What is privilege elevation?

Privilege elevation is a strategic approach you can utilize to grant temporary access to essential resources for employees who do not normally have such permissions. This method ensures that instead of providing permanent access, which could pose security risks, employees can access specific tools or information for a limited time to accomplish particular tasks.
For instance, if you need to access resources outside your typical responsibilities, you can receive temporary permissions as needed. Privilege elevation helps maintain compliance with access boundaries, minimizing the chances of inappropriate use of sensitive information. Implementing privilege elevation can significantly reduce such risks by minimizing the attack surface and enforcing the principle of least privilege.
What is PEDM?
PEDM is part of PAM. It allows non-admin users temporary access to specific privileges based on their needs. Using PEDM helps IT teams grant users access to privileged accounts and resources only when needed. This targeted approach reduces the risk of exposing accounts and passwords, which helps stop attackers and insiders from moving through an organization's sensitive areas. On the other hand, privilege account and session management (PASM) solutions provide access using digital password vaults based on the principle of least privilege (PoLP).
However, they usually grant access in a way that gives full permissions all at once. This means that users may receive temporary admin accounts, called ephemeral accounts, which allow them complete access to systems, including applications and services they do not need. If these accounts are shared among users or become compromised, an attacker could gain full control of the system.
PEDM vs. PASM
When discussing privilege access management, many are often unclear about the differences between PEDM and PASM. Here is a table below clearly shows the differences between PADM and PASM:
| Feature | PEDM | PASM |
| Definition | Manages temporary privilege elevation and delegation for users and applications | Secures, controls, and monitors privilege accounts and access |
| Primary goal | Provides just-in-time (JIT) privilege elevation to reduce excessive permissions | Protects privilege credentials and enforces least privilege access |
| Scope | Focuses on granting temporary or limited elevated privileges | Covers comprehensive privilege account management, including password vaulting and session monitoring |
| Key capabilities | Role-based access control (RBAC), JIT access, logging, and approval workflows | Credential vaulting, session recording, risk-based authentication, and audit trails |
| Usage scenarios | Allows IT support staff to restart critical services on servers without full admin rights | Securely vaults domain admin credentials and auto-rotate them after every use |
| Security focus | Minimizes the attack surface by granting only necessary privileges when needed | Prevents unauthorized access, credential theft, and privilege misuse |
| Compliance support | Helps meet compliance requirements like NIST, ISO 27001, and the GDPR by enforcing least privilege | Ensures regulatory compliance with SOX, HIPAA, the PCI DSS, and other security frameworks |
What problems can PEDM solve?
Modern enterprises face several challenges when it comes to privilege management. In 2023 alone, 74% of data breaches involved privileged credential abuse. PEDM helps solve these by enabling a more agile and secure way of granting access.
Here’s what PEDM helps address:
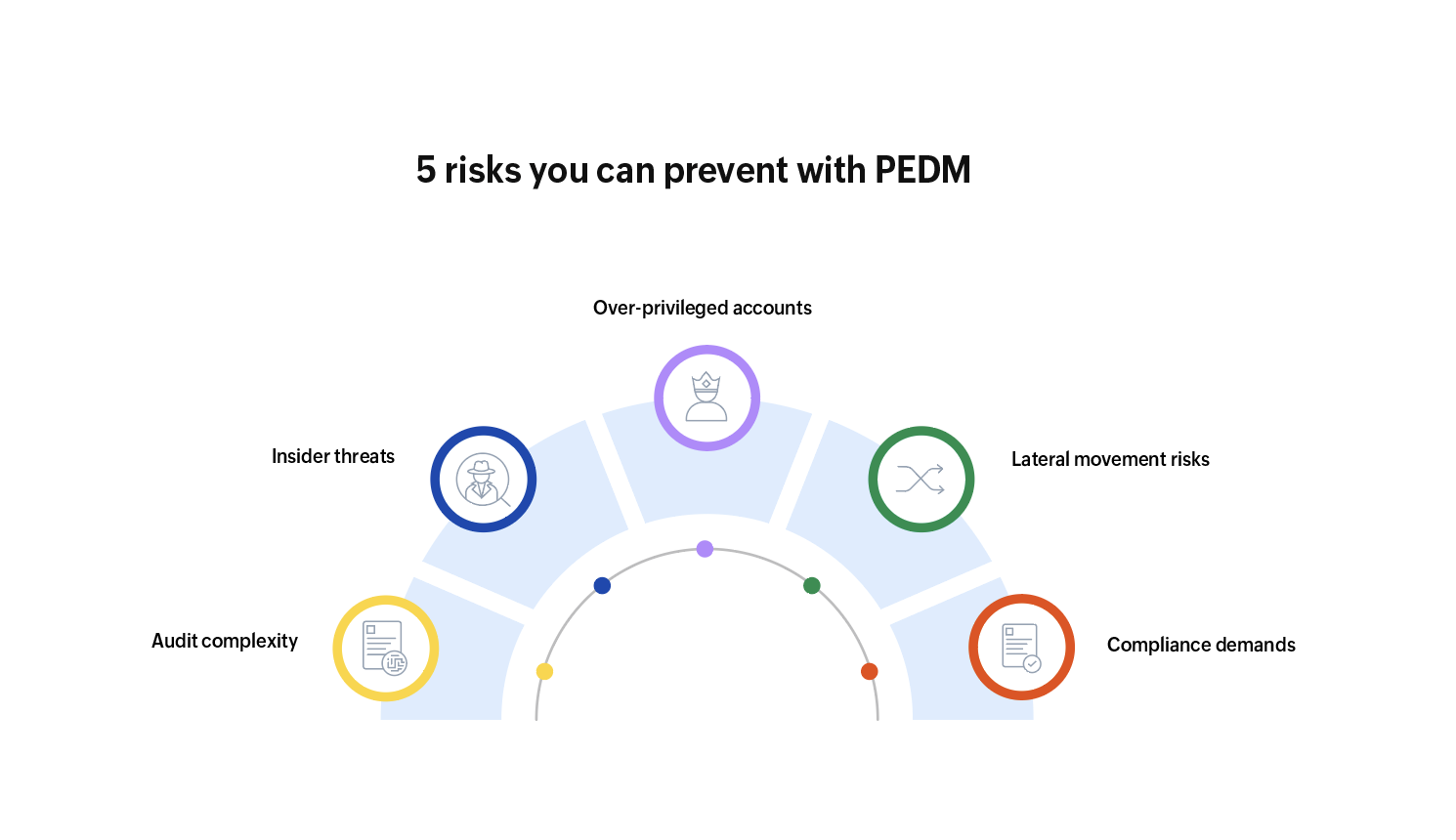
- Over-privileged accounts: Permanent admin rights increase the risk of accidental changes, misuse, or credential theft.
- Lateral movement risks: Attackers who gain access to an endpoint can move across the network using excessive privileges.
- Compliance demands: Regulations like ISO 27001, NIS2, the PCI DSS, and HIPAA mandate least privilege and auditable access.
- Insider threats: Even trusted users can pose risks when their privileges are unchecked or excessive.
- Audit complexity: Without clear visibility into who did what with elevated access, forensic investigations are delayed.
How does PEDM work?
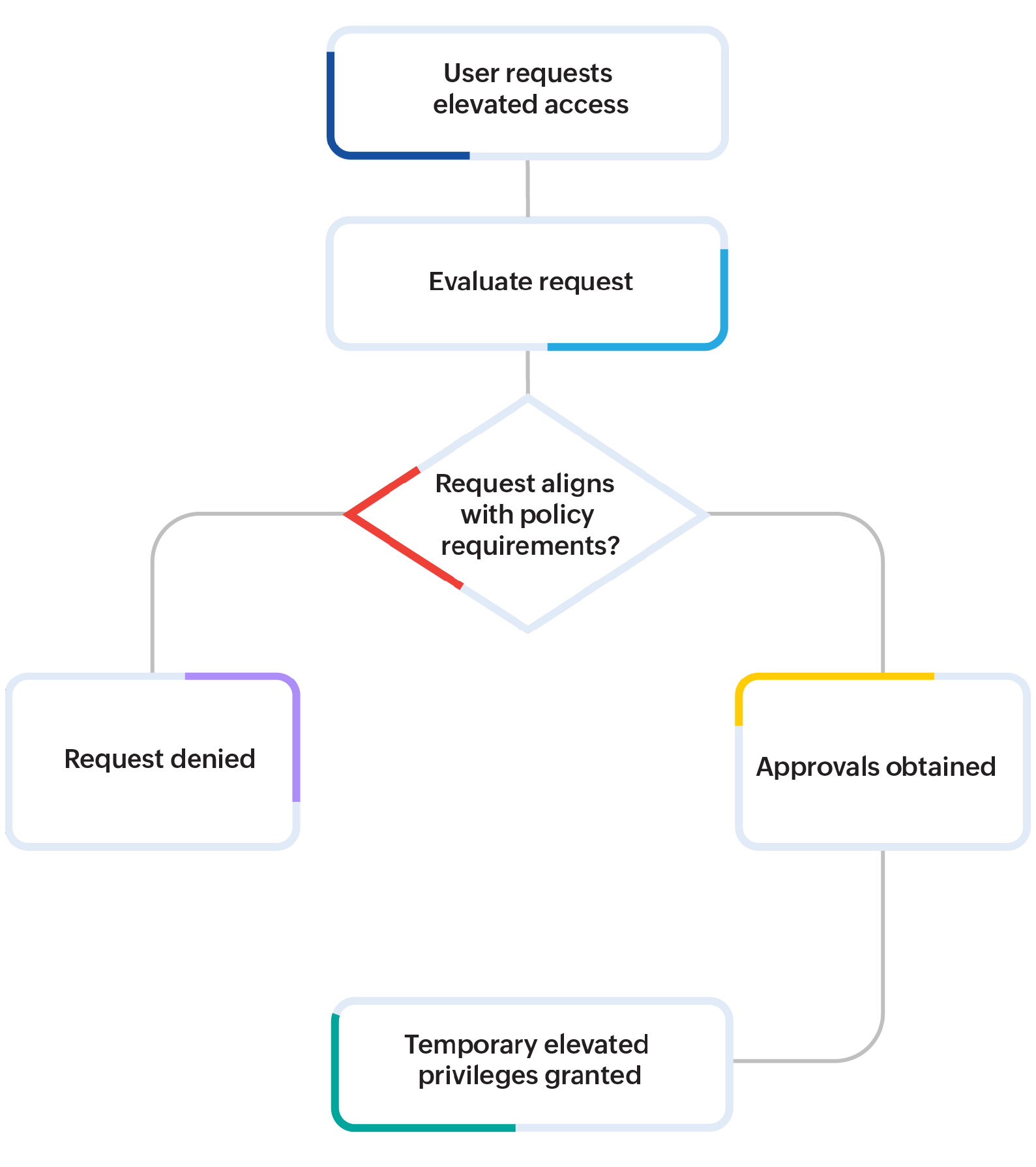
A typical PEDM workflow begins when a user—such as a developer, IT technician, or support staff—requests elevated access to perform a privileged task.
This could involve running an administrative script, changing a system configuration, or accessing a restricted application. Rather than granting admin rights, the system evaluates this request against predefined access policies.
These policies are aligned with the user's role, the nature of the request, and the associated risk level. If the request aligns with policy requirements, it may be automatically approved or routed to an administrator or manager for further authorization. Once the necessary approvals are in place, the system grants temporary elevated privileges, limited strictly to the task at hand.
All activities during this elevated session are tracked and logged for oversight and future audits. Once the task is completed or the time limit is reached, access is automatically revoked, mitigating risks associated with permanent admin rights and privilege escalation attacks. This case-by-case approach reinforces the principle of least privilege, allowing users to operate under standard accounts unless elevation is explicitly needed. Additionally, organizations can define trusted applications for elevation while blocking unauthorized tools, ensuring a secure and monitored access environment.
Business benefits of PEDM
Implementing PEDM offers tangible business value beyond just IT security. First and foremost, it significantly reduces the attack surface by ensuring that elevated privileges are only granted on a need-to-use basis. This limits the opportunities for lateral movement in the event of a breach, safeguarding critical systems and data.
PEDM also enhances operational efficiency. Instead of waiting for manual interventions or admin assistance every time elevated access is required, users can follow a self-service model, with approvals and policies in place. This leads to faster task execution without compromising compliance or governance.
From a compliance standpoint, PEDM helps meet stringent requirements set by standards like NIST, ISO 27001, and the GDPR. The ability to log, monitor, and audit privilege sessions not only strengthens security but also simplifies regulatory reporting and incident response.
How to implement a sound PEDM strategy
To create an effective PEDM strategy, fostering a strong access culture is essential. Here are some key steps to follow:
- Conduct an audit: Begin by auditing all privilege users, roles, and the specific tasks that require elevated access. This audit serves as the foundation for establishing fine-grained access policies.
- Establish approval workflows: Develop approval workflows that align with your organizational structure. Determine who needs to approve access requests and under what conditions. It’s best to integrate these workflows into your identity and access management systems when possible.
- Define elevation boundaries: Security teams should clearly define the boundaries for actions that can be elevated. This includes specifying what actions should be blocked and identifying the triggers that will generate alerts. For instance, certain types of DLLs, installers, or scripts might be flagged and automatically denied.
- Automate processes: Where possible, introduce automation. Implement time-bound access provisioning, real-time monitoring, and automatic revocation of access. This automation is crucial for scaling PEDM, especially in hybrid or cloud-native environments.
PEDM best practices
To get the most out of your PEDM implementation, it’s essential to follow key best practices:
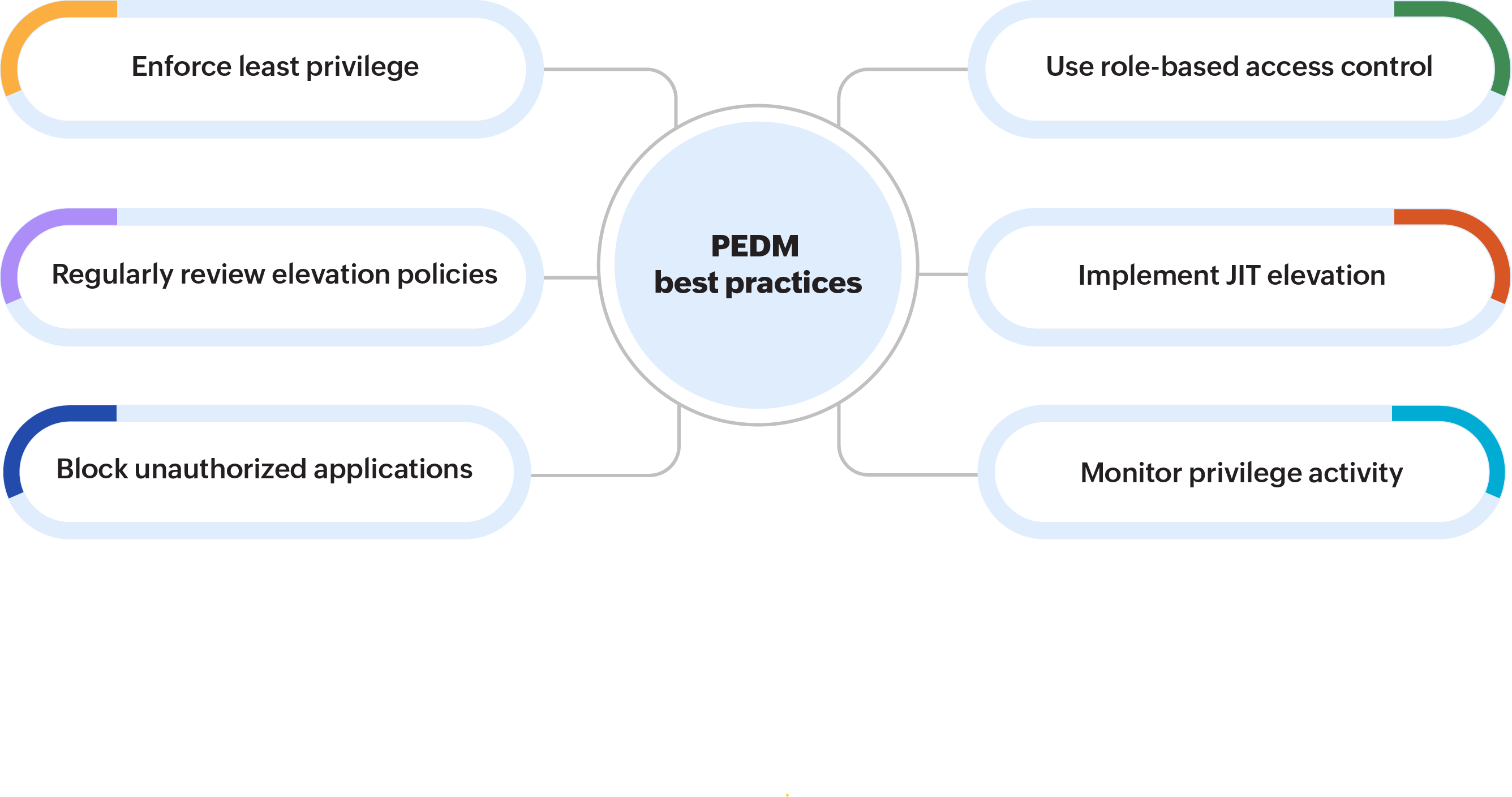
- Enforce the principle of least privilege: Default to standard user access and grant elevated rights only when necessary.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC): Define clear access policies based on job roles and responsibilities.
- Implement just-in-time (JIT) elevation: Avoid always-on admin accounts by provisioning access only for the duration of the task.
- Monitor and log all privilege activity: Maintain full visibility into who did what, when, and where to support compliance and forensics.
- Block unauthorized applications: Use allowlisting to ensure only approved commands, scripts, and executables can run with elevated privileges.
- Regularly review elevation policies: Update access rules based on changing job roles, threat landscapes, and compliance mandates.
Getting started with PEDM: Why choose PAM360?
If your organization is looking to create a reliable PEDM strategy, ManageEngine PAM360 is a strong choice. This tool offers traditional privilege account security management (PASM) features like secure storage for credentials and monitoring of sessions. It also provides essential PEDM features such as just-in-time access, detailed privilege delegation, command filtering, and workflow-based approvals.
What makes PAM360 special is how well it connects privilege access management with overall IT and security operations. Whether you are managing a few privileged accounts or implementing Zero Trust access controls for a large organization, PAM360 gives you the necessary tools to do this securely and efficiently. The platform allows for role-based access control, sets time limits on privileges, and ensures full visibility into every action taken with privilege access. This makes it perfect for organizations that want to implement PEDM without sacrificing productivity or compliance.