Self-Service Privilege Elevation for Windows and Windows Domain
PAM360 empowers administrators to configure Self-Service Privilege Elevation on target machines, enabling end-users to execute specific files or applications (.cmd, .exe, .msc, .msi, and .bat) with elevated account privileges, without ever disclosing the credentials of the privileged account. Refer to this document to learn more about the Self-Service Privilege Elevation in PAM360.
Caution
Before configuring Self-Service Plus Elevation, ensure that the PAM360 Agent with the Self-Service Privilege Elevation module is installed on the target machine where user privilege elevation is intended. This is a mandatory prerequisite for enabling elevation capabilities on the respective system.
Refer to the following links to know more about configuring the Self-Service Privilege Elevation in Windows and Windows Domain based environments:
- Setting Up Self-Service Privilege Elevation
- Managing the Self-Service Privilege Elevation Configuration
- Elevating Privileges Using Self-Service Privilege Elevation
- Troubleshooting Tips
1. Setting Up Self-Service Privilege Elevation
Follow the below steps to configure Self-Service Privilege Elevation for Windows or Windows Domain resources:
- Log in to PAM360 and navigate to Admin >>
Privileged Elevation >>Allowed Apps/Scripts. Here, you can view the list of all applications currently added for privilege elevation.
- To register a new application or file, click Add.
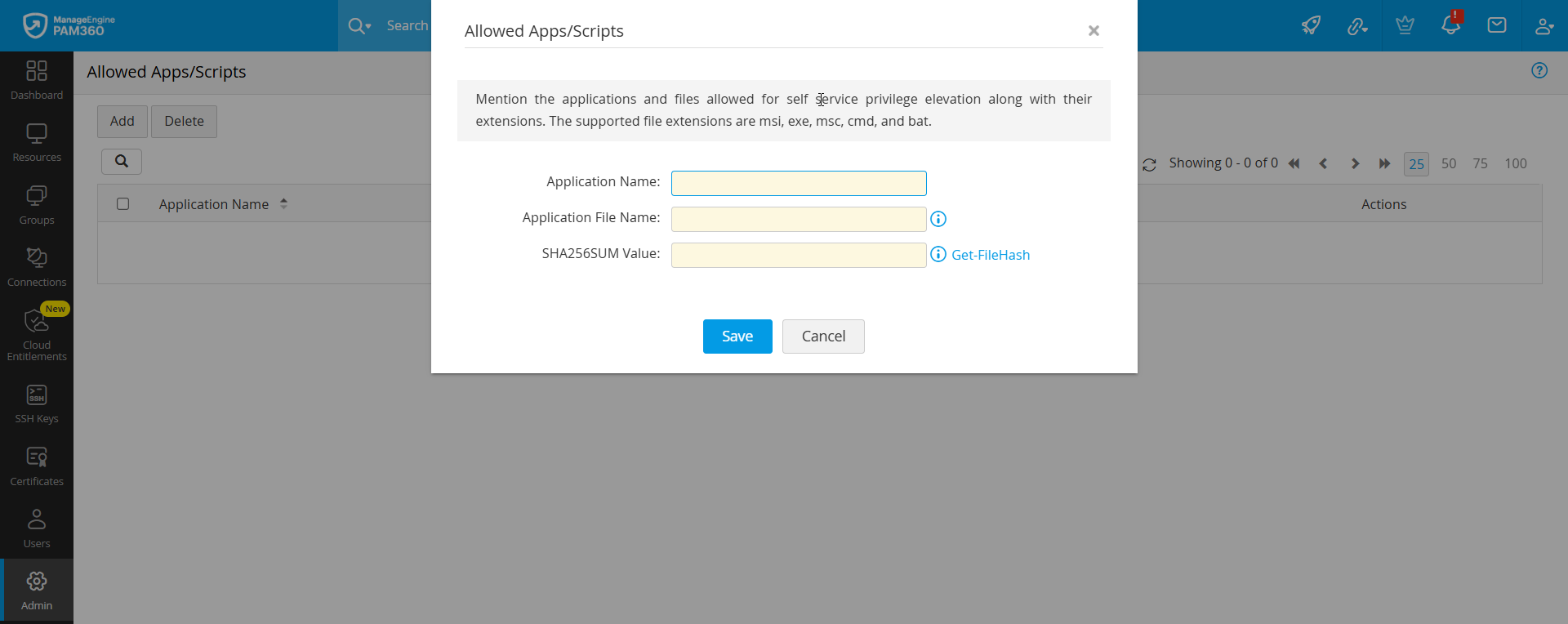
- In the Allowed Apps/Scripts dialog box that opens, provide the following details:
- Application Name: A user-friendly name for the application.
- Application File Name: The exact filename on the privileged resource with its extension (e.g., .exe, .cmd, .msc, .msi, .bat).
- SHA256 Hash Value: The cryptographic hash of the application file. Learn how to obtain it or use this application to generate it.
- Application Name: A user-friendly name for the application.
- Click Save to finalize the application registration.
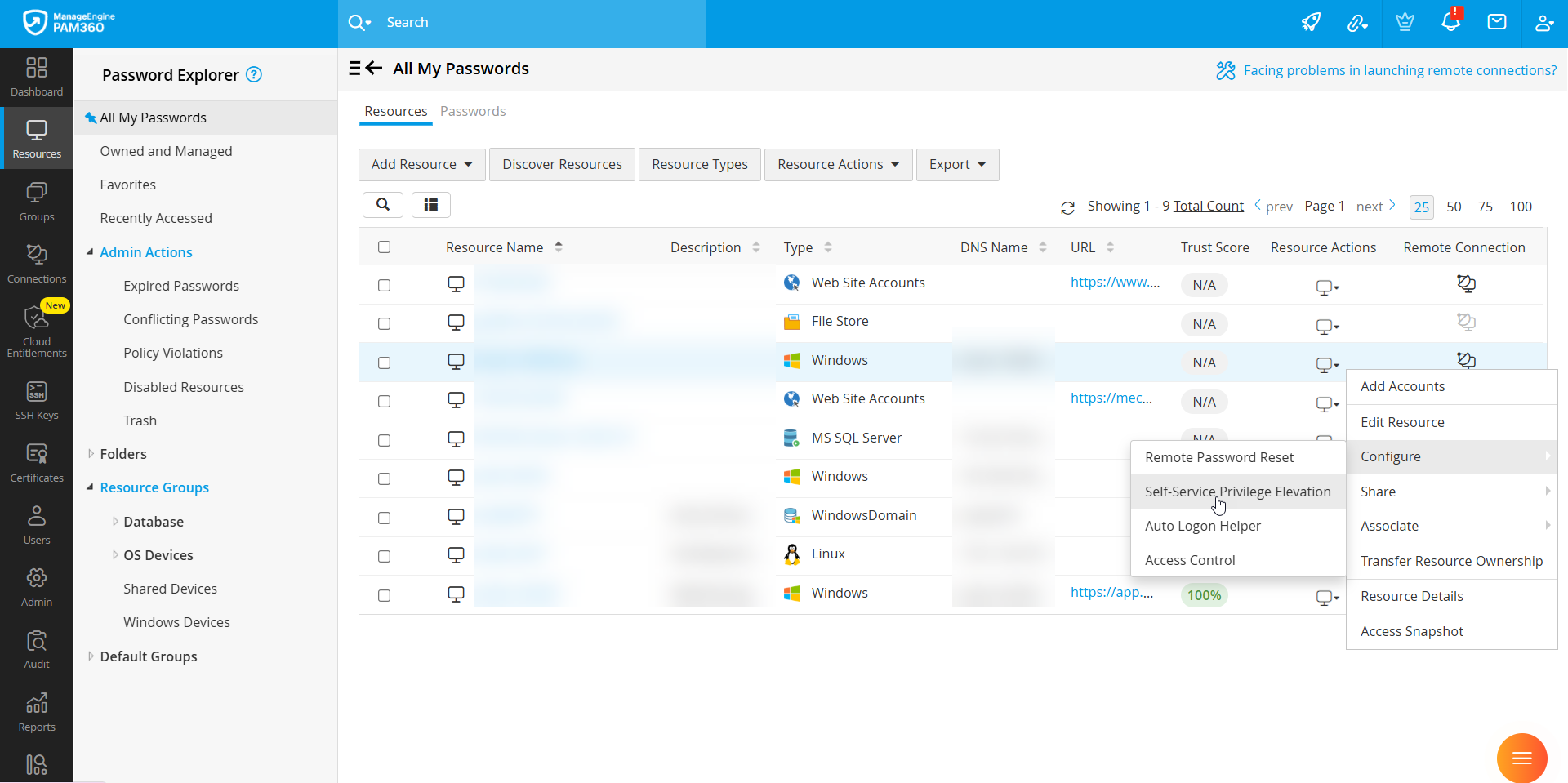
- Now, navigate to Resources >> All My Passwords >> Resources to associate the application or scripts with the privileged resource.
- Locate the desired resource for which the Self-Service Privilege Elevation to be configured. Click the Action icon next to it and click Configure >> Self-Service Privilege Elevation.
Caution
Ensure that the DNS name of the resource is specified. The configuration cannot proceed if it is left blank.
- In the pop-up configuration window, choose the Account Type:
- Domain Account: Select both the Domain Name and Account Name to allow privilege elevation via a domain account.
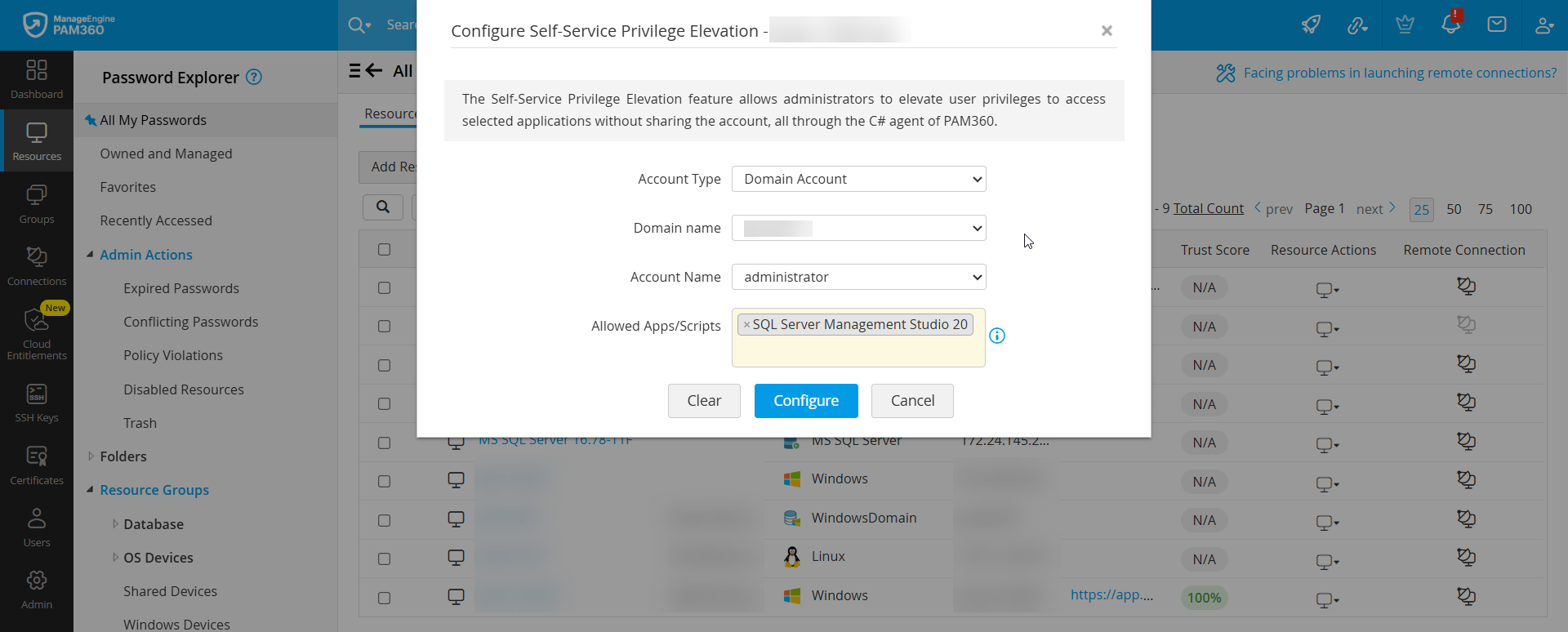
- Local Account: Select the Account Name of the privileged local account.

- Domain Account: Select both the Domain Name and Account Name to allow privilege elevation via a domain account.
- Under Allowed Apps/Scripts, list the applications that users are permitted to launch with elevated privileges. Examples include: cmd.exe, services.msc, etc.
- Click Configure to apply the configuration.
Once configured, the selected account will be used for privilege elevation across all agent-installed endpoints. When Access Control is enabled for an account, Self-Service Privilege Elevation will take precedence over password-based access control.
2. Managing the Self-Service Privilege Elevation Configuration
- To remove the privilege elevation configuration for a resource, click Clear in the Self-Service Privilege Elevation configuration pop-up.
- To delete a previously registered application, navigate to Admin >> Privileged Elevation >> Allowed Apps/Scripts, select the relevant applications, and click Delete.
- To view a list of resources with Self-Service Privilege Elevation configured, go to Reports >> Query Reports >> Resources, and search for Resources with self-service privilege elevation configuration. Two custom reports are also available under Reports >> Custom Reports: Authorized App Privilege Elevated and Unauthorized App Elevation Triggered. These reports help administrators monitor and audit all privilege elevation activities across the network.
3. Elevating Privileges Using Self-Service Privilege Elevation
Once Self-Service Privilege Elevation is configured, users can self-elevate privileges by following the steps below:
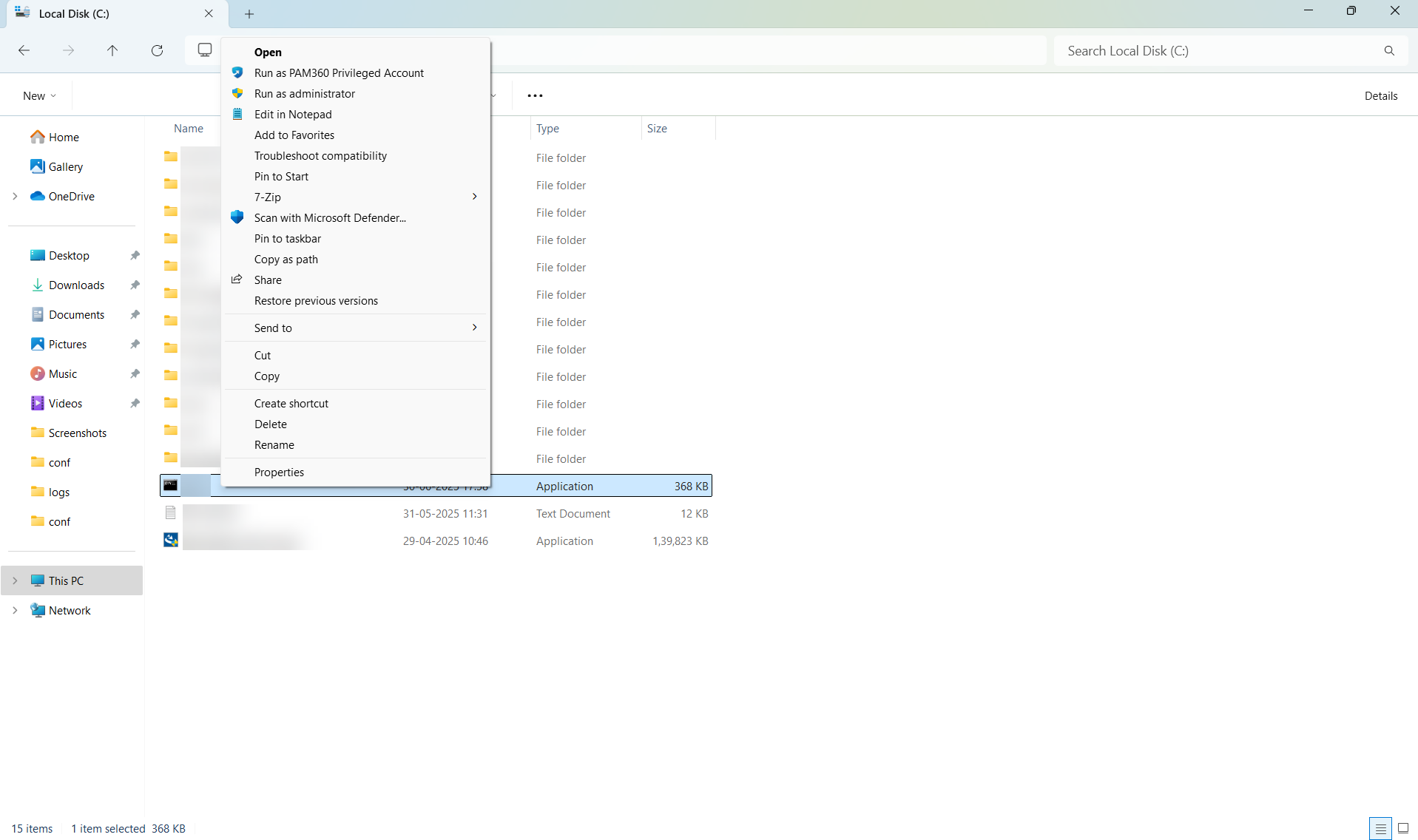
- Initiate a remote session and log in to a resource where Self-Service Privilege Elevation is enabled via PAM360.
- Right-click the desired application or file (e.g., .exe, .msc, .msi, .cmd, .bat) that has been authorized for privilege elevation and select Run as PAM360 Privileged Account.
- In the pop-up that opens, provide a mandatory reason for the elevation request and click Elevate.
The selected application or file will now run with elevated privileges, as defined by the administrator.
4. Troubleshooting Tips
1. Error: The directory name is invalid
Issue: This error occurs when attempting to elevate an application located in user-specific directories such as Downloads or Documents, which are linked to the currently logged-in user's profile.
Solution: Move the executable file (.exe) to a common or shared directory that is accessible by all users, such as D:\ or E:\. This allows the application to be accessed and elevated correctly during the SSPE process, regardless of the user profile currently in use.
2. Error: The requested operation requires elevation
Issue: This error appears when Windows fails to trigger the User Account Control (UAC) prompt during SSPE, causing the privilege elevation attempt to fail.
Solution: To resolve this, update the Agent.conf file located in the PAM360 installation directory by adding the following system property:
executeSSPEviaTerminal=cmd | powershell | false
cmd - Executes the application with elevated privileges using Command Prompt.
powershell - Executes the application with elevated privileges using PowerShell.
false - Uses the default SSPE mechanism for elevation.
Note: In previous build versions, the corresponding property name was: executeSSPEviaCMD=True | False