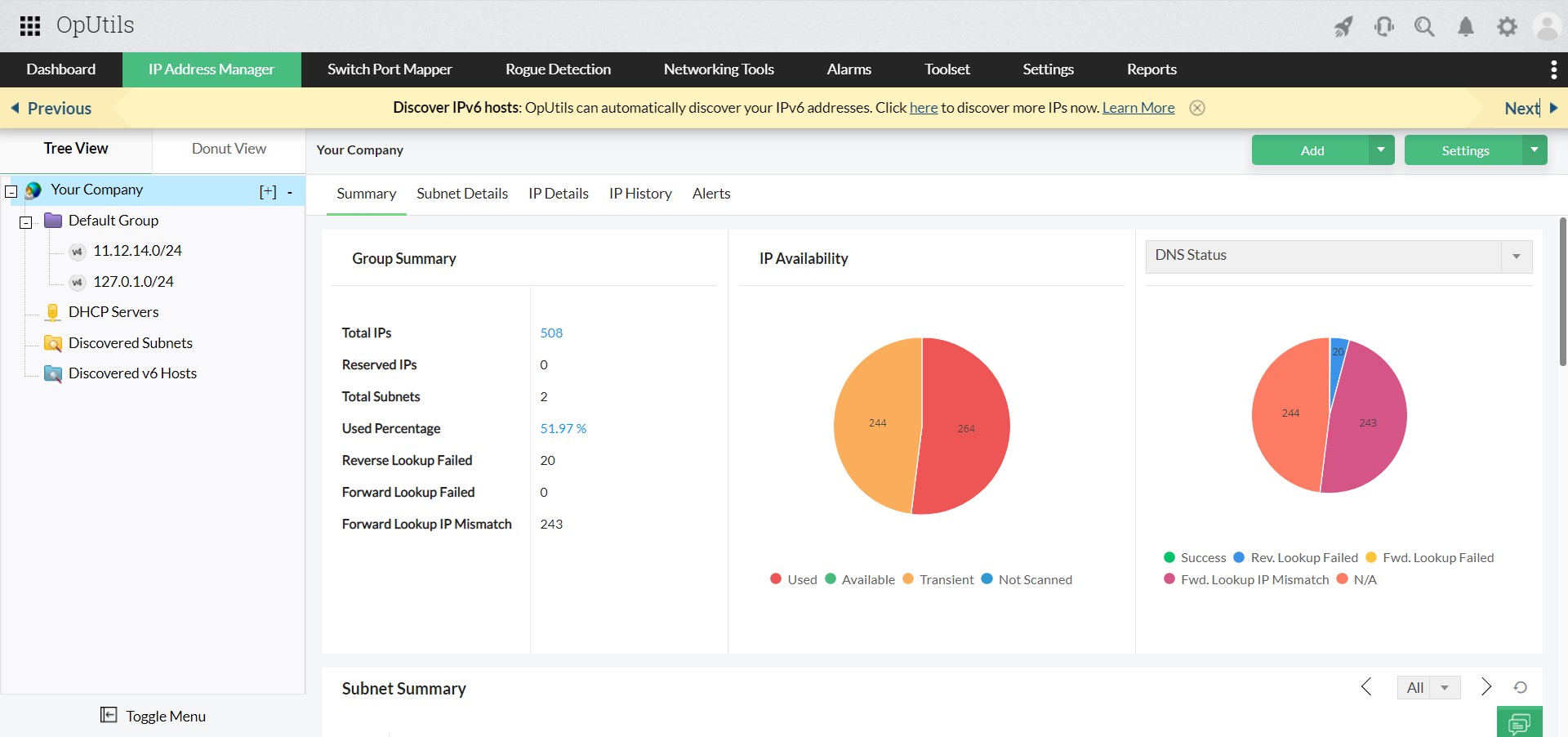
IP address conflicts are among the most frustrating network management issues, often going unnoticed until users experience slow connections, random disconnections, or even complete loss of access. By the time IT administrators are alerted, network performance is already disrupted.
The real challenge is that IP conflicts rarely trigger alerts. Without proactive monitoring, IT teams end up chasing symptoms instead of solving the root cause. This makes real-time detection essential, catching conflicts before they affect end users.
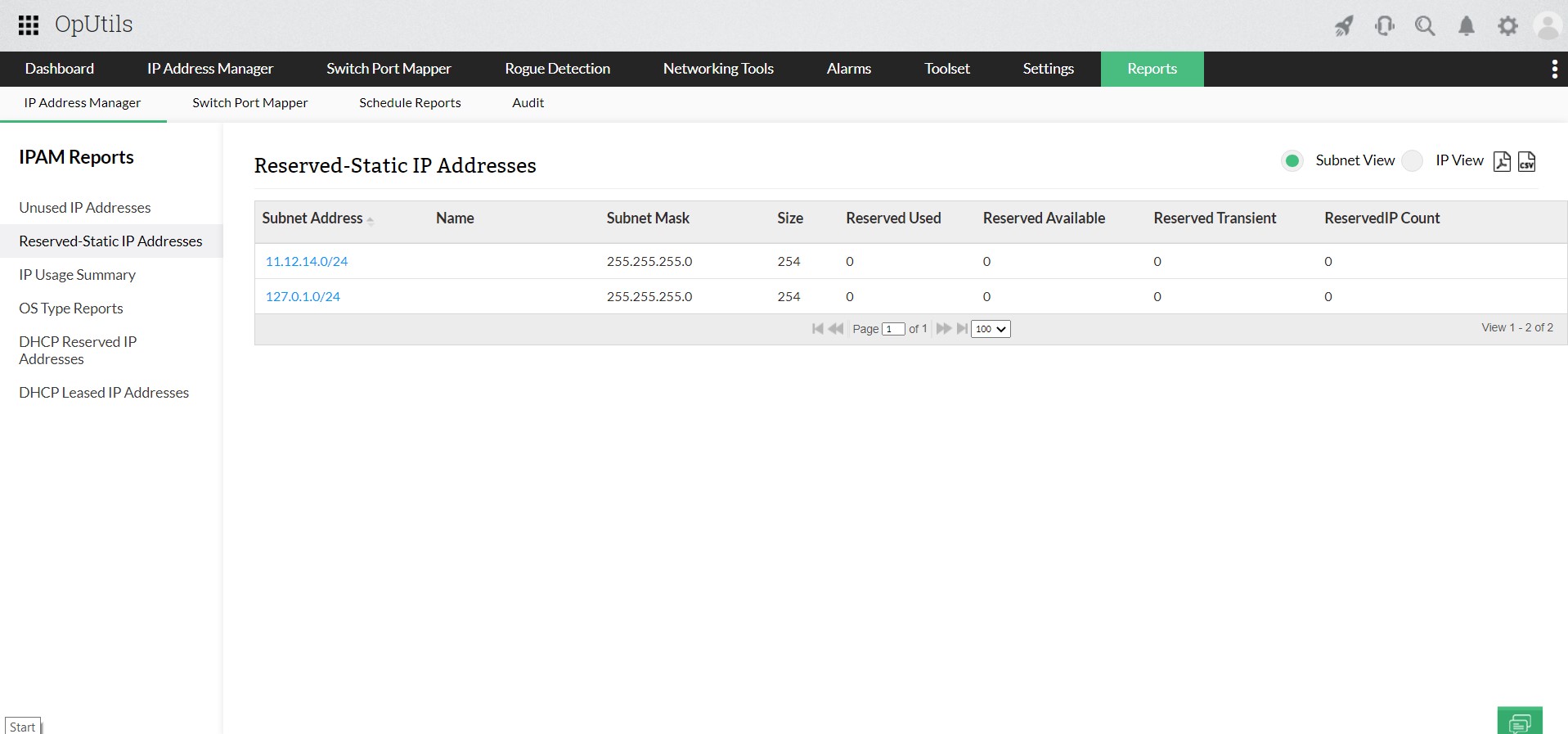
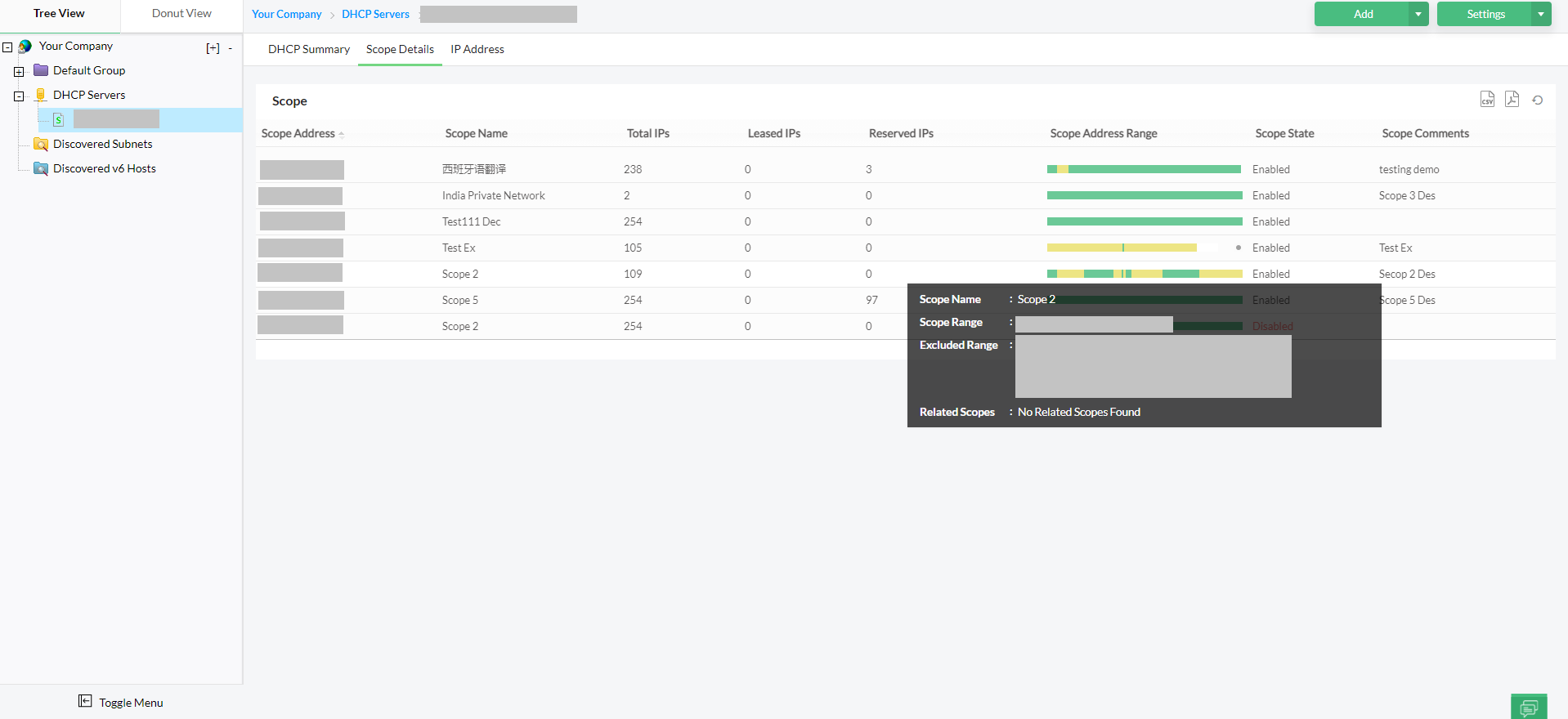
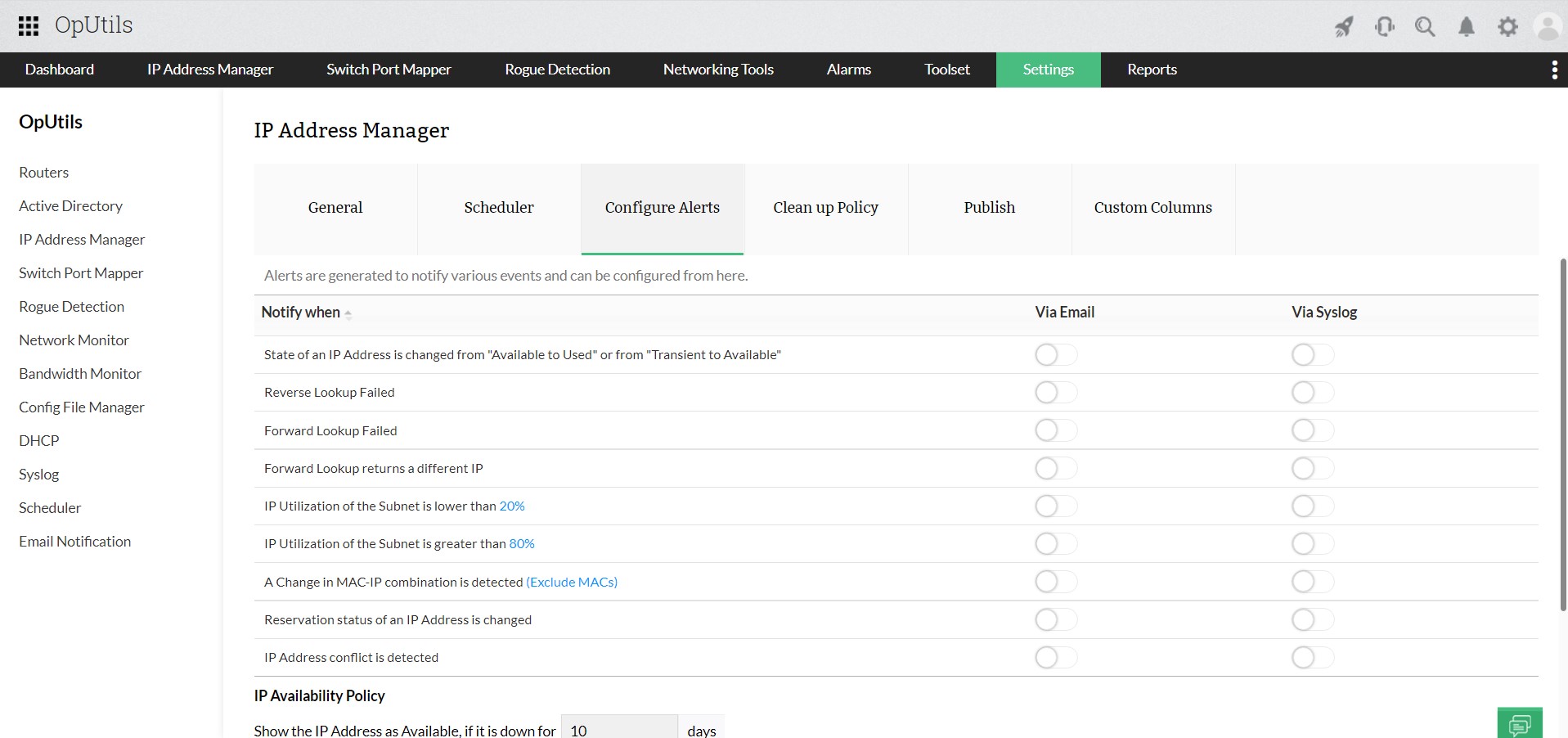
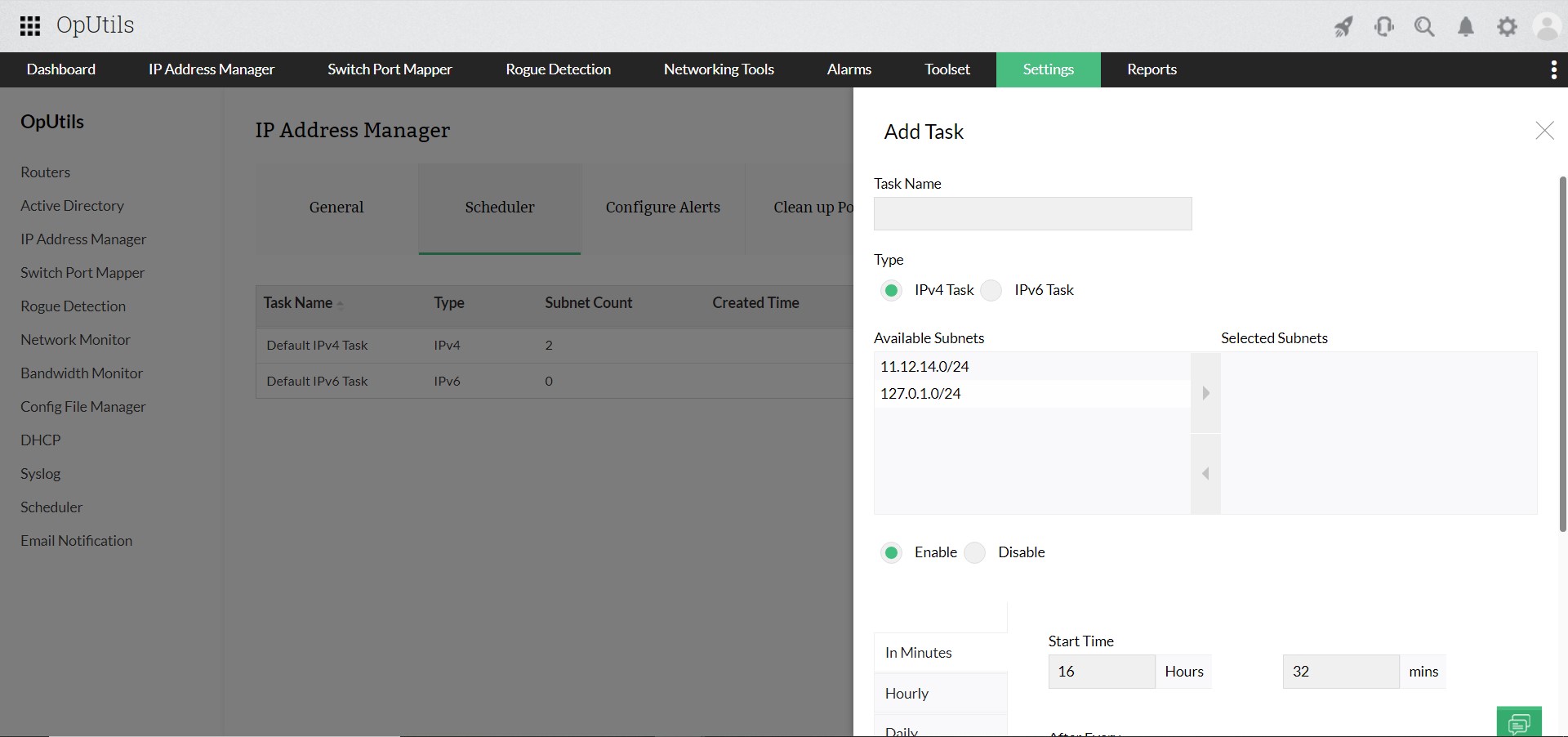
Relying on manual checks or waiting for user complaints is no longer practical. Modern IP conflict detection tools continuously scan for duplicate IP addresses, log historical incidents, and send instant alerts the moment a conflict occurs, helping teams minimize downtime and ensure seamless connectivity.
On this page, we’ll understand how to identify IP conflicts early, detect IP conflicts using both command-line and automated methods, and prevent them from recurring in dynamic, multi-device network environments. Let's get started with the basics right away.