How does MFA work?
MFA works by verifying users using authentication factors other than their usernames and passwords.
These authentication factors may be something they know (knowledge factor), something they have (possession
factor), and something they are (inheritance factor).
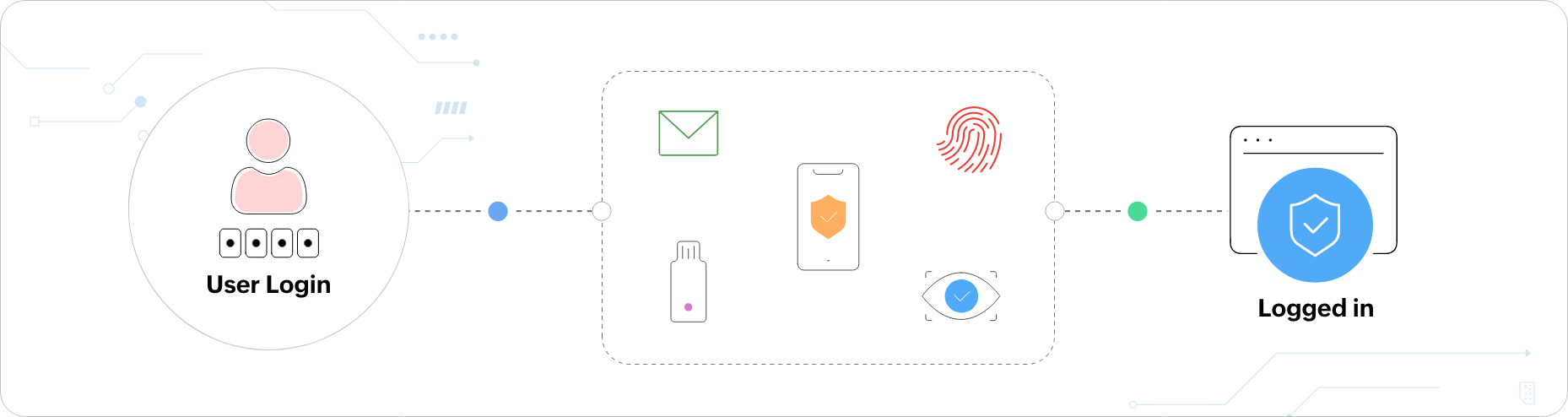
Knowledge factor:
As the name suggests, the knowledge factor includes information that only the
authorized user would know. Some common examples are:
- Passwords
- PINs
- Passphrases
- Answers to security questions
Security questions are not usually recommended since attackers might easily crack them.
Possession factor:
Here, authentication is performed with something the user possesses, like a mobile phone, a physical token,
or a smart card. For example, it could be a code generated via an app on the phone or communicated to the
user through an automated call.
Inheritance factor:
The inheritance factor, being the most secure of the three factors, involves
verifying identities with the help of inherited biometric means, such as:
- Fingerprint scanning
- Facial scanning
- Retinal scanning
- Voice recognition
In recent times, the location factor and the time factor have also gained importance. The location factor verifies
whether subsequent access attempts by a user are not from two completely different, impractical locations. The time
factor checks the user's access request time and challenges them with additional authenticators if the access is
requested at an odd hour.
Why is MFA important and
why should you use it?
Securing resources using just passwords does only the bare minimum to secure identities. There are numerous attacks that a hacker can use to breach passwords—like brute-force attacks, phishing attacks, dictionary attacks, and web app attacks—which is why it's important to implement additional layers of authentication to secure resources.
Users happen to be the weakest links of an organization's security chain. They might unknowingly choose weak passwords, repeat passwords for multiple resources, store passwords in plain sight, or retain the same password for an extended duration. Implementing MFA protects against these user vulnerabilities. So, even if an unauthorized person obtains a user's password, they still cannot gain access to the privileged resources since they would need additional information to complete the subsequent MFA methods.
Privileged accounts, such as admin or C-level executive accounts, are often prone to attacks. If an attacker gets hold of the credentials of any of these accounts, they’ll have access to the most important data and resources in the network, and the repercussions could be irreversible. To reduce risk, organizations must protect their high-risk accounts with additional layers of security.
Deploying MFA not only helps organizations fortify access, but also helps them comply with data regulatory norms, like the PCI DSS, the GDPR, NIST 800-63B, SOX, and HIPAA.
According to global statistics:
- 32% of black hat hackers admit
privileged accounts are their number one way to hack systems.
- 95%
of cybersecurity breaches are due to human error.
- 43% of cyberattacks target small businesses.
- Hackers create 300,000 new malware variants daily.
- Every 39 seconds, a hacker tries to steal
data.
- The average cost of a data breach is approximately
$3.9 million.
What is the difference
between 2FA and MFA?
2FA
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is quite synonymous to MFA. However, as the name suggests, 2FA includes a total of only two authentication factors, whereas MFA does not have any restriction on the number of authentication factors involved.
MFA
MFA is more widely used, as it secures resources better with multiple authentication methods. But for a legitimate user, having to prove their identity daily using multiple authentication methods can cause MFA fatigue. For simple and intelligent MFA, AI and machine learning have been integrated with MFA, birthing adaptive MFA.
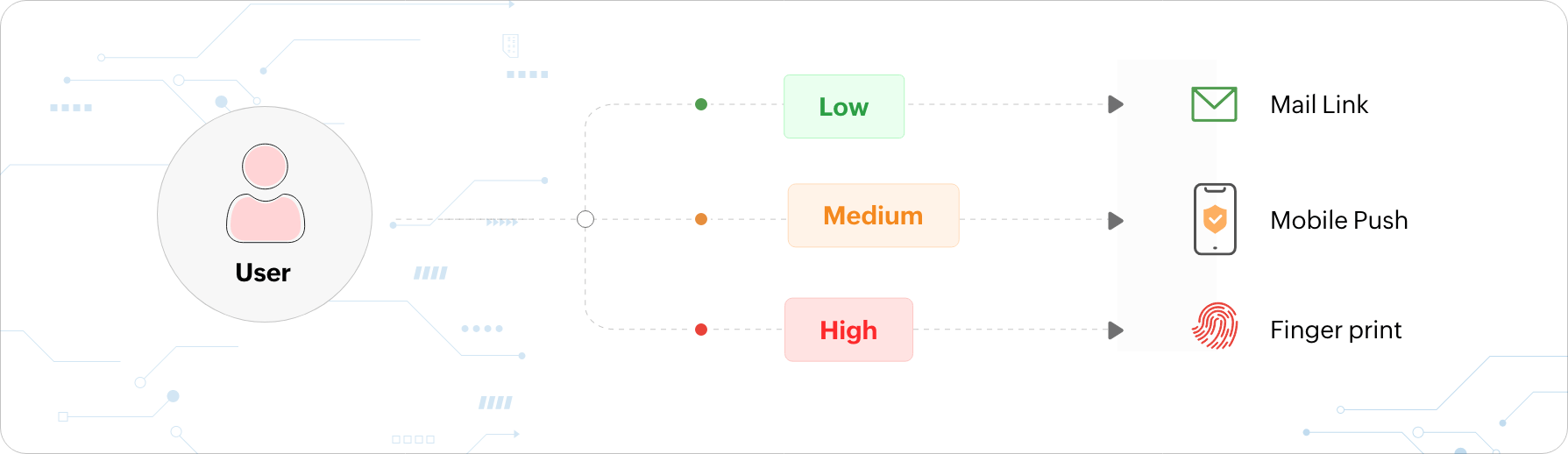
What is adaptive or risk-based MFA?
Adaptive MFA, otherwise known as risk-based MFA, provides users with authentication factors that adapt each time a
user logs in depending on the AI-determined risk level of the user based on contextual information. Contextual
information includes the following:
- The number of consecutive logon failures
- The user account and user role category
- The physical location (geolocation) of the user requesting access
- The physical distance (geo velocity) between consecutive logon attempts
- The resource to which access is requested
- The type of device
- Third-party threat intelligence data
- The day of the week and the time of the day
- The operating system type
- The IP address
The authentication factors presented to the user are based on the risk level that is calculated using the above contextual factors. For instance, consider a user trying to log in to their work machine at an untimely hour while on a vacation. The user behavior analytics (UBA) tool recognizes that the user's location and time of access are different, and they are automatically prompted with additional authentication factors to prove their identity.
Sometimes, when user login conditions are checked using AI and no risk is detected, the MFA process can be bypassed for the user. And sometimes, if the user's activity seems suspicious, they can also be denied access to the requested resource.
What are the
pros and cons of MFA?
Pros
- Helps secure sensitive data and user identities
- Shields against breached passwords and stolen user devices
- Easy to implement
- Helps build a secure environment, which helps gain customer trust and build a good reputation for the company
- Helps comply with data compliance regulations like the GDPR, the PCI DSS, HIPAA, and NIST 800-63B
- Easy for users to adapt to
Cons
- Authorized users may sometimes be denied access due to a misplaced device carrying the OTP for the second factor of authentication
- Consumes time and hinders users' productivity
- Possibility of wrong judgement in adaptive MFA, thus denying access to legitimate users
- Can be expensive to implement
Secure your network with
MFA using ADSelfService Plus
ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus is an identity security solution for ensuring secure and seamless access to enterprise resources and establishing a Zero Trust environment. With capabilities such as adaptive MFA, single sign-on, Workforce self-service, and password management and security, ADSelfService Plus provides your workforce secure yet easy access to resources.
ADSelfService Plus offers different types of advanced authentication techniques to enforce Active Directory MFA during:
- Machine logins (Windows, macOS, and Linux systems).
- RDP and VPN logins.
- Enterprise application logins through SSO.
- OWA logins.
FAQs
What does MFA stand for?
MFA stands for multi-factor authentication. It simply means verifying a user's identity using multiple authentication factors, apart from the traditional and less secure username and password authentication method. MFA can be used to guard user access to any type of resource in the network.
What is an example of multi-factor authentication?
Signing into your Gmail account from a new device is a good example to highlight the MFA process. Upon signing into your Google account from a new device, you are asked to verify your identity either using verification codes sent to your email ID or through TOTPs in addition to entering your password. Once your identity is verified, you are logged in. This sums up the MFA verification process that Google has enabled to secure user accounts.
What types of cyberattacks can MFA fight against?
MFA can be used to fight against common yet powerful cyberattacks like credential stuffing, dictionary attacks, brute-force attacks, reverse brute-force attacks, phishing, and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Why is implementing multi-factor authentication better than frequent password changes?
Changing passwords alone regularly without using MFA does not stop hackers from stealing passwords. They can still use a password that was stolen through advanced hacking techniques to barge into the system. Instead, when MFA is used, hackers have no use for a stolen password since there will be other authentication factors that they will have to pass through to gain access to the resources.
Does my organization need MFA?
Implementing MFA techniques in your business is highly recommended to improve security in your networks. The username and password method of authentication, as outdated as it is, cannot withstand today's advanced cyberattacks on its own. MFA secures your organizational resources and gives the right access to the right individuals. It helps create a Zero Trust environment within your business.
ADSelfService Plus single-handedly takes care of all your MFA needs with features like
adaptive authentication,
conditional access, and
passwordless authentication. Start a free trial
What regulatory standards does MFA help comply with?
What is conditional access? How is it different from adaptive MFA?
Conditional access is taking authentication decisions to verify a user's identity based on a few pre-configured conditions. That is, users are provided with authentication factors depending on whether certain set conditions are fulfilled or not. An example of a condition would be verifying a user with an additional authentication factor if they have requested resource access from a geolocation that is different from the configured ideal geolocation.
Adaptive MFA utilizes AI to calculate the risk level of users, based on which relevant authentication factors are provided to them for identity verification. This risk level is calculated based on users' contextual information, such as the number of consecutive logon failures, the physical location of the user requesting access, and the type of device used. Adaptive MFA is effective in creating the ultimate Zero Trust environment.
Explore related resources

E-book
Cyber insurance decoded: Security controls that help reduce risks and cyber insurance premiums
Download e-book

E-book
The essential guide to securing RDP and VPN access to sensitive resources
Download e-book



