The following are some of the standards that are essential for implementing cyber GRC:
On this page
What is GRC?
GRC stands for governance, risk management, and compliance. It is an organizational framework and a set of software capabilities that manage governance and risk while maintaining compliance in organizations. It aims to bring IT operations and business objectives together to ensure security and control over various business resources.
The GRC framework
The following three principles constitute the GRC framework:
1. Governance
Governance, in general, is ensuring that the activities of a business are aligned with its goals and objectives. It is achieved through a set of standard policies and procedures mandated by the various stakeholders of the business. It acts as a long-term strategy through which all the resources, facilities, infrastructures, technologies, and data in a company are controlled, streamlined, and secured.
2. Risk management
Risk management is the proactive process of identifying and controlling impending threats to a business. These threats might impact the security posture or the regulatory obligations of the business. Effective risk management pertains to the act of mapping potential risks beforehand and taking proactive measures to close the gaps before they become vulnerable.
3. Compliance
Compliance is the process of adhering to certain policies and procedures laid down by external entities to ensure business continuity and credibility. All types of businesses need to adhere to various industry standards, government policies, and legal obligations to preserve the integrity of their activities and the reliability of their products and services. For this, organizations are required to formulate, implement, and maintain a compliance management program that includes predefined protocols and a standard code of conduct for all activities in the business.
The importance of GRC in cybersecurity
In today's digital landscape, businesses are increasingly driven by data. From collection and processing to storage and protection, securing sensitive information is a critical priority. With rising privacy concerns around confidential business data, financial reports, and the personally identifiable information of employees and customers, controlling data access and monitoring transactions have become crucial.
This is where cyber GRC plays a pivotal role. Cyber GRC streamlines business operations, strengthens compliance, and improves data security practices. It defines who can access digital information as well as when, where, and how it can be accessed. By aligning with cyber GRC strategies, companies can enhance network security, maintain data privacy, and support a Zero Trust architecture. Incorporating GRC in cybersecurity not only reduces cyberthreats but also builds trust with stakeholders and improves long-term cyber resilience.
How do you implement cyber GRC?
Cyber GRC is a progressive strategy. It requires a continuous, step-by-step approach involving ongoing assessment, formulation, execution, documentation, and auditing.
The GRC capability model involves a set of guidelines that drive businesses towards principled performance and continuous development. This model can be assimilated with the cybersecurity interests of an organization to meet its long-term goals (Fig. 1).
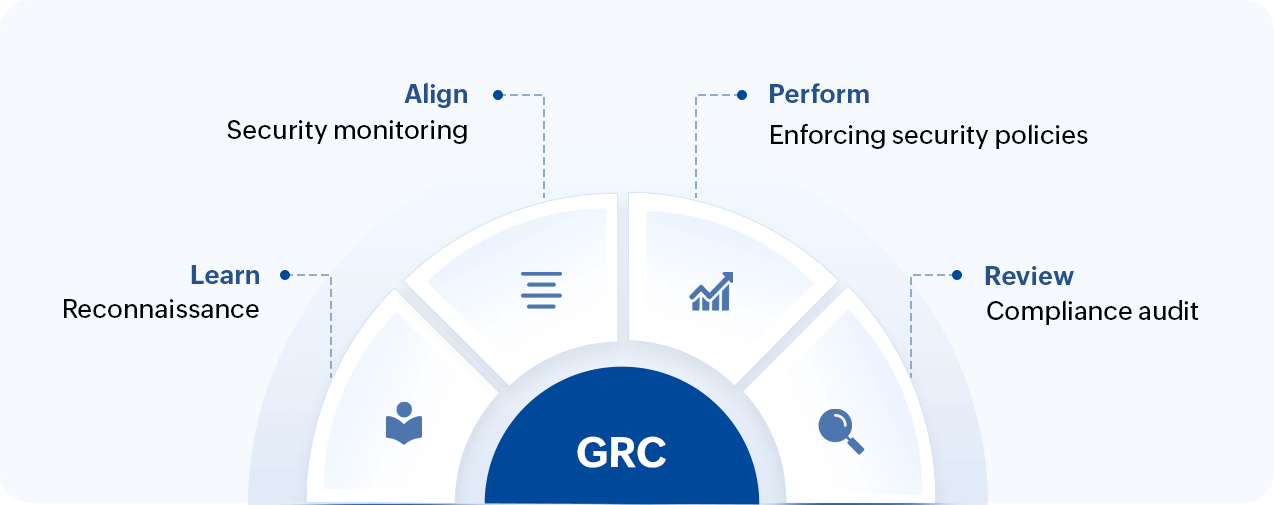
Figure 1: The GRC framework for cybersecurity
| The GRC capability model | The cyber GRC framework |
|---|---|
|
Learn
|
Reconnaissance
|
|
Align
|
Security monitoring
|
|
Perform
|
Security policy enforcement
|
|
Review
|
Compliance auditing
|
What is a GRC tool?
A GRC tool is software that helps organizations adhere to the principles of GRC. In the context of cyber GRC, GRC tools are designed for network monitoring, threat detection, risk assessments, user activity tracking, data tampering detection, anomaly monitoring, and compliance management.
Common GRC tools for cybersecurity
Some cybersecurity solutions that facilitate GRC include the following:
| GRC tool | Use case |
|---|---|
| Identity and access management (IAM) | An IAM tool governs user authentication, manages user accounts, controls user access, and monitors for privilege abuse. |
| Security information and event management (SIEM) | This tool audits all network activities and detects potential threats to workstations, servers, applications, databases, and cloud sources. Most SIEM solutions also act as compliance management tools that help prove adherence to major cybersecurity mandates. |
| User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) | UEBA solutions monitor user and entity activities to detect abnormal behavior, insider threats, data exfiltration attempts, and more. |
| File integrity monitoring (FIM) | A FIM solution is used to track unauthorized access and changes to sensitive files and folders in the network. It helps you prevent data tampering attempts and align with data security and privacy mandates. |
| Cloud access security broker (CASB) | With businesses expanding to the cloud, a CASB solution aids in monitoring for malicious activities in the cloud and preventing cloud data leakage. |
Frequently asked questions
The GRC framework is cross-functional and applied across various departments in an organization. Some of the key players include the following:
- Top management
- Finance department
- HR department
- IT team
- Legal team
GRC maturity is an organization's degree of adherence to GRC standards. A high GRC maturity score indicates good performance, whereas a low GRC maturity score indicates poor performance.
Related solutions
ManageEngine Log360 is a comprehensive SIEM solution with advanced network monitoring, FIM, UEBA, and CASB capabilities that are essential for cyber GRC. It also serves as a compliance management tool with out-of-the-box reports on various data security mandates, helping businesses align with the principles of GRC.
To learn more,
Sign up for a personalized demoManageEngine AD360 is a unified IAM solution that provides SSO, adaptive MFA, UBA-driven analytics, and role-based access controls. It governs user authentication and controls user access, ensuring security policy enforcement in alignment with cyber GRC principles.
To learn more,
Sign up for a personalized demoThis content has been reviewed and approved by Ram Vaidyanathan, IT security and technology consultant at ManageEngine.
