 | KRB_ERR_RESPONSE_TOO_BIG | Too much data |
The size of a ticket is too large to be transmitted reliably via UDP. In a Windows environment, this message is purely informational. A Windows computer will automatically try TCP if UDP fails. |
| 0x3C | KRB_ERR_GENERIC | Generic error |
|
| 0x3D | KRB_ERR_FIELD_TOOLONG | Field is too long for this implementation |
If a KDC that does not understand how to interpret a set high bit of the length encoding receives a request with the high order bit of the length set, it must return a KRB-ERROR message with the error KRB_ERR_FIELD_TOOLONG, and it must close the TCP stream Each request (KRB_KDC_REQ) and response (KRB_KDC_REP or KRB_ERROR) sent over the TCP stream is preceded by the length of the request as 4 octets in network byte order. The high bit of the length is reserved for future expansion and must currently be set to zero. |
| 0x3E | KDC_ERR_CLIENT_NOT_TRUSTED | The client trust failed or is not implemented |
|
| 0x3F | KDC_ERR_KDC_NOT_TRUSTED | The KDC server trust failed or could not be verified |
The trustedCertifiers field contains a list of CAs trusted by the client, just in case the client doesn’t possess the KDC's public key certificate. If the KDC has no certificate signed by any of the trustedCertifiers, then it returns this error code. |
| 0x40 | KDC_ERR_INVALID_SIG | The signature is invalid | This error is related to PKINIT. If a PKI trust relationship exists, the KDC then verifies the client's signature on AuthPack (TGT request signature). If that fails, the KDC returns this error code. |
| 0x41 | KDC_ERR_KEY_TOO_WEAK | A higher encryption level is needed | If the clientPublicValue field is filled in, indicating that the client wishes to use the Diffie-Hellman key agreement, then the KDC checks to see that the parameters satisfy its policy. If they do not (e.g. the prime size is insufficient for the expected encryption type), then the KDC returns this error code. |
| 0x42 | KRB_AP_ERR_USER_TO_USER_REQUIRED | User-to-user authorization is required | The client doesn't know that a service requires user-to-user authentication, so it requests, receives, and forwards a conventional KRB_AP_REP to the server; the server generates this error code in response. |
| 0x43 | KRB_AP_ERR_NO_TGT | No TGT was presented or available | The service doesn’t have a TGT for user-to-user authentication. |
| 0x44 | KDC_ERR_WRONG_REALM | Incorrect domain or principal |
The client presented a cross-realm TGT to a realm other than the one specified in the TGT. This error rarely occurs, but it’s typically caused by an incorrectly configured DNS. |
Transited Services: This field contains a list of SPNs which were requested if Kerberos delegation was used.
Les solutions d'audit comme ADAudit Plus offrent une surveillance en temps réel, une analyse du comportement des utilisateurs et entités, ainsi que des rapports. Ensemble, toutes ces fonctionnalités contribuent à sécuriser votre environnement AD.
Bien que vous puissiez attacher une tâche au journal de sécurité et demander à Windows de vous envoyer un e-mail, vous êtes limité à recevoir un e-mail chaque fois que l'ID d'événement 4769 est généré. Windows n'a pas non plus la capacité d'appliquer des filtres plus granulaires qui sont nécessaires pour répondre aux recommandations en matière de sécurité
Avec un outil comme ADAudit Plus, vous pouvez non seulement appliquer des filtres granulaires pour vous concentrer sur les menaces réelles, mais aussi être averti en temps réel par SMS.
Tirez parti des techniques avancées d'analyse statistique et d'apprentissage machine pour détecter les comportements anormaux sur votre réseau.
Respectez diverses normes de conformité, telles que SOX, HIPAA, PCI, FISMA, GLBA et RGPD, grâce à des rapports de conformité prêts à l'emploi.
Le téléchargement d'ADAudit Plus permet de recevoir des alertes en temps réel en moins de 30 minutes. Avec plus de 200 rapports et alertes préconfigurés, ADAudit Plus garantit la sécurité et la conformité de votre Active Directory.