Adding API User Accounts in PAM360
For procedures prior to build 6700, refer to this help document.
PAM360 allows you to add API users manually according to the need for access to the available APIs in the PAM360. API user accounts available in PAM360 are:
- SSH CLI User - API user account for password management APIs in Application-to-Application or Application-to-Database password management.
- REST and Application User - API user account for generic PAM360 operations based on the provided user role and access.
While creating the API user accounts, you can attach the API user account to a single endpoint using the hostname (typically a server or a desktop from which the API is used, so that the user accounts are uniquely identified - for example, as user@hostname).
1. Creating an API User Account with SSH CLI Access
To create an API user account for accessing PAM360 password management APIs in Application-to-Application or Application-to-Database password management, do the steps that follow:
- Navigate to Users >> Users >> Add API User >> SSH CLI User.
- Username: Enter here a unique name as this identifies the API user.
Caution
It is important that the same name should be used as the 'Common Name' (CN) in the corresponding SSL certificate. In MSP edition, in addition to the 'Common Name'(CN), the Organization Name (O) in the certificate should be same as the organization display name in PAM360.
- Hostname Validation: Enable this validation to verify user machines from which API calls are invoked. Enabling this feature restricts API invocation from the machines that are not predefined in the Host Name field.
- Hostname: If you have enabled the Hostname Validation, enter the Hostname of the machine from which the user is allowed to perform the password management operations. Internally, the user name and the host together is used to uniquely identify the API user. For example, a user with the name 'test' from the host 'test-server' will be considered as 'test@test-server' to uniquely identify the API user.
- Full Name refers to the name with which the API user would be identified in the external world, such as reports, audit trails, and other places where user activities are traced. By default, the 'User Name' - 'Host Name' combination with the suffix 'API User' is used as 'Full Name'. In the above example, it will be test@test-server - API User. However, if you want to have a different name, you are free to define that.
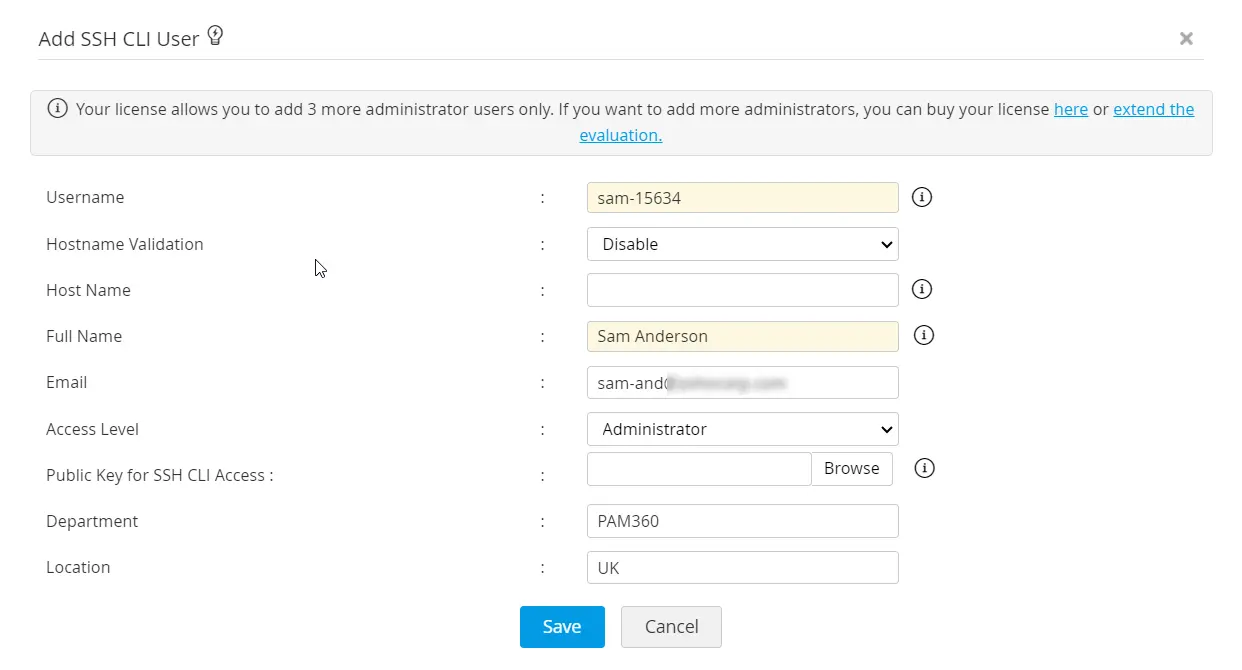
- Email: Enter the user's email address where the user will be notified for updates.
- Role: Select an appropriate Role for the API user being added - Privileged Administrator/Administrator/Password Administrator/Password User/Custom Roles.
- Public Key for SSH CLI Access: Upload here the public key of the user machine from where the user accesses the SSH CLI APIs. SSH connects and logs into the specified host with username specified above. The user must prove his identity to the remote machine using public key authentication. If you wish to make use of the SSH CLI access, browse and select the open SSH format public key of the CLI user. If you want to create a new SSH key pair, follow these steps:
- Launch a command prompt and run the following command to generate a new SSH key pair:
ssh-keygen
- By default, the private key is saved in a file named id_rsa, and the corresponding public key is saved in id_rsa.pub. These files are stored in the .ssh directory under your user home directory. If you prefer, you can specify a different directory to store the key files. During key generation, you will be prompted to provide a file path.
For example: Enter file in which to save the key (/home/xyz/.ssh/id_rsa): /home/xyz/.ssh/pam360_identity - For an added layer of security, you can set a passphrase on your SSH key. After entering a passphrase, you will need to provide it every time you use the key. If you choose to use a passphrase, you will be prompted to enter and confirm.
- Once the key pair is generated, you will receive confirmation with the file paths. You will also see the key fingerprint, which provides a unique identifier for the SSH key.
- To use the generated key in PAM360, import the public key (id_rsa.pub). This file needs to be stored in the authorized_keys file under the following directory /home/xyz/.ssh/authorized_keys.
- Now, browse and locate the public key file in the field Public Key for SSH CLI Access.
The above example shows how to generate the key pair using open SSH. You may use any other standard tool to generate the keys as you wish.
- Launch a command prompt and run the following command to generate a new SSH key pair:
- Department | Location: Enter the department and the location where the user belongs to. These fields are not mandatory. However, populating valid data in these fields with the correct values will be helpful while searching or grouping the users.
- Click Save to create the user account with the above-provided details.
Caution
API user creation is specific to the host from where an application contacts PAM360 for passwords. To use Password Management APIs from more than one host, you need to create as many API users as the number of hosts. Conversely, if you wish to have many users on a single host, then again, you need to create as many API users as needed.
2. Creating an API User Account with REST and SDK Access
To create an API user account for accessing PAM360 REST APIs or SDK via services or applications, do the steps that follow:
Best Practice
PAM360 users granted with web access can later be given REST and SDK access as needed. However, users created via REST and Application User will have no web access to PAM360 permanently. Therefore, we always recommend creating a standard user with REST or SDK access, allowing for future modifications to include web access if necessary.
- Navigate to Users >> Users >> Add API User >> REST and Application User.
- First Name and Last Name: Enter here the user's first name and last name.
- Username: Enter here a unique name. This name identifies the API user.
- Email: Enter the user's email address where the user will be notified of any modifications to the account, access, or role.
- Role: Select an appropriate role for the user from the drop-down; this will determine the type of role and privilege this user will have in PAM360. Refer to this section to learn more about the user roles available in PAM360.
- Scope: By default, users created in PAM360 are assigned the scope of Passwords Owned and Shared. This means they can access passwords owned by them or shared with them by other PAM360 users.
- Department and Location: Enter the department and the location where the user belongs to. These fields are not mandatory. However, populating valid data in these fields with the correct values will be helpful while searching or grouping the users.
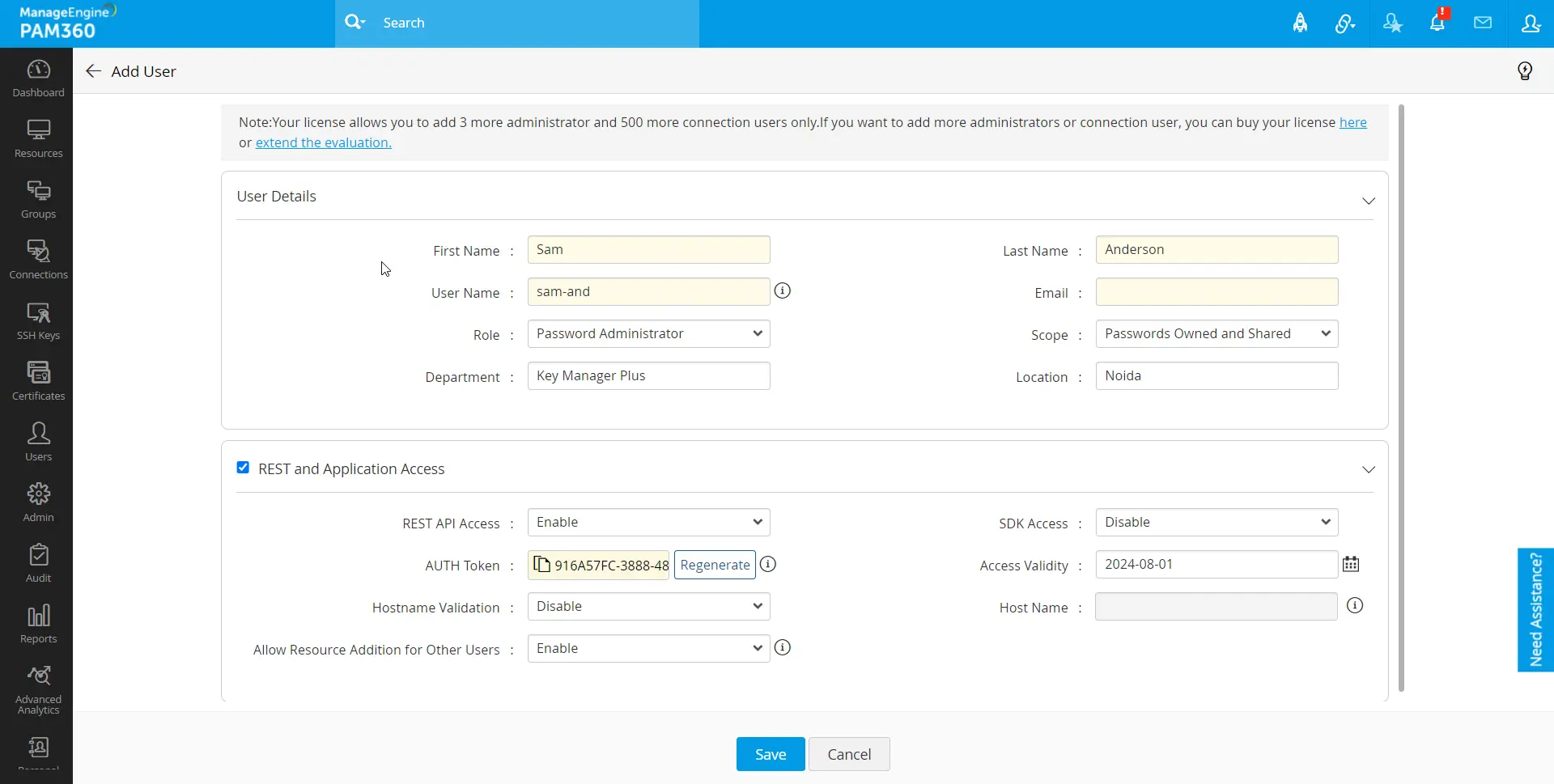
- REST API Access: Enable this option if the user account requires access to the PAM360 REST API.
- SDK Access: Enable this option if the user account requires access to the PAM360 API via the PAM360 SDK.
- Authentication Token: Generate an Authentication Token from here if providing the above access. This token serves as a user validation key for API calls received from other applications or services.
Caution
After creating a user account, the user must regenerate their authentication token before accessing PAM360 APIs. This can be done using the authentication token regeneration API or from the User Settings under the My Profile dropdown in the PAM360 user interface. Additionally, whenever the authentication token is regenerated by an administrator, the user is required to regenerate it again before making any API requests in PAM360.
- Access Validity: Select a date until which the authentication token will remain valid. Exceeding the provided date will invalidate the authentication token, requiring the generation of a new token by the administrator to extend validity for further use of PAM360 REST APIs.
Caution
Starting from build 7200, access validity for authentication tokens must be specified in terms of days. For instance, if the administrator sets the validity period to 90 days, users are required to regenerate their authentication tokens periodically every 90 days to maintain access. Failure to do so will result in token expiration, after which only the administrator can regenerate the tokens on behalf of the user.
- Hostname Validation: Enable this validation to verify user machines from which API calls are invoked. Enabling this feature restricts API invocation from the machines that are not predefined in the Hostname field.
- Hostname: Enter the Hostname of the machine from which the user is allowed to perform REST and Application operations.
- Allow Resource Addition for Other Users: Enabling this option permits users to create resources via the API and assign them to other users.
- Click Save to add the user account to the PAM360 repository.