AWS Monitoring Best Practices and Strategies for Cloud Environments
Category: Cloud Monitoring
Published on: Nov 18, 2025
7 minutes
As enterprises increasingly move workloads to the cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has become the foundation for modern IT infrastructure. While AWS offers scalability, flexibility, and innovation, it also introduces complexity in monitoring and management. To ensure reliability, performance, and cost efficiency, organizations must adopt robust AWS monitoring strategies.
This blog explores AWS monitoring best practices and proven monitoring strategies for AWS cloud environments . We’ll highlight the key areas to monitor, how monitoring differs from observability, and how you can implement effective practices with the help of ManageEngine Applications Manager .
What is AWS Monitoring and why is it important?
AWS monitoring involves collecting, analyzing, and acting on data related to your AWS resources and applications. It ensures systems are performing as expected and helps identify potential risks before they escalate into outages.
Key reasons why AWS monitoring is essential include:
- Proactive issue detection: Identify failures before they impact end users.
- Performance optimization: Track metrics to improve resource utilization.
- Security, compliance, and governance: Detect unusual activity, track access and configuration changes, and ensure your AWS environment meets regulatory and organizational standards.
- Cost management: Avoid unnecessary spending by monitoring usage.
Without effective monitoring, organizations risk downtime, poor customer experiences, and inflated costs.
AWS Monitoring vs. AWS Observability
While often used interchangeably, monitoring and observability serve different but complementary purposes:
- Monitoring focuses on tracking known metrics (CPU, memory, disk I/O, response times) and alerting when thresholds are breached.
- Observability provides a holistic view of system behavior, enabling teams to uncover
and debug unknown issues
using metrics, logs, traces, and events.
An effective AWS strategy requires both . Applications Manager bridges the gap by combining traditional monitoring with advanced capabilities like anomaly detection, log analysis, and transaction tracing—features that enhance visibility, whether you’re monitoring known thresholds or investigating deeper system behaviors.
Key areas to monitor in AWS Cloud Environments
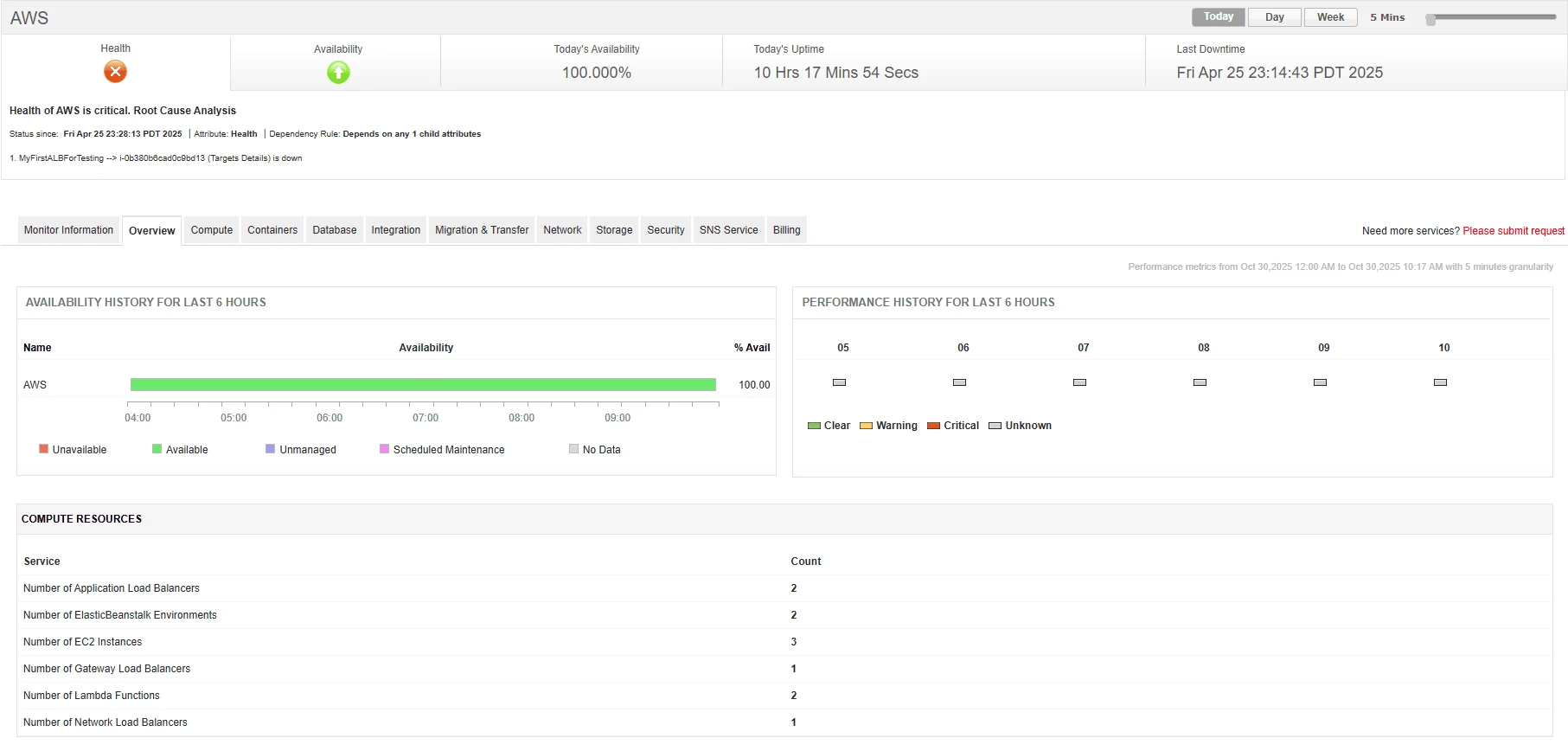
A strong AWS monitoring strategy should extend across multiple layers of your cloud stack, from infrastructure to applications. Some critical areas include:
1. Compute Resources
Monitoring EC2 instances ensures CPU, memory, and disk utilization remain within optimal ranges, while tracking containerized workloads in ECS , EKS , and Fargate provides visibility into cluster health, pod status, and scaling behavior. For serverless setups, AWS Lambda metrics such as invocation errors, duration, and throttles highlight performance bottlenecks.
2. Networking Components
Networking health is vital for application availability. Keeping an eye on load balancers (ELB, ALB, NLB) helps detect uneven traffic distribution or failed targets. Monitoring NAT Gateways, VPC traffic, and Route 53 health checks ensures smooth connectivity, secure routing, and reliable DNS resolution.
3. Databases and Storage
AWS databases like RDS and DynamoDB require close tracking of query performance, connection limits, and replication lag. For storage services, monitoring S3 bucket activity, FSx performance, and ElastiCache latency helps prevent data bottlenecks and ensures efficient operations.
4. Application Performance
Beyond infrastructure, application-level metrics such as latency, throughput, error rates, and request traces provide deeper insights into user experience. Monitoring these KPIs allows quick detection of performance degradations using APM Insight for deep application tracing.
5. Security and Compliance
Security monitoring spans IAM activity, CloudTrail logs, GuardDuty findings, and Config rules to detect anomalies, misconfigurations, or unauthorized access. This not only safeguards infrastructure but also helps maintain regulatory compliance in industries with strict governance requirements.
6. Cost and Usage Metrics
Unmonitored AWS usage can lead to ballooning costs. Tracking billing reports, resource utilization, idle instances, and over-provisioned assets helps optimize spend. Proactive monitoring also supports cost forecasting and budget adherence.
With Applications Manager, IT teams can unify monitoring across all these domains—compute, networking, storage, applications, security, and costs—ensuring end-to-end visibility into AWS health and performance from a single console.
Best practices for successful AWS monitoring
1. Define monitoring objectives
A successful AWS monitoring strategy begins with aligning monitoring goals to business priorities. Not all applications have the same requirements:
- E-commerce platforms need strict uptime and fast response times to protect revenue.
- Analytics-heavy workloads demand visibility into database query performance, throughput, and storage efficiency.
- Customer-facing SaaS apps may need end-to-end user experience monitoring.
By defining these objectives upfront, IT teams can prioritize which metrics to track, what thresholds to set, and how alerts should be structured. Applications Manager supports customizable thresholds, SLAs, and KPIs, ensuring monitoring remains business-driven.
2. Enable Centralized Monitoring
AWS offers powerful tools like CloudWatch (metrics/monitoring) and CloudTrail (audit/logging) . However, when used in isolation, they create silos of information. A centralized monitoring solution aggregates performance metrics, logs, and events across AWS, hybrid , and multi-cloud setups, providing a single source of truth.
With Applications Manager, organizations can consolidate AWS data alongside on-premises and other cloud services. This reduces blind spots, simplifies management, and provides end-to-end visibility for faster troubleshooting.
3. Automate alerting and incident response
Manual monitoring cannot scale in dynamic AWS environments. Automated alerts and workflows ensure that performance issues or security risks are addressed in real-time. For example:
- CPU or memory spikes can trigger auto-scaling policies .
- Application errors can prompt automated restarts or failover actions.
- Security anomalies can initiate automated incident workflows
.
Applications Manager supports rule-based alerts, automated remediation, and ITSM integrations (ServiceDesk Plus, ServiceNow, etc.), reducing downtime and accelerating incident resolution.
4. Leverage Reports and Dashboards
Monitoring data is only valuable when insights are accessible. Custom dashboards allow technical and business teams to visualize KPIs like latency, availability, and cost trends. Reports provide historical analysis to support capacity planning, SLA compliance, and governance.
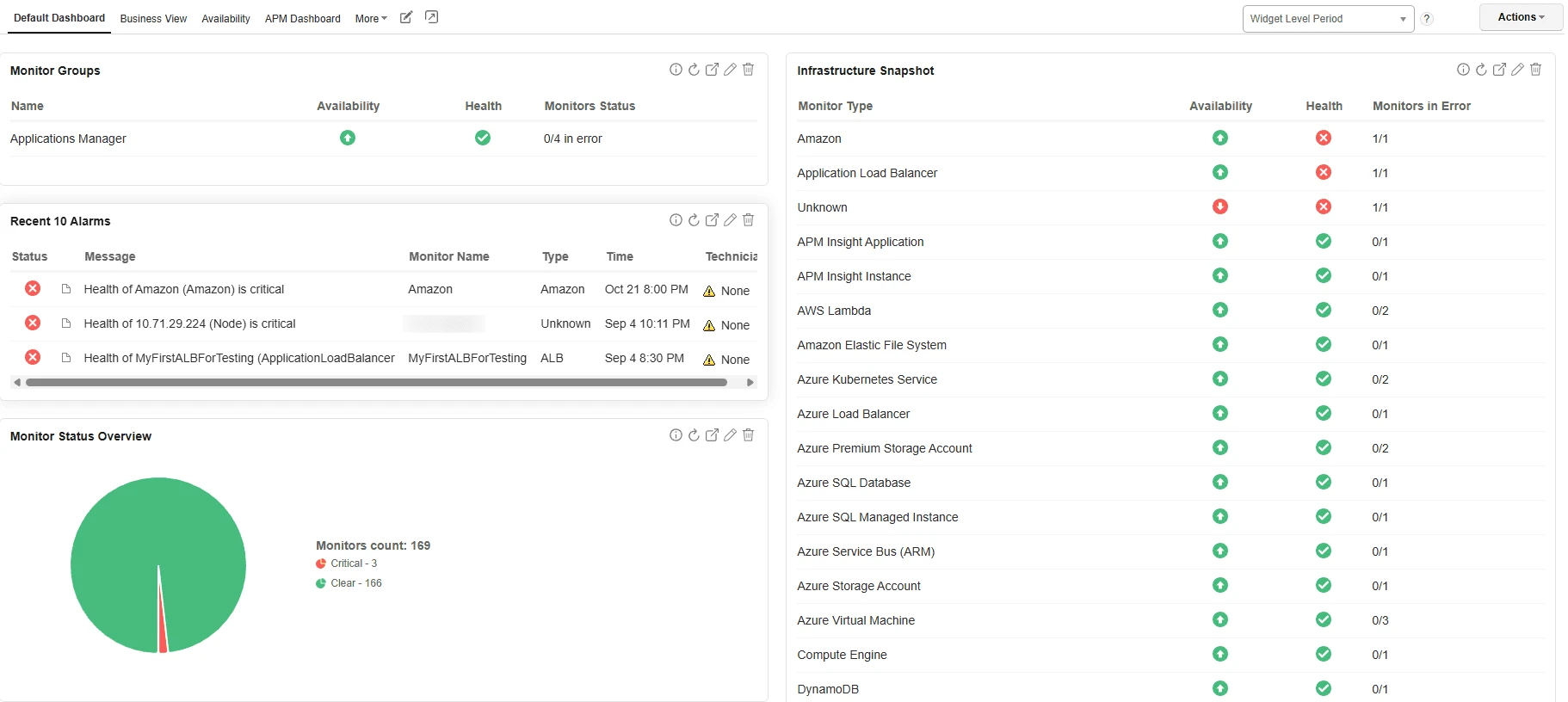
With Applications Manager , teams can build interactive dashboards tailored to stakeholders—whether developers, operations, or management—and schedule automated reporting for compliance and executive reviews.
5. Incorporate AI/ML for Smarter Monitoring
As AWS environments scale, the volume of monitoring data grows exponentially. Relying solely on manual thresholds can lead to missed issues or alert fatigue. AI/ML-driven monitoring enables anomaly detection, predictive alerts, and smarter root cause analysis.
For instance, Applications Manager uses anomaly detection to identify unusual performance deviations—like sudden spikes in response time or unusual network traffic—helping teams respond before users are impacted.
6. Optimize for cost efficiency
Cloud cost management is inseparable from monitoring. Unused or underutilized resources can quickly inflate bills. Best practices include:
- Tracking resource utilization to identify idle instances.
- Right-sizing compute resources based on workloads.
- Monitoring data transfer and storage costs.
- Reviewing cost anomalies against budgets.
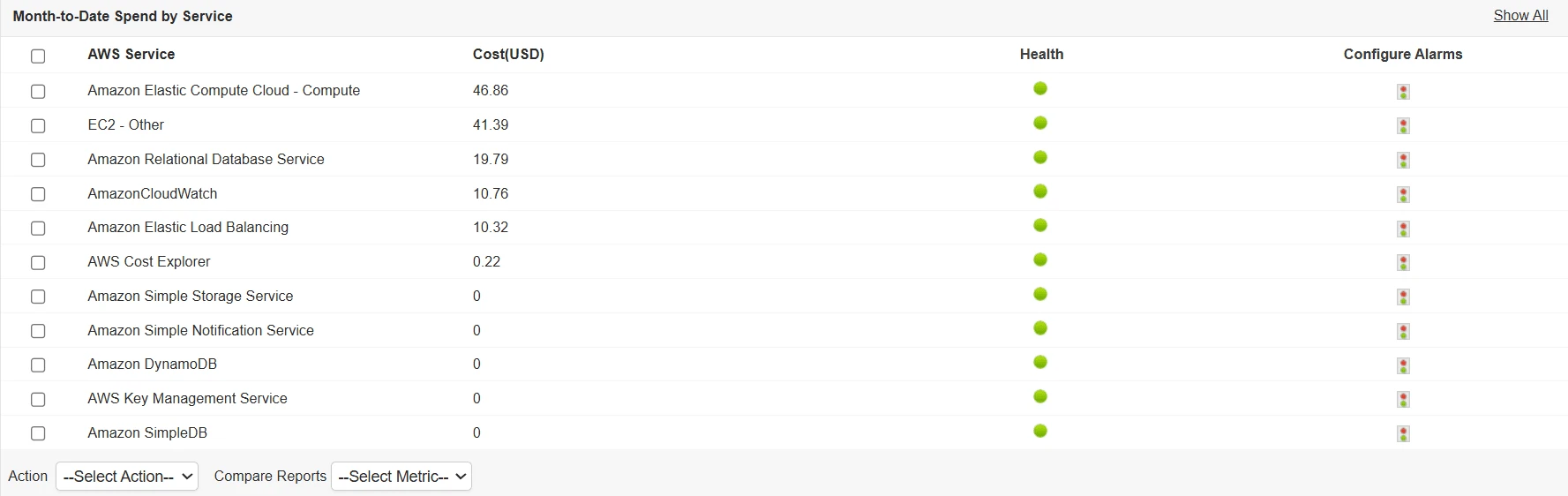
Applications Manager integrates AWS cost and usage metrics with performance data, helping teams optimize for both efficiency and savings.
7. Continuous monitoring and improvement
AWS environments evolve constantly with new deployments, scaling activities, and configuration changes. A “set it and forget it” approach does not work. Continuous monitoring ensures that changes don’t introduce risks, inefficiencies, or compliance gaps.
Regularly refining thresholds, reviewing cost trends, and analyzing incident reports helps teams improve continuously. Applications Manager enhances this process with trend analysis, anomaly detection, and intelligent alerts, making monitoring adaptive to evolving AWS landscapes.
Choosing the right AWS Monitoring Tool
Selecting the right monitoring solution is just as important as the monitoring strategy itself. For the right fit, look for tools that:
- Provide end-to-end visibility – Monitor AWS resources, applications, and hybrid/multi-cloud environments from a single platform.
- Support unified observability – Cover traditional metrics and thresholds while also enabling log analysis, tracing, and anomaly detection.
- Simplify setup and integration – Reduce reliance on manual configurations by offering out-of-the-box dashboards, reports, and alerts.
- Enable cost and performance optimization – Deliver insights into resource usage, idle instances, and spend patterns to balance performance with cost efficiency.
- Ensure security, compliance, and governance – Detect unauthorized access, track audit trails, and align with organizational and regulatory policies.
- Scale with business needs – Handle growing workloads, multiple accounts, and
cross-region monitoring without
adding complexity.
Applications Manager meets these requirements by consolidating AWS metrics, logs, and events with on-premises and multi-cloud monitoring, helping organizations gain deeper visibility and actionable insights.
Conclusion
Monitoring AWS cloud environments isn’t just about keeping systems online—it’s about aligning performance, security, and costs with business outcomes. A well-rounded strategy that blends observability, automation, governance, and continuous improvement helps organizations stay resilient and competitive.
With ManageEngine Applications Manager , IT teams get a unified platform to monitor AWS alongside hybrid and multi-cloud resources. From anomaly detection to cost insights, it empowers teams to shift from reactive issue resolution to proactive optimization.
Start building a smarter, future-ready AWS monitoring strategy today with Applications Manager.

