×![]()
×
×![]()
×
×
OS Deployer Architecture: Local & Remote Offices | ManageEngine
Overview
OS Deployer lets you capture a single, standardized Windows image and deploy it across multiple sites. In a WAN setup, the Local Office hosts the primary image repository, while each Remote Office uses a Distribution Server with a PXE service and its own local image store to minimize WAN usage.
- Standardize at scale: Create one golden image for diverse hardware using Hardware-Independent Deployment (HID).
- Save bandwidth: Replicate images from the Local Office to each Remote Office image repository over HTTP/HTTPS.
- Zero-touch rollouts: Deploy via PXE/USB/ISO with automated post-deployment steps (naming, domain/OU, apps).
Architecture diagram
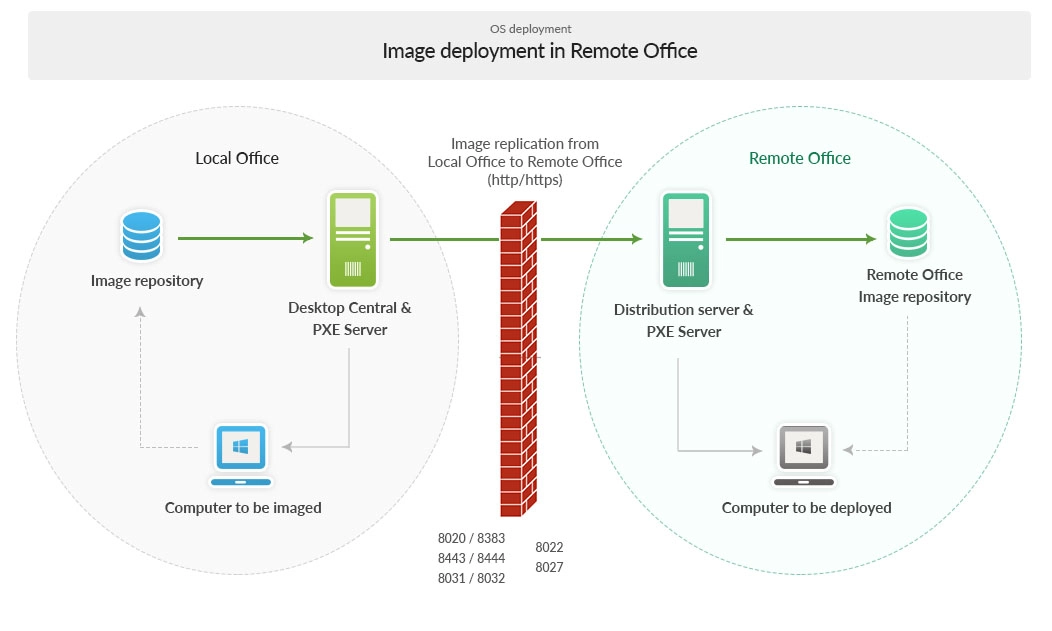
Core components
| Component | Role in the architecture |
|---|---|
| Central Server (Local Office) | Hosts the OS Deployer service, PXE/TFTP services, and the primary Image Repository. |
| Image Repository (Local Office) | Stores captured online/offline images (the “golden” images) that are replicated to remote sites. |
| Distribution Server (Remote Office) | Receives image replicas from the Local Office and serves them to target endpoints within the site. |
| PXE Server (Local/Remote) | Network-boots target devices into WinPE to start zero-touch deployment with driver injection (HID). |
| Remote Office Image Repository | Local cache of replicated images for fast, bandwidth-efficient deployments within the remote site. |
| Target Computers | Devices to be imaged or re-imaged via PXE/USB/ISO; post-deployment tasks complete device configuration. |
End-to-end flow
- Capture: Create the golden image from a reference device (online or offline) and store it in the Local Office image repository.
- Replicate: Replicate images from the Local Office to each Remote Office over HTTP/HTTPS on allowed WAN ports.
- Boot: Targets in the remote site boot via PXE (or USB/ISO) to load WinPE and contact the Distribution Server.
- Deploy: The image is applied from the Remote Office image repository; HID injects the right drivers.
- Post-deployment: Naming, domain/OU join, profile migration, and app/script installs run automatically.
Network ports
Open the following ports between Local and Remote Offices as indicated by the diagram:
Server ports
| Port | Purpose | Type | Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8383 | For communication between the OS Deployer Components / Distribution Server and the OS Deployer server in secured mode. | HTTPS | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
| 8443 | For communication between the OS Deployer Components and the OS Deployer server. | HTTPS | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
| 8384 | For communication between the OS Deployer Components and Distribution server. | HTTPS | Inbound to Distribution server |
| 69, 4011 | TFTP PXE communication between the target machine and OS Deployer server. | UDP | Inbound to OS Deployer server and Distribution server |
Active Directory ports
| Port | Purpose | Type | Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 135 | RPC Endpoint Mapper. | TCP, UDP | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
| 137 | NetBIOS name service. | TCP, UDP | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
| 138 | NetBIOS datagram service. | UDP | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
| 139 | NetBIOS session service. | TCP | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
| 445 | SMB over IP (Microsoft-DS). | TCP, UDP | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
| 389 | LDAP. | TCP, UDP | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
| 636 | LDAP over SSL. | TCP | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
| 3268 | Global Catalog LDAP. | TCP | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
| 3269 | Global Catalog LDAP over SSL. | TCP | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
| 88 | Kerberos. | TCP, UDP | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
| 53 | DNS. | TCP, UDP | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
| 1512 | WINS resolution. | TCP, UDP | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
| 42 | WINS replication. | TCP, UDP | Inbound to OS Deployer server |
Scalability & best practices
- Maintain a clean, patched reference image; recapture after major updates.
- Use Hardware-Independent Deployment (HID) with a curated driver repository for diverse models.
- Stage replication during off-peak hours; leverage site-local deployment to minimize WAN load.
- Pilot in a small device group before broad rollouts; monitor success/failure logs.


 Yes
Yes