Table of contents
What is MFA for VPN logins?
MFA for VPN logins adds an extra layer of security beyond just passwords, ensuring only authorized users can access your network. By requiring a second verification step, MFA prevents unauthorized access even if credentials are compromised. Identity360 supports MFA for VPN through RADIUS and SAML authentication, offering flexible options like TOTP apps, FIDO2 passkeys, and more to secure remote and hybrid workforces.
Who needs MFA for VPNs?
Remote workers
Employees working from home, hybrid environments, or other off-site locations require secure access to internal systems.
Business travelers
On-the-go professionals accessing corporate networks while traveling, especially over public Wi-Fi networks in airports or hotels, face increased security risks.
Third-party contractors
External vendors and temporary workers accessing VPNs via personal devices pose security risks due to temporary credentials and multiple client engagements.
Regulated industries
Highly regulated sectors, including healthcare, finance, and government agencies, adhering to compliance standards such as the NIST SP 800-63B, GDPR, HIPAA, NYCRR, FFIEC, PCI DSS, and RBI guidelines.
How MFA for VPN works in Identity360
Identity360 enables MFA for VPN access using both Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) and Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) authentication protocols.
When configuring MFA for your VPN, the first step is to choose the authentication mode depending on the authenticators and type of MFA prompts you want to use. You can select from the following options:
- VPN Client Verification: The user receives an MFA prompt directly from the VPN client during the login process.
- SecureLink Email Verification: The user receives a verification link at their primary email address, which they must click to verify their identity through a browser.
VPN MFA using RADIUS
The RADIUS protocol is widely used for network access control, including VPN authentication. Identity360 integrates with RADIUS-based VPNs through a Network Policy Server (NPS) extension.
Note: Refer to this page to know more about the requirements and compatibility details for each mode.
| Supported vendors | Supported authenticators |
|---|---|
|
VPN Client Verification
SecureLink Email Verification
|
How it works
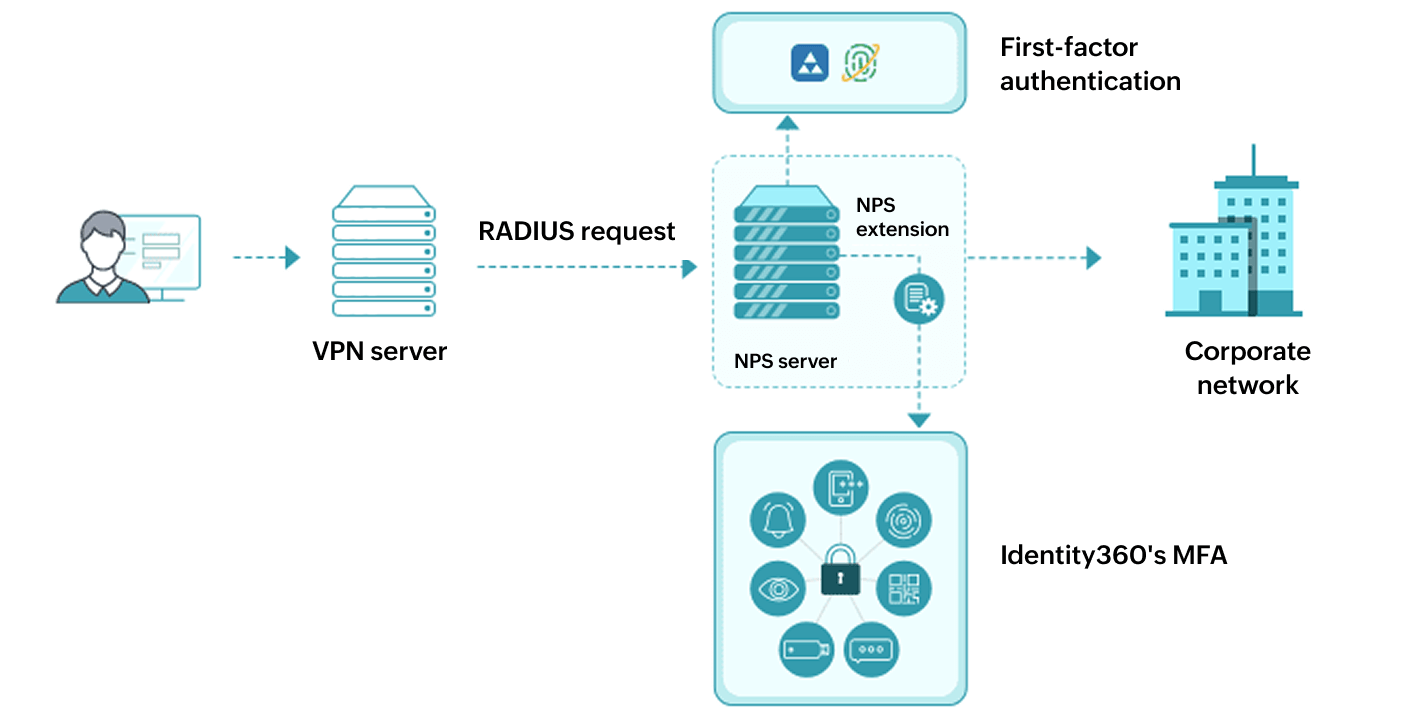
Once your VPN or endpoint server is set up with RADIUS authentication and Identity360’s NPS extension is installed, here’s what happens when a user logs in:
The user enters their username and password to connect to the VPN.
The server forwards this login request to the NPS equipped with Identity360's NPS extension.
The NPS server checks the provided credentials against Active Directory (AD). If passwordless authentication is set up, Identity360 manages this primary authentication.
The NPS extension prompts Identity360 to carry out MFA.
Identity360 processes the MFA and sends the outcome back to the NPS extension.
Upon successful authentication, the NPS server informs the VPN or endpoint server to allow access, establishing a secure, encrypted connection to the internal network.
VPN MFA using SAML
SAML enables SSO by facilitating the exchange of authentication data between an identity provider (IdP) and a service provider (SP). Identity360 integrates with SAML-based VPNs, allowing users to authenticate through Identity360.
Note: The VPN vendor should support authentication via the SAML protocol, which requires opening the web portal from the VPN client software.
| Supported vendors | Supported authenticators |
|---|---|
|
All 10 authenticators supported by Identity360 |
How it works
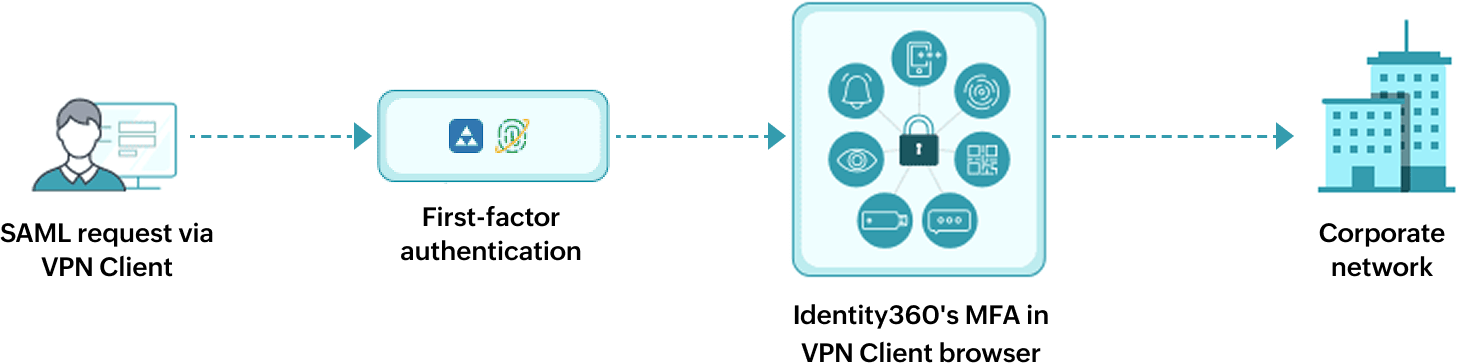
A user initiates a VPN connection, which redirects them to the IdP for authentication.
The IdP authenticates the user, including any additional MFA challenges.
Upon successful authentication, the IdP sends a SAML assertion back to the VPN, granting access.
SAML vs. RADIUS-based VPN MFA
| Criteria | MFA via RADIUS | MFA via SAML |
|---|---|---|
| Supported VPN logins | Both VPN clients (e.g., Cisco AnyConnect, Fortinet) and browser-based VPN logins | Browser-based VPN logins |
| Primary authentication with AD | Supported | Not supported |
| Authenticator support |
VPN Client Verification: Limited authenticators supported in Identity360 SecureLink Email Verification: All authenticators supported in Identity360 |
All authenticators supported in Identity360 |
| Setup complexity | Requires NPS extension for AD authentication | Simple (no extensions needed) |
| Vendor support | Major VPN vendors support RADIUS authentication | Limited vendors support SAML authentication |
Use cases: When to use MFA for VPN via SAML vs. RADIUS in Identity360
Use case 1: A cloud-first organization with multiple IdPs
Scenario
A growing SaaS company has a fully cloud-based IT infrastructure. Its workforce accesses VPN through a browser-based authentication portal, and it uses Identity360 for identity management.
Solution
Since the company relies on multiple IdPs and prefers a lightweight setup without additional configuration s, M FA for VPN via SAML is recommended in Identity360. This allows seamless authentication across different cloud directories without the need for NPS servers or additional RADIUS configurations.
Why SAML?
- Supports all MFA authenticators.
- Works well for browser-based VPN logins.
- Minimal setup, no NPS patch maintenance.
- No outbound connections from in-house servers (like NPS) to Identity360.
Use case 2: A traditional enterprise with on-premises AD
Scenario
A global banking institution primarily uses AD for user authentication. Its employees connect to the VPN using Cisco AnyConnect and Fortinet, which require authentication at the client level (not browser-based).
Solution
Since the institution requires AD authentication, MFA for VPN via RADIUS is recommended in Identity360. Identity360 integrates with NPS, allowing employees to authenticate using their AD credentials while enforcing MFA.
Why RADIUS?
- Works with major VPN clients (not just browser-based).
- Supports AD authentication.
- Compatible with both client-based and browser-based VPN logins.
Use case 3: A hybrid IT environment with both cloud and on-premises users
Scenario
A private limited company operates in a hybrid model—some teams are cloud-based, while others rely on on-premises AD authentication. It has Fortinet VPN for remote employees and uses Okta as its cloud-based IdP.
Solution
A hybrid approach is recommended in Identity360:
- For cloud users logging into a VPN portal → MFA via SAML is recommended.
- For on-premises AD users who require VPN access → MFA via RADIUS with NPS for AD authentication is recommended.
Why a hybrid approach?
- Provides flexibility for both cloud and AD users.
- Ensures seamless MFA without additional complexity for cloud users.
- Supports VPN clients for on-premises users requiring AD authentication.
