Why network detection and response (NDR) is your cybersecurity power move in 2025

Summary
Cyber threats have evolved—and so must your defenses. In this deep-dive, we break down how network threat detection and response (NDR) works, why it matters to IT leaders in 2025, and how to choose the right solution for your hybrid infrastructure. From encrypted traffic inspection to automated threat response, this guide covers it all.
Read on to discover the real business value of NDR and what to look for in a next-gen solution.
Let’s be honest: cyber threats aren’t just getting more frequent—they’re getting more sophisticated. Traditional perimeter defenses? They're like using a padlock in a world of lockpicks, lasers, and encrypted tunnels.
That’s why network threat detection and response (NDR) isn’t just a “nice to have” anymore. It’s becoming one of the smartest moves an IT leader can make to secure their business in a hybrid, distributed, and cloud-first world.
So, what exactly is NDR?
According to Gartner, network detection and response (NDR) solutions leverage behavioral analytics to identify unusual system activity by monitoring network traffic. These tools continuously examine either raw network packets or metadata from both internal (east-west) and external (north-south) communications to detect potential threats.
Let's understand how NDR works in your network
Here’s a deeper dive into the core mechanics of a modern NDR solution:
- Traffic collection: NDR tools passively ingest network telemetry from sources like SPAN ports, TAPs, or cloud traffic mirrors. This includes NetFlow, sFlow, and full packet capture depending on the deployment. Traffic is often decrypted where possible to analyze application-level metadata.
- Protocol decoding and metadata extraction: The system decodes common protocols (e.g., DNS, HTTP/S, SMB, LDAP) and extracts rich metadata for every session, such as timing, payload size, connection state, and user identity if available (via integration with Active Directory or identity providers).
- Behavioral modeling and anomaly detection: Using statistical baselining, unsupervised machine learning, and clustering techniques, the NDR platform builds a model of “normal” communication patterns between users, devices, services, and applications. Any deviation—like a database server initiating outbound connections—is flagged as anomalous.
- Threat detection logic: In addition to behavioral analytics, many NDR tools incorporate rule-based detection, threat intelligence feeds, and indicators of compromise (IOCs) for known tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). This layered approach increases fidelity.
- Risk scoring and alert enrichment: Detected threats are scored based on severity, asset value, and threat context. Alerts are enriched with additional context like user identity, geolocation, device type, and prior behavior history to aid incident triage.
- Response orchestration: Based on pre-defined playbooks or integrations with SOAR and EDR platforms, the NDR tool can trigger automated or semi-automated responses. This may include isolating a device, blocking traffic, notifying an analyst, or generating a ticket.
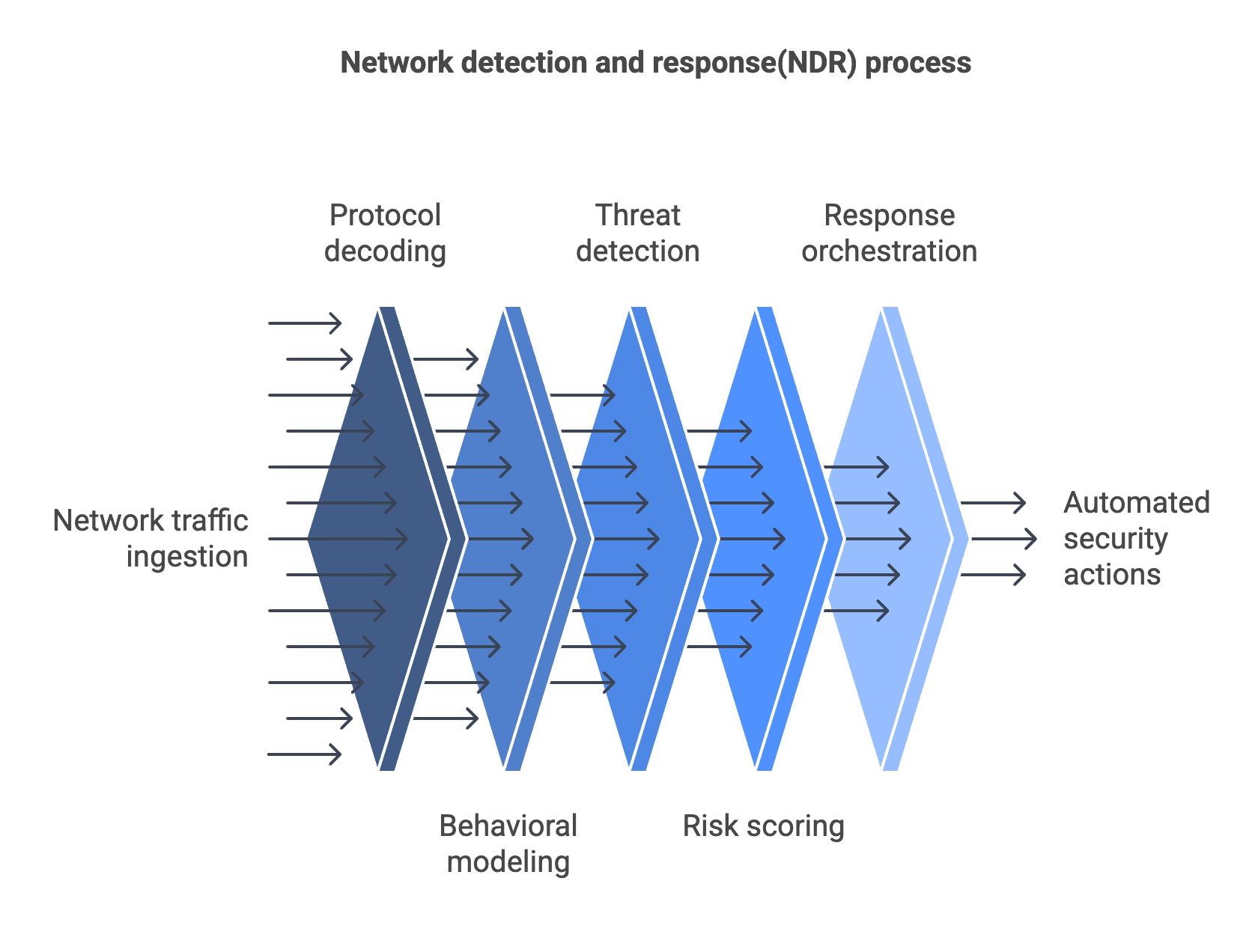
NDR is essentially a brain that watches your network in real time, learns continuously, and reacts with precision.
Why should NDR matter to you, as an IT decision-maker?
Network Detection and Response (NDR) platforms are purpose-built to detect malicious or anomalous behavior within enterprise networks. This offers a crucial layer of visibility for critical security tasks such as insider threat detection, which translates into several networking and business benefits, including:
1. You gain deep, real-time visibility across the entire network
NDR tools passively collect and analyze network traffic, including full packet capture (PCAP), flow data like NetFlow and IPFIX, and enriched metadata from switches, firewalls, and cloud environments. This gives you deep visibility into both intra-network (east-west) and perimeter (north-south) activity.
By monitoring lateral movement within your environment, NDR helps detect threats that would otherwise remain hidden—especially in segmented or cloud-heavy networks where endpoint coverage is inconsistent.
Use case: A multinational bank can use NDR to trace an attacker’s lateral movement between segmented VLANs after a phishing compromise. Even if the attacker had bypassed EDR and SIEM detection, anomalous SMB and RDP traffic can trigger behavioral flags in the NDR engine.
2. You reduce attacker dwell time with behavioral threat detection
NDR platforms use ML-based statistical base lining, and threat intelligence to detect subtle changes in traffic behavior—like unusual beaconing patterns, unexpected protocol use, or anomalous session lengths. This allows security teams to catch early signs of compromise before attackers can escalate privileges or exfiltrate data.
Unlike signature-based tools that only catch known threats, NDR focuses on behavioral anomalies—even for zero-day or custom-built exploits.
Use case: A healthcare organization can identify irregular DNS tunneling activity from a compromised endpoint. NDR can flag the slow, encrypted exfiltration technique by analyzing session frequency and payload entropy, cutting dwell time from weeks to hours.
3. You reduce alert fatigue with context-driven analytics
One of the major challenges for SOC teams is alert overload. Traditional network tools and IDS/IPS systems generate massive volumes of alerts—many of which are low-fidelity or false positives. NDR combats this by correlating network events and applying contextual analytics.
Advanced NDR platforms use unsupervised learning models to group related anomalies into high-confidence incidents. They enrich these with context such as affected assets, lateral movement paths, and risk scores—so analysts know what matters and why.
Use case: Organizations can use this to see a reduction in low-value alerts. Instead of sifting through humongous amounts of firewall and IDS notifications per day, teams can focus on a handful of high-priority threats automatically enriched with MITRE ATT&CK context.
4. You inspect encrypted traffic without violating privacy or performance
With more and more enterprise traffic now encrypted, traditional monitoring tools struggle to maintain visibility. Decrypting traffic introduces compliance issues and performance overhead.
Modern NDR platforms solve this by analyzing encrypted traffic metadata—including flow duration, packet size distributions, JA3/JA3S SSL fingerprinting, and session behavior—to infer malicious activity without decryption.
Use case: A global e-commerce company detected encrypted C2 traffic masquerading as HTTPS. The NDR solution used TLS fingerprinting and anomaly-based analysis (unusual session intervals, packet burst patterns) to flag the threat—without ever touching the payload.
How it fits into your broader cybersecurity ecosystem
NDR complements, rather than replaces, your existing security stack. It integrates with:
- SIEM integration: NDR sends enriched, high-fidelity network telemetry such as lateral movement and anomalous traffic patterns to your SIEM—reducing alert noise and enhancing correlation with logs and endpoint data.
- SOAR automation: NDR detections can trigger automated response playbooks—like isolating compromised hosts, enforcing MFA, or blocking outbound traffic—streamlining your incident response process.
- EDR/XDR correlation: NDR fills endpoint visibility gaps by detecting threats on unmanaged or stealthy hosts. It complements EDR/XDR by correlating process activity with network behavior for stronger, multi-layered detection.
- Threat intelligence application: NDR applies indicators of compromise (IOCs) and tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) from threat intel feeds in real time—flagging known malicious activity and matching behavior to frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK.
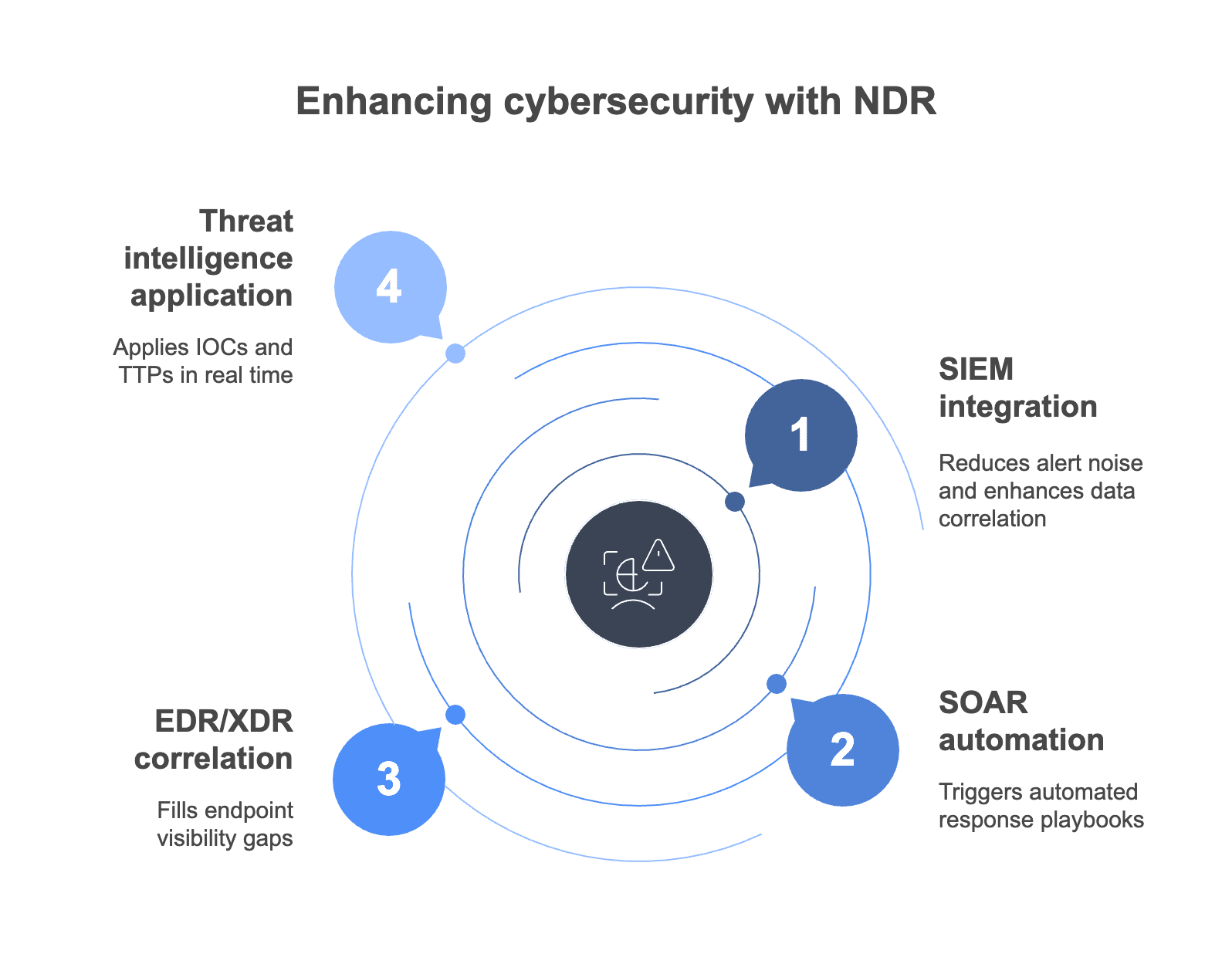
This fusion gives you a more complete security posture and network hardening to block threats and drive faster mean time to detection (MTTD) and mean time to response (MTTR).
7 key features to look for in a solid NDR solution
When evaluating NDR solutions, look for capabilities that not only detect threats but also integrate smoothly into your infrastructure, scale with your environment, and support your incident response workflows. Here’s what matters:
- Advanced analytics: Look for behavioral models that go beyond static baselines. Solutions should use deep learning, clustering, and time-series analysis to detect anomalies over time, including low-and-slow data exfiltration or lateral movement patterns that change dynamically.
- Encrypted traffic inspection: Ensure the platform can analyze encrypted traffic without decryption. Key capabilities include TLS fingerprinting, flow-based anomaly detection, and entropy analysis to detect encrypted C2 channels or covert tunnels while preserving privacy and performance.
- Cloud-native visibility: Your NDR solution should support cloud-native traffic sources including AWS VPC Traffic Mirroring, Azure vTAP, and Google Cloud Packet Mirroring. Bonus if it supports container traffic monitoring and overlays like Istio or Envoy.
- Custom detection rules and integrations: Check for flexible detection logic and support for custom rules using metadata fields, regular expressions, or threat intel. Also check for native integrations with SIEM, SOAR, EDR/XDR, and threat intel platforms for smooth cross-platform automation.
- Scalable architecture: Look for a distributed, horizontally scalable design that can handle multi-gigabit environments across data centers and cloud. Solutions should support both centralized and edge deployment models, with optional packet brokers or sensor-based ingestion.
- Threat hunting and investigation tools: Look for built-in tools that let your analysts pivot quickly from a detection to session metadata, PCAPs, and related assets. Visualizations like connection graphs or time-sequence flows help accelerate root cause analysis and incident scoping.
- Automated response hooks: Ensure the platform supports outbound integrations via REST APIs or direct SOAR connectors. This allows for automatic containment actions such as firewall rule updates, endpoint isolation, or ticket generation based on NDR findings.
Ready to adopt NDR? Start here
Here’s how to begin your journey:
- Assess current network visibility: Identify blind spots, including internal traffic and cloud east-west flows.
- Classify critical assets and users: Define what’s most valuable and most at risk.
- Conduct a proof of concept (PoC): Deploy NDR in a controlled environment to evaluate detection quality and integration.
- Align with incident response plans: Ensure NDR is part of your response workflows.
- Review and refine continuously: As your environment evolves, keep tuning models and rules.
Adversaries are more patient and covert than ever, often infiltrating networks weeks before launching an attack. Network threat detection and response gives you a proactive edge by surfacing hidden threats, speeding up investigation, and automating containment.
As threats evolve, so must your detection capabilities. If you’re serious about threat visibility in 2025 and beyond, NDR should be on your roadmap.
Want help choosing the right NDR solution for your environment? Or curious how it fits into a hybrid IT setup? Let’s talk—drop your questions at cxo-focus@manageengine.com