Server domains/IP addresses should be whitelisted in firewall, proxy, anti-virus, web filters etc. Find the list of domains here. To verify domain reachability - Open your browser, type https://domain name and check whether the https requests are successful without requiring any user intervention.
To make agent communicate via proxy - proxy should be configured for remote office. This can be done by navigating to Agent -> Remote Offices -> Edit Remote Office.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is the security protocol used for encrypting the communication between web servers and endpoints. Support for older version of versions 1.0 and 1.1 are withdrawn due to security concerns. TLS1.2 is made mandatory for communicating with the cloud server (Refer here). In some legacy windows devices such as windows 7, windows server 2008 R2, windows server 2012, TLS1.2 is not enabled by default. Navigate to the following link to enable TLS1.2.
Some Proxies might intercept the agent-server communication by providing their own self-signed certificate. In such cases, a proxy root certificate has to be installed in the machine's trust store. Manual Certificate Installation Steps, Certificate Installation via GPO steps are attached below.
Root Certificates are used to authenticate a website's identity and enable encrypted communication with the server. Windows Root Certificate Program enables trusted root certificates to be distributed automatically in Windows.
Some of the reasons for the missing root certificates:
| Registy Path | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Microsoft\SystemCertificates\AuthRoot |
| Registry Name | DisableRootAutoUpdate |
| Registry Value | 1 [REG_DWORD] |
The following root certificates are used to authenticate the server domains. If the root certificate is missing in few machines, the certificate can be installed manually.
Steps to import root certificate manually
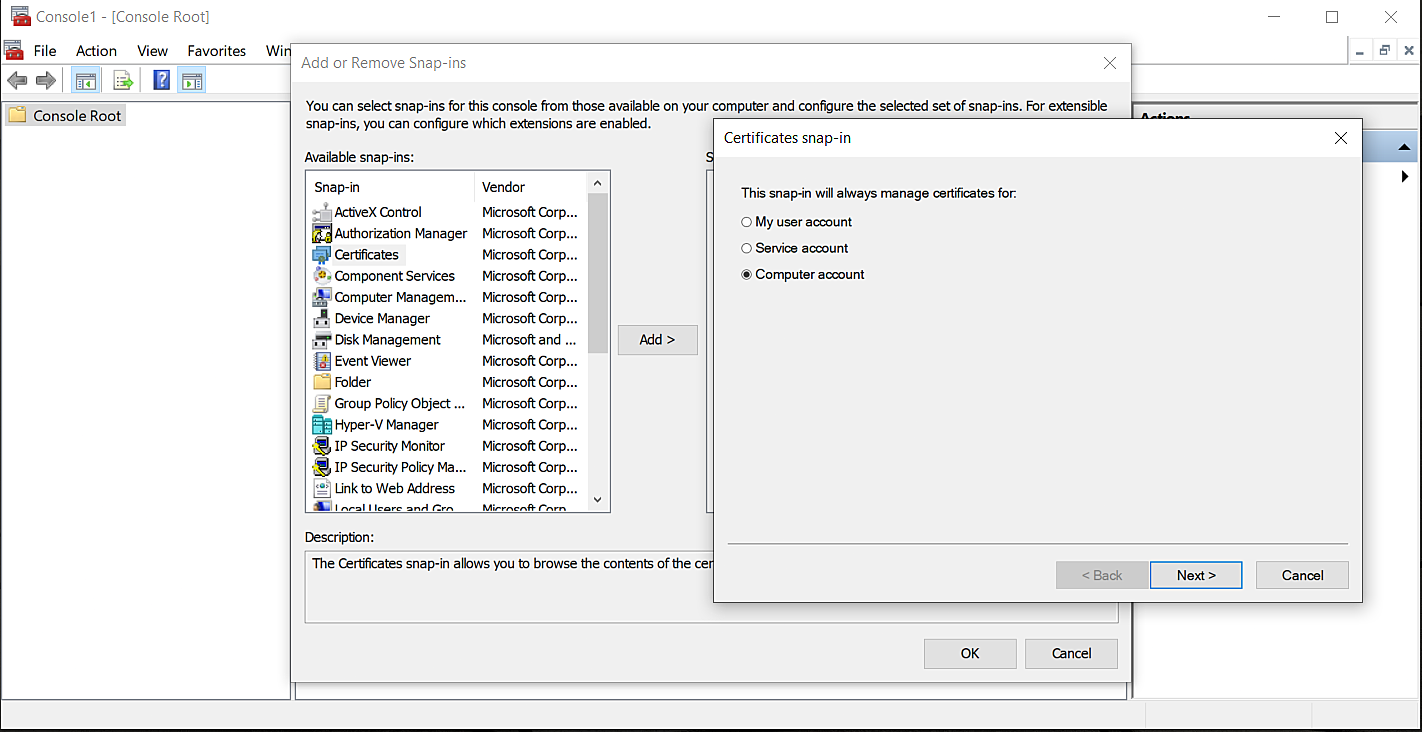
If root certificate is missing in many machines, certificates can be installed via GPO. Refer the following steps for Certificate Installation Via GPO.