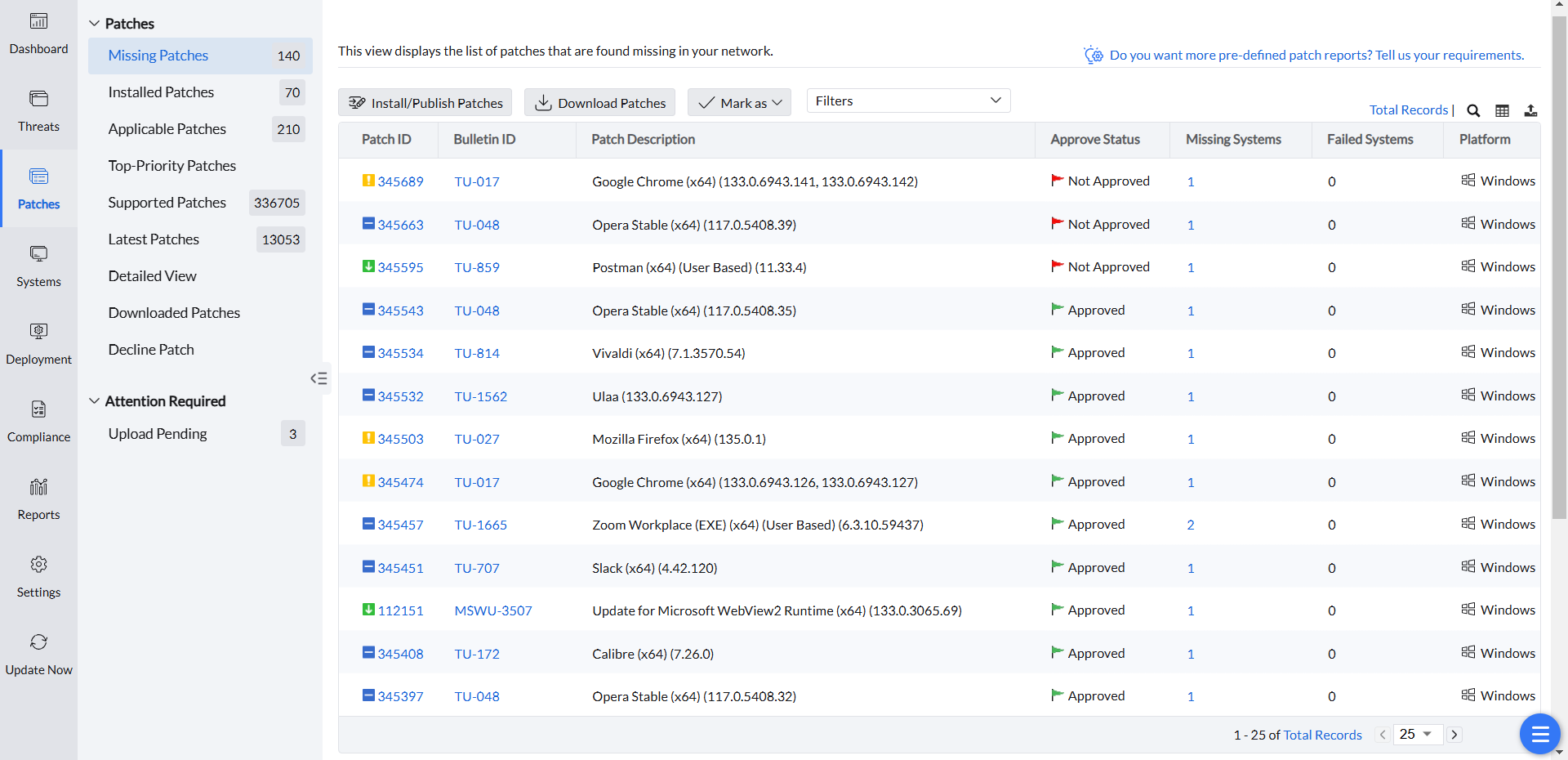
What is vulnerability scanning?
It is a critical cybersecurity process that detects vulnerabilities, enabling organizations to address them before attackers can exploit them. This process eliminates security blind spots and provides actionable insights, such as recommendations to patch vulnerable software, adjust security configurations, or close high-risk entry points. Failure to address these vulnerabilities can result in unauthorized access to enterprise networks, leading to data theft, malware propagation, and disruption of business operations. Vulnerability scanning can be performed internally or externally with different types of scans, including network-based, host-based, application-based, and wireless.
Why does vulnerability scanning matter?
A modern organization’s digital environment comprises interconnected devices like laptops, servers, smartphones, and TVs, each running its own operating system (OS) and applications. System administrators must keep these OSs and applications up to date, but with a constant influx of software updates and security patches, it can be challenging to stay current. This is where vulnerability scanning is crucial.
Beyond closing security gaps, automating vulnerability scanning enables companies to achieve long-term cost savings and improved operational efficiency. This approach enhances data and software security while ensuring compliance with SOC 2, ISO 27001, and NIST 800-53 frameworks. It also aligns with regulatory standards such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR.
How does vulnerability scanning work?
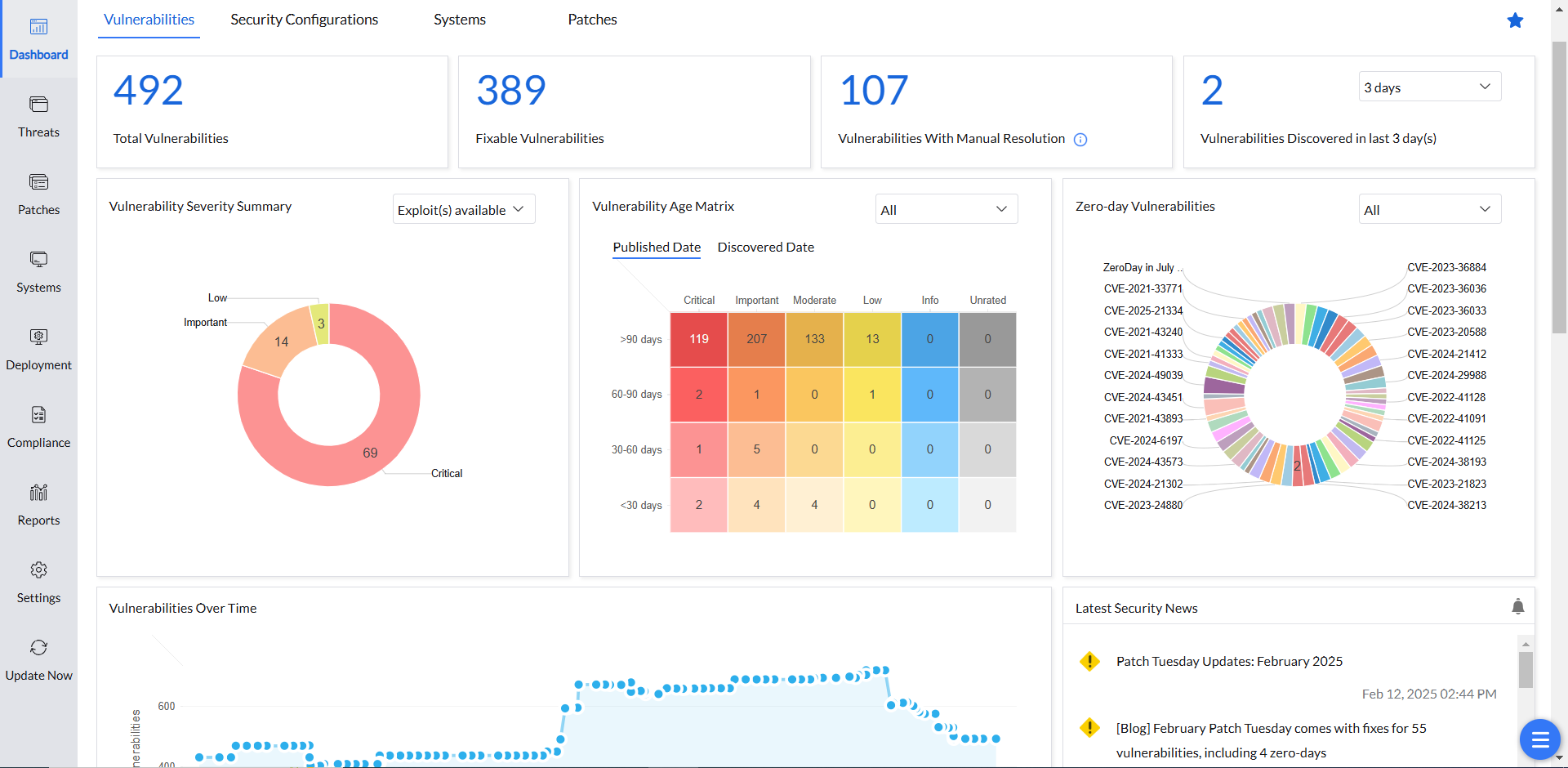
Vulnerability scanning works in four key ways: vulnerability discovery, vulnerability assessment, vulnerability remediation, and vulnerability reporting. Each step plays a crucial role in identifying security gaps and ensuring a robust defense. Let’s explore each in detail.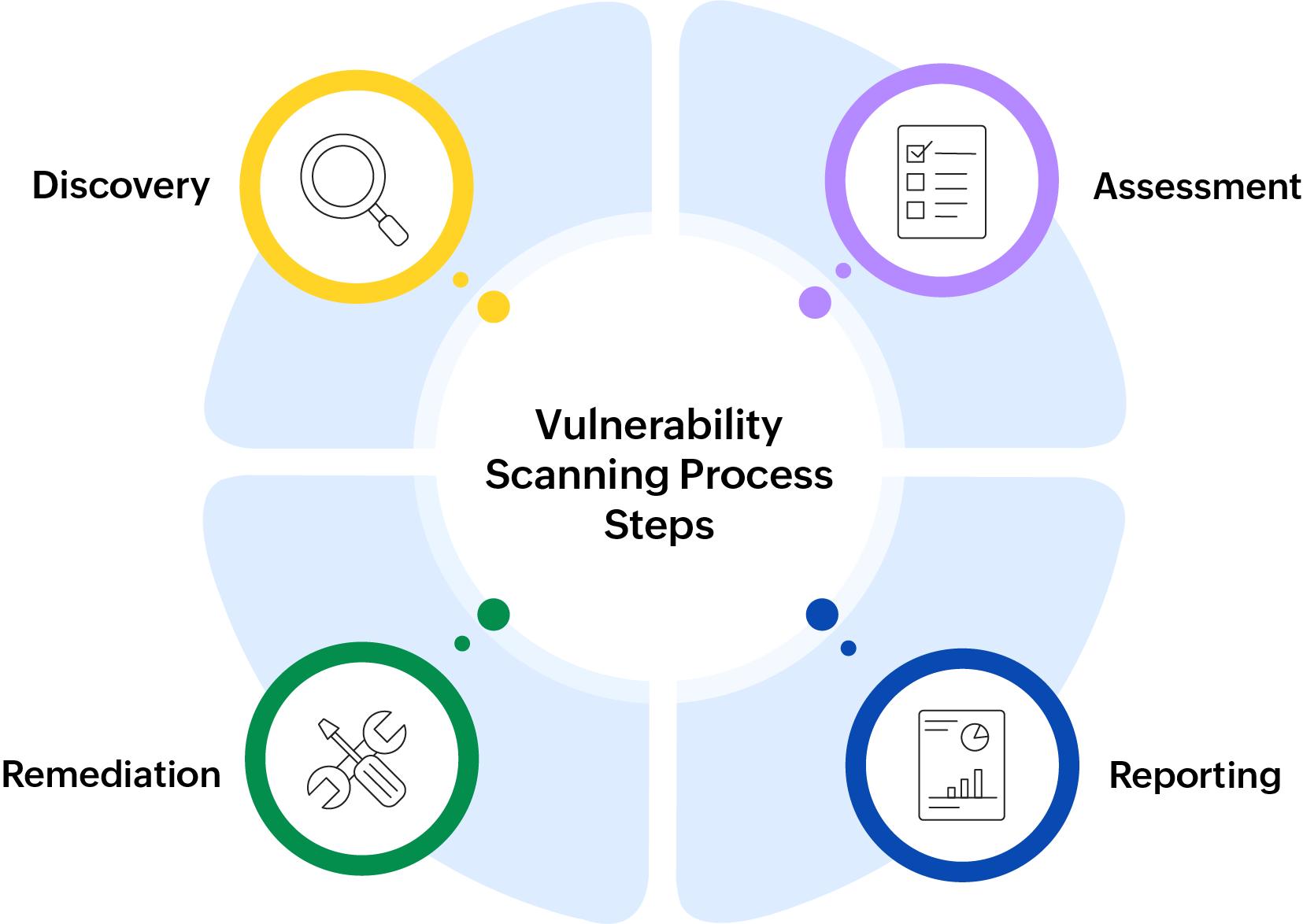
Vulnerability discovery: Detecting risks ahead of time
The vulnerability discovery step is for finding weaknesses in a system before they are exploited and turned into serious threats. This involves scanning systems, networks, and applications for known vulnerabilities using the most up-to-date vulnerability database, which outlines every issue concerning risks, impacts, and resolutions.
To help IT teams prioritize, vulnerabilities are assigned a severity score based on the common vulnerability scoring system (CVSS). This score ranges from 0 to 10—critical threats (9+) demand urgent action, while lower scores indicate less immediate risk. But it’s not just about flagging problems; effective vulnerability discovery gives teams the insights needed to stay ahead of threats, protect sensitive data, and keep business operations running smoothly.
Vulnerability assessment: Evaluating risks before they impact security
The vulnerability assessment step identifies security gaps within an IT environment through a systematic process, assesses the damage that might be caused by them, and prescribes suggestions on targeted actions to neutralize the risk. Thorough vulnerability assessments enable organizations to measure their security preparedness to determine how effectively they will respond to threats. Identifying and mitigating risks early is a fundamental step in achieving cyber resilience, as this approach helps safeguard critical systems, protect sensitive data, and ensure the long-term stability and security of the organization.
Vulnerability remediation: Fixing issues to enhance security
This step focuses on addressing and resolving identified security vulnerabilities to eliminate potential entry points for attackers. This process involves implementing corrective actions—such as applying patches, reconfiguring systems, or mitigating risks—to close security gaps effectively. Remediation is crucial for protecting critical systems, maintaining regulatory compliance, and preventing vulnerabilities from leading to actual breaches. In the context of rapidly evolving threats and stricter regulations, timely and effective vulnerability remediation is essential for ensuring organizational security.
Vulnerability reporting: Documenting threats for smarter actions
A vulnerability report turns raw data into valuable insights to help organizations forestall cyber threats. Vulnerability reporting should start with a clear executive summary highlighting key findings and recommendations. The report should include details about how the assessment was conducted, a list of vulnerabilities with their impact and risk levels, and specific steps to fix and prevent issues in the future.
Benefits of vulnerability scanning
Proactive security measures
Vulnerability scans are crucial for organizations to detect system changes and identify emerging threats. This enhances security awareness and preparedness. Consistent scanning fosters a proactive security culture focused on protection and resilience, while also enabling better resource management.
Smarter resource management
By running vulnerability scans, organizations get near real-time information about their most vulnerable areas and can determine weak points early before they become significant security risks. Identifying where vulnerabilities cluster helps organizations strategically allocate their security investments. This allows them to avoid wasting resources on guesswork and focus on critical areas that need protection, such as optimizing costs and strengthening their defenses.
Cost-effectiveness
Data breaches can lead to substantial financial penalties and damage to an organization's reputation. The associated costs may include regulatory fines, legal fees, loss of customer trust, and disruptions to operations. Implementing preventative measures, like vulnerability scanning, is generally more cost-effective than dealing with the consequences of a breach. Implementing security practices helps organizations reduce risks while balancing costs, efficiency, and long-term resilience.
Increased credibility
Strong data security measures safeguard an organization’s critical assets, ensuring the confidentiality of information. Regular vulnerability scanning is an essential part of a solid security plan. A well-rounded approach that includes regular scanning protects your data and builds your reputation as a company that values integrity and accountability.
Adhering to compliance and regulations
Non-compliance with regulatory requirements can lead to significant legal and reputational consequences, including fines and lawsuits. Vulnerability scanners help organizations identify risks, remediate security weaknesses, and maintain compliance with industry regulations, maintaining a secure operational environment.
Challenges of vulnerability scanning
Let’s dive into the complexities vulnerability scanning reveals and why managing it effectively is just as important as the scan itself.
False positives and false negatives
False positives occur when a security scanner incorrectly identifies a non-existent vulnerability, wasting time and resources. False negatives, on the other hand, happen when a scanner fails to detect an actual vulnerability, leaving systems exposed to cyber threats. Both scenarios can undermine the effectiveness of vulnerability management. Cross-validation using multiple scanning tools is recommended to minimize these inaccuracies, providing a more precise and reliable assessment of an organization’s security posture.
Lack of contextual reporting
When a scan runs, it generates a vast amount of data—some crucial, some redundant, and sometimes in overwhelming amounts. Raw scan reports often resemble an avalanche of information, making it challenging to separate urgent threats from low-risk issues. By refining scan results, organizations can focus on the vulnerabilities that genuinely matter, reduce clutter, improve clarity, and strengthen security without drowning in data.
Scan compliance and governance
Scanning without proper authorization might inadvertently contravene data protection legislation, breach contractual agreements, or even jeopardize your organization's reputation. Hence, always obtain prior approval from owners before executing any scans. This safeguards your organization from litigation but simultaneously earns it the trust factor and transparency in the security operation.
Types of vulnerability scanning
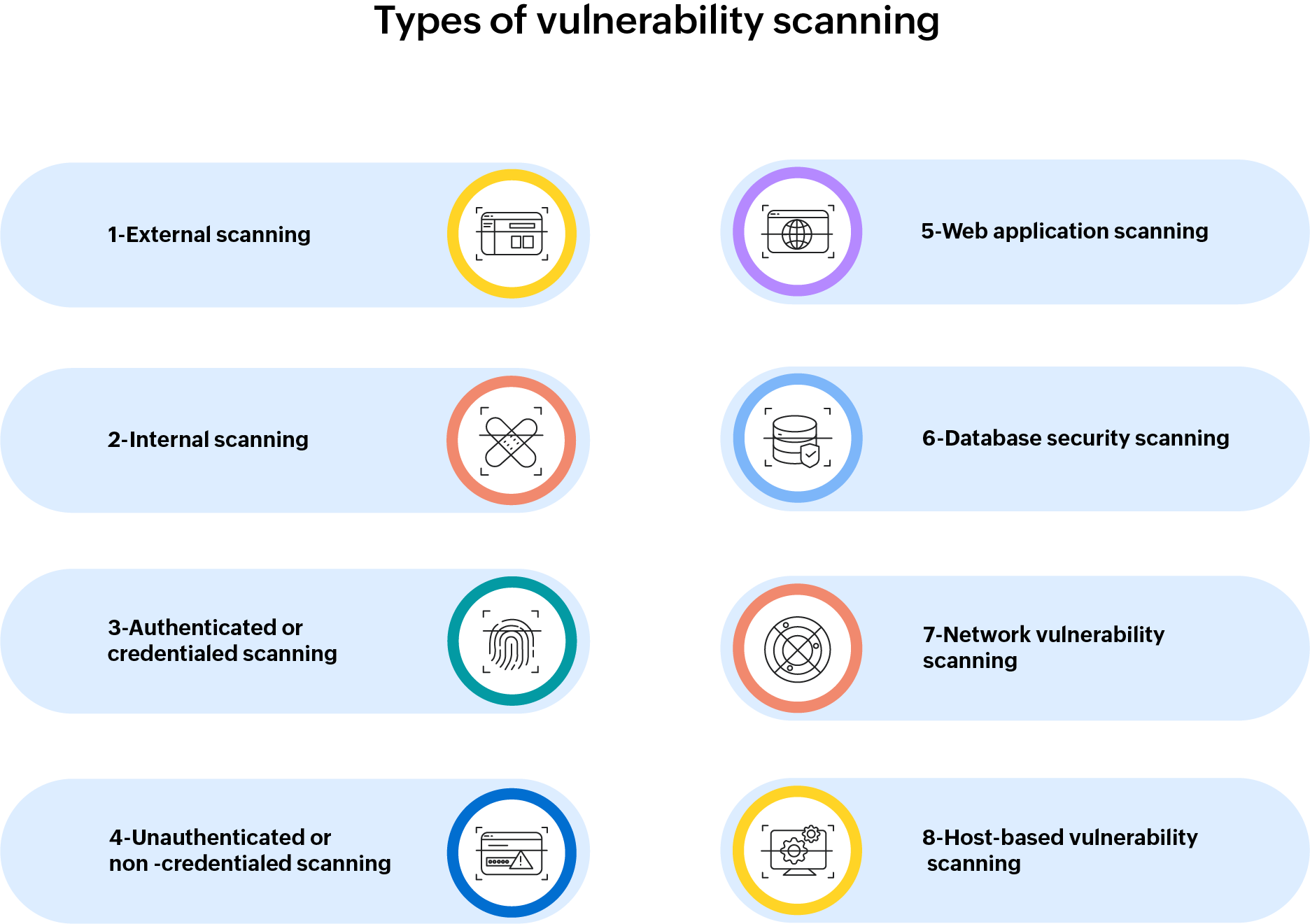
External scanning
This scanning involves analyzing vulnerabilities with an external face within all the organization-internet exposures such as websites, portals, and applications. These scans are looking for security gaps that cybercriminals might exploit to breach an organization's security perimeter from the outside. External scanning helps businesses ensure that they strengthen digital defenses and remain a step ahead of any future cyber threats
Internal scanning
A preventive security measure that focuses on threats that may not be covered by external vulnerability scanning. This type of scanning involves scanning the enterprise network from inside to detect any unpatched vulnerabilities, confirm the success of deployed patches, and detect other threats that may be exploited by malicious insiders or experienced cybercriminals. As opposed to external scans that examine the network security from an outsider's point of view, internal scans penetrate the core of your infrastructure: endpoints, servers, databases, and internal communication pathways.
Authenticated or credentialed scanning
Authenticated scanning, also referred to as credentialed scanning, is a vulnerability assessment method that requires user credentials such as passwords and access tokens to log in to a system. It works from within the organization to obtain more profound insight into its applications, configurations, and security, typically at an administrative level. Authenticated scanning goes under the skin, uncovering concealed vulnerabilities within internal systems, applications, and network configurations and giving indications of a far more thorough and proactive security assessment.
Unauthenticated or non-credentialed scanning
Unauthenticated scanning is simply the opposite of authenticated scanning. For this type of vulnerability scan, the assessment begins without a username, password, or any other credential. If any vulnerabilities are found, it indicates possible points of entry into the application that don't require privileged access. In simple terms, unauthenticated scanning is a no-keys-allowed, outside-looking-in approach to security that keeps organizations a step ahead in the fight against cyber threats.
Web application scanning
This process occurs in five distinct stages:
1. Discovery: Scanning for vulnerabilities that expose an application to an attack.
2. Simulation: Using automated tools to simulate attacks and assess the defenses of the system.
3. Assessment: Analyzing the results of the assessment for severity and potential impact;
4. Reporting: Developing rich descriptions for developers and security teams to address risk as efficiently as possible.
5. Continuous monitoring: Ensuring constant observation to guarantee that the application maintains its level of security against new and emerging threats.
Database security scanning
Database security scanning systematically examines databases to uncover vulnerabilities that could jeopardize an organization’s confidentiality and integrity. Left unchecked, these weaknesses can become gateways for cyber threats, leading to data breaches, compliance violations, and costly downtime. Organizations may strengthen their databases, reduce attack surfaces, and stop disruptions before they happen by identifying threats early and putting security measures in place.
Network vulnerability scanning
Businesses may substantially reduce the risk of data breaches by spotting weaknesses and thwarting possible threats before they can be exploited by attackers. With network vulnerability scanning, organizations make it challenging for attackers to break into the network perimeter by eliminating these vulnerabilities. This lowers the possibility that attackers may infiltrate vital areas like product development systems after gaining access to another system (such as HR systems). With this approach, businesses can make well-informed decisions on handling security threats, optimize resource allocation, and strengthen their overall cybersecurity posture.
Host-based vulnerability scanning
Host-based vulnerability scanning identifies security gaps within individual network hosts—workstations, servers, and endpoint devices—by analyzing their OS, configurations, software, and updates. There are three scanning methods: agent-server (real-time evaluations via endpoint agents reporting to a central server), agentless (remote scans using admin credentials, requiring a stable network), and standalone (software installed on each host, ideal for isolated systems but impractical for large networks). Regardless of the method, results are analyzed and reported to address vulnerabilities effectively.
Penetration testing versus vulnerability scanning
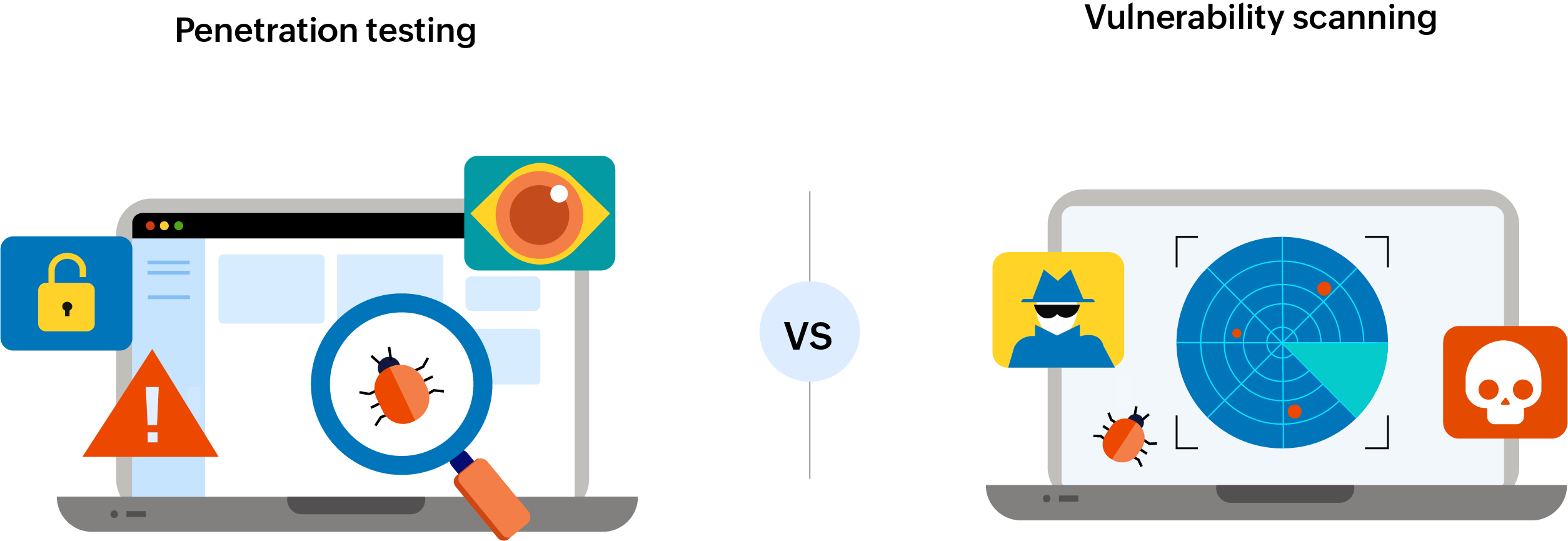
Penetration testing
Penetration testing (or pen testing) uses hacking techniques to uncover vulnerabilities within your systems. The goal is to stress-test your security defenses and identify exploitable weaknesses before cybercriminals do. Unlike vulnerability scanning, pen testing is adversarial, meaning it doesn’t rely on prior system knowledge—it’s designed to mimic an outsider attempting to breach your network.
Key aspects of penetration testing:
- Mimics assaults in the real world.
- Finds security flaws by actively exploiting them.
- Assesses how well security measures like firewalls are working.
- Reveals hidden dangers, including misconfigurations and malicious code injections.
Vulnerability scanning
Vulnerability scanning scans your systems for known security weaknesses. It’s an automated and non-intrusive approach, using approved tools to assess risks and generate reports for remediation. Unlike penetration testing, vulnerability scanning operates with full system knowledge, ensuring a thorough analysis of potential weaknesses.
Key aspects of vulnerability scanning:
- Uses automated tools to detect security flaws.
- Provides detailed insights into system weaknesses.
- Helps organizations prioritize and mitigate risks.
- Focuses on identifying, not exploiting, vulnerabilities.
Pen testing versus vulnerability scanning: The core difference
While both methods are essential to cybersecurity, the main distinction is in their approach:
- Penetration testing is an offensive tactic and aggressively attempts to enter the system like an attacker
- Vulnerability scanning is a defensive tactic, finding threats and suggesting non-exploitable solutions.
Organizations require both for a strong security strategy: penetration testing to verify defenses against actual assaults and vulnerability scanning to identify possible risks early.
How to choose the right vulnerability scanning tool for your organization
Key considerations | Descriptions |
Up-to-date threat database | Your vulnerability scanner should include an up-to-date database with outdated and current threats. This enables complete coverage of potential threats while offering specific insights for effective remediation. |
Seamless integration | Your testing and development environments must be easily integrated with the tool. This helps identify vulnerabilities early, allowing for automatic scans as code changes occur, thereby minimizing errors and disruptions. |
Efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness | The tool should be adaptable and capable of scaling with your expanding codebase. It should also be economical and provide strong security without compromising your budget or long-term sustainability. |
Evolving with your needs | Choose a solution that is efficient and adaptable, capable of growing with your expanding codebase. It should provide strong security at an affordable cost and ensure long-term viability. |
Enhance your endpoint security with ManageEngine
ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus is a complete solution to handle the increasing complexity of vulnerability management and endpoint security. Providing 360-degree visibility into security exposure helps businesses identify, evaluate, and control vulnerabilities on Linux, macOS, and Windows operating systems. Vulnerability Manager Plus guarantees that your endpoints adhere to industry standards with features like web server hardening, compliance auditing, automated patch management, and zero-day vulnerability mitigation.