SQL Server audit and database audit
In this page
- Enabling SQL Server audit specifications
- Database audit specifications
- Creating a database audit specification using Transact SQL
Audit specifications can have three categories of actions:
- Server-level actions
- Database-level actions
- Audit-level actions
This article discusses how server-level actions and database-level actions are enabled for auditing on an SQL server using audit specifications.
Enabling server audit specifications
These are the audit specifications for actions carried out at the server level. They are available in all editions of SQL Server. There can be only one server audit specification per audit.
To create a server audit specification, the user needs:
- Permission to connect to the database.
- The ALTER ANY SERVER AUDIT permission to edit.
- The CONTROL SERVER permission to allow the audit to be viewed by the user.
Steps to create a server audit specification:
-
Create a server audit.
- Navigate to the Security folder in Object Explorer.
- Right-click the Audits folder and select New Audit.
- When you finish selecting options, select OK.
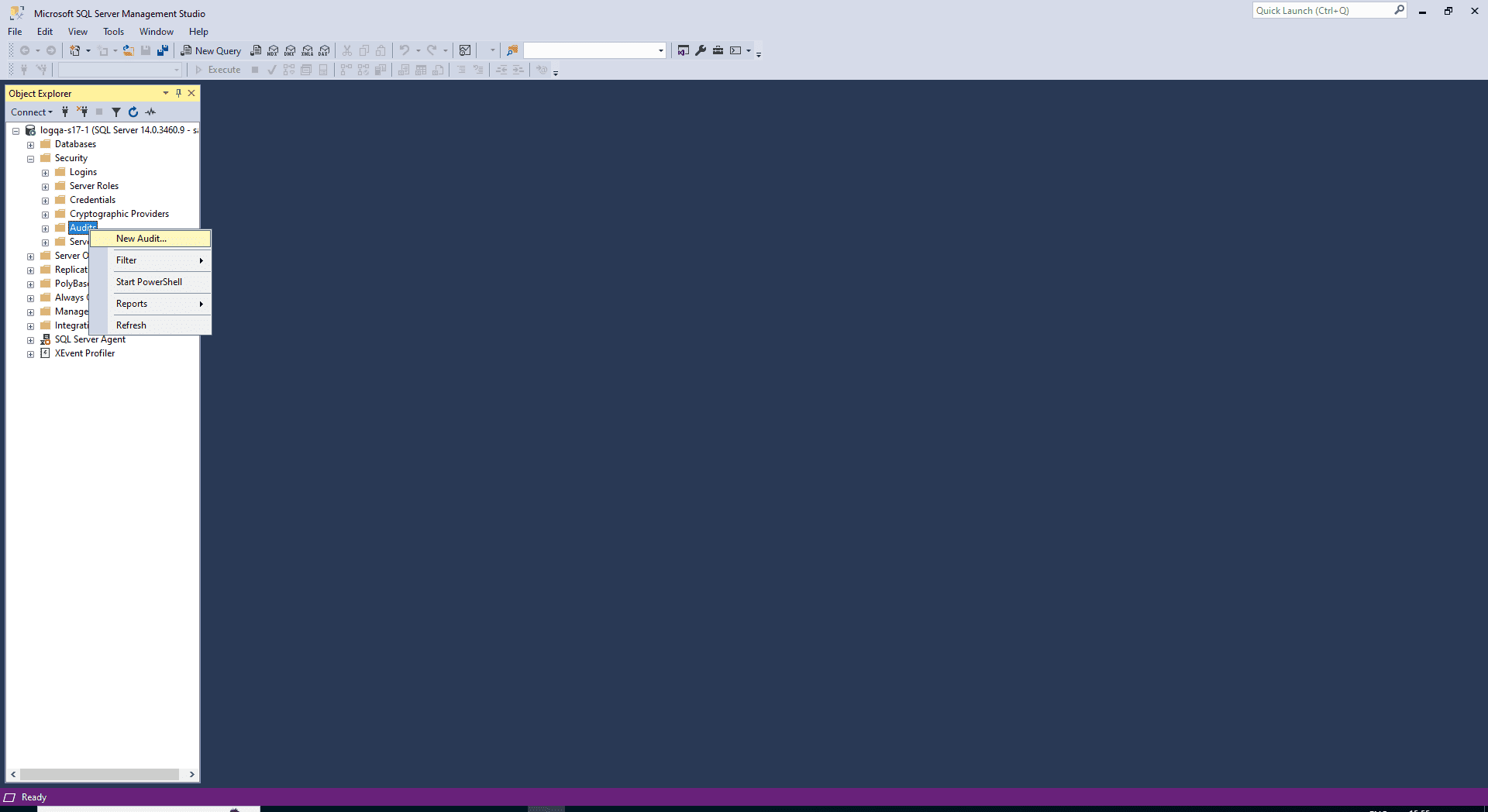
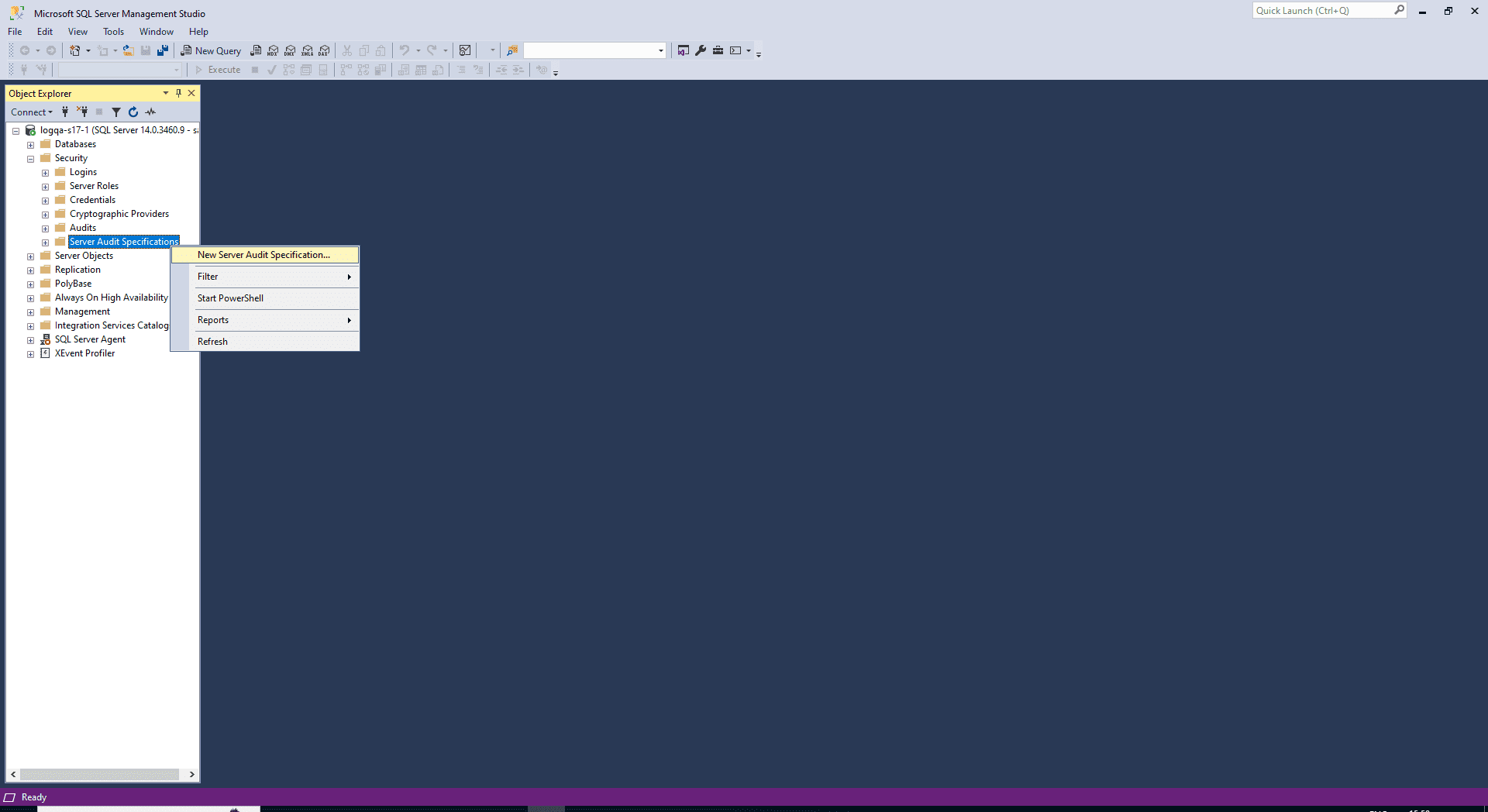
- Navigate to the Security folder > Server Audit Specifications.
-
Right-click Server Audit Specifications and select New Server Audit Specification.
-
Specify the following:
- Name: Provide a name. If left empty, a default name is assigned.
- Server Audit: Provide the target machine to which these events should be logged.
-
From the Audit list, select the audit object created in step 1.
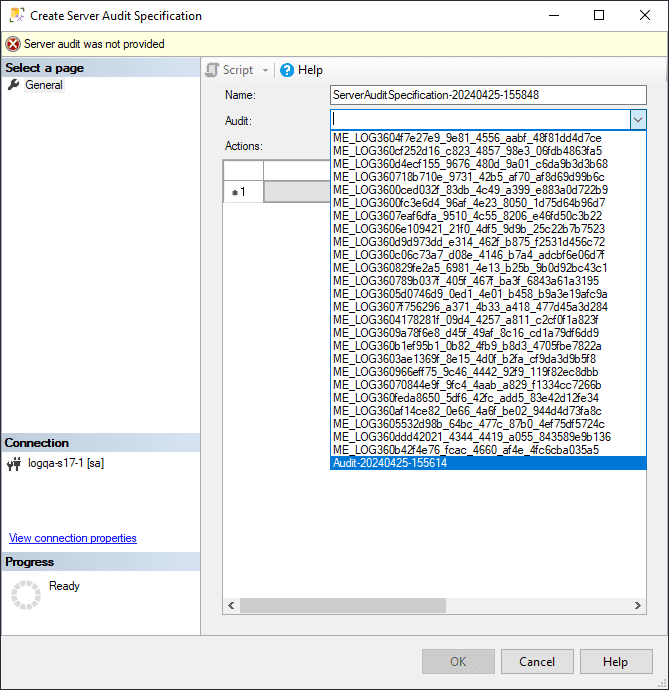
- In the Actions pane, add actions and objects to the server audit.
-
Right-click your server audit specification and select Enable Server Audit Specification.
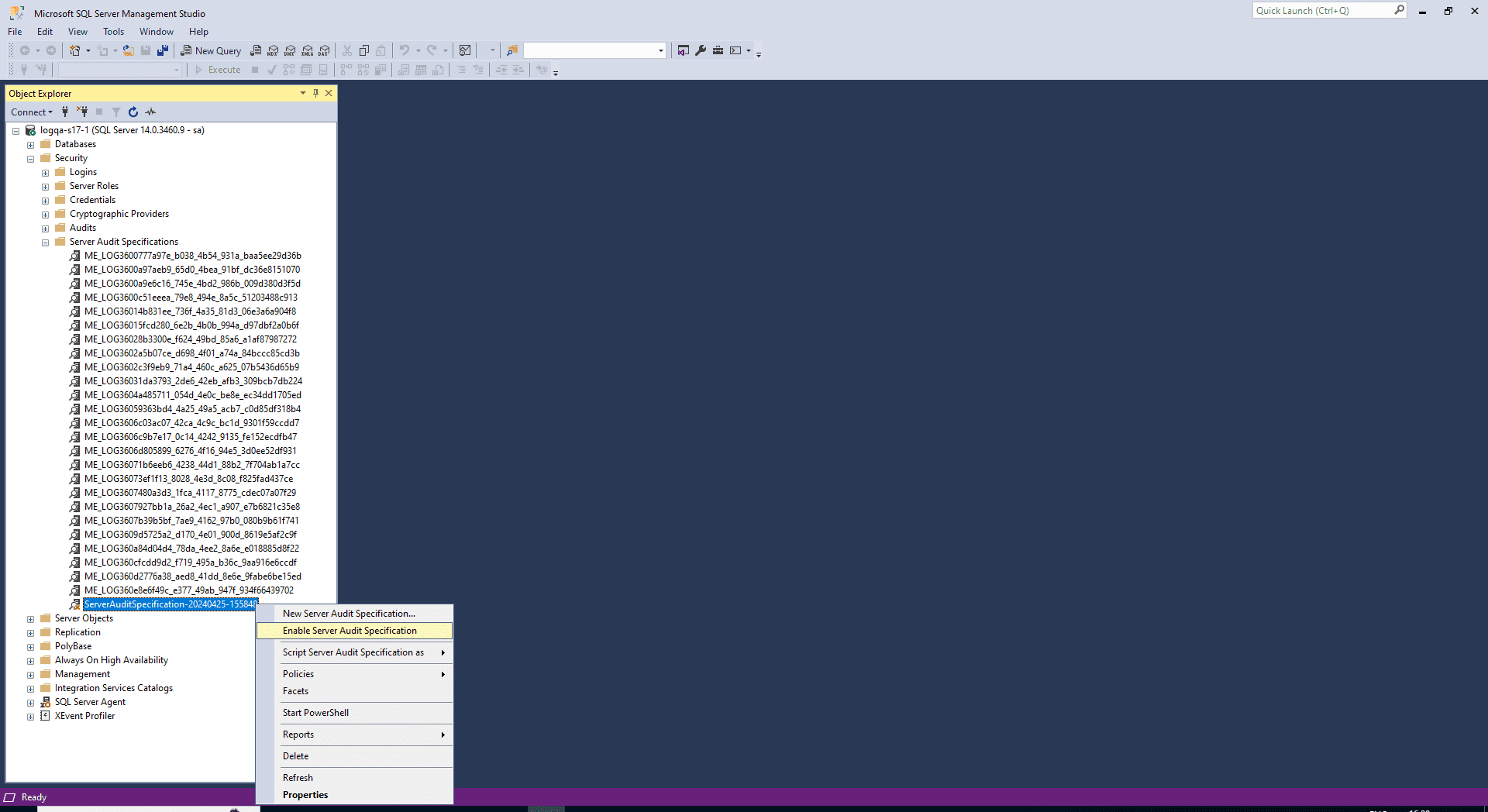
Database audit specification
These are the audit specifications for actions carried out at the database level. Database audit specifications are available only in the Enterprise edition of SQL Server and can be carried out at the object or user level.
To create a database audit specification, the user needs:
- Permission to connect to the database.
- The ALTER ANY DATABASE AUDIT SPECIFICATION or ALTER permission.
- The CONTROL permission for the database to which they would like to add the audit.
Steps to create a database audit specification:
-
Navigate to the Security node > Database Audit Specifications.
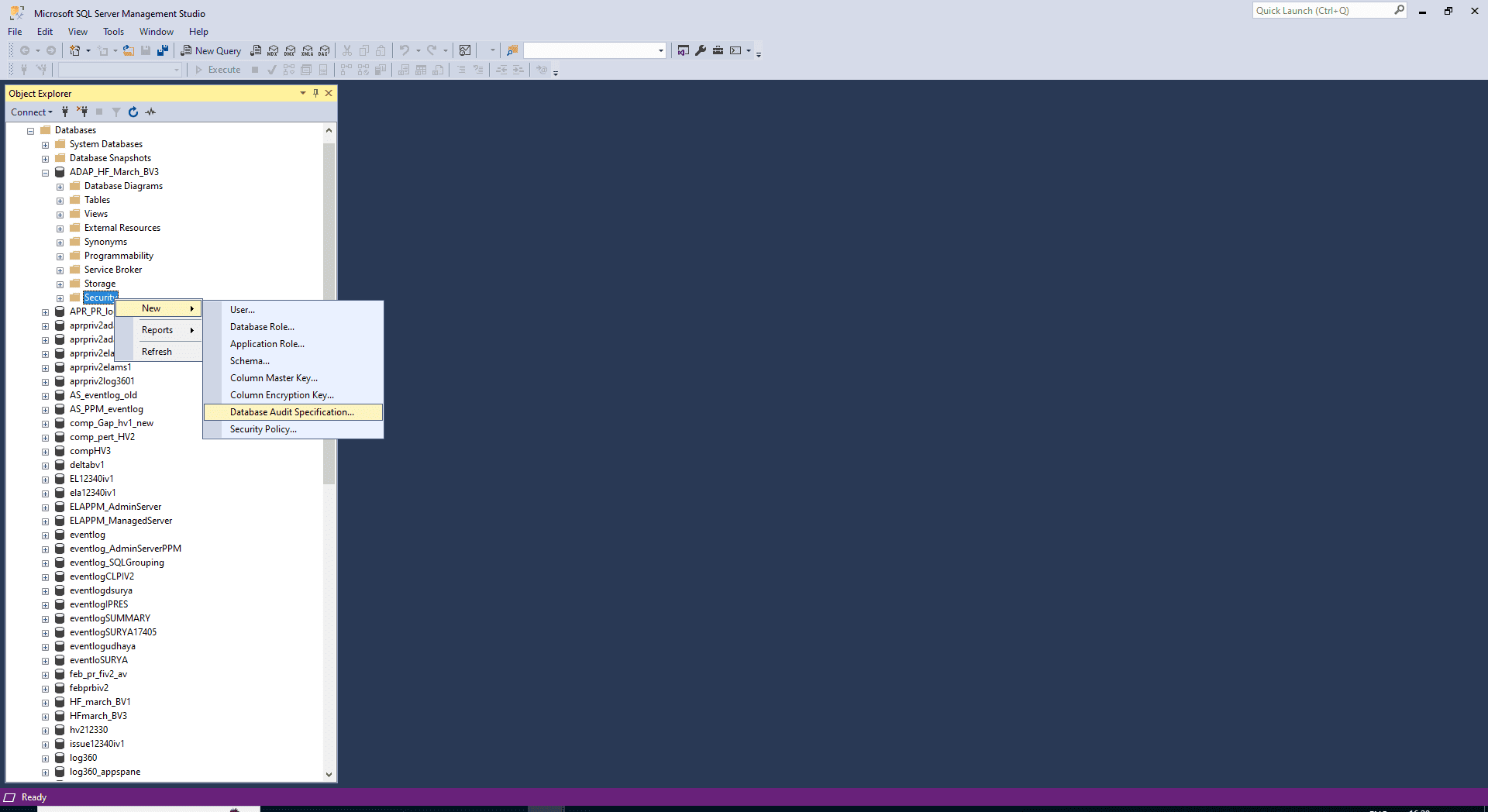
- Right-click Database Audit Specifications and select New Database Audit Specification.
-
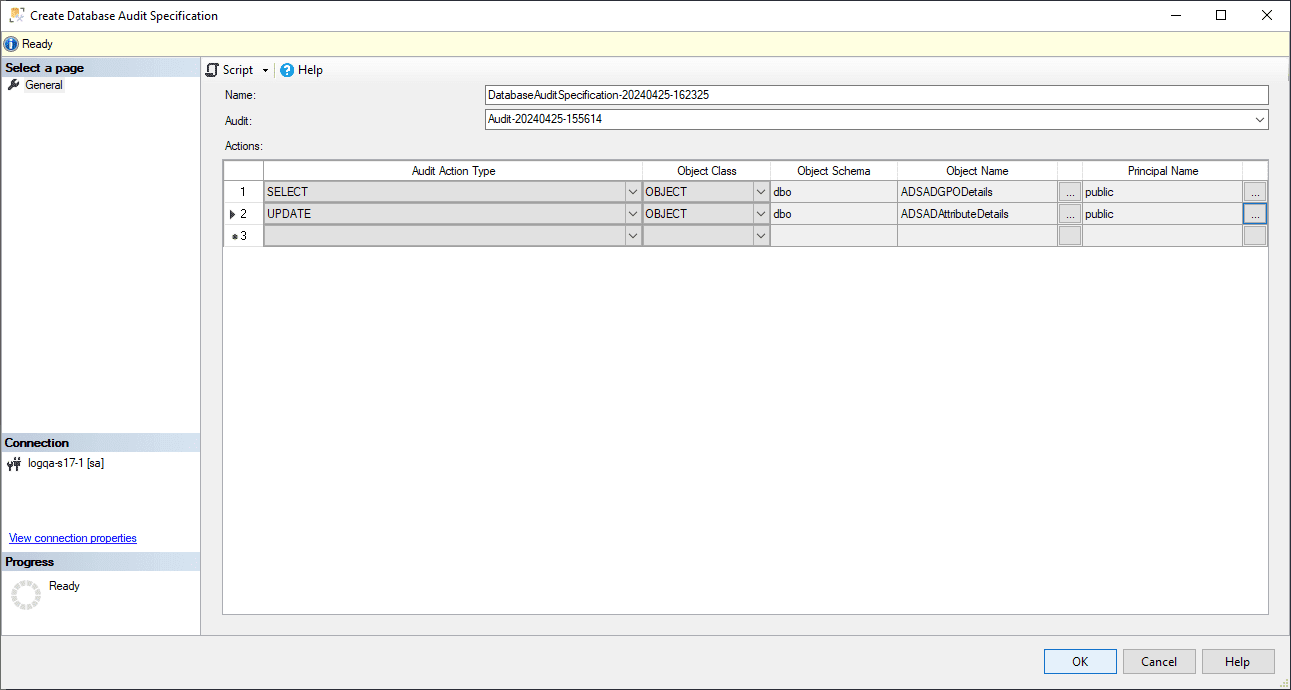
Specify the following fields:
- Name: Provide a name. If left empty, a name is assigned by default.
- Audit: Provide the name of the existing Server Audit object.
- Audit Action Type: Select from both Audit Actions and Audit Action Groups.
- Object Name: Provide the name of the object to be audited when an Audit Action has been selected.
- Schema: Provide the schema of the selected object.
- Principal Name: To audit all users, use the keyword public in this field.
-
Click OK.
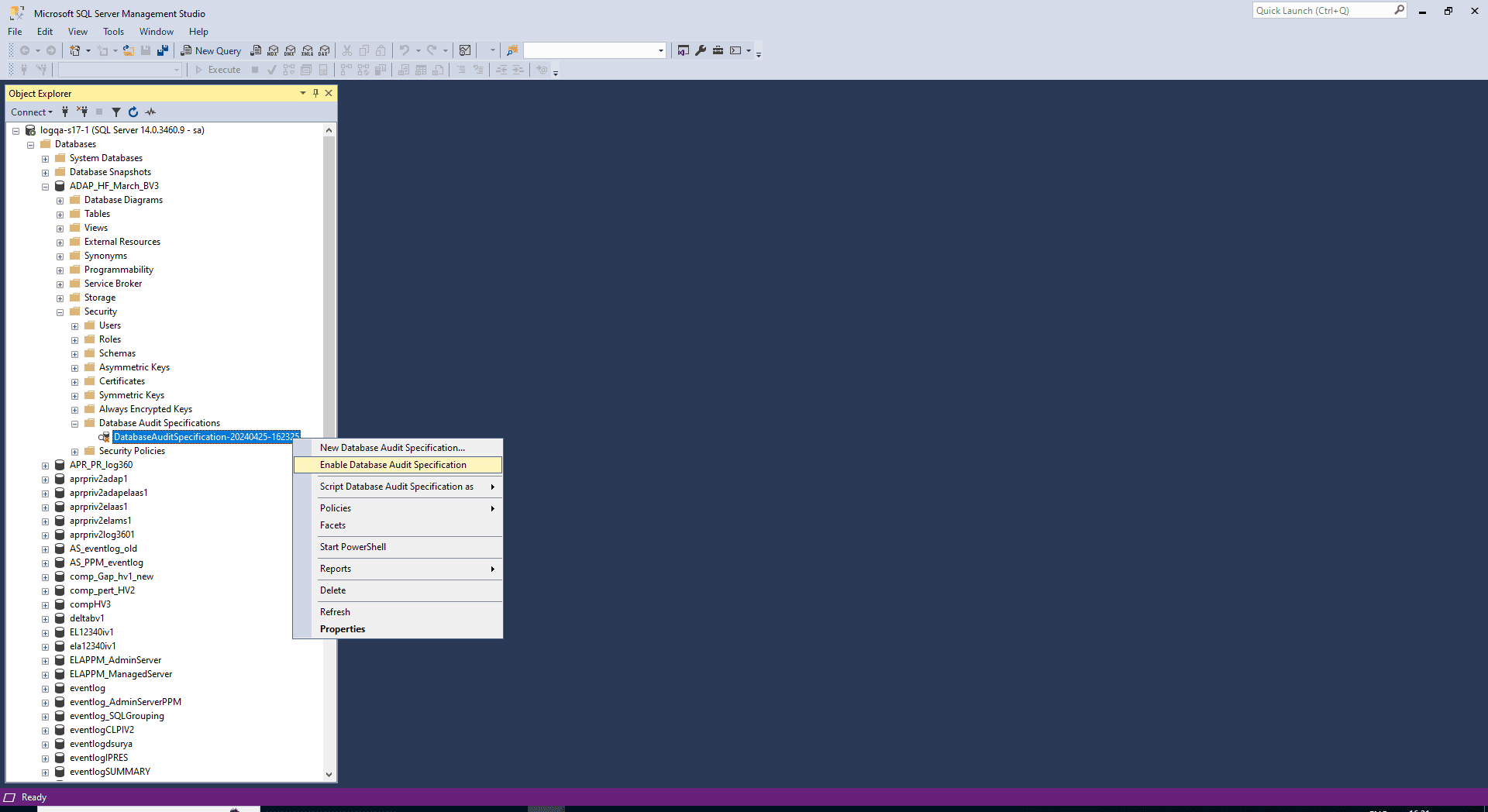
-
Right-click your database audit specification and select Enable Database Audit Specification.
To audit server scope objects, create a database audit specification in the master database.
Specifications can also be created with Transact SQL.
Creating a database audit specification using Transact SQL
Consider a scenario in which you want to audit the changes made to an employee pay history table. Assume that the employee details are stored in a table called HumanResource.EmployeePayHistory. First, define a server audit called Payrole_Security_Auditc and enable it. Then, create a database audit specification called Audit_Pay_Tables. This specification audits SELECT and INSERT statements by the dbo user for the table, as required.
Steps to enable auditing for the above scenario:
- Connect to an instance of the Database Engine in the Object Explorer.
- Select New Query from the standard bar.
- Paste the following example code into the query window and select Execute.
USE master ;
GO
-- Create the server audit.
CREATE SERVER AUDIT Payrole_Security_Audit
TO FILE ( FILEPATH =
'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL14.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA' ) ;
GO
-- Enable the server audit.
ALTER SERVER AUDIT Payrole_Security_Audit
WITH (STATE = ON) ;
- Repeat the first three steps for the example code below.
USE AdventureWorks2024 ;
GO
-- Create the database audit specification.
CREATE DATABASE AUDIT SPECIFICATION Audit_Pay_Tables
FOR SERVER AUDIT Payrole_Security_Audit
ADD (SELECT , INSERT
ON HumanResources.EmployeePayHistory BY dbo )
WITH (STATE = ON) ;
GO
Auditing procedures like these are often time-consuming and labor-intensive, and still might not offer a complete view of your SQL database's security. ManageEngine's EventLog Analyzer, an extensive log management tool, covers both SQL server and SQL database auditing. It delivers ready-to-use reports, real-time alerts, and an easy-to-use dashboard. You can drill down to the logs, filter reports, customize alerts, perform log searches, and archive logs for powerful and effective management of SQL servers.