Add Formulas
Formulas, as the name indicates are calculations that you could define in ManageEngine Analytics Plus to help you create the required reports. ManageEngine Analytics Plus provides a powerful formula engine to create any type of calculations required, to enable creating the required reports. Formulas are mathematical expressions that you create, which contains any combination of numbers, references of table columns, operators and functions etc. Functions are predefined mathematical formulas which are designed to perform specific well-known calculations.
ManageEngine Analytics Plus supports different flavors of formulas. The following is a summary of the various types of formulas that are supported in ManageEngine Analytics Plus:
- Custom Formula Columns: These are formula types where you could add a new column to your data table, whose values are derived based on the calculation/formula defined. You can define any powerful mathematical formula which uses the table columns in combination with operators and in-built functions. As the output of the formula adds a new column in the table is called a Formula Column.
- In-built Formulas: ManageEngine Analytics Plus provides a useful set of in-built custom formulas, available by default, to perform common calculations easily. These formulas can be applied only to single column. The result of a calculation (formula) will be added as another column to the base table.
- Aggregate Formulas: Aggregate Formulas are formulas where you should use aggregate functions (SUM, AVG..) in the calculation. The result of Aggregate Formulas will not be added as another column in the base table. They will just be associated to the table on which it has been created and can be used in creating reports (Charts, Pivot Tables and Summary Views) like any other table columns.
Custom Formula
ManageEngine Analytics Plus allows you to define your own powerful formulas to meet your specific reporting requirements. This enables you to easily perform from simple calculations such as addition and subtraction to a complex combination of in-built functions. As the output of the formula adds a new column in the table is called a Formula Column. You can use these formula columns in creating reports in the same way you use other columns in a table.
ManageEngine Analytics Plus provides you with a variety of in-built functions which are predefined mathematical formulas which are designed to perform specific well-known calculations easily. These in-built functions can be used in combination with the table columns and basic arithmetic operators like +, -, / and * to create your formula column.
To create and use custom formula columns:
- From the Explorer tab of the workspace, select the table to which you want to add the formula column.
- Select Add > Formula Column option from the toolbar or select a column in the table and choose Formula Column from the right click pop-up menu.
- The Formula Column dialog box will open as shown below. This dialog box provides easy access to the names of the columns in your table, as well as to many of the in-built functions that are available to create formulas. A brief description of the function with syntax and an example will be displayed at the bottom of the dialog box when you hover your mouse over a function.
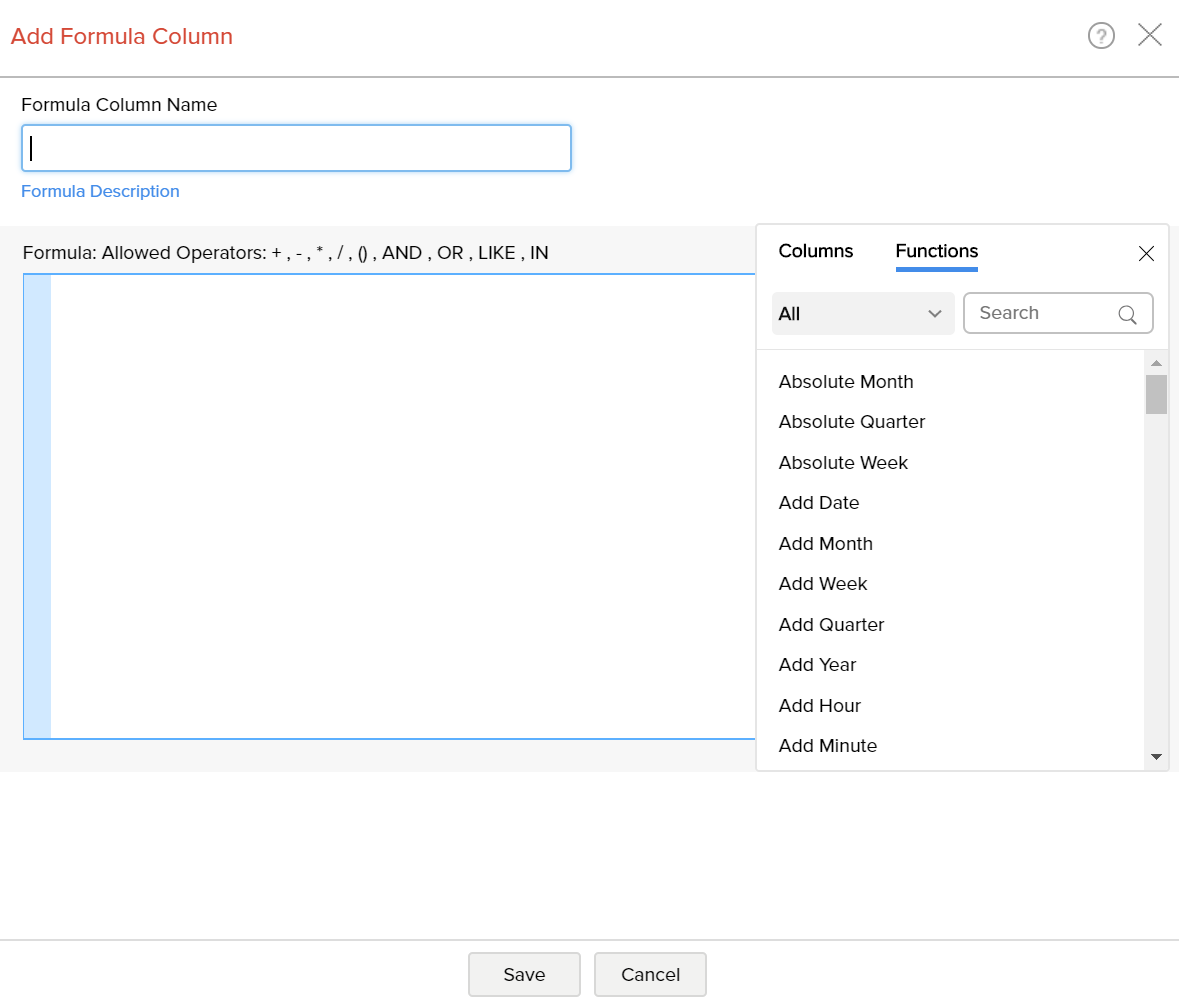
- In the Formula Column dialog box, select the columns and functions that you want to insert from the list under the Columns and the Function boxes.
For example, to build a custom formula that adds particular number of days to a given date:
- Select the Add Date function under the Functions box. You will notice that adddate() syntax appears in the Formula text box.
- In the Formula text box, position the cursor in between the parenthesis, select the date column to which you wanted to add date using the Columns option.
- Enter the number of days (say 10) that you want to add separated by a comma.
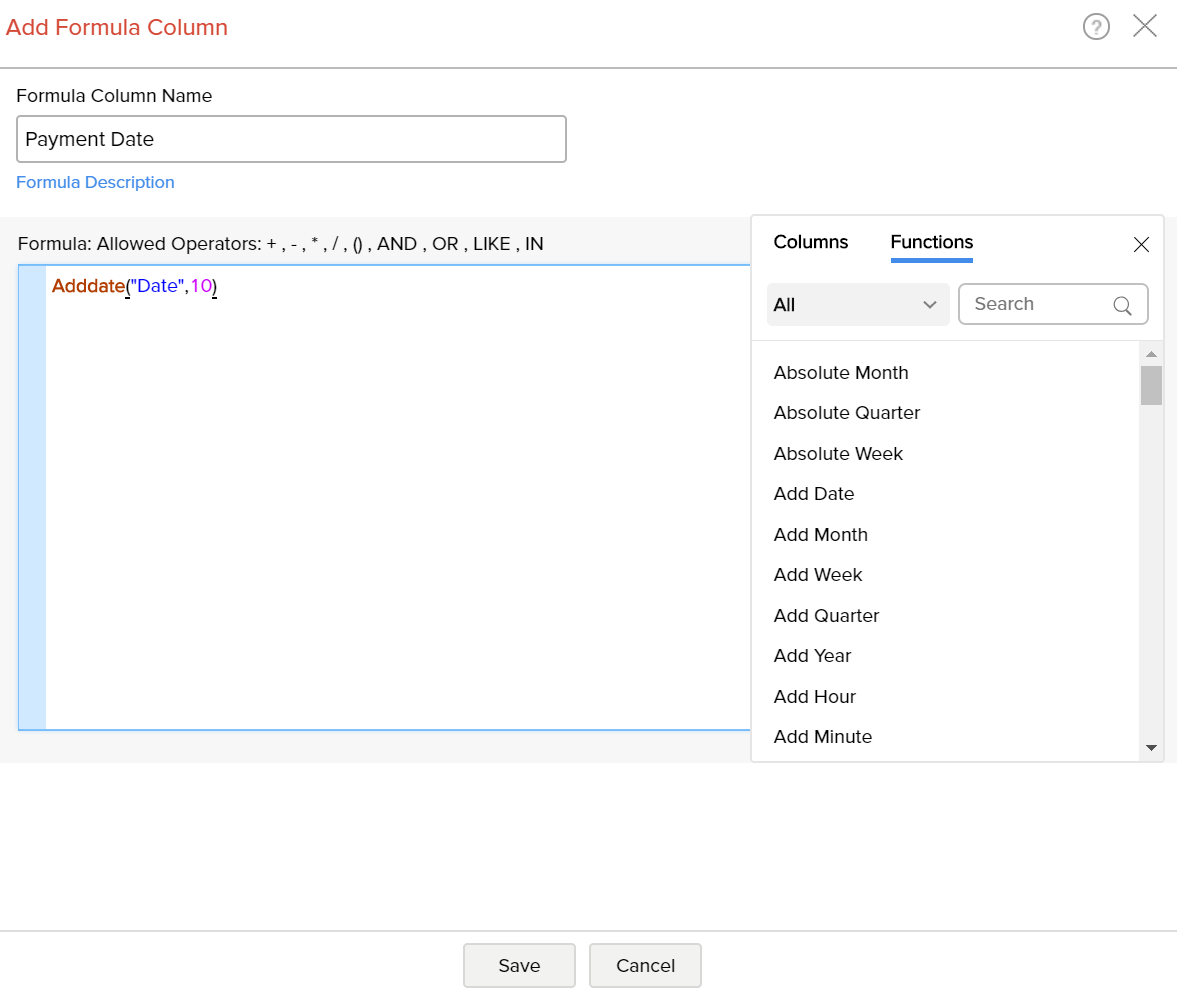
To create a formula column with this expression, type column name in the Formula Column Name text box and then click OK. A new formula column will be created in your table as shown below.
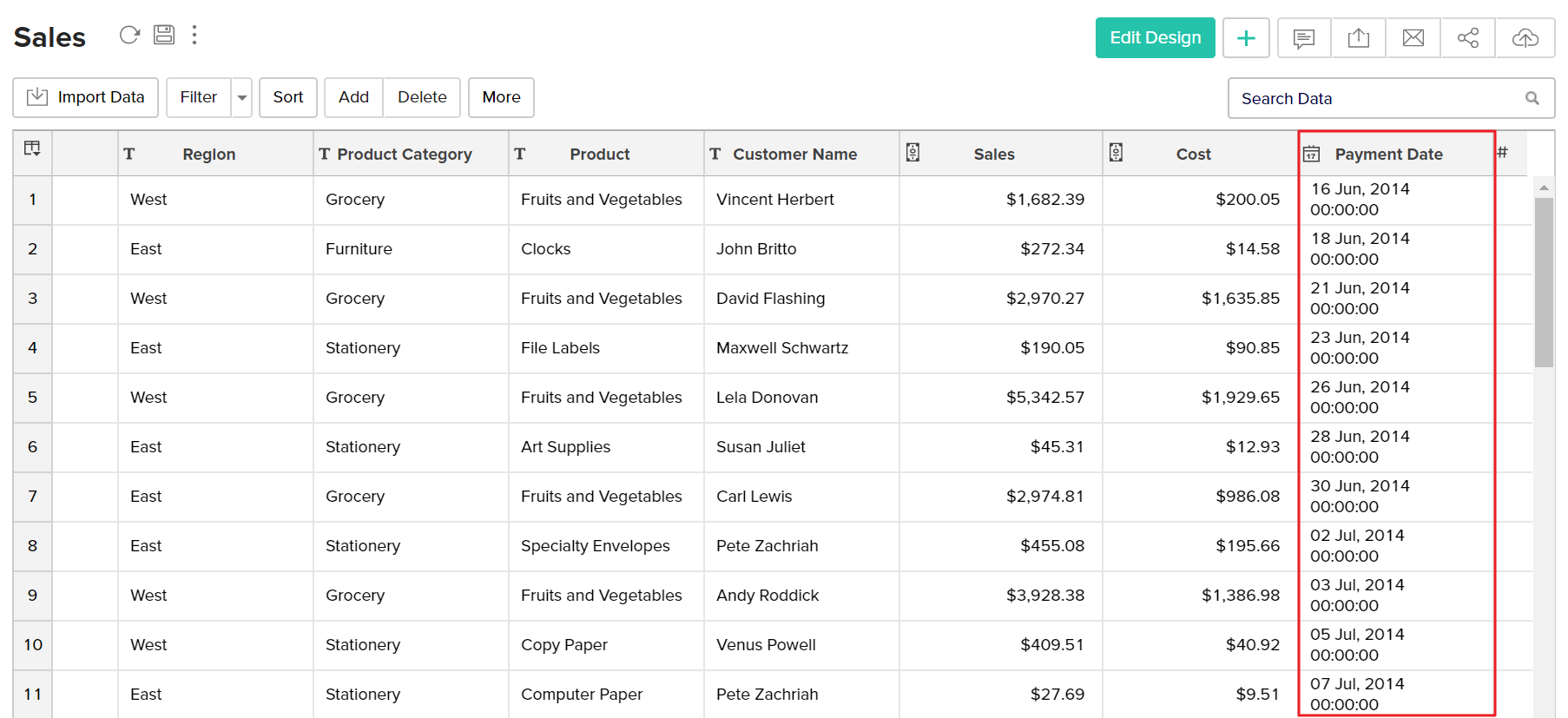
You can edit the formula column any time by right clicking on the formula column listed in the table and clicking Edit Custom Formula in the popup menu. Also refer to View/Edit Formulas to know how you could view all the formulas defined on a table and handle edition or deletion of the same.
Quick Add option for Formula Columns
ManageEngine Analytics Plus provides an easy and convenient way to add formula columns which are based on a limited set of widely used functions. You can find this quick add option as follow.
- Select a column based on which you want to add the formula column.
- Click Add > Add Formula option on the toolbar.
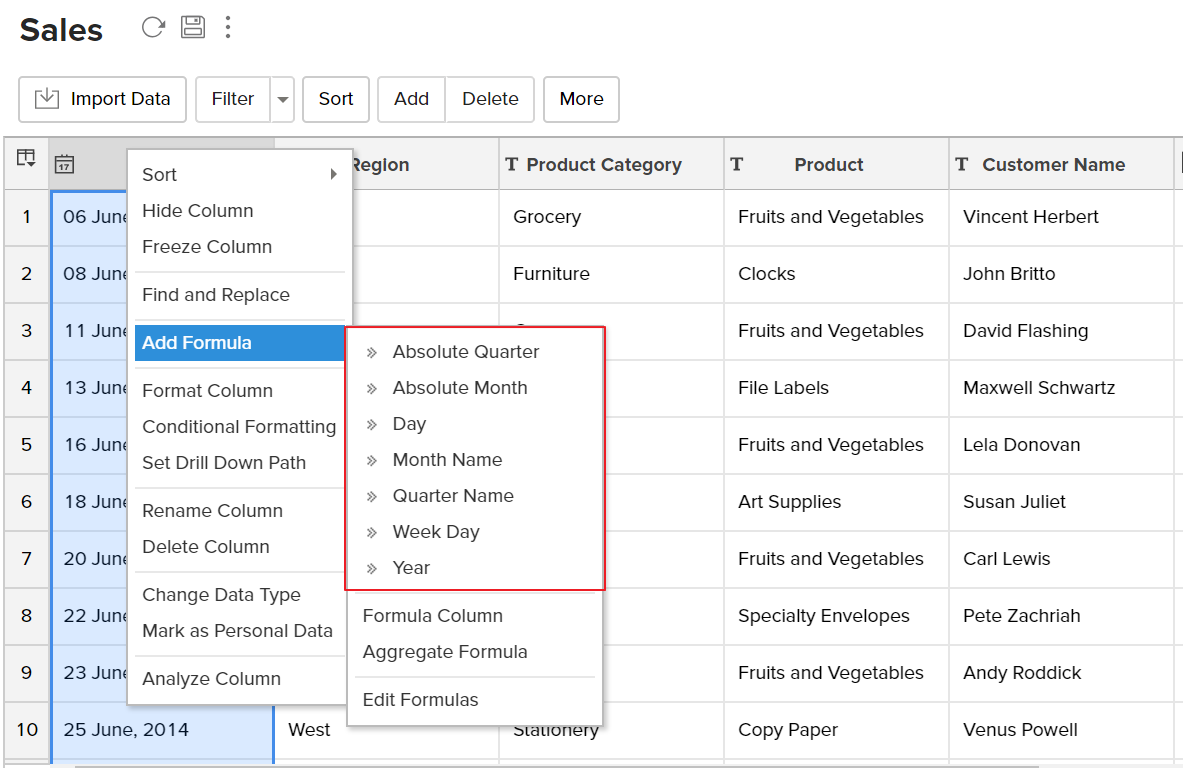
- ManageEngine Analytics Plus automatically identifies the data type of the column selected and displays a list of widely used pre-defined formulas which are applicable to that as shown in the screenshot below.
- On selecting the required formula from the list, ManageEngine Analytics Plus applies the formula on the corresponding column and adds a new formula column, at the right end of the table.
In-built functions provided by ManageEngine Analytics Plus
ManageEngine Analytics Plus provides you with a variety of in-built functions which are predefined mathematical formulas designed to perform specific well-known calculations easily. The following table gives a list of inbuilt functions provided by ManageEngine Analytics Plus which can be used to create any formula. The inbuilt formulas are categorized/grouped based on type of function.
Date Functions | ||
| FUNCTION | DESCRIPTION | EXAMPLE |
| Absolute Month - absmonth(date_column) | This function will return month and year from a given date value with the format (Month, yyyy). | absmonth('2011/8/7') = August, 2011 |
| Absolute Quarter - absquarter(date_column) | This function will return Quarter and year from a given date value with the format (Quarter, yyyy). | absquarter('2011/8/7') = Q3, 2011 |
| Absolute Week - absweek(date_column) | This function will return week and year from a given date value with the format (Week, yyyy). | absweek('06/04/2011') = W14, 2011 |
| Add Date - adddate(date_column, num_of_days) | This function will add the specified number of days(num_of_days) to the given date value. | adddate('2011/8/7',10) = 2011/8/1 |
| Add Week addweek(date_column, num_of_weeks) | This function will add the specified number of weeks(num_of_weeks) to the given date value. | addweek('2013-08-27',10) = 2013-11-05 |
| Add Month addmonth(date_column, num_of_months) | This function will add the specified number of months(num_of_months) to the given date value. | addmonth('2013-08-27',10) = 2014-06-27 |
| Add Quarter addquarter(date_column, num_of_quarters) | This function will add the specified number of quarter(num_of_quarter) to the given date value. | addquarter('2013-08-27',10) = 2016-02-27 |
| Add Year addyear(date_column, num_of_years) | This function will add the specified number of year(num_of_year) to the given date value. | addyear('2013-08-27',10) = 2023-08-27 |
| Add Time - addtime(data_column, time) | This function returns the day by adding the time to the given date column. | addtime ('2002/02/21 18:23:26', '01:20:10') = 2002/02/21 19:43:36 |
| Add Hours addhour(date_column, num_of_hours) | This function returns the day by adding the number of hours to the given date column. | addhour('2013-08-27',10) = 2013-08-27 10:00:00 |
| Add Minutes addminute(date_column, num_of_minutes) | This function returns the day by adding the number of minutes to the given date column. | addminute('2013-08-27',10) = 2013-08-27 00:10:00 |
| Add Seconds addsecond(date_column, num_of_seconds) | This function returns the day by adding the number of seconds to the given date column. | addsecond('2013-08-27',10) = 2013-08-27 00:00:10 |
| Peroid Add period_add(year_month, num_of_months) | Adds the specified number of months to the period and returns in the format 'yrmth'. | period_add(198608,6) = 198702 |
| Age Months age_months(from_date, to_date [Optional]) | This function returns the age in months between the two given date columns | age_months('2013-08-27','2014-06-28') = 10 |
| Age Years age_years(from_date, to_date [Optional]) | This function returns the age in months between the two given date columns | age_years('2013-08-27','2018-08-03') = 4 |
| Business Completion Day business_completion_day(from_date, num_of_days, exclude_weekends [Optional]) | This function returns the date adding the given number of days excluding the specified weekends. In case weekends is not provided, then Saturday and Sunday are considered as weekends by default. | business_completion_day('2018-01-01',10) = 2018-01-15 |
| Business Days business_days(from_date, to_date, exclude_weekends [Optional]) | This function returns the count of the business days between the two given date columns excluding specified weekends. In case weekends is not provided, then Saturday and Sunday are considered as weekends by default. | business_days('2018-01-27','2018-08-03') = 134 |
| Business Hours business_hours(from_datetime, to_datetime, work_start_time, work_end_time, exclude_weekends [Optional]) | This function returns the count of business hours in the business days between the two given datetime columns. In case weekends is not provided, then Saturday and Sunday are considered as weekends by default. | business_hours('2018-01-27 10:00:00','2018-08-03 08:00:00','09:00:00','10:00:00','1000001') = 134 |
| Convert String to Date convert_string_to_date(string_column, date_format_of_the_value) | Converts the string into date and returns it in the specified format. | convert_string_to_date('24/12/2009', '%d/%m/%Y') = 2009-12-24 |
| Convert to Datetime convert_to_datetime(string_column, date_format) | This function returns the date-time value by converting the given string. | convert_to_datetime('2013 Aug 27','yyyy MMM dd') = 27 Aug, 2013 |
| Convert TZ convert_tz(date_column, current_timezone_offset, timezone_to_be_converted_offset) | This function converts the timestamp or a date time value from one time zone to another. The parameters to specify the time zone can be given as Time Zone identifiers, Time Zone Abbreviations orOffsets. To consider the daylight savings during conversion automatically, use Time zone identifiers as parameters. |
|
| Current Date currentdate() | This function updates the current date of the computer or server automatically | currentdate() = 27 Sep, 2024 10:06:18 |
| Current Time current_time() | This function updates the current time automatically | current_time() = 27-11-2024, 14:30 |
| Current Timestamp current_timestamp() | This function updates the current date and time automatically | current_timestamp()=2024-11-27 14:30:15 |
| Now now() | This function updates the current date and time automatically | now()= 27 Sep, 2024 10:06:18 |
| Today today() | This function updates the current date automatically | today()=27 Sep, 2024 |
| Tomorrow tomorrow() | This function returns the date one day after the current date | tomorrow()=28 Sep,2024 |
| Yesterday yesterday() | This function returns the date for the previous day | yesterday()=26 Sep, 2024 |
| UTC date utc_date() | Returns the current UTC date. | utc_date()=27 Sep, 2024 |
| UTC time utc_time() | Returns the current UTC time. | utc_time()= 2024-11-27 14:30 |
| UTC date-time utc_timestamp() | Returns the current UTC date-time value. | utc_timestamp()= 2024-11-27 14:35:45 |
| Date date(date_column) | This function returns the date part of the given date and time value. | date('2013-08-07 14:15:16') = 2013-08-07 |
| Date Format date_format(date_column, date_format_to_be_converted) | This function returns the string form of the date for given date format. | date_format('2008-08-03','%W %M %Y') = Sunday August 2008 |
| Date and Time Diff - dateand timediff(Unit, From Date, To Date[optional] | This function returns the date and time difference between two date columns based on the units specified. The supported units are SECOND, MINUTE, HOUR, DAY, WEEK, MONTH, QUARTER, YEAR. | dateandtimediff(DAY, '2015-01-01', '2015-05-01')=120 The above example returns the difference between the given dates in Days. |
| Date and Time Diff in Duration - datetime_diff_in_duration(date_column, date_column [Optional]) | Calculates the date-time difference between the given columns, and returns it as duration. |
|
| Date Diff datediff(date_column1, date_column2) | This function returns the difference between the two given date columns. | datediff('2011/8/11','2010/9/11') = 334 |
| Period Diff period_diff(year_month, year_month) | Returns the difference between two periods in months. | period_diff(198608,198602) = 2 |
| Day - day(date_column) | This function returns the day of the given date value. | day( '2024/11/27') = Wednesday |
| Day Name dayname(date_column) | This function returns the name of the weekday for the given date value(Sunday,Monday,...). | dayname('1990-08-07') = Tuesday |
| Day of Week dayofweek(date_column) | This function will return the number of the day of week of the given date value (Sunday = 1, Monday = 2,...). | dayofweek('2011/9/9') = 6 |
| Day of Month dayofmonth(date_column) | This function returns the day of the month for the given date value. | dayofmonth('1990-08-07') = 7 |
| Day of Quarter dayofquarter(date_column) | This function returns the count of days from the start day of the quarter to the given date value. | dayofquarter('2017-08-07') = 38 |
| Day of Year - dayofyear(date_column) | This function will return the number of the day of the year of the given date value (0 through 365). | dayofyear('2011/9/2') = 245 |
| Days Between days_between(from_date, to_date [Optional]) | This function returns the count of day between the two given date. | days_between('2018-01-27','2018-08-03') = 188 |
| End date end_day(date_units, date_column) | This function returns the end date for the given date value and date units. | end_day(month,'2018-08-27') = 2018-08-31 |
| First Date Current Week first_date_current_week(date_column, week_start_day [Optional]) | This function returns the day the current week begins with. You can choose to set the start day of your week in the parameter week_start_day by specifying 1 - Sunday, 2- Monday,... 7 - Saturday. By default Sunday is the first day of the week. | first_date_current_week('2013-10-11') = 2013-10-06 |
| From Unixtime - fromunixtime(seconds) | This function returns the unix time for the given seconds value. | fromunixtime('1000') = 1970/01/01 05:46:40 |
| Hour - hour(date_column) | This function returns the hour of the given date value. | hour('2011/8/7 10:35:23') = 10 |
| Last Day - lastday(date_column) | This function returns the last day of the month for the given date value. | lastday('2011/9/7') = 2011/9/30 |
| Last N Days last_nday(date_column, num_of_days) | This function returns a date that is N number of days before the given date. | last_nday('2018-08-04',15) = 2018-07-21 |
| Last N Months last_nmonth(date_column, num_of_months) | This function returns the date value for the given year and num_of_days values. | last_nmonth('2018-08-04',15) = 2017-06-04 |
| Next N Days next_nday(date_column, num_of_days) | Returns a date that is N number of days after the given date. This is calculated from a day after the given date. | next_nday('2018-08-04',15) = 2018-08-19 |
| Next N Month next_nmonth(date_column, num_of_months) | Returns a date that is N number of months after the given date. This is calculated from a day after the given date. | next_nmonth('2018-08-04',15) = 2019-11-04 |
| Next Weekday next_weekday(date_column, weekday) | Returns the next date when the specified weekday falls. | next_weekday('2018-08-01',1) = 2018-08-05 |
| Previous N Day previous_nday(date_column, num_of_days) | Returns a date that is N number of days before the given date. This is calculated from a day before the given date. | previous_nday('2018-08-04',15) = 2018-07-20 |
| Previous N Months previous_nmonth(date_column, num_of_months) | Returns a date that is N number of months before the given date. This is calculated from a day before the given date. | previous_nmonth('2018-08-04',15) = 2017-05-04 |
| Make Date - makedate(year,num_of_days) | This function returns the date value for the given year and number of the day value (0 through 365) | makedate('2011','23') = 2011/1/23 |
| Microsecond microsecond(date_column) | This function returns the microsecond value from the given date-time argument value. | microsecond('1990-08-07 10:35:23.3427') = 342700 |
| Minute - minute(date_column) | This function returns the minutes of the given date value. | minute('2011/8/7 10:35:23') = 35 |
| Second - second(date_column) | This function returns the seconds of the given date/time value. | second('2011/9/7 10:35:23') = 23 |
| Modified Time -modifiedtime() | This function returns the created time of the record (if the record is newly added) or the last modified time of the record. When you apply this function, initially it will return the time at which the formula has been created. Subsequently it will return only the modified time of the record. | |
| Month - month(date_column) | This function returns the name of the month of the given date value. | month('2011/9/7') = September |
| Month Name monthname(date_column) | This function returns the name of the month of the given date value. | monthname('2011/9/7') = September |
| Month Number - monthnum(date_column) | This function returns the number of the month of the given date value. | monthnum('2011/9/7') = 9 |
| Months Between months_between(from_date, to_date [Optional], iswhole_value [Optional]) | Returns the count of months in fractional value considering 31 days as a month. | months_between('2013-08-27','2018-08-03',1) = 59 |
| Quarter - quarter(date_column) | This function returns the quarter of the given date value. | quarter('2011/8/7') = Q3 |
| Quarter Name quartername(date_column, fiscal_start_month [Optional]) | Returns the quarter name of the given date value as a string. | quartername('1990-08-07') = Q3 |
| Quarter Number quarternum(date_column, fiscal_start_month [Optional]) | Returns the quarter of the given date in numeric format. | quarternum('1990-08-07') = 3 |
| Second to Time sec_to_time(seconds) | Converts the given number of seconds to time and returns it in hours, minutes and seconds. | sec_to_time(86399) = 23:59:59 |
| Second second(date_column) | Returns the seconds of the given date value. | second('1990-08-07 10:35:23') = 23 |
| Start Date start_day(date_units, date_column) | Returns the start date for given date value and date units. | start_day(month,'2018-08-27') = 2018-08-01 |
| Sub Date - subdate(date_column,num_of_days) | This function returns the date by subtracting the number of days(num_of_days) from the given date value. | subdate('2011/9/15','6') = 1990/9/9 |
| Sub Time - subtime(date_column,time) | This function returns the date by subtracting the time from the given date with time value. | subtime('2011/02/21 18:23:26','01:20:10') = 2011/02/21 17:03:16 |
| Time time(date_column) | Returns the time value of the given date-time value argument. | time('2013-08-07 14:15:16') = 14:15:16 |
| Time Format time_format(time, time_format_to_be_converted) | Converts the time to the specified format and returns the same. | time_format('19:30:41.32','%H %h %i %s %f') = 19 07 30 41 320000 |
| Time to Sec time_to_sec(date_column) | Converts the time value in hours and minutes to seconds and returns the same. | time_to_sec('2013-08-07 14:15:16') = 51316 |
| Time Diff timediff(to_date, from_date) | Returns the difference between two time values passed in the 2 arguments. | timediff('1990-08-17 16:15:14','1990-08-17 14:15:16') = 01:59:58 |
| Timestamp timestamp(date_column) | Returns the date time expression for a given date value. | timestamp('2008-11-05') = 2008-11-05 00:00:00 |
| Timestamp Add timestampadd(unit, numeric_column, date_column) | Returns the date time after adding the specified number of interval. | timestampadd(week,1,'2008-11-05 19:00:00') = 2008-11-12 19:00:00 |
| Timestamp Diff timestampdiff(unit, from_date, to_date) | Subtracts the first argument from the second argument and returns the value in the specified unit. | timestampdiff(year,'2002-05-01','2001-01-01') = -1 |
| Timestamp Diff in Duration - timestamp_diff_in_duration(date_column, date_column) | Calculates the date time difference between the given timestamp columns and returns it as duration. | timestamp_diff_in_duration('1990-08-17 16:15:14', '1990-08-17 14:15:16') = 0.1:59:58 |
| Unix Timestamp unix_timestamp(date_column [Optional]) | Calculates the total number of seconds fromï¿1⁄2 the date '1970-01-01 00:00:00' to the given date-timeï¿1⁄2 and returns the same. | unix_timestamp('2018-10-10 12:35:45') = 1539174945 |
| Week week(date_column) | Returns the week of the given date. | week('2008-01-14') = 2 |
| Weekday weekday(date_column) | Returns weekday of the given date value. | weekday('1990-08-07') = Tuesday |
| Week of Month weekofmonth(date_column) | Returns the week number of the month for the given date value. | weekofmonth('2008-01-14') = 3 |
| Week of Year weekofyear(date_column, week_start_day [Optional], week_mode [Optional], fiscal_start_month [Optional] | Returns the week number of the given date as numeric value. | weekofyear('1990-08-07') = 32 |
| Year - year(date_column) | This function returns year from the given date value. | year('2011/9/7') = 2011 |
| Year Week yearweek(date_column) | Returns the year and week of the given date. | yearweek('2008-01-14') = 200802 |
Duration Functions | ||
| FUNCTION | DESCRIPTION | EXAMPLE |
| Add Duration - add_duration( duration_column, duration_column) | Returns the duration in the default format ('%D.%H:%m:%s') by adding the values in the specified duration columns. |
|
| Add Days to Duration - add_days_to_duration( duration_column, num_of_days) | Returns the duration in the default format ('%D.%H:%m:%s') by adding the number of days to the specified duration column. | add_days_to_duration ('100.11:22:33', 5)= 105.11:22:33 |
| Add Hours to Duration - add_hours_to_duration( duration_column, num_of_hours) | Returns the duration in the default format ('%D.%H:%m:%s') by adding the given number of hours to the specified duration column. | add_hours_to_duration ('100.11:22:33', 5) = 100.16:22:33 |
| Add Minutes to Duration - add_minutes_to_duration( duration_column, num_of_minutes) | Returns the duration in the default format ('%D.%H:%m:%s')by adding the given number of minutes to the specified duration column. | add_minutes_to_duration ('100.11:22:33', 5) = 100.11:27:33 |
| Add Seconds to Duration - add_seconds_to_duration( duration_column, num_of_seconds) | Returns the duration in the default format ('%D.%H:%m:%s') by adding the given number of seconds to the specified duration column. | add_seconds_to_duration ('100.11:22:33', 5) = 100.11:22:38 |
| Add Weeks to Duration -add_weeks_to_duration( duration_column, num_of_weeks) | Returns the duration in the default format ('%D.%H:%m:%s') by adding the given number of weeks to the specified duration column. | add_weeks_to_duration ('100.11:22:33', 5) = 135.11:22:33 |
| Duration to Month - Duration_to_months (duration_column) | Identifies the number of months present in the duration value and return it as a number. | duration_to_months ('500.10:35:23') = 16 |
| Duration to Days - duration_to_days( duration_column ) | Identifies the number of days present in the duration argument and returns it as a number. | duration_to_days ('500.10:35:23') = 500 |
| Duration to Hours - duration_to_hours( duration_column ) | Identifies the number of hours present in the duration argument and returns it as a number. | duration_to_hours ('500.10:35:23') = 12010 |
| Duration to Minutes - duration_to_minutes( duration_column) | Identifies the number of minutes present in the duration argument and returns it as a number. | duration_to_minutes ('500.10:35:23') = 720635 |
| Duration to Seconds - duration_to_seconds( duration_column) | Identifies the number of seconds present in the duration argument and returns it as a number. | duration_to_seconds( '500.10:35:23') = 43238123 |
| Duration to Weeks - duration_to_weeks(duration_column) | Identifies the number of weeks present in the duration argument and returns it as a number. | duration_to_weeks( '500.10:35:23') = 71 |
| Duration to Years - duration_to_years(duration_column) | Identifies the number of years present in the duration argument and returns it as a number. | duration_to_years ('500.10:35:23') = 1 |
| Make Duration - make_duration (num_of_years, num_of_months, num_of_weeks, num_of_days, num_of_hours, num_of_minutes, num_of_seconds) | Calculates the duration using the given number of years, months, weeks, days, hours, minutes and seconds. Returns the calculated values in the default format ('%D.%H:%m:%s'). Enter 0 if any of the specified arguments (years, months, weeks, days, hours, minutes, and seconds) does not have a value. | make_duration ('1', '11', 0, '21', '9', 50,' 5.777') = 721.10:59:23 |
| Subtract Duration - sub_duration(duration_column, duration_column) | Returns the duration in the default format ('%D.%H:%m:%s') by subtracting the values in the specified duration columns. |
|
| Subtract Days from Duration - sub_days_from_duration (duration_column, num_of_days) | Returns the duration in the default format ('%D.%H:%m:%s') by subtracting the given number of days to the specified duration column. |
|
| Subtract Hours from Duration - sub_hours_from_duration (duration_column, num_of_hours) | Returns the duration in the default format ('%D.%H:%m:%s') by subtracting the given number of hours to the specified duration column. |
|
| Subtract Minutes from Duration -sub_minutes_from_duration (duration_column, num_of_minutes) | Returns the duration in the default format ('%D.%H:%m:%s') by subtracting the given number of minutes to the specified duration column. |
|
| Subtract Seconds from Duration -sub_seconds_from_duration (duration_column, num_of_seconds ) | Returns the duration in the default format ('%D.%H:%m:%s') by subtracting the given number of seconds to the specified duration column. |
|
| Subtract Weeks from Duration -sub_weeks_from_duration( duration_column, num_of_weeks) | Returns the duration in the default format ('%D.%H:%m:%s') by subtracting the given number of weeks to the specified duration column. | Sub_weeks_from_durrom_duration ('200.07:06:06', 5) = 165.07:06:06 |
| To Duration - to_duration(numeric_column,[duration_unit]) | Converts the numeric column into duration data type. The conversion is based on the duration unit specified. By default, the duration unit is taken as second. |
|
| Round Duration - round_duration(duration_column,duration_scale) | Returns the duration value rounded to the given duration scale. |
|
Numeric Functions | ||
| FUNCTION | DESCRIPTION | EXAMPLE |
| Abs - abs(numeric_column) | This function returns the absolute value (number without sign) of the 'numeric_column' | pi() = 3.14159265358979 |
| Acos - acos(numeric_column) | This function returns the arc cosine value of the specified 'numeric_column'. Returns NULL if the 'numeric_column' is not in the range-1 to 1. | pow(2,3) = 8 |
| Asin - asin(numeric_column) | This function returns the arc sine value of the specified 'numeric_column'. Returns NULL if the 'numeric_column' is not in the range-1 to 1. | rand() = 0.282164005825449 |
| Atan - atan(numeric_column) | This function returns the arc tangent value of the specified 'numeric_column'. | atan(2) = 1.107149 |
| Atan2 - atan2(numeric_column1, numeric_column2) | This function returns the arc tangent of the specified columns 'numeric_column1' / 'numeric_column2 | atan2(0.8, 0.6) = 0.927295 |
| Ceil - ceil(numeric_column) | This functions rounds the 'numeric_column' to the nearest integer which is greater than the 'numeric_column' | ceil(11.56) = 12 |
| Ceiling ceiling(numeric_column) | Returns the smallest integer that is greater than or equal to the value of the argument. | ceiling(10.43) = 11 |
| Conv conv(column, current_base, to_be_converted_base) | Converts the number string from the given base to the required base. | conv('a',16,2) = 1010 |
Convert base convertbase(column, current_base, to_be_converted_base) | Returns the converted string representation of the number N, from current base to the to be converted base. | convertbase('a',16,2) = 1010 |
| Cos - cos(numeric_column) | This function returns the cosine value of the specified 'numeric_column' | cos(0) = 1 |
| Cot - cot(numeric_column) | This function returns the cotangent value of the specified 'numeric_column' | cot(0.25) = 3.916317 |
| CRC32 crc32(string_column) | Returns a 32 bit unsigned output after calculating the cyclic redundency check. | crc32('111') = 1298878781 |
| Degrees - degrees(numeric_column) | This function returns the angle in Degrees equivalent to the given Radians | degrees(1) = 57.2957795 |
| Exp - exp(numeric_column) | This function returns the exponential value of the 'numeric_column' | exp(2) = 7.389056 |
| Floor - floor(numeric_column) | Rounds the 'numeric_column' to the nearest integer which is less than the 'numeric_column' | floor(11.56) = 11 |
| Format format(numeric_column1, numeric_column2) | Formats the number by rounding off the number to decimal places specified in the second argument and returns the value. | format(1.0001111,5) = 1.00011 |
| Greatest - greatest(numeric_column,..., numeric_column) | Gives the greatest of the given arguments. | greatest(10,20,5) = 20 |
| Least - least(numeric_column,..., numeric_column) | Gives the least of the given arguments. | log10(3) = 0.477121 |
| Ln - ln(numeric_column) | This function returns the natural logarithm of the specified 'numeric_column' | ln(5) = 1.609438 |
| Log log2(numeric_column) | Returns the logarithm to the base-2 of the numeric column. | log2(32) = 5 |
| Log10 - log10(numeric_column) | This function returns the logarithm to the base-10 of the specified 'numeric_column' | log10(3) = 0.477121 |
| Log2 - log2(numeric_column) | This function returns the logarithm to the base-2 of the 'numeric_column | log2(32) = 5 |
| Mod - mod(numeric_column1, numeric_column2) | Returns the remainder of the 'numeric_column1' divided by 'numeric_column2' | mod(10,3) = 1 |
| OCT oct(column) | Returns the octal value of the number given in the argument. | oct(12) = 14 |
| Pi - pi() | This function returns the numeric value of the pi. | pi() = 3.14159265358979 |
| Power - pow(numeric_column1, numeric_column2) | This function returns the value of 'numeric_column1' raised to the power of 'numeric_column2' | pow(2,3) = 8 |
| Random - rand() | Returns a random value between 0 and 1. | rand() = 0.9233482386203 |
| Radians - radians(numeric_column) | Returns the angle in radians equivalent to the given degrees | radians(180) = 3.1415926 |
| Round - round(numeric_column) | Returns the rounded integer value of the 'numeric_column'. | round(10.67) = 11 |
| Sign - sign(numeric_column) | Returns-1, 0, or 1, if the 'numeric_column' is negative, zero, or positive. | sign(-23) =-1 |
| Sin - sin(numeric_column) | Returns the sine value of the 'numeric_column'. | sin(0) = 0 |
| Square - square(numeric_column) | Returns the square of the specified 'numeric_column'. | square(10) = 100 |
| Square Root - sqrt(numeric_column) | Returns the square root of the specified 'numeric_column'. | sqrt(16) = 4 |
| Tan - tan(numeric_column) | Returns the tangent value of the specified 'numeric_column'. | tan(0.5) = 0.546302 |
String Functions | ||
| FUNCTION | DESCRIPTION | EXAMPLE |
| ASCII ascii(string_column) | Returns the ASCII value of the first character of the given argument. | ascii('abcddb') = 97 |
| Bit Length bit_length(string_column) | Returns the value of the length of the string argument in bits. | bit_length('AA') = 16 |
| Char char(numeric_column) | Returns a String of characters formed from the code values of the ASCII code given in the arguments. | char(97,98) = ab |
| Char Length char_length(string_column) | Returns the number of characters present in the argument. | char_length('aa1') = 3 |
| Character Length character_length(string_column) | Returns the number of characters present in the argument. | character_length('aa1') = 3 |
| Concat - concat(string_column,...,string_column) | Returns the concatenated string of the given arguments. If any one of the argument is null, it returns null. | concat('abcd','ef','db') = abcdefdbd |
| Concat Ignore Null concat_ignore_null(string_column1, string_column2, ...) | Returns the concatenated string of the given value ignoring null. | concat('abcd','ef',null,'db') = abcdefdb |
| Concat_WS - concat_ws(separator,string_column1 ,....,string_columnN) | Returns the concatenated string of the given arguments separated by the given separator. If the separator is null, it returns null. | concat_ws('-','abcd','ef','db') = abcd-ef-db |
| ELT elt(numeric_column, string_column1, string_column2, ...) | Returns the string value available at the index number specified in the first argument. | elt('2','red','rose','is','beautiful') = rose |
| extract_json extract_json(json data, path 1, path 2, ...) | Extracts the value from the given JSON based on the key and index provided. | extract_json(' "Name": "Jane Doe", "Address": ["Los Angeles", "California"1}', 'Address', '[0]') = Los Angeles |
| Field field(string_column1, string_column2, ...) | Searches the value in the first argument with all the rest of the arguments and returns the position of the argument where the first match is found. | field('as','has','as','have') = 2 |
| Find in Set find_in_set(string_column, string_column) | Searches the value in the first argument with the substrings in the second argument, seperated by commas, and returns the position of the substring where the first match is found. | find_in_set('10','2,5,8,10') = 4 |
| Hex hex(string_column) | Returns the corresponding hexadecimal number for each character of the given string. | hex(255) = FF |
| Insert - insert(string_column, start_pos, len, new_string) | Returns the string 'string_column', with the substring beginning at position 'start_pos' and 'len' characters long replaced by the string 'new_string'. 'start_pos' should be greater than 0. When len is zero, the 'new_string' is inserted previous to the position 'start_pos'. | insert('abcddb', 3, 2, 'efgh') = abefghdb |
| Initial Cap initcap(string_column) | Converts the first character to upper case. | initcap('analytics') = Analytics |
| Index of - indexof(string_column, sub_string) | Returns the index of the first occurrence of the string 'sub_string' in string 'string_column'. | indexof('abcddb','db') = 5 |
| Instr instr(string_column, sub_string) | Returns the position of the first match of second string argument in the first argument. | instr('impossible','possible') = 3 |
| Lcase lcase(string_column) | Returns the string 'string_column' with all characters of the given column changed to lowercase. | lcase('ABCd') = abcd |
| Left - left(string_column, len) | Returns the 'len' number of characters from the left-hand side of the string 'string_column'. | left('abcdef',3) = abc |
| Length - length(string_column) | Returns the character length of the string. | length('abcddb') = 6 |
| Locate locate(sub_string, string_column, start_pos) | Returns the index of the first occurence of the string 'sub_string' in string 'string_column' starting at the position 'start_pos'. | locate('db','zohodbdb',6) = 7 |
| Lower lower(string_column) | Returns the string 'string_column' with all characters of the given column changed to lowercase. | lower('AbCD') = abcd |
| Lowercase - lowercase(string_column) | Returns the string 'string_column' with all characters changed to lowercase. | lowercase('AbCD') = abcd |
| Lpad - lpad(string_column, len, pad_string) | Returns the string 'string_column', left-padded to a length of 'len' characters with the string 'pad_string'. If length of the string 'string_column' is greater than 'len', then the first 'len' characters of 'string_column' is returned. | lpad('DB',5,'a') = aaaDB |
| Ltrim - ltrim(string_column) | Returns the string 'string_column' with leading spaces removed. | ltrim(' abcd') = abcd |
| Make Set make_set(numeric_column, string_column, ...) | Returns the corresponding 'set' of arguments from the string arguments that have the bit specified in the first argument. | make_set(1,'a','b','c') = a |
| Mid mid(string_column, start_pos, string_len) | Return a string from 'string_column' starting at position 'start_pos' with a character length of 'len'. | mid('abcddb', 1, 4) = abcd |
| Octet Length octet_length(string_column) | Returns the byte length of the string. | octet_length('abcddb') = 6 |
| ORD ord(string_column) | If the first character of the string argument is a multi-byte character, then the code calculated from the below formula is returned. 1st byte code + (2nd byte code * 256) + (3rd byte code * 256 * 256) + . . . | ord('2') = 50 |
| Repeat - repeat(string_column,count) | repeat('Abcd',3) = 'AbcdAbcdAbcd' | |
| Replace - replace(string_column, from_string, to_string) | Returns the string with all occurrences of the string 'from_str' replaced by the string 'to_str' | replace('abcdac','ac','db') = abcddb |
| Reverse - reverse(string_column) | Returns the reverse string of 'string_column'. | reverse('abcd') = dcba |
| Right - right(string_column, len) | Returns the 'len' number of characters from the right-hand side of the string 'string_column' | right('abcdef',4) = cdef |
| Rpad - rpad(string_column, len, pad_string) | Returns the string 'string_column', right-padded to a length of 'len' characters with the string 'pad_string'. If length of the string 'string_column' is greater than 'len', then the first 'len' characters of 'string_column' is returned | rpad('DB',5,'a') = DBaaa |
| Rtrim - rtrim(string_column) | Returns the string 'string_column' with trailing spaces removed. | rtrim('abcd ') = abcd |
| Soundex soundex(string_column) | Returns a soundex string from 'string_column'. The soundex string is similar for same sounding strings. | soundex('Hello') = H400 |
| Space space(numeric_column) | The argument value is returned as the number of space characters. | space(6) = ' ' |
| Strcmp - strcmp(string_column1, string_column2) | Returns -1 if the 'string_column1' is smaller than the 'string_column2', 0 if the two strings are same, and 1 if the 'string_column1' is greater than the 'string_column2'. | strcmp('abcd', 'abcde') =-1 |
| Substr substr(string_column, start_pos, string_len [Optional]) | Returns the substring formed by cutting off the string argument passed according to the needs. | substr('abcddb', 2,) = bcddb |
| Substring - substring(string_column, start_pos, string_len) | Returns a substring from 'string_column'. The substring begins at position 'start_pos' with the character length of 'string_len'. | substring('abcddb', 1, 4) = abcd |
| Substring Between substring_between(string_column, sub_string, sub_string, start_pos [Optional]) | Returns the characters between the two given substrings in the main string. | substring_between('abcddb','b','d',1) = c |
| Substring Count substring_count(string_column, sub_string) | Returns the count of substring occurred in the main string. | substring_count('abcddb','cd') = 1 |
| Substring Index substring_index(string_column, delimiter, delimiter_count) | Returns the substring from string 'string_column' before count 'delimiter_count' occurrences of the delimiter 'delimiter'. | substring_index('how.are.you', '.', 2) = how.are |
| Substring Position substring_position(string_column, sub_string, start_pos [Optional]) | Returns the position of substring in the main string. | substring_position('abcddb','cd') = 3 |
| Trim - trim(string_column) | Returns the string with all spaces removed in prefix and suffix of the string. | trim(' abcd ') = abcd |
| Ucase ucase(string_column) | Returns the string 'string_column' with all characters changed to uppercase. | ucase('abcD') = ABCD |
| Unhex unhex(string_column) | Returns the corresponding character for each pair of hexadecimal digits. | unhex('21') = ! |
| Upper upper(string_column) | Returns the string 'string_column' with all characters changed to uppercase. | upper('abcD') = ABCD |
| Uppercase - uppercase(string_column) | Returns the string 'string_column' with all characters changed to uppercase. | uppercase('abcD') = ABCD |
Logical Functions | ||
| FUNCTION | DESCRIPTION | EXAMPLE |
| IF - if(expr1,expr2,expr3) | Returns expr2 if expr1 is true else it returns expr3 | if(5> 10,100,3) = 3 |
| If Case if_case(column, matchExpr1, returnValue1, matchExpr2, returnValue2, ..., elseValue [Optional]) | Returns the 'returnValue' if the given column satisfied with 'matchExpr'. | if_case('Subject','issue','Issue List',equals('bug'),'Bug List','Support List') = if the 'Subject' column equals issue then it returns 'Issue List' else if 'Subject' column equals 'bug' then it returns 'Bug List' else it returns 'Support List' if_case('Subject',startswith('issue','bug'),'Issue List',contains('help','Call'),'Call List','Support List') = if the 'Subject' column starts with 'issue' or 'bug' then it returns 'Issue List' else if 'Subject' column contains 'help' or 'Call' then it returns 'Call List' else it returns 'Support List' |
| Ifnull - ifnull(expr1,expr2) | Returns expr1 if expr1 is not null, else it return expr2 | ifnull(null,10) = 10 |
| Is Empty isempty(column) | Returns '1' if the given column does not have any value. Returns '0' if the given column have some value. | isempty(null) = 1 |
| isnull( ) - isnull(expr1) | Returns 1 if expr1 is null, else it returns 0. | isnull(null)- 1 |
General Functions | ||
| FUNCTION | DESCRIPTION | EXAMPLE |
To Email Syntax: to_email(column) | Converts the plain text column in email format to email datatype. | to_email(test@abc.com) = test@abc.com |
To Currency Syntax: to_currency(numeric_column) | Converts the numeric column to currency data type, | to_currency(3854) = $3854 |
To Percentage Syntax: to_percentage(numeric_column) | Converts the numeric column to percentage datatype. | to_percentage(83) = 83% to_percentage(83.54) = 83.54% |
To positive integer Syntax: to_positive_integer(column) | Converts the negative values in the numeric column to positive number datatype. | to_positive_integer(-40) = 40 |
To decision box Syntax: to_decision_box(column) | Converts plain text values and boolean values like yes, no, true, false, on, off, 1 and 0 to decision box (Yes/No) data type. Values other than the above mentioned value will be returned as Null. | to_decision_box(yes) = Yes |
Coalesce Syntax: coalesce(column1, column2,..) | Returns the first non-null value. Returns null if all the values are null. | coalesce(null,null,4) = 4 |
Creating Formulas Over Formula Column
Formula columns are similar to other columns of the table. You can make use of existing formula columns while creating a new formula column, as you do with other columns of the table. Reusing existing formulas column to create new formula columns helps you create powerful formula combination, as well as eases in maintenance of these formula structure in your workspace. Refer to the above section to know how to create formula column.
Creating Reports Using Custom Formula Column
Custom Formula columns can be used while creating reports as you would use a column in a table. When you create a new report over the table, in which you have added the custom formula column, all these formula columns will be listed in the Columns list pane on the left, which can be drag and drop to create the report.
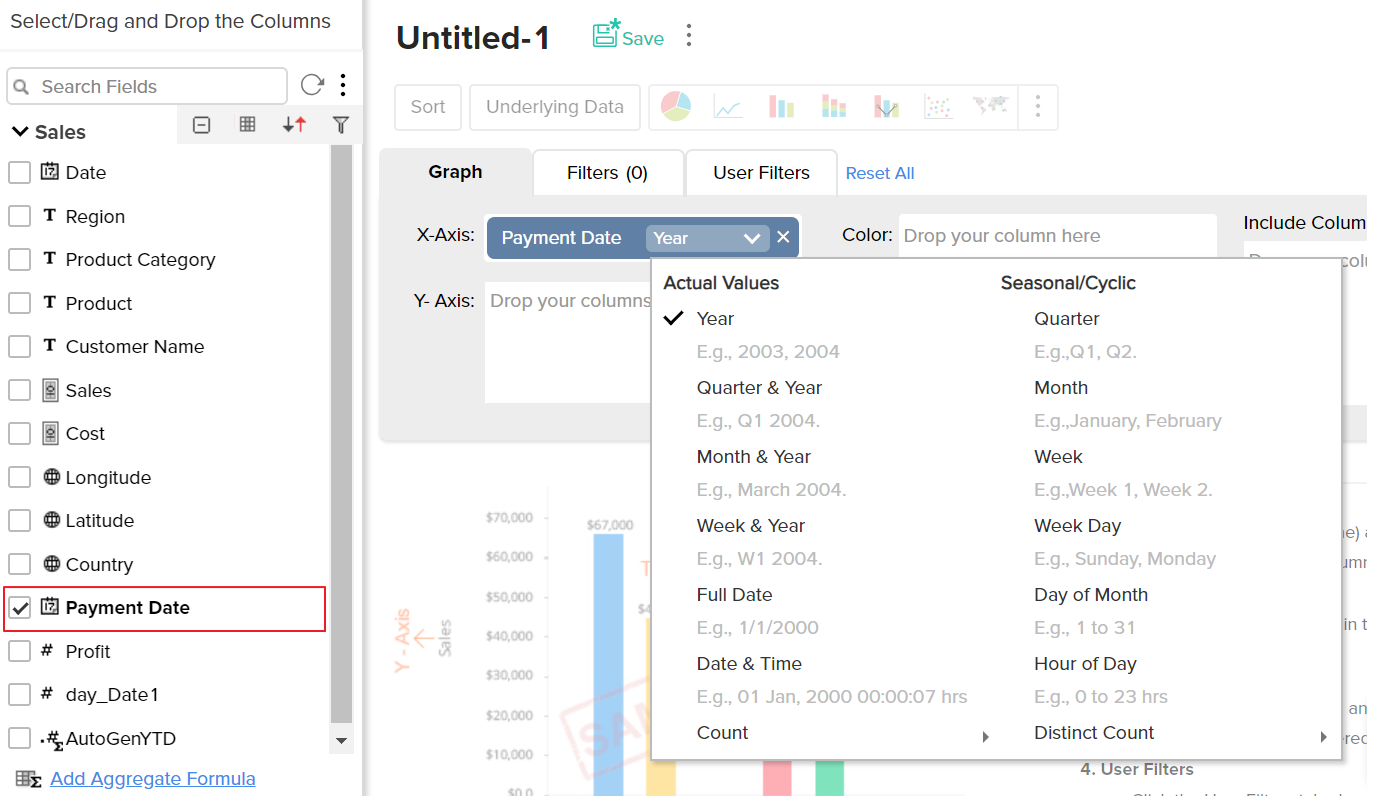
You can apply functions on the formula column, as you do for other columns, using the combo box that is displayed over the column when dropped in the design area of the report.
Sharing Custom Formulas
Once a Custom Formula column is created, it behaves like any other column in a table. When you share a table, all the existing custom formula columns will also be shared to the user.
Note:
- The shared user will not be able to edit, delete or format the shared formulas. Also the shared user will not be able to add his own formula column over the shared table, unless the shared user is a Workspace Owner.
Aggregate Formulas
In reporting the most common data analysis that we do is to apply aggregate functions over the data (like SUM, AVG, COUNT etc.,) and analyze the same. The important aspect to be taken care in such calculations is to compute the aggregation in the context in which the function is applied to provide accurate results. Aggregate Formulas in ManageEngine Analytics Plus is meant to address this need.
Aggregate Formulas are formulas that you define in ManageEngine Analytics Plus which uses at least one aggregate function (SUM, AVG..) in the calculation. The output of such calculations is always a numeric value (metric). Aggregate formulas are mainly used in creating powerful reports. These formulas can be used in Charts, Pivot Tables and Summary View report types in ManageEngine Analytics Plus .
- The result of an Aggregate Formula is always a numeric value.
- Aggregate Formulas will not be added as another column in the base, it is associated with, like Custom Formulas. But it will be available for report creation when you create a report over the table (listed as part of the columns list).
- The value of an aggregate formula will be computed for each data point that is displayed in the report in which it is used (i.e., the result is not just a single value). This makes it very powerful.
- Aggregate formula can be constructed in a similar way as that of a Custom Formula.
ManageEngine Analytics Plus offers a range of in-built aggregate functions which can be used as part of the Aggregate Formulas. You can construct the formulas using these in-built aggregate functions combining it with the basic arithmetic operators like +, -, / and *.
Creating Aggregate Formulas
To create an aggregate formula:
- Select Add > Aggregate Formula option from the toolbar as shown below.
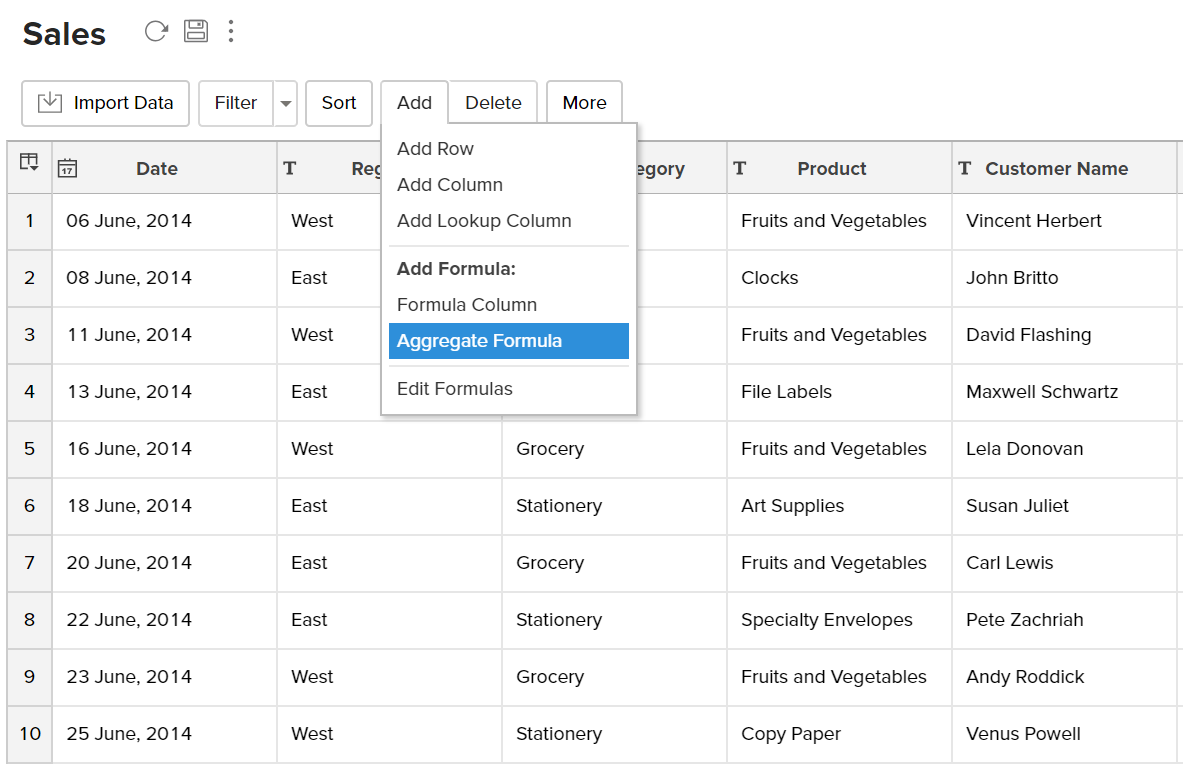
- The Add Aggregate Formula dialog box will open as shown below. This dialog box provides easy access to the names of the columns in your table, as well as to all the in-built functions that are available for you to create the formula. A brief description of the function with syntax and an example will be displayed at the bottom of the dialog box when you hover your mouse over a function.
- In the Formula Column Name text box, type the name that you want to give to the formula.
- Choose the data type of the aggregate result from the DataType drop-down. The supported data types include Number, Positive Number, Decimal Number, Currency, Percentage, Duration, Plain Text, and Date.
In the Formula text area provide the actual formula. You can select the columns and functions that you want to insert into the formula from the list from the Columns and the Function boxes.
Note: You can also insert columns from related tables joined through Lookup Column. The drop-down lists all the parent table associated with the base table. Select the required table, the columns in this table will be listed below. You can insert this in the formula by clicking.
- For example, to apply an aggregate formula to calculate % Profit the formula could be something like (SUM("SALE")- SUM("COST"))/SUM("COST")*100 as shown in the screenshot below.
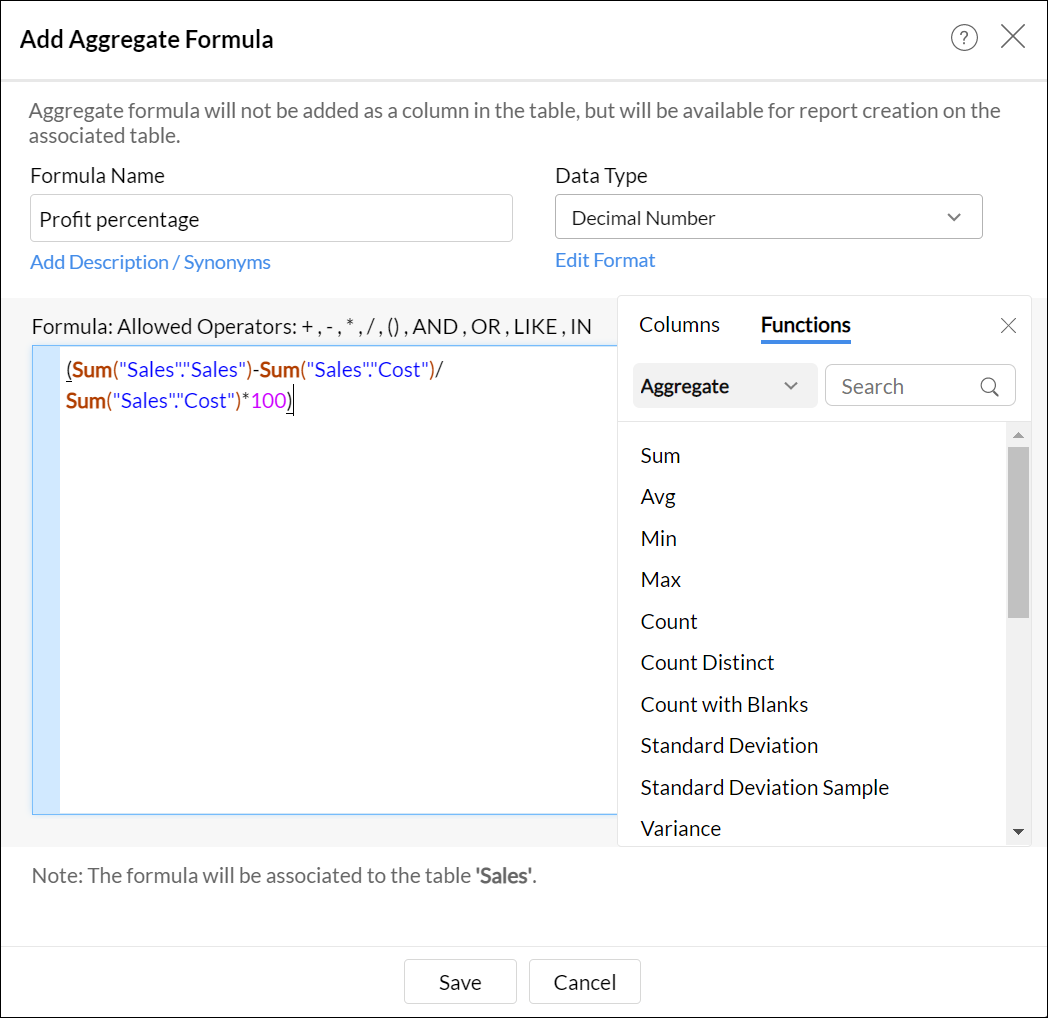
- Click OK.
The result of Aggregate Formulas will not be added as a column in the base table. It will be listed in the column panel while creating reports. You can access (view) or edit it by clicking Add > Edit Formulas in the toolbar. Viewing & Editing Formulas is discussed in the next section.
In-built Aggregate Functions
While you create an aggregate formula you can use a wide range of powerful in-built functions that are supported by ManageEngine Analytics Plus . You can use the in-built functions, that are applicable while creating custom formulas, even when you create an Aggregate formula, provided it meets the required conditions for an Aggregate formula. There are also specific functions which are more relevant & applicable for creating Aggregate formulas. The following table describes these functions:
Creating Aggregate Formula over existing Aggregate Formulas
ManageEngine Analytics Plus enables you to build aggregate formulas using existing aggregate formulas. Reusing existing formulas to create new aggregate formula helps you create powerful formula combination, as well as eases maintenance of these formula structure in your workspace.
When you create a new aggregate formula, existing formulas will be listed in the Click to Insert Columns box along with other columns. All the aggregate formulas will be indicated in brown with the ∑ symbol. You can insert these formulas into your new formula definition by clicking them, as you do for the other columns in the table.
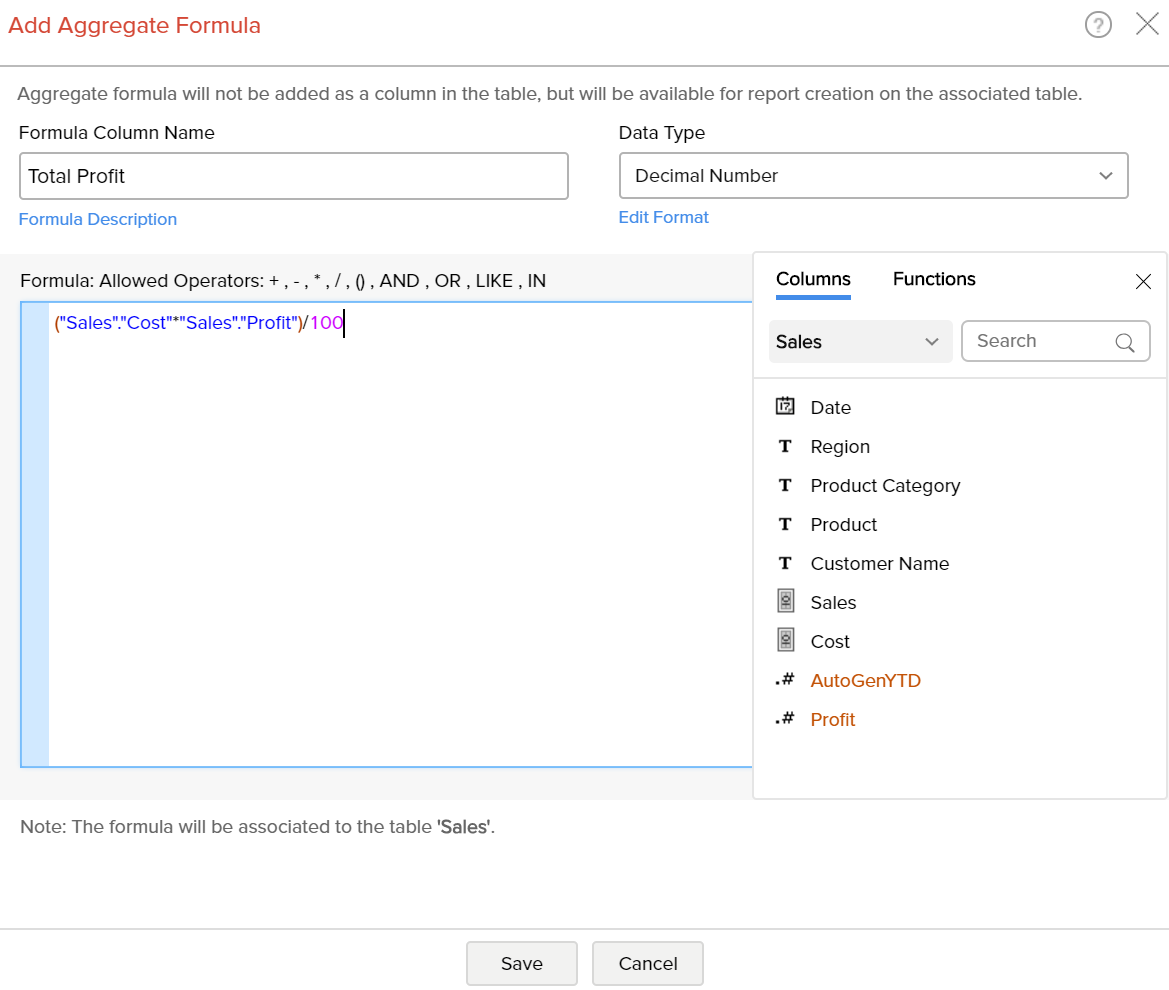
For example, Let's assume that you have already calculated profit percentage and total cost and you want to calculate total profit gained. Then you can use the existing aggregate formulas to calculate total profit gained. The formula could be something like ("Total Cost" * "Profit") / 100.
Creating Reports using Aggregate Formulas
Aggregate formulas can be used while creating all reports (charts, pivot tables and summary views) as you would use a column in a table. When you create a new report over the table, in which you have added the aggregate formula, all the formulas will be listed in the Columns list pane on the left, which can be drag & dropped to create the report.
The following screenshot shows the % Profit aggregate formula, that we added, listed in the columns list page. All the aggregate formulas will be indicated with an icon which contains the symbol.
From the Explorer tab of the workspace, select the table to which you want to add the aggregate formula.
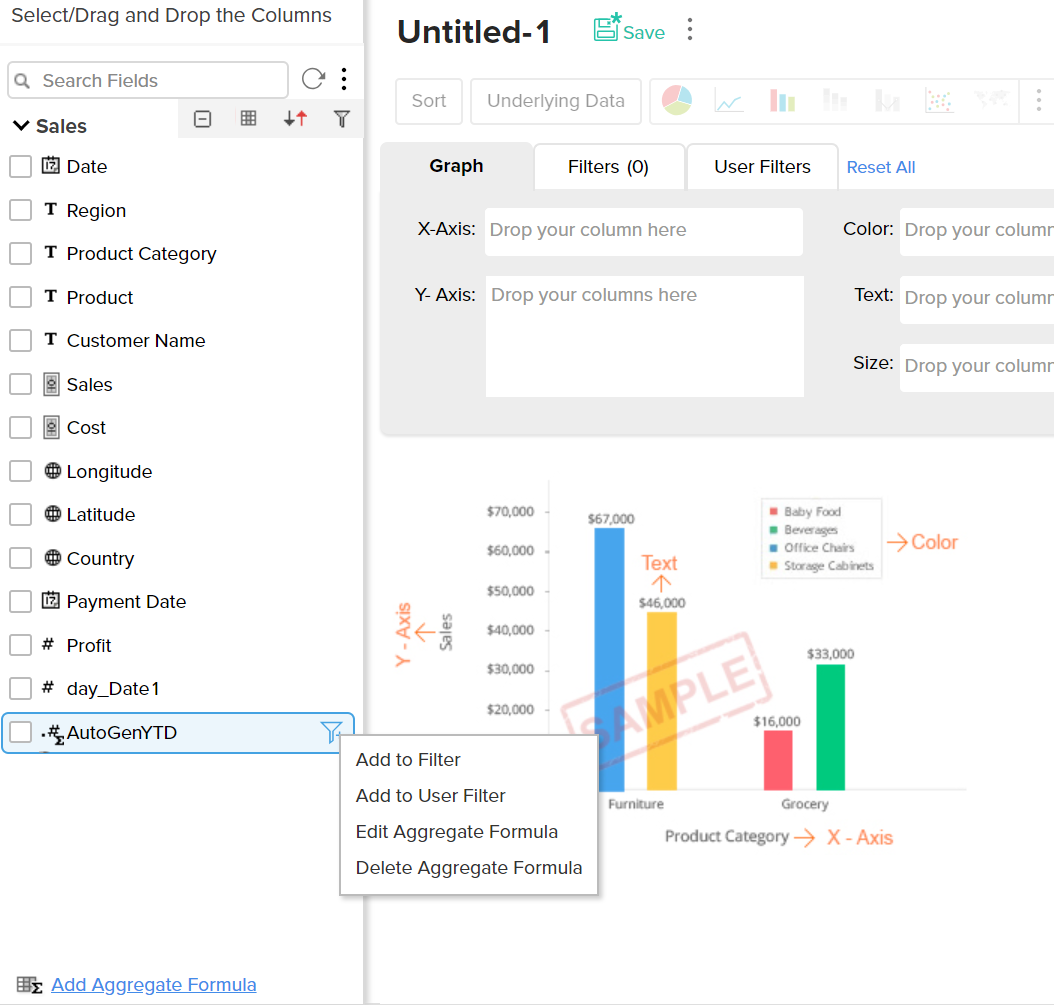
Aggregate formulas can be used in the report as you use any other data columns in the table. The value of the aggregate formula will be computed for each data point that is displayed in the report in which it is used (i.e., the result is not just a single value). In the chart shown in the screenshot below, the percentage of profit (%Profit) is plotted against the Year. As you see, the value of the Profit percentage is calculated for each year and plotted in the graph.
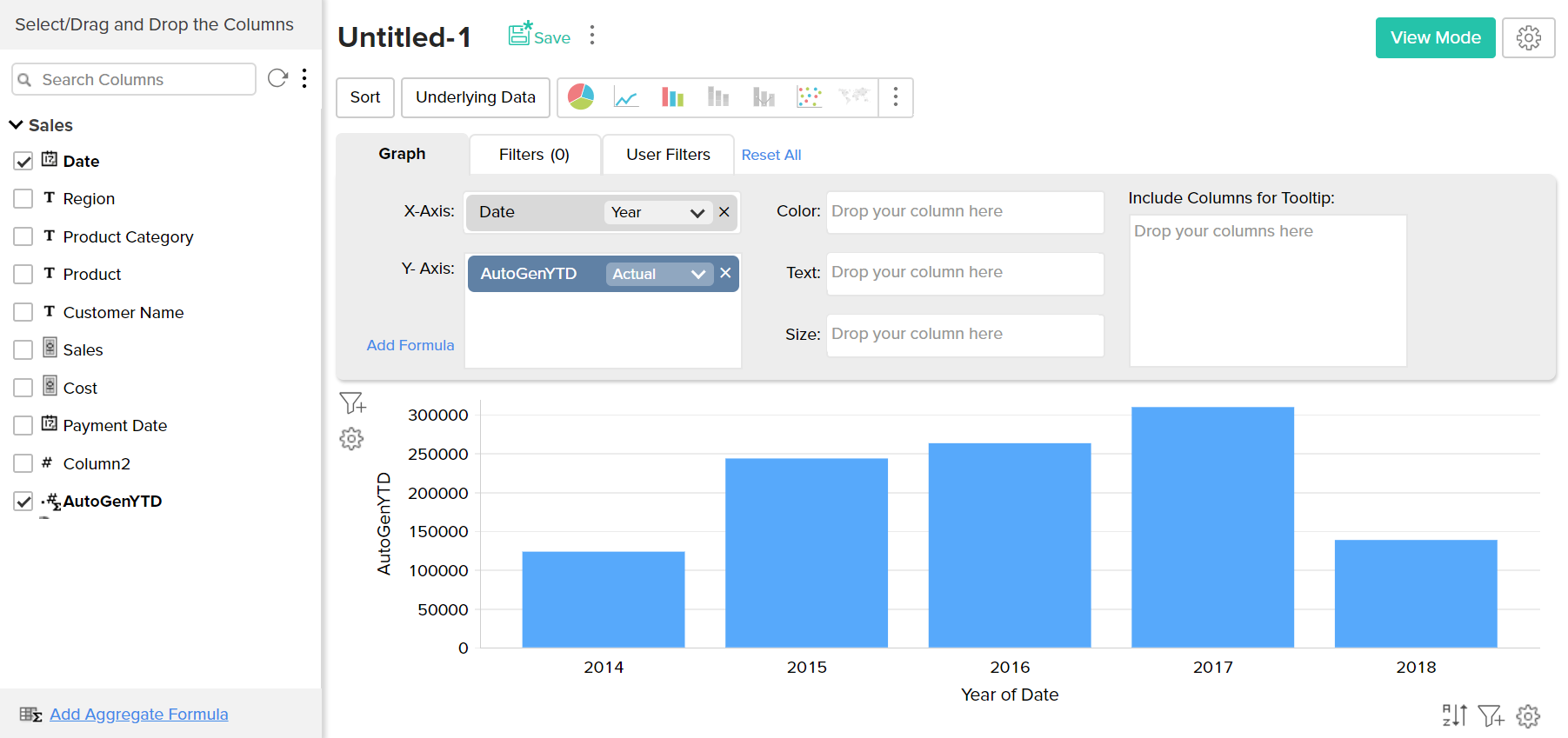
When you use an Aggregate formula in a report, you will not be able to apply other functions on the formula (as you do for other columns). The function will always be selected as 'Actual' and cannot be modified.
Sharing Aggregate Formulas
With respect to sharing and collaboration, Aggregate Formulas behave similar to how a column in a table behaves. When you share a table, all the aggregate formulas that are created over the table will be also shared to the user to whom you are sharing the table. Hence the shared user will be able to use these formulas while creating any report over the data table.
Note:
- The shared user will not be able to edit, delete or format the shared aggregate formula, but can just use it in report creation. Also the shared user will not be able to add his own Aggregate formulas over the shared table, unless the user is a Workspace Owner.
View/Edit Formulas
ManageEngine Analytics Plus allows you to view, edit, format and delete all the formulas defined for a table through the Edit Formula option. You can view & edit both Custom Formulas and Aggregate Formulas using this option. To view/edit existing custom or aggregate formulas:
- Select the required table.
- Select Add > Edit Formulas option from the toolbar.
- The Edit Formula dialog box with a list of all the formulas associated to the table will open as shown below:
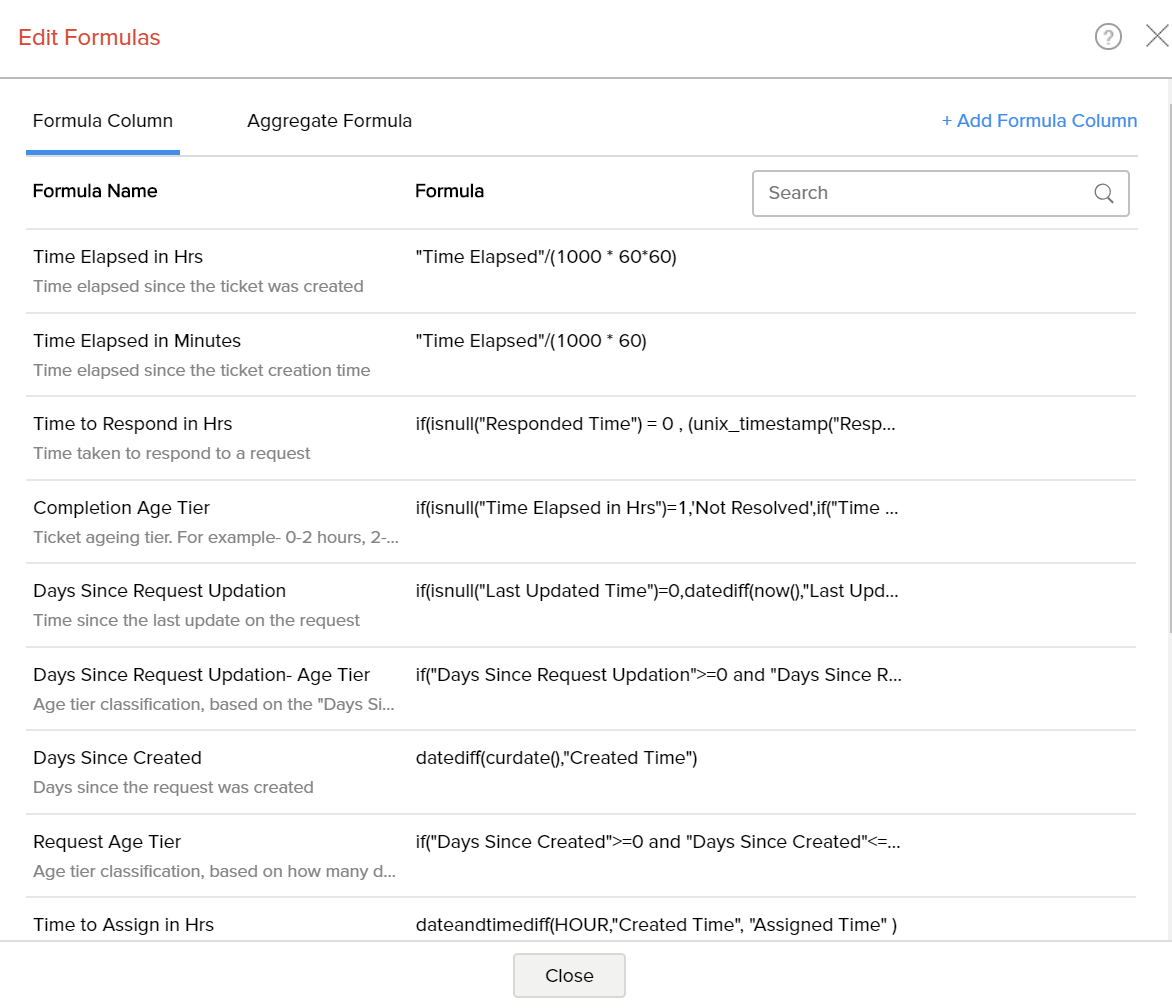
On hovering over a specific formula, the Edit, Remove and Format options are available.
- Edit Formula: You can edit the constructed formula using the Edit link provided next to the corresponding formula. The Edit Formula/ Aggregate Formula (depending on the type of formula) dialog box will open, and you can modify the existing formula the same way you would when creating a new formula.
- Delete Formula: You can delete an existing Formula any time from the table using the Remove link provided next to the corresponding formula.
- Format Formula: You can change the format of the Formula result, like alignment, decimal places, date format, currency symbols etc., depending on its data type of the formula using the Format link provided. It's similar to how you format a data column. Refer here to know how to format a column.