A data protection impact assessment (DPIA) is a crucial tool for organizations to evaluate the effects of data processing activities on individuals' privacy and manage potential risks. The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act highlights the significance of DPIAs in ensuring compliance and protecting personal data.
Organizations are required to assess the impact of their data processing activities, systems, and technologies to align with the DPDP Act's standards. Similar to the GDPR, the DPDP Act mandates DPIAs, especially for projects posing significant privacy risks. Non-compliance can result in substantial penalties, emphasizing the importance of thorough privacy evaluations. While the DPDP Act focuses on data protection within India, organizations handling the data of Indian citizens, including international entities, must comply with DPDP requirements, which include conducting DPIAs if necessary. This ensures a consistent approach to safeguarding personal data and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Conducting DPIAs proactively helps identify and address privacy risks, ensuring compliance with the DPDP Act while fostering trust among individuals. Integrating DPIAs into routine compliance processes supports continuous vigilance, adaptation to evolving regulations, and mitigation of emerging privacy concerns. By aligning DPIAs with the DPDP Act, organizations can strengthen their data protection strategies and safeguard personal data effectively.
How to determine if your organization needs to conduct a DPIA
It is mandatory for Significant Data Fiduciaries (SDFs) to conduct DPIAs. The DPDP Act requires SDFs to evaluate the impact of their data processing activities on individuals' privacy and to submit key findings to the Data Protection Board of India (DPBI). This ensures that privacy risks are identified and mitigated effectively, maintaining compliance with the Act.
SDF is a category defined under the DPDP Act. The Central Government identifies certain data fiduciaries as SDFs based on specific criteria, such as:
- Volume and sensitivity of data: Organizations that process substantial amounts of personal data or manage highly sensitive information are more likely to be classified as SDFs.
- Risk to data principals: If an organization's data processing activities pose significant risks to the rights and privacy of individuals (data principals), it may be designated as an SDF.
- Impact on national interests: Organizations whose data processing activities could affect the sovereignty, integrity, security of the state, public order, or electoral democracy may also be classified as SDFs.
How to get started with a DPIA
Initiating a DPIA early in the project's life cycle, before data processing starts, ensures it runs concurrently with the planning and development phases. Here are the key steps to follow in a DPIA process.
Note: These steps are derived from the DPIA methodology recommended by the ICO, ensuring alignment with GDPR standards.
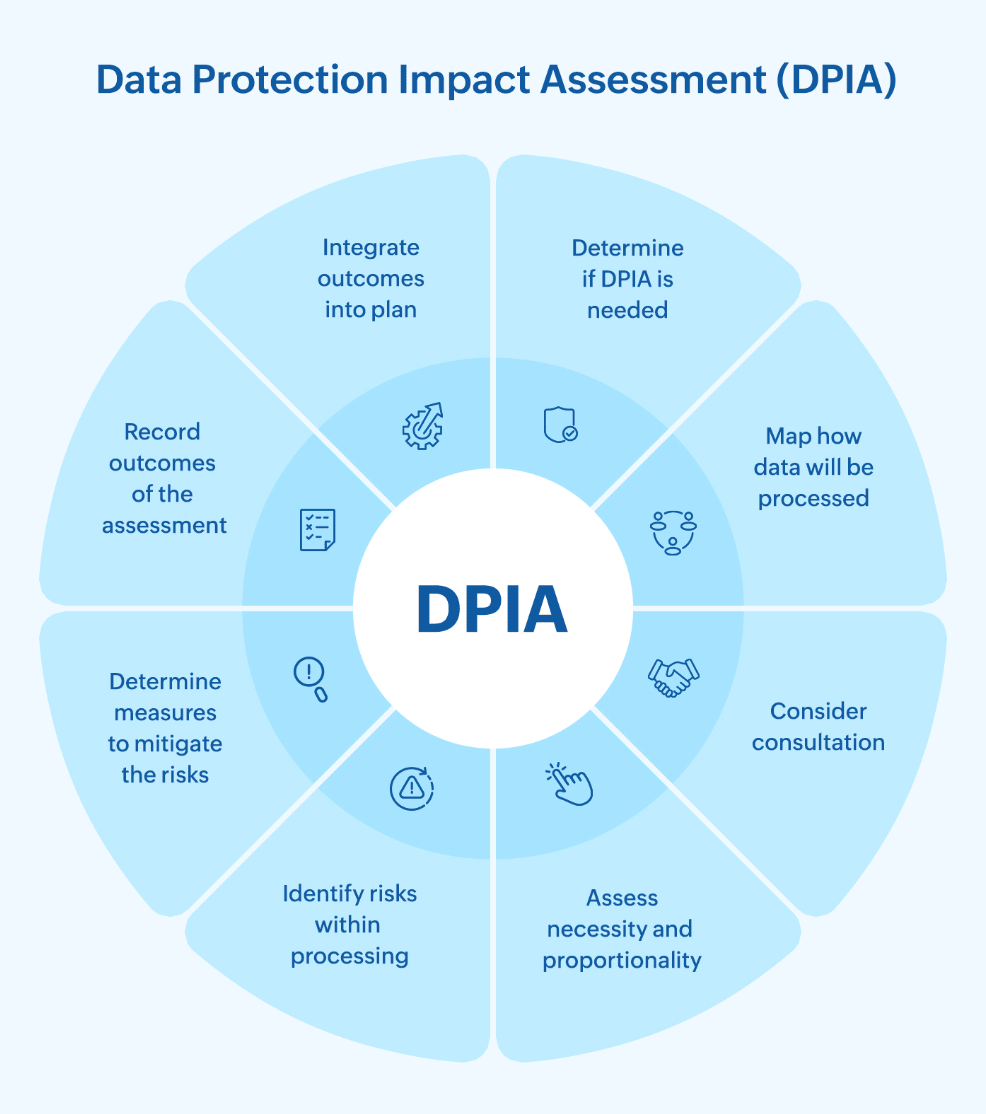
Steps to conduct a DPIA for your organization
Determine if a DPIA is needed
The initial step is to evaluate whether a DPIA is needed. This entails examining the nature of the data processing activities and pinpointing any possible privacy risks. If the processing involves sensitive personal data or poses significant risks to individuals' privacy, a DPIA is required. If your organization is considered an SDF by the DPDP Act, conducting a DPIA is mandatory.
Map how data will be processed
After determining the necessity of a DPIA, the next step is to offer a comprehensive description of the data processing activities. This includes outlining the types of personal data collected; the purpose of processing; data sources; and how the data will be used, stored, and shared. A data flow diagram can help with process visualization.
To describe how and why you plan to use personal data, include the nature, scope, context, and purposes of processing.
- Nature covers: data collection, storage, use, access, sharing, processors, retention, security, new technologies, novel processing, and high-risk screening criteria.
- Scope includes: data nature, volume, variety, sensitivity, extent, frequency, duration, subjects involved, and geographical area.
- Context involves: data source, relationship with individuals, control over data, expectations, vulnerable groups, technology advances, public concerns, and compliance with relevant codes.
- Purpose explains: legitimate interests, outcomes for individuals, and societal benefits.
Consider consultation
Consultation with stakeholders, including data subjects, legal advisors, and other relevant parties, is a crucial part of the DPIA process. Gathering feedback and input from stakeholders helps ensure that all potential privacy concerns are addressed.
Assess necessity and proportionality
Evaluate the necessity and proportionality of the data processing activities. This step involves determining whether the data processing is essential for achieving the intended purpose and if the benefits outweigh the privacy risks. Ensure that the processing aligns with legal requirements and data protection principles.
Identify risks within processing
Determine the possible privacy risks linked to data processing activities. Assess the likelihood and severity of each risk, considering factors such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and misuse of data. This step helps prioritize risks and focus on the most significant threats to data privacy.
Determine measures to mitigate the risks
Create and apply strategies to reduce the identified privacy risks. This could involve technical solutions, such as encryption and access controls; organizational actions, like staff training and policy implementation; and procedural safeguards. Document the mitigation measures and their effectiveness in reducing risks.
Record outcomes of the assessment
Once the DPIA is complete, obtain sign-off from relevant authorities or management. Record the outcomes of the DPIA, including the identified risks, mitigation measures, and any recommendations for further action. Ensure that the DPIA is documented and accessible for future reference.
Post-DPIA steps
After the DPIA is signed off, integrate the outcomes and recommendations into the projet plan. This ensures that privacy considerations are incorporated into the development and implementation of the project. Keep the DPIA under review and update it regularly to reflect any changes in data processing activities or privacy risks. Throughout this process, continue to consult with stakeholders and address any new concerns that arise.
Take the lead in data protection best practices with our unified SIEM solution!