What is an MSP (Managed Services Provider)?
An MSP (Managed Services Provider) is a third-party company that manages and supports a business’s IT infrastructure and operations. Instead of handling IT in-house, businesses partner with MSPs to ensure their systems run smoothly, stay secure, and remain cost-efficient.
The primary goal of an MSP is to keep clients’ IT environments functional, secure, and aligned with business needs. They handle everything from routine maintenance and monitoring to advanced cybersecurity and compliance management. By doing so, MSPs help businesses reduce downtime, prevent cyber threats, and achieve better operational efficiency without heavy internal investment.
MSPs typically operate on a subscription or service-based model, offering predictable costs and proactive IT support that adapts to evolving technology demands.
Table of contents
- Why are MSPs important?
- What are the benefits of MSPs for businesses?
- What services do MSPs provide?
- What are the different types of MSPs?
- What challenges do MSPs face?
- How do you choose the right MSP?
- How does MSP pricing work?
- MSP vs In-House IT: What are the key differences?
- How do MSP solutions help businesses grow?
Why are MSPs important?
According to Gartner, the average cost of IT downtime is approximately $5,600 per minute. For small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), even a short disruption can lead to significant loss of revenue, compromised productivity, and reputational damage.
This is where MSPs prove essential. By proactively managing IT infrastructure, MSPs help businesses prevent unplanned outages, reduce operational overheads, and strengthen cybersecurity defenses.
Key reasons why MSPs matter:
- Minimize downtime: MSPs continuously monitor systems, detect anomalies early, and act swiftly to resolve issues; often before they impact business operations.
- Control IT costs: Instead of overspending on scattered tools and reactive fixes, businesses get predictable, fixed-cost IT management.
- Bridge skill gaps: Many SMBs lack the internal bandwidth to handle IT maintenance, updates, and security. MSPs bring deep expertise without the overhead.
- Ensure scalability and agility: As your business grows, MSPs adapt the IT setup accordingly, helping you scale without friction.
- Enhance cybersecurity: With rising threats, MSPs implement advanced protection, real-time threat monitoring, and compliance readiness.
Ultimately, an MSP helps businesses do more with less; delivering enterprise-grade IT outcomes at a fraction of the traditional cost.
What are the benefits of MSPs for businesses?
Managed Services Providers (MSPs) offer businesses a smarter, more scalable way to manage IT operations. While in-house IT teams often struggle to keep pace with evolving demands, MSPs bring in-depth expertise, proactive support, and enterprise-grade tools to help organizations stay ahead.
Here’s how businesses benefit from partnering with an MSP:
- Enhanced Cybersecurity Coverage: Cybercrime damages are projected to reach $10.5 trillion globally by 2025. MSPs offer layered protection against threats like ransomware, phishing, and malware. With around-the-clock monitoring, threat intelligence, and rapid incident response, MSPs significantly reduce risk exposure.
- Access to Deep IT Expertise: MSPs are built on technical excellence. Their teams consist of certified professionals who specialize in infrastructure, cloud, networking, security, and more; bringing high-level skillsets that are often difficult or expensive to hire in-house.
- Simplified Compliance Management:From GDPR to HIPAA, global regulations are complex and ever-evolving. MSPs stay current with compliance requirements and help businesses implement and maintain policies that meet regulatory standards, minimizing risk of fines or penalties.
- Predictable and Cost-Effective IT: Instead of spending on ad-hoc fixes and capital-intensive upgrades, MSPs offer subscription-based pricing models that consolidate support, tools, and infrastructure into a fixed monthly fee; offering clear ROI and better financial planning.
- Early Access to Advanced IT Tools: MSPs often partner with leading vendors and have early access to the latest technologies. This means businesses can adopt cutting-edge tools and automation strategies faster without needing to overhaul their internal systems or retrain staff.
- Greater Focus on Core Business: By offloading routine IT tasks and problem-solving to experts, internal teams can focus on strategic projects, innovation, and customer delivery rather than being stuck in fire-fighting mode.
What services do MSPs provide?
Managed Services Providers (MSPs) deliver a wide range of IT services designed to reduce operational burdens, improve security posture, and ensure business continuity. Here are the core service areas MSPs typically offer:
Cybersecurity Services: MSPs are at the frontline of ransomware protection, endpoint security, and managed detection and response (MDR). With rising cyber threats, cybersecurity remains the most sought-after service among businesses today.
Automation & AI-Powered IT Support: From automated ticket routing to proactive remediation, AI in IT operations helps MSPs offer faster and smarter services. Businesses benefit from reduced manual intervention and improved service delivery speed.
Backup, Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity: Automated data backup and disaster recovery planning ensure business continuity in case of outages, breaches, or human error. MSPs help set up and manage these critical services seamlessly.
Cloud Services & Multi-Cloud Management: MSPs help businesses migrate to the cloud, manage hybrid infrastructure, and optimise cloud spend making cloud computing efficient and secure.
Network & Endpoint Monitoring: Through tools like RMM (Remote Monitoring & Management), MSPs offer real-time monitoring of networks and endpoints, identify anomalies early, and ensure smooth IT performance.
Compliance & Governance: Meeting compliance requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS can be time-consuming. MSPs help automate audits, maintain logs, and ensure your business stays compliant.
Productivity & Collaboration Tools: MSPs manage and support platforms like Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and unified communication systems; enabling seamless collaboration across teams, especially in remote-first environments.
Managed IT Support Services (Helpdesk): 24/7 technical support, remote issue resolution, and break/fix support are core to MSP value. This ensures your users get quick help without burdening your internal IT team.
Managed Print Services: For industries that rely heavily on documentation, MSPs provide print management, secure printing, and supply automation to improve efficiency and reduce print-related costs.
What are the different types of MSPs?
Managed Service Providers vary in focus and service depth. Understanding these distinctions can help businesses choose the right partner:
- Pure‑play MSPs: These providers focus on core IT monitoring and support functions, such as network performance monitoring, application uptime reporting, and remote troubleshooting. They offer streamlined service with minimal overhead and are suited for SMBs seeking essential IT operations.
- Staffing Legacy MSPs: Targeting mid-market and enterprise clients, these MSPs offer a broad service portfolio, including infrastructure management, software deployment, and help desk services. They often maintain internal teams and legacy systems to support varied IT needs.
- High‑level MSPs: These top-tier providers serve enterprises and large organizations, offering comprehensive, end‑to‑end IT outsourcing. Their services span security, cloud, automation, compliance, and infrastructure, designed for full-stack IT management.
- MSSPs (Managed Security Service Providers): These specialists focus primarily on cybersecurity services; such as SIEM monitoring, intrusion detection, vulnerability assessments, firewall management, and dedicated SOC operations. Some MSPs now integrate these into broader offerings.
- Co‑Managed IT Service Providers (Co‑MITs): These MSPs partner with existing internal IT teams to share responsibilities; handling overflow, specialized projects, or niche tasks, while retaining in‑house control over core systems. They add flexibility and enhanced capability without fully outsourcing.
What challenges do MSPs face?
Managed service providers operate in a highly demanding environment. As they grow their customer base and expand services, several operational and strategic challenges begin to surface.
- Difficulty in Scaling Operations: Adding new clients is easy. Scaling service delivery is not. Many MSPs lack standardized processes or automation to support growth, leading to missed SLAs and increased pressure on internal teams.
- Too Many Tools, Not Enough Visibility: To meet varying client needs, MSPs adopt multiple tools across different categories. But with every new tool comes more data silos, alert noise, and integration overhead. Managing everything across disconnected platforms slows down delivery.
- Staff Shortages and Retention Issues: Attracting and retaining skilled IT professionals is a constant challenge. With evolving tech landscapes, teams must stay trained, certified, and motivated.
- Rising Security Expectations: MSPs are expected to offer full-stack protection, from endpoint to cloud. But not all providers are equipped to meet modern security standards or respond to evolving threats like ransomware, phishing, and insider risks.
- Handling Diverse Client Requirements: Each client brings different technologies, processes, and compliance needs. Without a flexible architecture and repeatable playbooks, servicing them becomes a resource-heavy exercise.
- Adapting to New Technology Trends: Cloud-first, AI-powered, and remote-friendly solutions are now the norm. But not all MSPs are ready to pivot quickly. Staying current without disrupting existing services is a tight balancing act.
- Bridging Business and IT Expectations: Clients want more than technical fixes; they want strategic alignment. MSPs often struggle to move from a reactive support role to a proactive partner delivering measurable business value.
- Proving Value Without Dropping Prices: As competition grows, clients tend to compare providers based on pricing. MSPs must justify their costs through outcomes, not just uptime, and show continuous service improvement.
- Standing Out in a Crowded Market: Many MSPs offer similar services with similar messaging. Without a clear differentiator or strong brand presence, even technically strong providers find it hard to attract the right clients.
How do you choose the right MSP?
Assessing an MSP involves more than reviewing services, it demands deep evaluation across credibility, capabilities, and future fit. Here's a refined checklist based on industry standards:
- Verify MSP Credibility: Review third-party ratings (e.g., G2, Trustpilot) and case studies to gauge credibility and consistency. Check membership in agent communities, partner programs, and certifications, which signal ongoing engagement in the MSP segment.
- Align Pricing with Value: Compare service pricing with the value delivered, not just salary or hours billed. Ask for optimized processes or automation benefits to demonstrate ROI, rather than just time-based billing.
- Gauge Technology Integration (Post-M&A Risks): MSPs formed through mergers or acquisitions may operate siloed tools and fragmented teams. Seek providers with built-in platforms and cohesive workflows; not patchworks of acquisitions.
- Evaluate Operational Strength: Ask how they onboard new clients: discovery, transition, training, and escalation paths matter for smooth operations. Check SLA structures, uptime guarantees, escalation timelines, and renewal mechanisms.
- Assess Expertise & Technical Depth: Confirm expertise across your tech stack, verticals, and anticipated future needs. Look for vCIO capabilities or strategic advisory support if relevant. Examine certifications, integrator partnerships, and documented technical success stories.
- Review Security & Compliance Protocols: Ensure the MSP implements security best practices: regular patching, penetration testing, access controls, and audit logs. Verify compliance readiness across HIPAA, GDPR, ISO standards, with data protection measures in place.
How does MSP pricing work?
MSPs price their services based on the scope and nature of support they provide. Once the proposal is finalized, the cost is determined by the underlying components; ranging from device count to user volume and service depth. Here are the common pricing models you’ll come across:
- Pay-as-You-Go: Clients are billed only for the services they consume. This flexible model suits businesses with fluctuating IT needs or those testing MSP services before long-term engagement.
- Per-Device: A flat rate is charged for each device managed—be it desktops, servers, routers, or mobile devices. This model offers predictable billing and is easy to scale as the infrastructure grows.
- Per-User: Here, the pricing is calculated per employee or user account, covering all devices used by the individual. It's ideal for businesses with mobile or remote workers using multiple endpoints.
- All-Inclusive (Flat Fee): This model covers a broad range of services under one monthly or annual cost. It offers simplicity and cost control, especially for businesses looking for end-to-end IT support.
Note: While annual plans are available, most MSP engagements follow a monthly billing cycle for better cost tracking and service adaptability.
MSP vs In-House IT: What are the key differences?
Choosing between a managed service provider (MSP) and building an in-house IT team comes down to a balance of cost, expertise, scalability, and control. MSPs offer the advantage of predictable monthly spending, thanks to their subscription-based pricing. This reduces the burden of fixed salaries, ongoing training, and infrastructure maintenance. Since MSPs work with multiple clients, they bring in broader expertise, access to updated technology stacks, and awareness of evolving cybersecurity practices; something in-house teams may struggle to keep up with.
Another key difference is scalability. MSPs are built to expand with your business, offering 24/7 support, proactive monitoring, and flexibility in coverage. This is particularly useful for growing companies or those operating across time zones. In-house IT, on the other hand, is more integrated with the company’s culture and internal workflows. Internal teams may respond faster to context-specific issues and adapt better to internal policies and tools.
While MSPs work on service level agreements (SLAs) that enforce uptime, response, and resolution metrics, in-house teams often rely on internal expectations without clear benchmarks. However, MSPs might require time to understand your business’s internal systems and workflows, especially if those are unique or legacy-driven. That’s why many businesses opt for a hybrid approach—letting MSPs handle core IT operations, while internal staff focus on aligning technology with broader business strategies.
How do MSP solutions help businesses grow?
MSP solutions drive business growth by streamlining client management and automating repetitive tasks. They bring together essential IT functions, like RMM, cybersecurity, help desk, and reporting; under one platform, enabling faster service delivery. With intuitive tools, technicians can focus on learning adjacent skills while maintaining consistent service quality. This unified approach not only boosts efficiency but also helps MSPs scale operations without adding overhead.
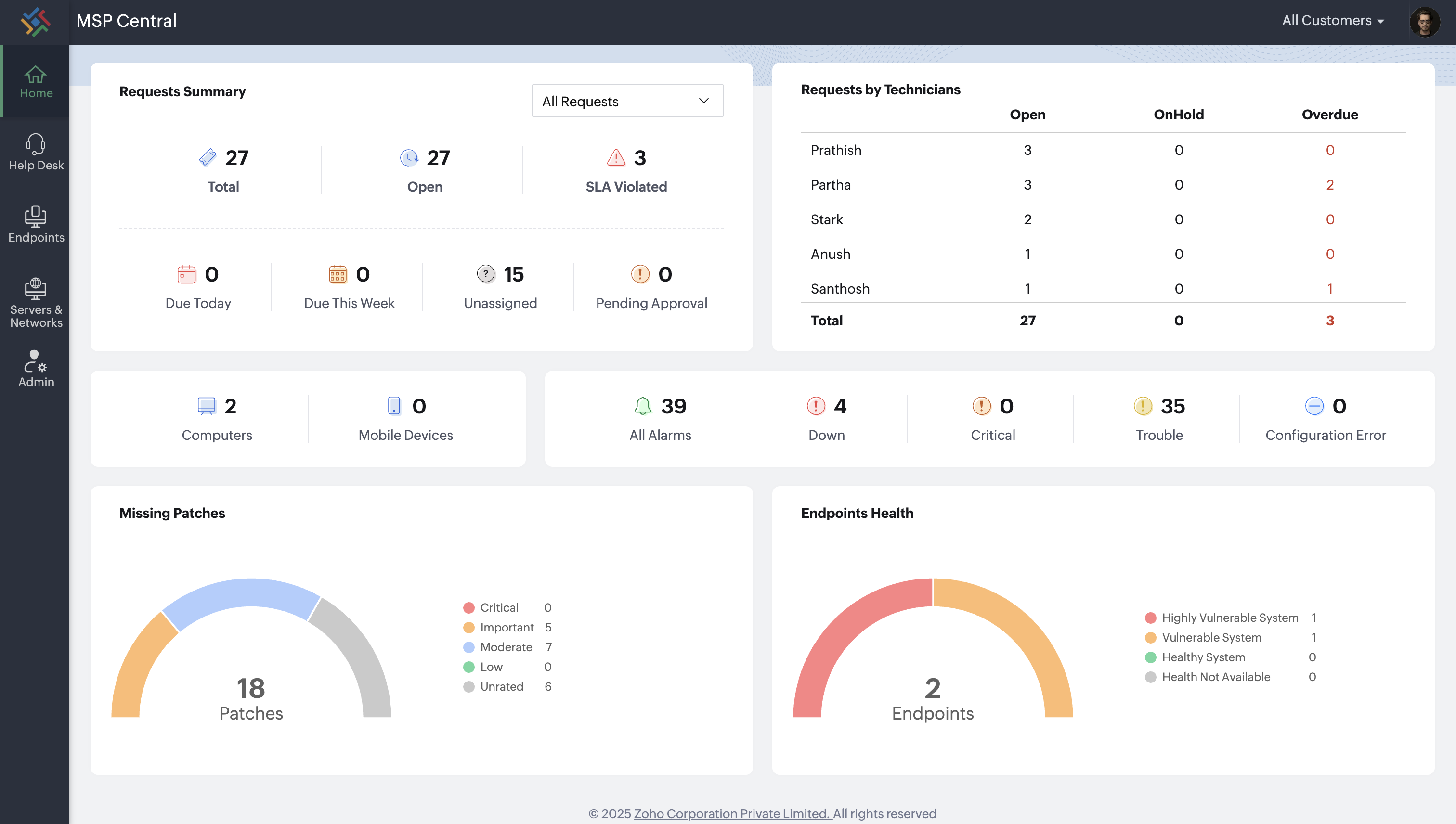
Introducing MSP Central
While MSP solutions have already proven to accelerate growth, platforms take it a step further. MSP Central, an IT management platform; brings together multiple tools into one unified space; breaking down silos and creating a single source of truth. With integrated data, service delivery becomes faster, more transparent, and easier to manage. It’s not just about streamlining operations, but enabling growth at scale with clarity and control.
Explore how MSP Central can redefine your service delivery.
