Adding SQL server
Key features of SQL auditing in EventLog Analyzer
DDL/DML monitoring
- Comprehensive tracking of data definition language (DDL) and data manipulation language (DML) activities.
- Monitors user actions, executed statements, and application details to provide a complete audit trail.
Advanced auditing
- Scheduled collection of detailed server and database information.
- Generates reports for insights into database structure, activity, and security changes.
Column integrity monitoring
- Tracks changes at the column level in tables, including both old and updated values during modifications.
- Ensures granular visibility into table data updates for enhanced integrity and accountability.
Risk posture analysis
- EventLog Analyzer provides Risk Posture Analysis by verifying various configuration details, identifying potential security risks. For more details, visit this page.
Prerequisites
1. Supported SQL server versions
- Windows SQL Server 2012 and above
2. Windows application log file size
Once a SQL server is configured in EventLog Analyzer, the audit policies are automatically applied to the SQL server. The SQL server then starts generating logs in the Windows Application Logs, which are fetched by EventLog Analyzer. However, if the event generation rate is too high, Windows may overwrite older logs before EventLog Analyzer can collect them. To prevent data loss, it is necessary to increase the log file size based on log inflow. Below are the recommended file size settings based on log volume.
Device Monitoring Interval: 10 mins or real time
| Logs /second |
Application File Size |
| 250 logs/sec |
1.0 GB |
| 500 logs/sec |
2.0 GB |
| 750 logs/sec |
3.0 GB |
| 1000 logs/sec |
4.0 GB |
| 2000 logs/sec |
8.0 GB |
3. SQL server discovery
EventLog Analyzer automatically discovers available SQL servers on the network allowing you to easily select the instances and add them to the product. However, for this to work, the SQL Server Browser Service must be running and able to communicate over port 1433.
4. SQL server configuration
- Ensure SQL server machine is reachable from the EventLog Analyzer server.
- Ensure TCP/IP port is enabled. To enable TCP/IP, follow the given steps.
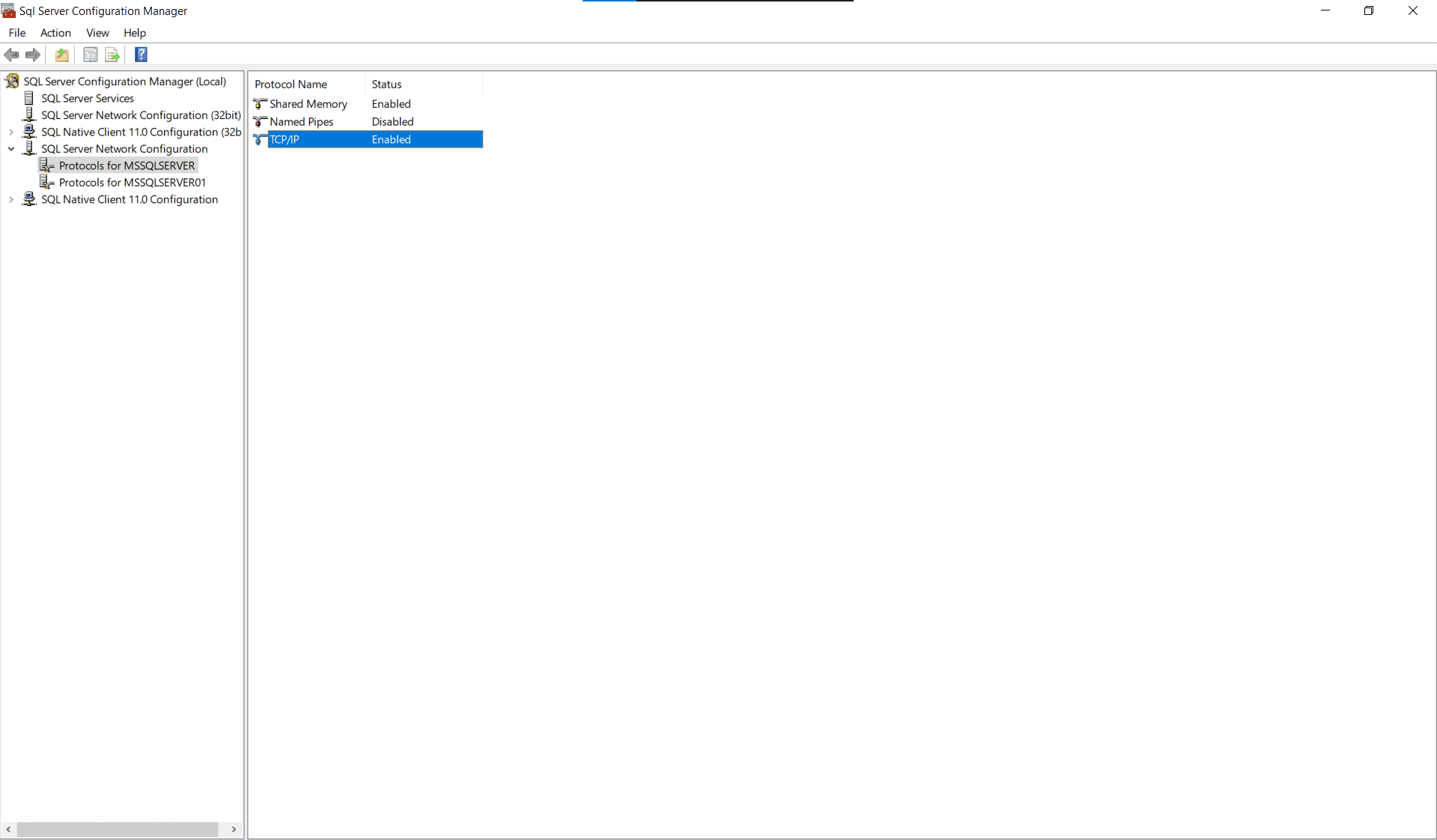
- Navigate to the SQL server Hosting machine
- Navigate to SQL server Configuration Manager → SQL server Network Configuration.
- Right click on TCP/IP and enable it.
- Configure a valid port number. To do so right-click on Properties and enter the port number.
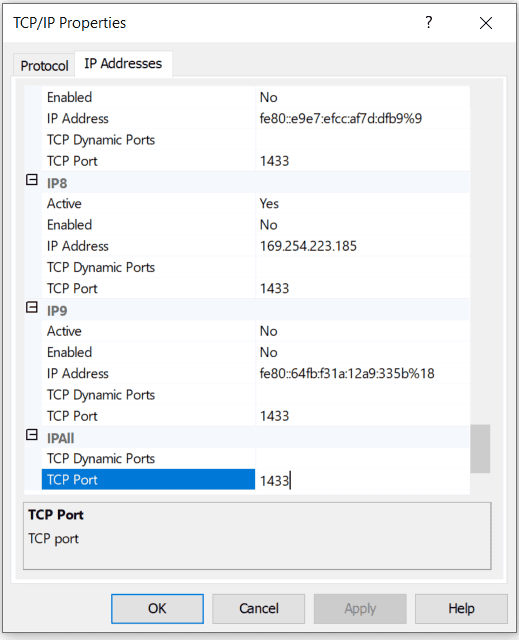
- Ensure that the TCP/IP port used by SQL server is reachable from EventLog Analyzer. Verify that the firewall is not blocking the port to allow proper communication and data collection.
- Ensure that the user account used for SQL server configuration in EvenLog Analyzer has all the required permissions as detailed in here.
Steps to configure SQL server instance in EventLog Analyzer
To configure and monitor SQL server logs, follow these steps:
- Navigate to Settings → Log Source Configuration →Database Audit →SQL Servers to view monitored SQL servers.
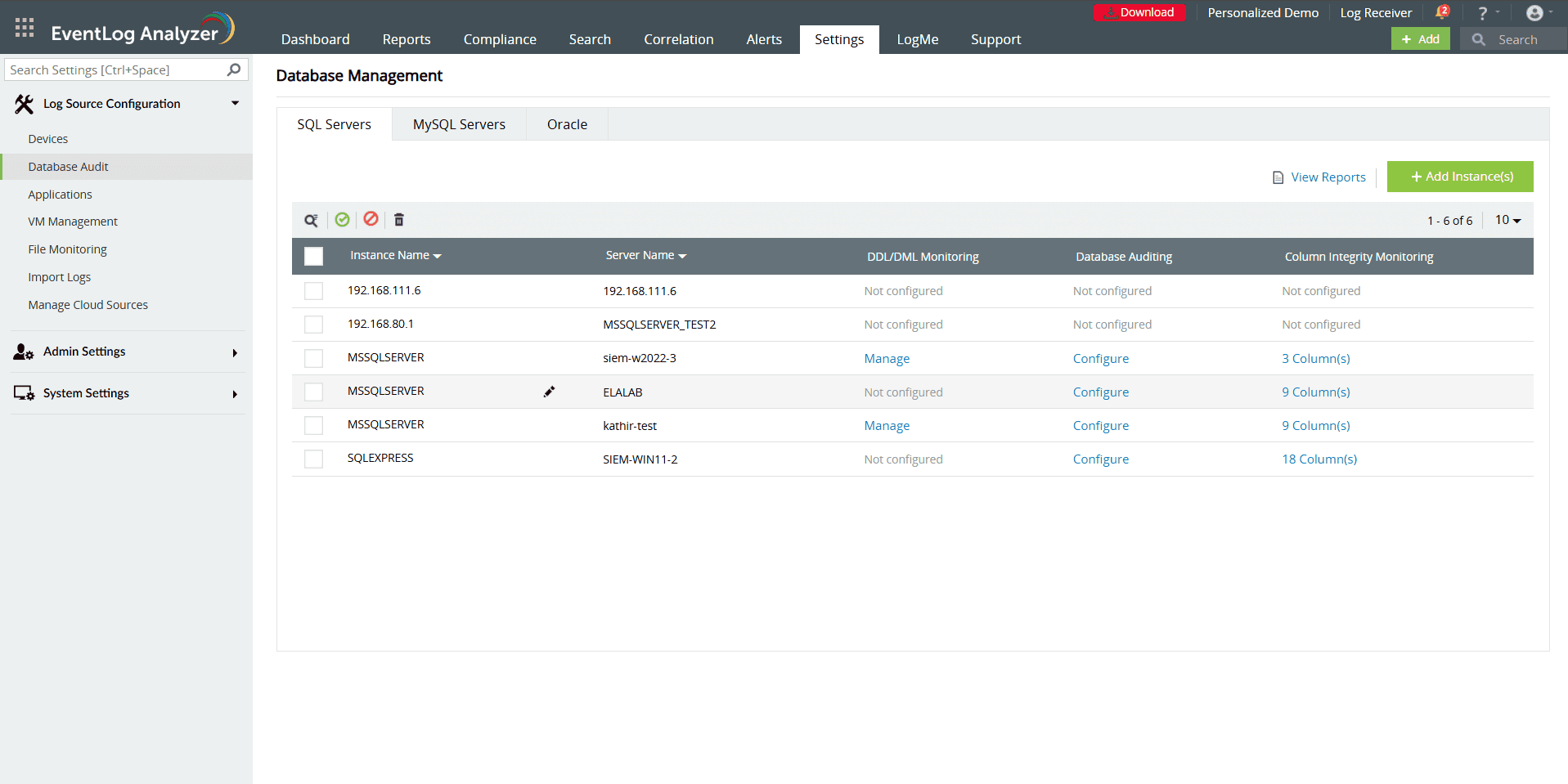
- To add a new SQL server, click Add Instance.
- Select the instance(s) to configure and click Add.
- Once added, click Update in the Actions column to update the device and SQL server credentials.
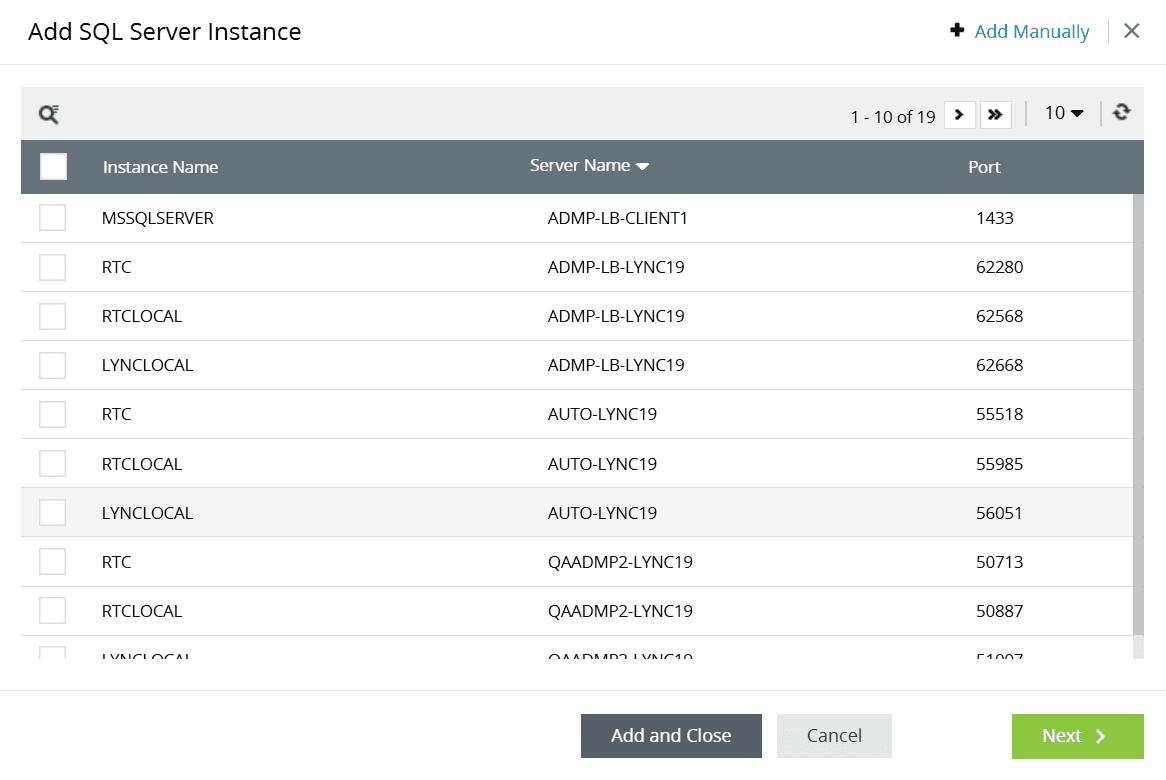
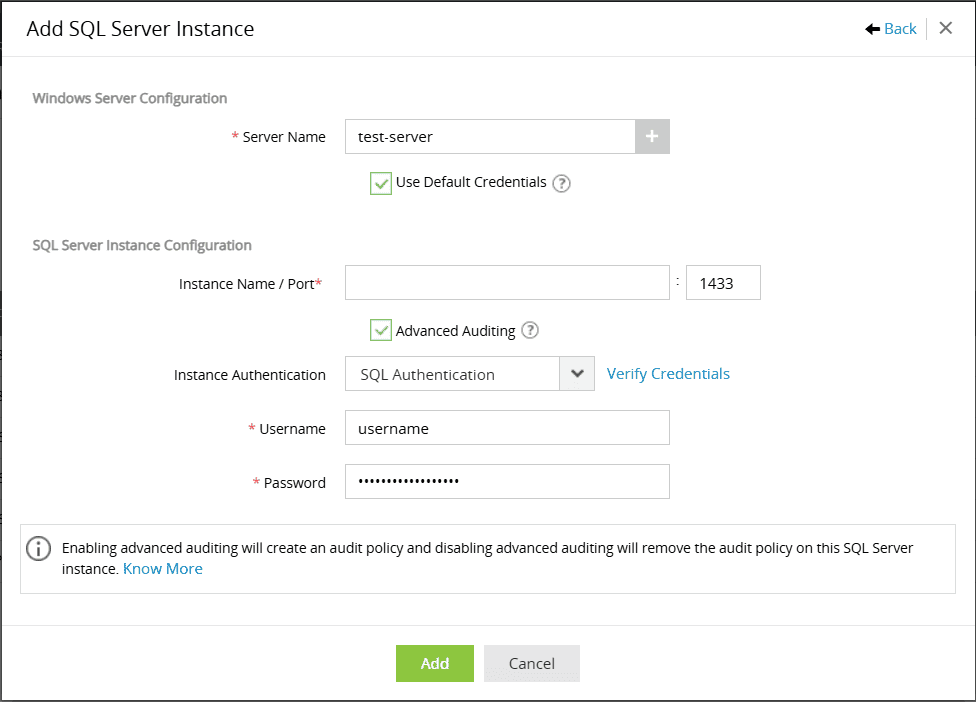
Alternatively, you can also use Add Manually option to manually configure the instance(s). To manually configure the SQL server, follow these step:
- Windows server configuration
- Select the Windows server hosting the SQL server and enter valid credentials. You can also use default credentials.
- SQL server instance configuration
- Enter the Instance Name (optional), Port and authentication credentials.
- Advanced Auditing
- When you enable Advanced Auditing, the system creates the audit policy in the SQL server.
- Disabling it removes the audit policy on selected SQL server instances.
- If you wish to keep advanced auditing disabled, you can manually configure the audit policy and EventLog Analyzer would still fetch the logs from the device. To configure the audit policy manually, click here.
- Instance Authentication
- Select the instance authentication method from the drop-down.You can either choose Windows authentication or SQL authentication.
- Enter valid credentials and click Add.
Minimum permissions for creating audits
Note: These permissions are only required for enabling, disabling, deleting, or creating audits, not for the actual auditing.
| Server roles |
User mapping |
Securables |
- public
- server admin
|
public |
- Connect SQL
- Alter any server audit
|
SQL server auditing mechanism in EventLog Analyzer
DDL/DML monitoring
- When Advanced Auditing is enabled for an instance, the system creates a server-level audit specification in the SQL server instance with the following audit action types:
- SCHEMA_OBJECT_ACCESS_GROUP
- BACKUP_RESTORE_GROUP
- DATABASE_ROLE_MEMBER_CHANGE_GROUP
- SERVER_ROLE_MEMBER_CHANGE_GROUP
- FAILED_LOGIN_GROUP
- SUCCESSFUL_LOGIN_GROUP
- DATABASE_CHANGE_GROUP
- DATABASE_OBJECT_CHANGE_GROUP
- DATABASE_PRINCIPAL_CHANGE_GROUP
- SCHEMA_OBJECT_CHANGE_GROUP
- SERVER_PRINCIPAL_CHANGE_GROUP
- LOGIN_CHANGE_PASSWORD_GROUP
- SERVER_STATE_CHANGE_GROUP
- The system uses Application type events collected from the corresponding Windows device for this auditing mode.
- The following report groups (Reports tab → Applications → SQL Server) are available with this auditing mode:
- SQL Server Events
- SQLServer Trend Report
- DDL Auditing Report
- DML Auditing Report
- Auditing Account Management
- Auditing Server Report
- Attack Reports
- Additional Security Reports
Note: Advanced Auditing must be enabled for the server-level audit specification to be created automatically. However, if created manually, the system will fetch the required logs even if Advanced Auditing is disabled in Eventlog Analyzer.
Database auditing
- When Advanced Auditing is enabled for an instance, the system executes queries nightly at 11 PM to collect events.
- The following reports (Reports → Applications → SQL Server→ Advanced Auditing Reports) are available with this auditing mode:
- Logins Information Report
- Table Information Report
- Table Update Report
- Server Information Report
- Waits Information Report
- Blocked Processes Report
- Schema Change History
- Object Change History
- Security Changes Report
- Permissions Information Report
- Last Backup of Database
- Last DBCC Activity
Note: The queries will only fetch logs if Advanced Auditing is enabled.
Column integrity monitoring
- When Column Integrity Monitoring is configured, EventLog Analyzer creates a trigger in the SQL server instance. This trigger automatically writes the events in the Event Viewer when someone modifies the monitored column value of the given table (i.e., executes an UPDATE query).
- The Column Integrity Monitoring report shows:
- Who changed the value
- When the value was changed
- The database and table where the change occurred
- The old and new values
- Choose columns for monitoring carefully, as triggers are performance-intensive operations.
- The predefined report for this action can be viewed in the following path: Reports → Applications → SQL Server→ Advanced Auditing Reports → Column Modified Reports
Prerequisites for column monitoring
- Advanced Auditing must be enabled initially to create a Trigger in the SQL server.
- The table must have a primary key for the "AFTER TRIGGER" to function.
- Column cannot have text, ntext, or image as the data type.
Minimum permissions required for creating triggers
Note: These permissions are only needed for deleting/creating triggers, not for the actual auditing.
| Server roles |
User mapping |
Securables |
- public
|
- public
- db_securityadmin
- db_ddladmin
Map all databases to be added for Column integrity monitoring with the above permissions.
|
- Connect SQL
- Alter Trace
|
Steps to create a SQL server audit object manually
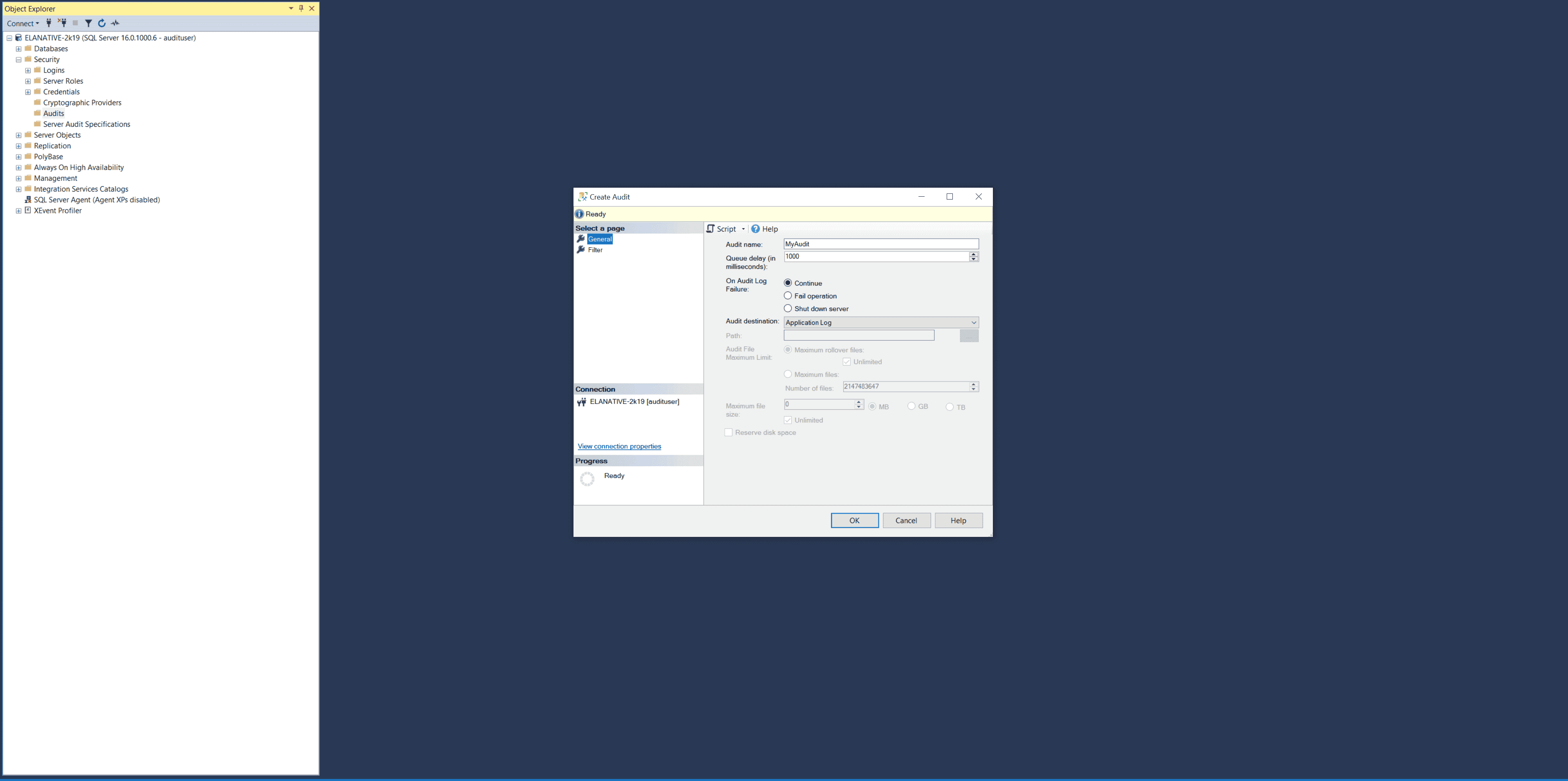
- Open MSSQL Server Management Studio and navigate to Object Explorer.
- Expand the Security node.
- Right-click the Audits folder and choose New Audit.
- In the Create New Audit page:
- Enter a suitable name in the Audit Name field.
- Select Application Log as the Audit Destination.
- Keep other settings as default.
- Click Save.
- Right-click the newly created audit and select Enable Audit.
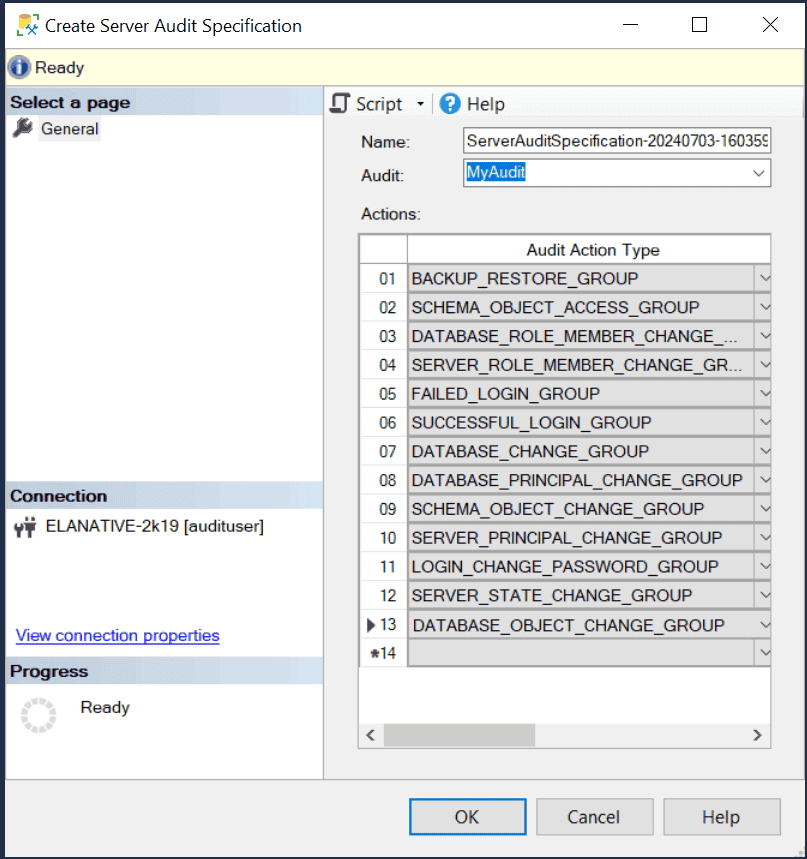
- Right-click the Server Audit Specification folder and choose New Server Audit Specification.
- In the Create Audit Specification window,
- Select the audit created in step 4 from the Audit field.
- Add the following audit action types, and click OK.
- SCHEMA_OBJECT_ACCESS_GROUP
- DATABASE_ROLE_MEMBER_CHANGE_GROUP
- SERVER_ROLE_MEMBER_CHANGE_GROUP
- FAILED_LOGIN_GROUP
- SUCCESSFUL_LOGIN_GROUP
- DATABASE_CHANGE_GROUP
- DATABASE_OBJECT_CHANGE_GROUP
- DATABASE_PRINCIPAL_CHANGE_GROUP
- SCHEMA_OBJECT_CHANGE_GROUP
- SERVER_PRINCIPAL_CHANGE_GROUP
- LOGIN_CHANGE_PASSWORD_GROUP
- SERVER_STATE_CHANGE_GROUP
- BACKUP_RESTORE_GROUP
- Right-click on the created Audit Specification and click Enable Server Audit Specification.
 Click here to expand
Click here to expand






