In NetFlow Analyzer’s Security Analytics, accurate IP-to-hostname mapping is critical for effective asset-based anomaly detection. This is primarily achieved using DHCP Syslogs.
Manual mapping is static and limited to known, fixed IP devices. Active Directory is updated periodically and might not reflect real-time changes. Whereas, DHCP Syslog provides real-time, accurate data, making management of assets better.
DHCP Syslog provides dynamic mapping of:
IP Address ↔ MAC Address ↔ Hostname
This mapping is crucial because IP addresses change frequently due to DHCP leasing and a single machine (asset) might use different IPs over time. Hostnames remain consistent, helping to identify the true source regardless of changing IPs. Hence, Security Analytics is asset-based, not IP-based.
To resolve IPs to hostnames, Security Analytics uses the following priority order:
In NetFlow Analyzer, configure the DHCP Syslog profile under IP Mapping.
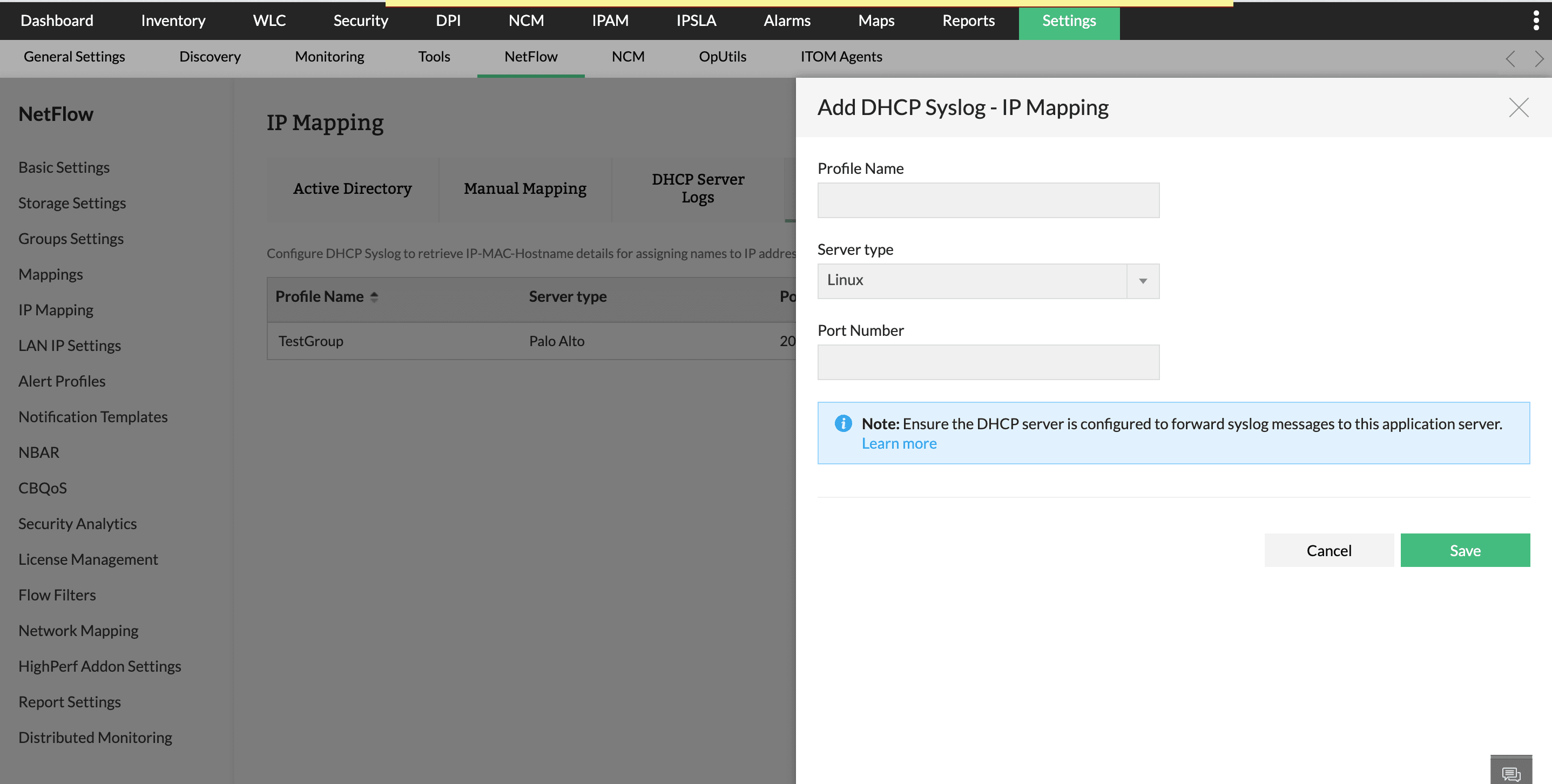
To configure DHCP Syslog in NetFlow Analyzer:
Choosing the correct server type ensures accurate extraction of IP–MAC–Hostname details from Syslog messages.
The details of the columns of the table are given below:
Note:The same port configured in NetFlow Analyzer must be used while exporting DHCP Syslog.
Following are the steps to configure syslog forwarding based on your DHCP server type.
Supported DHCP server types include,
(In this setup, we use the local7 syslog facility for DHCP logs)
Edit the DHCP configuration file:
/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
Add or update the following line:
log-facility local7;
•log-facility local7 instructs dhcpd to send all DHCP-related logs to the local7 syslog facility
•This allows easy separation of DHCP logs from other system logs
Edit the rsyslog configuration file:
/etc/rsyslog.conf
(or create a dedicated file under /etc/rsyslog.d/, e.g. dhcp-forward.conf)
Add the following entry:
local7.* @10.XX.XX.XX:1540
•local7.* captures all log levels from the local7 facility
•"@" indicates UDP transport (@@ would indicate TCP)
•10.XX.XX.XX:1540 is a remote log server IP and UDP port
To keep a local copy of DHCP logs, add:
local7.* /var/log/dhcpd.log
Then create the log file and set permissions:
touch /var/log/dhcpd.log
chmod 644 /var/log/dhcpd.log
Restart the required services for changes to take effect:
systemctl restart rsyslog
systemctl restart dhcpd
Step 5: Verify Log Forwarding Check local DHCP logs
tail -f /var/log/dhcpd.log
Check rsyslog status
systemctl status rsyslog
Verify on Central Log Server
•Confirm logs are received on UDP port 1540
•Ensure firewall rules allow UDP traffic on this port
Firewall Considerations
Ensure outbound UDP traffic is allowed from the DHCP server:
UDP 1540 → 10.XX.X.XX
If firewall is enabled:
firewall-cmd --add-port=1540/udp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reload
Windows DHCP servers do not natively support sending logs using the syslog protocol. To forward DHCP logs, you must use a third-party syslog forwarding agent. Once it is installed and configured, DHCP logs can be forwarded to NetFlow Analyzer over UDP for IP to hostname correlation and security analysis.
For detailed configuration instructions, and sample third-party NXLog configurations check: https://docs.nxlog.co/integrate/windows-dhcp-server.html
To forward DHCP server logs, from a Palo Alto firewall configured as a DHCP server, you must enable and configure syslog forwarding on the device. Once enabled, the firewall can transmit these logs over UDP to NetFlow Analyzer for further analysis and monitoring.
For step-by-step instructions on forwarding system logs to a syslog server, check this page: https://knowledgebase.paloaltonetworks.com/KCSArticleDetail?id=kA10g000000ClM9CAK
To forward DHCP logs from an ISC DHCP (dhcpd) server via UDP, configure a log collection agent to capture DHCP-server messages from the local syslog service and transmit them to a syslog server.
For detailed configuration examples and sample nxlog.conf segment, refer to the official NXLog guide: https://docs.nxlog.co/integrate/dhcpd.html
To forward DHCP logs from an ISC Kea DHCP server over UDP, you must first configure Kea’s built-in logging settings to write DHCP events to either the system log or a log file.
For detailed instructions on configuring logging within Kea, refer: https://kb.isc.org/docs/kea-logging-configuration
The DHCP server component of Cisco Prime Network Registrar (CPNR) generates logs for DHCP operations such as IP address assignments, renewals, releases, and lease expirations.
To forward these logs over UDP to a centralized syslog server, you must configure:
For detailed, step-by-step configuration instructions, refer to the official Cisco documentation: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/net_mgmt/prime/network_registrar/11-2/dhcp/guide/DHCP_Guide/DHCP_Guide_chapter_01.html#con_1049660
Important Note:
Thank you for your feedback!