On this page
How safe is a school's student information system (SIS) against cyberattacks and insider threats? In 2024, the PowerSchool data breach exposed the records of over 62 million students and educators, highlighting the fragility of academic data. Exploits targeting a school's SIS doesn't just compromise privacy; it can undermine institutional trust through grade manipulation. Luckily, educational institutions can stay resilient against these rising threats by leveraging SIEM for real-time monitoring and IAM for strict access controls. Together, these solutions safeguard student data integrity and ensure accountability across systems.
What makes an SIS attractive to attackers?
Here are the top five reasons why a school's SIS is a prime target for attackers:
- Rich personal data: The SIS stores sensitive student and staff records, including PII, addresses, Social Security numbers, and financial details, that can be monetized on the dark web.
- Academic integrity manipulation: Attackers can exploit the SIS to alter grades, transcripts, or attendance, leading to reputational damage and loss of confidence in institutions.
- Weaker security posture: Many educational institutions run outdated systems with limited cybersecurity budgets, making them easier targets compared to enterprises.
- High system interconnectivity: An SIS often integrates with a school's learning management system (LMS), payment portals, and third-party apps, expanding the attack surface.
- Low detection and response maturity: Schools and universities frequently lack dedicated SOC teams, leaving SIS exploits and insider threats unnoticed for longer periods.
Why is SIS security a growing concern?
Educational institutions are paying more attention to SIS security than ever. Here's why:
- Data privacy risks: An SIS holds highly sensitive information such as student identities, financial records, and even health details, which attackers can steal and sell on the dark web.
- Academic manipulation threats: Hackers or malicious insiders may change grades, transcripts, or attendance data, directly affecting academic credibility and even students' futures.
- Financial and compliance risks: Since an SIS often links with fee payment systems, attackers can exploit it for fraud; breaches can also result in heavy fines under regulations like FERPA or the GDPR.
- Operational disruption: Attacks like ransomware or DDoS can shut down SIS access during critical periods such as admissions or exams, causing chaos for students and staff.
- Third-party and supply-chain vulnerabilities: SIS platforms frequently integrate with external apps (e.g., LMS, ed-tech tools, payment portals), and any weak link in these connections can give attackers a way in.
- Insider threats: Authorized users, whether staff or students, may misuse their access to manipulate records or leak information if proper monitoring is absent.
- Low cybersecurity maturity: Many schools and universities operate on tight budgets and outdated systems, leaving them more exposed compared to enterprises with strong defenses.
What are the vulnerabilities of an SIS and how do attackers exploit them?
An SIS can be easily exploitable due to:
- Weak or shared authentication: Simple passwords, reused or shared accounts, and lack of MFA enables attackers to gain initial access via brute force, credential stuffing, or phishing.
- Legacy systems: Unpatched SIS software and legacy components lack modern controls and known fixes, creating exploitable software vulnerabilities.
- Insecure third-party integrations: Poorly secured LMS, ed-tech apps, payment gateways, or APIs introduce indirect access paths and supply-chain risk.
- Excessive or poorly managed privileges: Over-provisioned roles and missing role-based access controls allow attackers (and insiders) to escalate access and modify sensitive records.
- Unprotected data in transit or at rest: Lack of strong encryption for databases, backups, or network traffic exposes PII, grades, and financial data to interception or theft.
- Weak network controls and remote access: Missing segmentation, VPNs, or network access controls permit lateral movement and remote intrusions.
- Lack of monitoring, logging, and detection: Absence of SIEM's centralized logging or alerting means breaches, grade manipulation, or data exfiltration can go unnoticed for long periods.
- Insider threats and credential misuse: Authorized users (including faculty, staff, and students) with legitimate access can intentionally or accidentally tamper with records or leak data.
- Operational attacks: Ransomware, destructive malware, or denial-of-service attacks can lock systems or disrupt critical activities like admissions, exams, and grading.
- Financial and compliance exposure: Vulnerable payment flows, insecure APIs, or improper handling of regulated data open avenues for fraud and regulatory violations.
What happens when an SIS is exploited?
When an SIS is exploited, there can be major consequences. These include:
- Compromised academic integrity: Grade manipulation erodes trust in the institution, impacts students' futures, and damages the credibility of academic records.
- Data breaches and identity theft: Exploited access control gaps allow attackers to steal sensitive student and staff data, leading to identity theft and financial fraud.
- Operational disruptions: Exploits targeting the SIS or outdated software can cause system downtime during critical academic periods like admissions, exams, or graduation.
- Regulatory and legal penalties: Breaches of student information systems can violate compliance requirements like FERPA or the GDPR, leading to lawsuits, fines, and reputational harm.
- Financial and reputational losses: Institutions face ransom demands, fraud losses, and long-term reputational damage, making it harder to attract students and maintain trust.
How can a defense framework help prevent attacks on the SIS?
The following defense framework can help CISOs prevent an attack:
| People |
|
| Process |
|
| Technology |
|
How does SIEM strengthen SIS security?
Here's how SIEM helps educational systems stay secure:
| Feature | Benefit | Example scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time threat detection | Monitors logs from the SIS, connected apps, and servers to detect unusual activity. | If multiple failed login attempts are made on a SIS admin account from an unknown location, SIEM raises an alert before brute force succeeds. |
| UEBA | Builds baselines for student, teacher, and staff account activity and flags anomalies. | If a teacher account suddenly exports student databases late at night, SIEM detects it as abnormal and alerts security teams. |
| Threat intelligence integration | Correlates SIS activity with global threat feeds to block known malicious IPs and domains. | If a SIS login attempt comes from an IP listed in threat intelligence as linked to ransomware, SIEM blocks and reports it. |
| File integrity monitoring | Tracks unauthorized changes to SIS configuration or database files. | If a SIS login attempt comes from an IP listed in threat intelligence as linked to ransomware, SIEM blocks and reports it. |
| SOAR | Automates actions like disabling accounts or blocking IPs on suspicious SIS events. | If SIEM detects a ransomware pattern on SIS logs, it auto-isolates the affected system before data is encrypted. |
How does IAM strengthen SIS security?
Here's how IAM helps educational institutions maintain SIS security:
| Feature | Benefit | Example scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Granular access control | Implements role-based and least-privilege access for SIS users. | A student worker can only view attendance data, not alter grades, preventing accidental or intentional misuse. |
| MFA | Adds extra verification layers for SIS logins. | Even if an attacker phishes a teacher’s SIS credentials, they can’t log in without MFA. |
| Life cycle and provisioning management | Automates account creation, updates, and deactivation across the SIS. | When a student graduates, SIEM automatically deactivates their SIS account, removing potential insider threats. |
| SSO with audit trials | Provides centralized authentication for SIS and related apps with full audit visibility. | Admins can track every SIS login session from teachers, parents, or students, reducing blind spots. |
| Password policy enforcement and self service | Enforces strong password rules and enables users to reset passwords securely without IT help. | Prevents weak or reused SIS passwords from being exploited while reducing helpdesk overhead. |
How does SIEM and IAM work together to strengthen SIS security?
The following is how unifying SIEM and IAM help:
- Cross-validation of access and activity
- IAM enforces who can access the SIS, while SIEM validates how that access is being used.
- Scenario: IAM restricts access to transcripts; if an authorized faculty member still downloads hundreds of records unusually, SIEM alerts on insider misuse.
- End-to-end threat detection and response
- IAM blocks unauthorized SIS logins, while SIEM detects post-login anomalies.
- Scenario: An attacker phishes a valid teacher account. IAM enforces MFA (preventing login from unknown device), but if bypassed, SIEM detects suspicious grade edits and auto-triggers response workflows.
- Unified compliance and audit assurance
- Together, they provide both access control evidence (IAM) and activity monitoring evidence (SIEM).
- Scenario: During a FERPA audit, IAM shows access control policies, while SIEM provides forensic logs of SIS activities covering both “who accessed” and “what they did.”
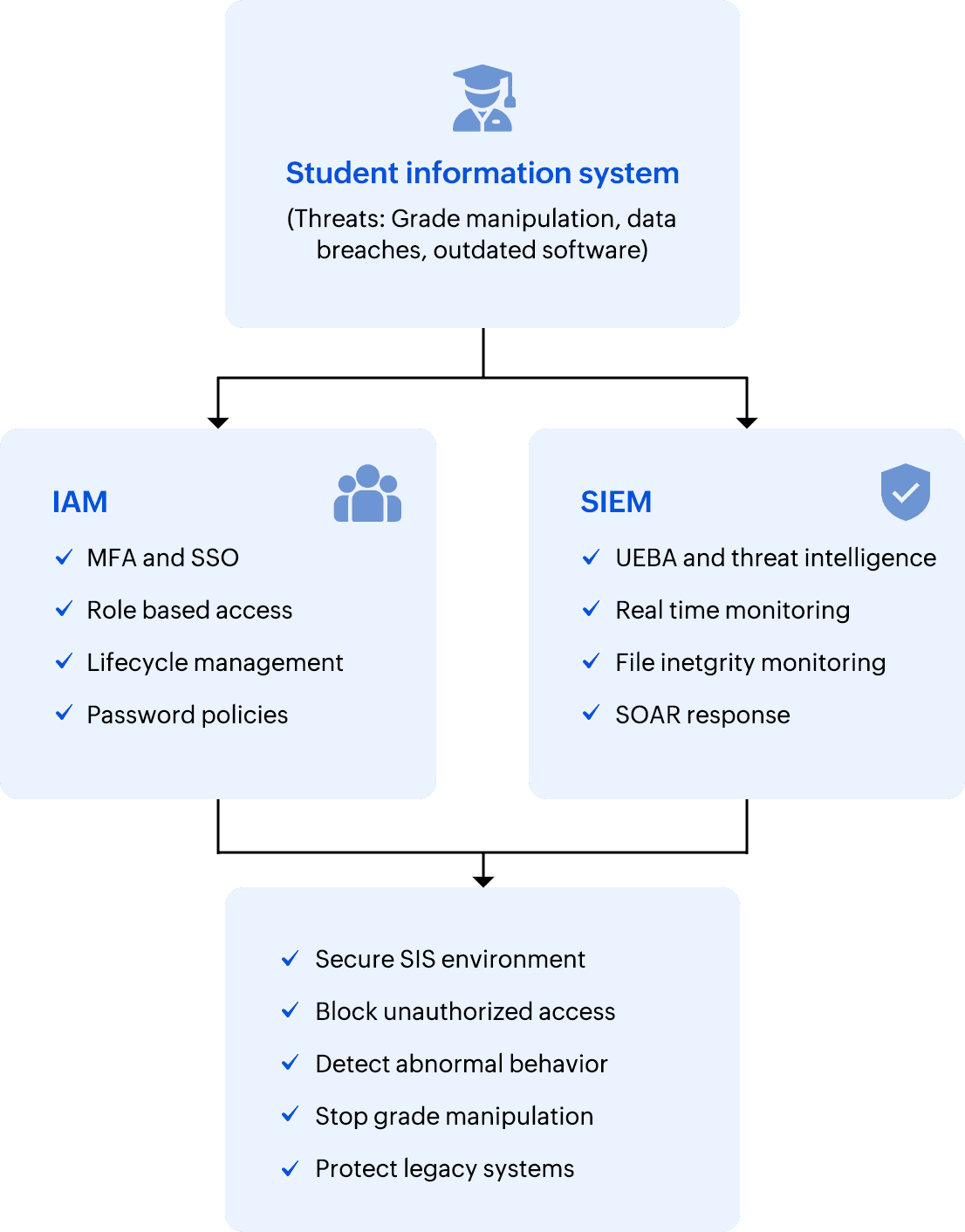
Figure 1: SIEM and IAM for enhanced student information system protection
Conclusion
Securing the SIS is no longer optional, especially as K–12 institutions and universities continue to rely on digital platforms for critical academic operations. With many schools still running on legacy student systems, attackers exploit weaknesses through SQL injection, phishing, and poor access control mechanisms. The risks involved in information management extend beyond privacy breaches; they include grade manipulation, operational downtime, and loss of trust in the institution. Insider threats further complicate the landscape, as even authorized users can misuse privileges if they're not properly monitored. Finally, outdated software leaves exploitable gaps that modern attackers are quick to target. A layered defense with SIEM and IAM ensures that institutions stay resilient against these evolving risks while preserving the integrity of student data.
Related solutions
ManageEngine Log360 is a SIEM solution that combines DLP, CASB, machine learning, and MITRE ATT&CK® mapping to deliver real-time threat detection, automated response, streamlined incident management, and compliance across hybrid IT environments. To learn more:
Sign up for a personalized demoManageEngine AD360 is a unified IAM solution that simplifies identity, access, and security management across on-premises and cloud platforms with features like user provisioning, SSO, self-service password management, and auditing. To learn more:
Sign up for a personalized demoThis content has been reviewed and approved by Ram Vaidyanathan, IT security and technology consultant at ManageEngine.
