Self-Signed Certificates, CSRs and Certificate Signing
PAM360 goes beyond the standard certificate discovery process by enabling administrators to create self-signed certificates, generate Certificate Signing Requests (CSRs), and sign CSRs directly within the application. These features are designed to simplify certificate management and improve security within your organization.
At the end of this document, you will have learned about the following operations performed from the PAM360 interface:
- Creating Self-Signed Certificates
- Generating Certificate Signed Requests
- Certificate Signing via PAM360
1. Creating Self-Signed Certificates
PAM360 empowers administrators to generate their own self-signed certificates using the Java Keytool. Upon successful creation, these certificates are automatically imported into the PAM360 repository, streamlining their deployment and management.
Follow the steps below to create a self-signed certificate in PAM360. To create a self-signed certificate directly from the PAM360 interface, navigate to Certificates >> Certificates and click the Create button. In the window that appears:
- Enter a Common Name for the certificate.
- If you have a valid template with the organization and certificate requirement details select it from the Choose From Template field. Else, fill in the following certificate field manually: Organization Unit, Organization, Location, State, Country, Key Algorithm, Key Size, Signature Algorithm, and Keystore Type.
- Choose the Validity Type as either Hours or Minutes, then specify the desired Validity duration. The certificate will automatically expire after the defined time frame.
- Provide a keystore password in the Store Password field.
- Provide an email address in the Expiry Notification Email to receive expiry notifications for the created certificate.

- If the created certificate needs to serve as a root certificate, enable the Generate root certificate checkbox.
- If required, expand the Advanced Options menu to include additional properties for the certificate:
- Key Usage: Configure usage flags such as Non-Repudiation, Digital Signature, Data Encipherment, Key Encipherment, etc. You can mark any of these as critical using the Critical checkbox.
- Extended Key Usage: Configure usage flags to denote the specific purposes for which the certificate will be used.
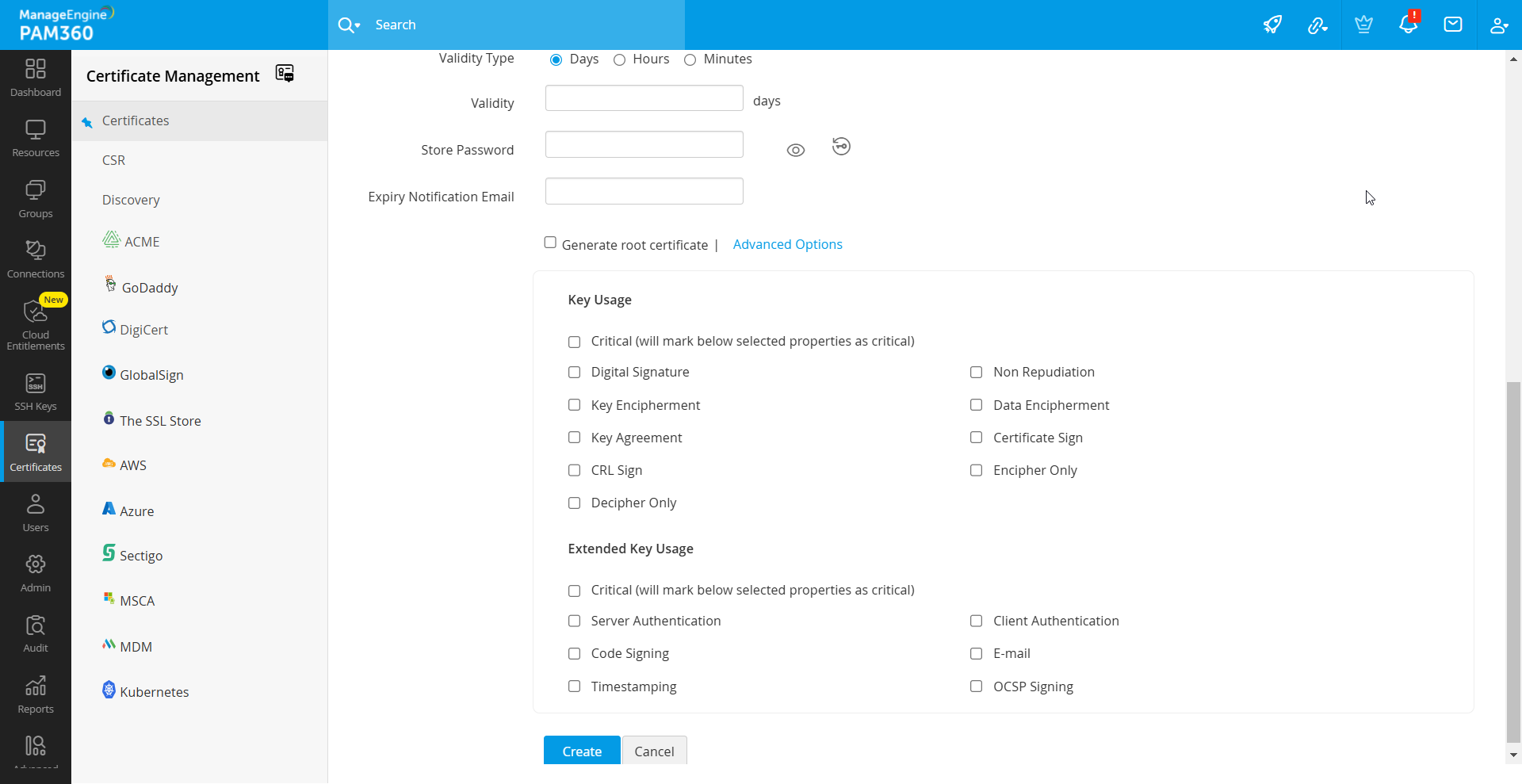
- Click the Create button. This action redirects you to the certificate window where the newly created certificate's content is displayed.
- Upon certificate creation, you can:
- Copy: Copy the certificate content directly from the interface.
- Export: Select the Export Certificate button to save the certificate to your system. You can also export the certificate as a keystore using the Export Key Store button.
- Email: Enable the Email checkbox to send the certificate file to the specified email address.
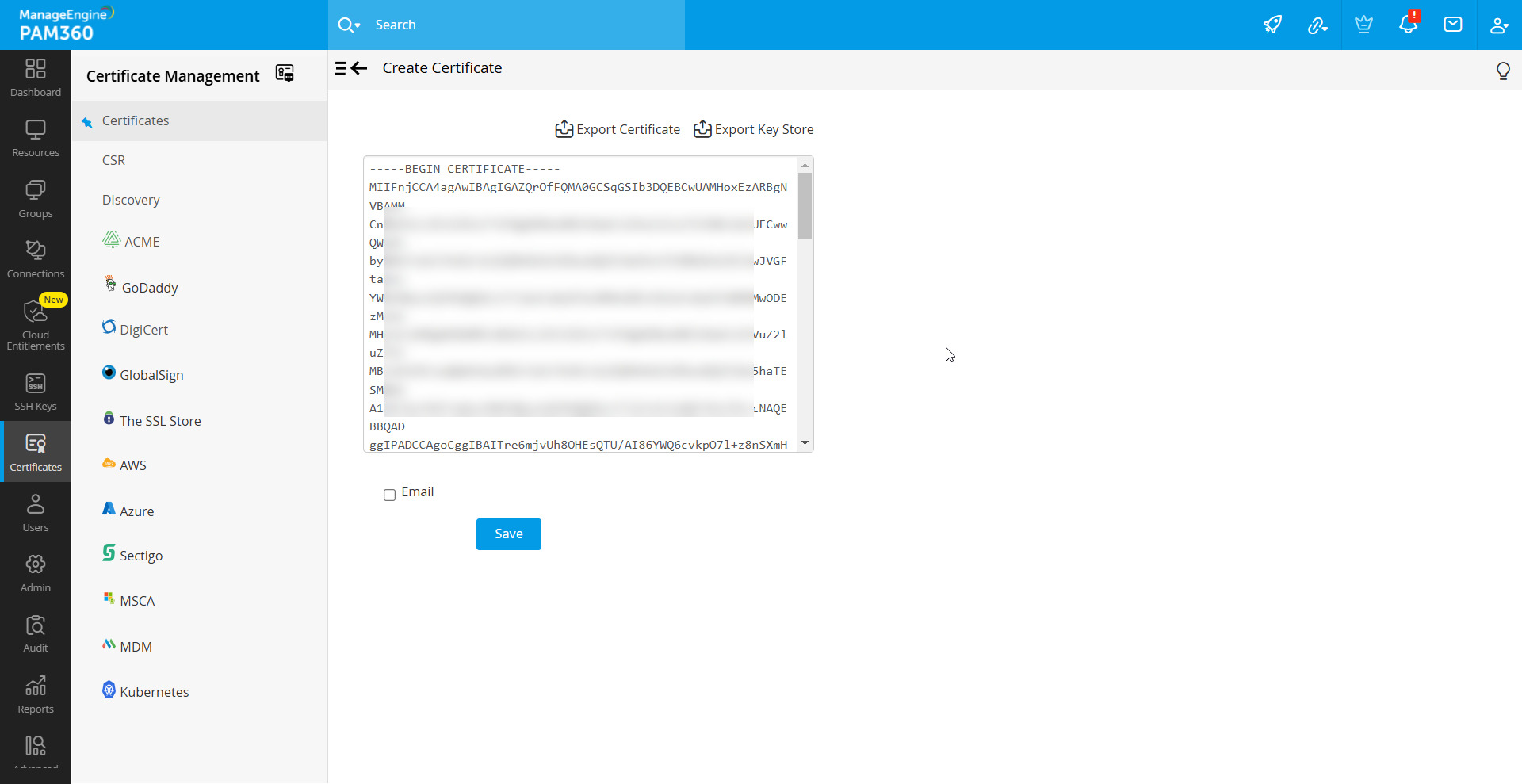
- Click the Save button to finalize the process, ensuring the certificate is stored in the PAM360 repository and exported if opted for.
Caution
Apart from having a wildcard certificate name in the Common Name field, you can add the wildcard name in the SAN field while creating a self-signed certificate. With wildcard certificates, one can secure an unlimited number of subdomains for a registered base-domain. For example, a wildcard certificate for .example.com can secure sub1.example.com, sub2.example.com, and so on.
2. Generating Certificate Signed Requests
A Certificate Signing Request (CSR) is a file containing information about the entity requesting a certificate, which is then sent to a internal or external Certificate Authority (CA) to obtain a signed digital certificate. CSRs are essential for enabling secure communication over SSL/TLS protocols, as they establish the identity of the requesting entity and ensure the authenticity of the certificate issued.
In PAM360, administrators can create, manage, and utilize CSRs efficiently through a centralized interface. The application provides options to generate CSRs manually or by leveraging existing keystore files, ensuring flexibility and ease of use. PAM360 also supports various algorithms and signature methods, enabling compliance with organizational and industry-specific security standards. Follow the below steps to create a CSR directly from the PAM360 interface:
- Navigate to Certificates >> CSR to access the CSR management interface. The CSR list view displays all existing CSRs along with key details such as: Domain Name, Created By, Created Time, Key Size, Key Algorithm, etc,.
- Click on Create to begin generating a new CSR.
- In the form that appears, choose one of the following options: Create CSR to generate a CSR manually by filling in the required detail or Create CSR From Keystore to use an existing keystore file to generate the CSR.
- If you choose to Create CSR From Keystore, follow these steps:
- Select the keystore file by clicking Browse.
- Enter the Private Key Password associated with the selected keystore.
- Provide an Expiry Notification Email for timely alerts.
- Click Create to generate the CSR.
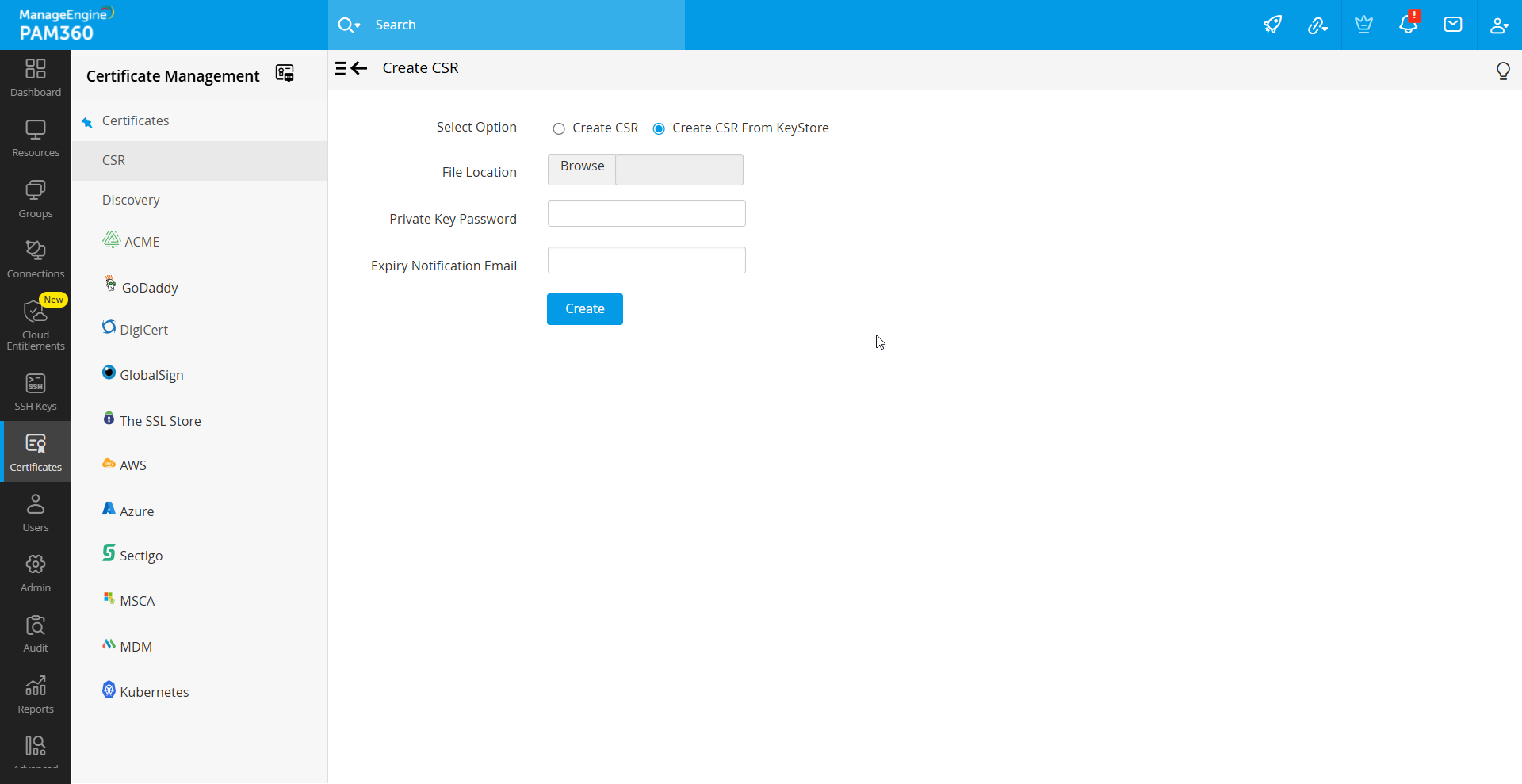
- If you choose to Create CSR manually, follow these steps:
- Fill in the following fields manually: Organization Unit, Organization, Location, State, Country, Key Algorithm, Key Size, Signature Algorithm, and Keystore Type.
- Choose the Validity Type as either Hours or Minutes, then specify the desired Validity duration. The certificate will automatically expire after the defined time frame.
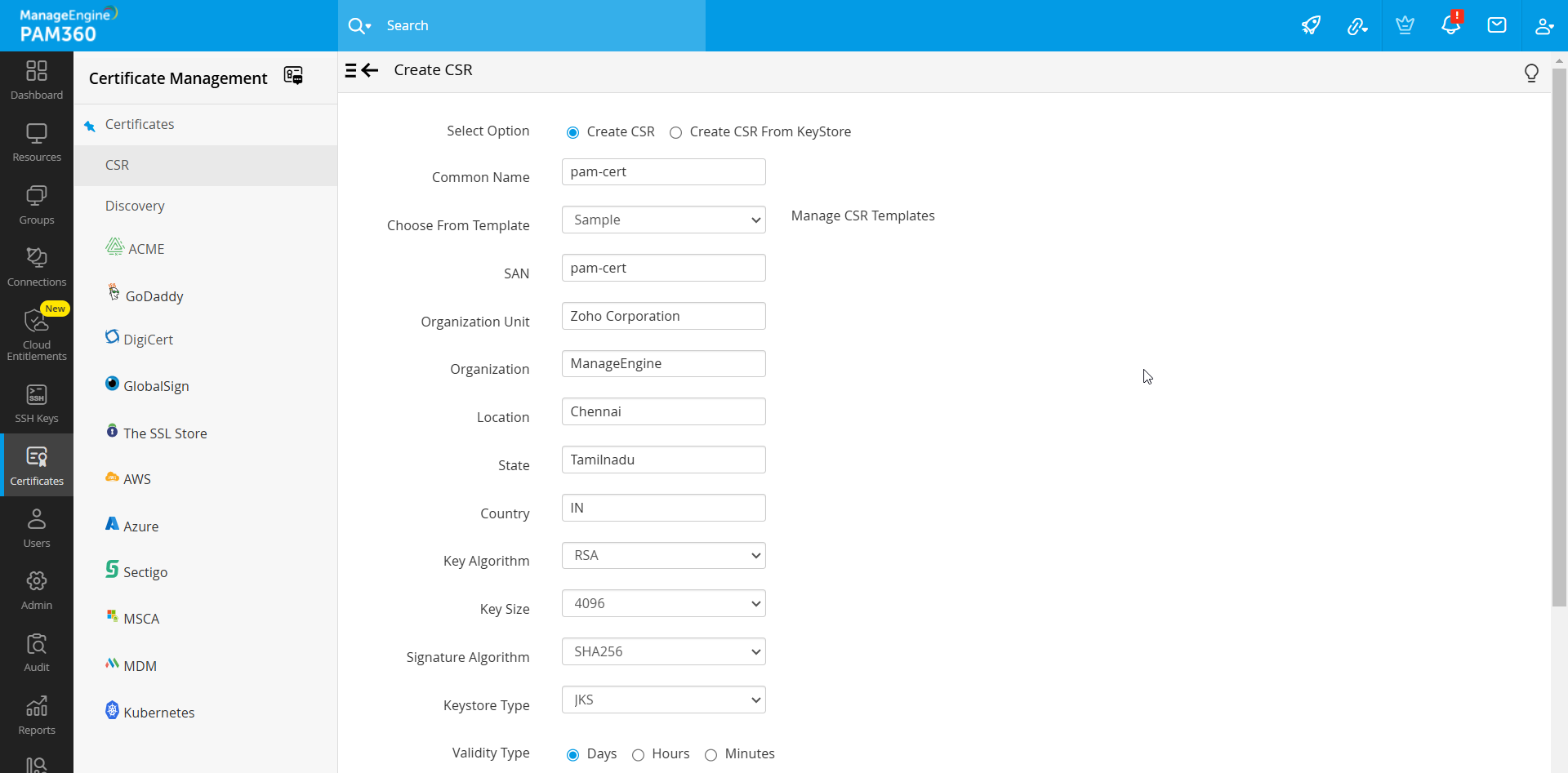

- Enter the Store Password and an Expiry Notification Email. Use the Generate Password icon for assistance.
- Specify the Sign Type or opt to ---Select--- to sign the CSR later.
- Click Create to proceed.
- The generated CSR will be displayed in a dedicated window for review.
- You have successfully created a CSR and it has been added to the list view. The CSR will be assigned to the user who created it.
Caution
Apart from having a wildcard certificate name in the Common Name field, you can add the wildcard name in the SAN field while creating a self-signed certificate. With wildcard certificates, one can secure an unlimited number of subdomains for a registered base-domain. For example, a wildcard certificate for .example.com can secure sub1.example.com, sub2.example.com, and so on.
- To generate a CSR from an SSL certificate available in the PAM360 repository, perform the following steps:
- Go to the Certificates tab.
- Select the desired SSL certificate from which to derive the keystore.
- Click More in the top pane and select Create CSR.
- In the pop-up, provide an Expiry Notification Email.
- Click Create to generate the CSR.
2.1 Managing Certificate Signing Request from PAM360 Interface
- Navigate to Certificates >> CSR to view all saved CSRs. Use the list view to access details or perform actions on individual CSRs.
- Use the Show Passphrase icon to view the keystore password for a specific CSR.
- Click the Export icon to send the CSR via email to a specified recipient.
- If you choose to import the existing CSRs into PAM360 click Import:
- In the pop-up that opens, browse and select the CSR file and the associated key file.
- Enter the Private Key Password and click Import.
- The CSR and its corresponding private key will be added to the centralized repository.
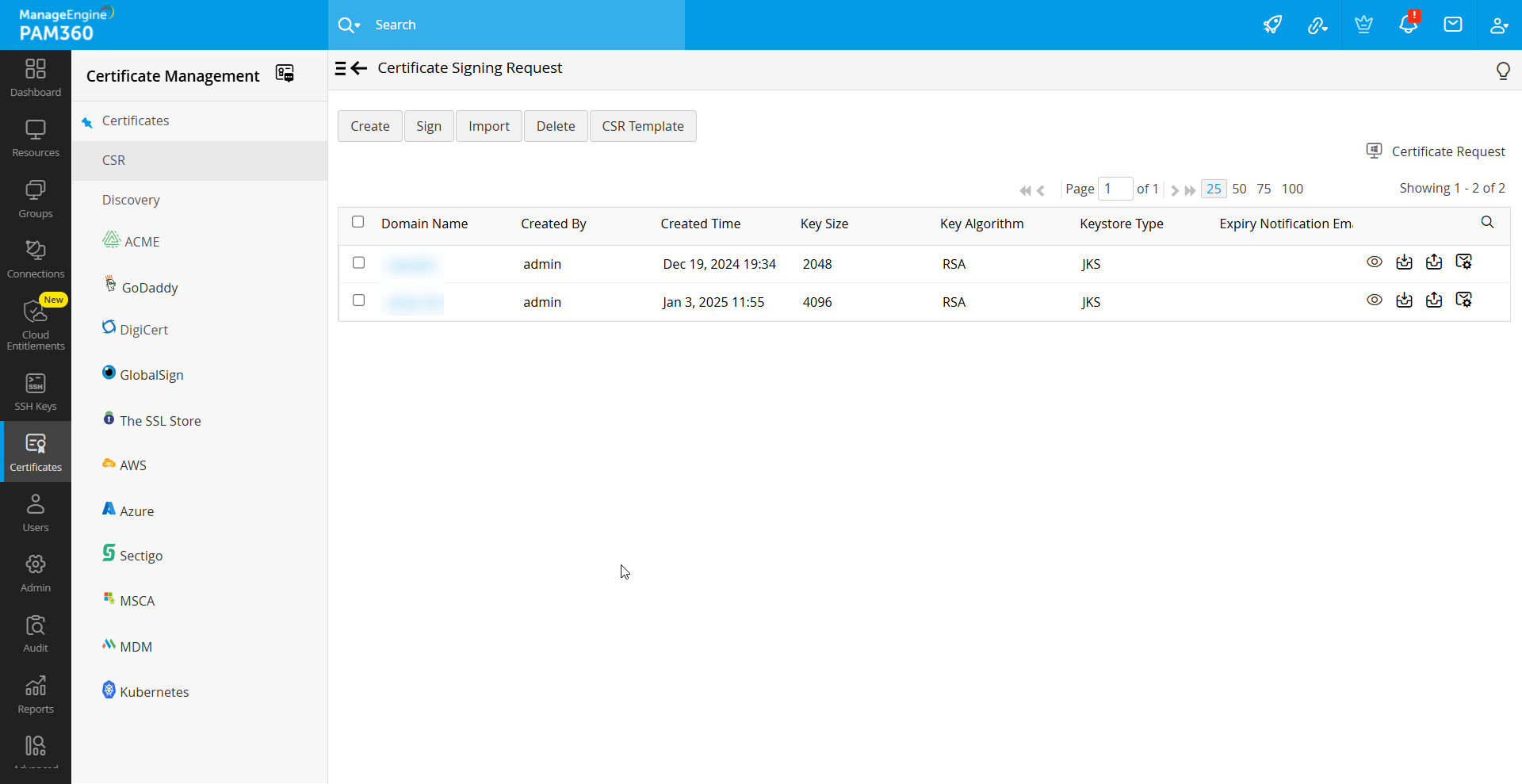
- To delete a CSR, select the CSR from the list and click Delete. Confirm the action in the pop-up by clicking OK.
- Manage templates by clicking CSR Template to add, delete, or edit them for reuse.
The CSR management features in PAM360 simplify certificate request workflows, ensuring robust security and streamlined operations. With support for advanced algorithms, detailed customization, and centralized repository integration, PAM360 caters to diverse organizational needs effectively.
3. Certificate Signing via PAM360
PAM360 offers a comprehensive certificate signing solution to help organizations streamline their certificate management processes. It allows users to sign and issue certificates to clients across their network using either Microsoft (MS) Certificate Authority (CA) or a custom root CA certificate trusted within the environment. The platform simplifies the certificate lifecycle, from generating Certificate Signing Requests (CSRs) to signing and deploying certificates. This section outlines the three primary methods for certificate signing in PAM360, providing step-by-step instructions for each.
3.1 Certificate Signing via Microsoft Certificate Authority
This method is suitable if the MS CA server resides within your organization and maintains a valid connection with the PAM360 server. Follow these steps to sign a CSR using MS CA:
- Navigate to Certificates >> CSR, select the required CSR and click Sign from the top menu.
- In the pop-up that opens, set the Sign Type to Microsoft CA.
- Provide the following details:
- Server Name: Specify the name of the server hosting the MS CA.
- Certificate Authority Name: Enter the CA name.
- Certificate Template: Choose a template based on your requirements or click Get Template to access predefined options.
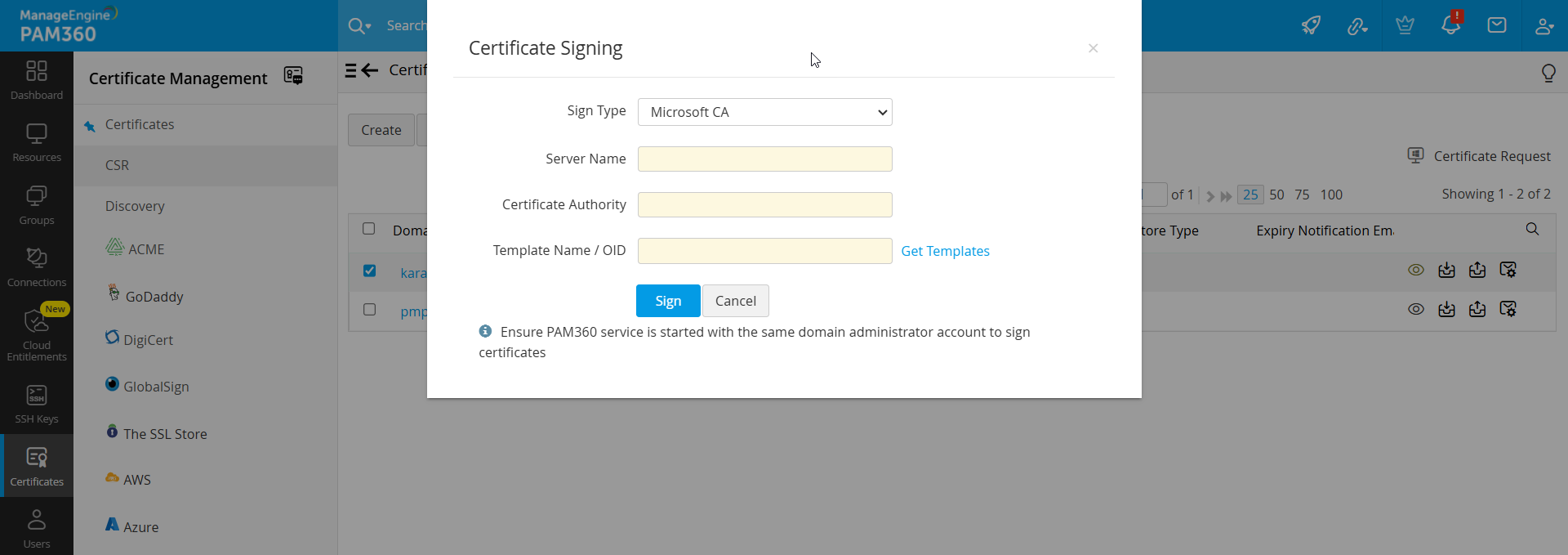
- Click Sign to complete the process.
- View the signed certificate under Certificates >> Certificates.
3.2 Certificate Signing via Agent Deployed in Microsoft Certificate Authority
When the MS CA server resides outside the organization or lacks a direct connection to the PAM360 server, the agent-based signing method is recommended.
Caution
Ensure the SSL agent is installed on the MS CA server.
- Select the required CSR from the list view and click Sign from the top menu.
- In the pop-up that opens, set the Sign Type to MSCA using Agent.
- Specify the following:
- Agent: Choose an agent from the drop-down list. Manage agents via the provided link.
- Template Name / OID Template: Choose an existing certificate template or click Get Template to fetch new ones.
- Timeout: Enter the timeout duration (in seconds) for the agent response. Unresponsive operations are logged as failed.
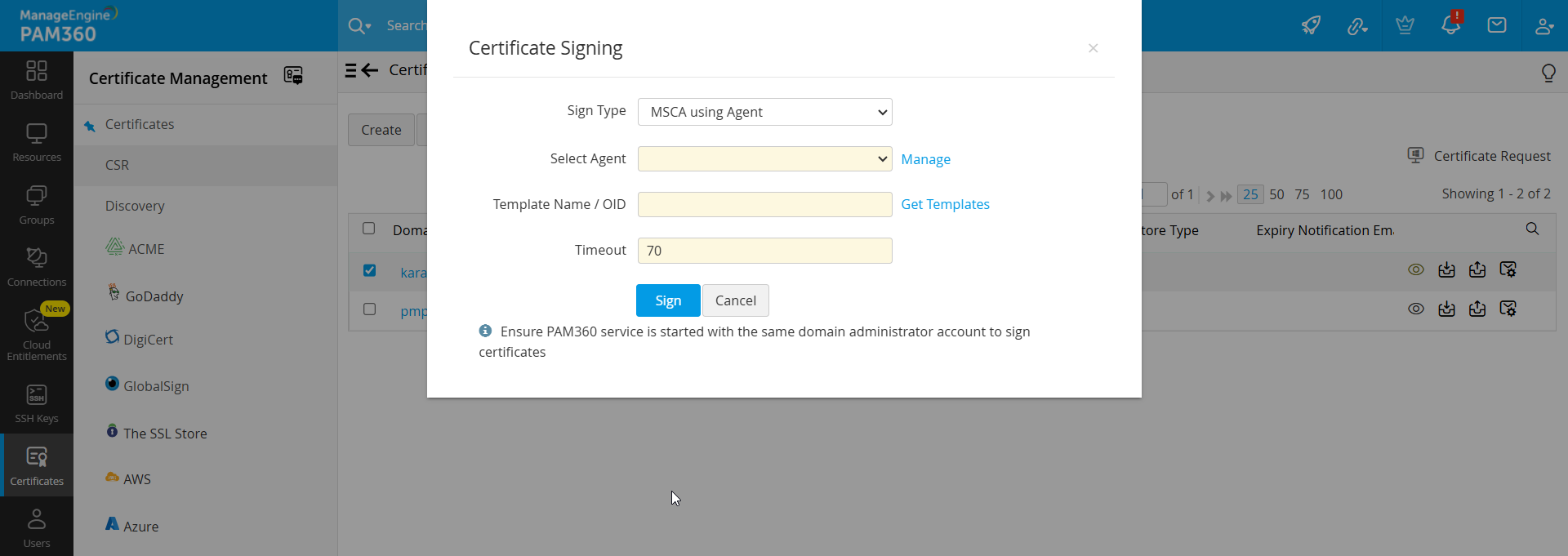
- Click Sign to process the request.
- Access the signed certificate under Certificates >> Certificates.
3.3 Certificate Signing via Custom Root Certificate
PAM360 offers the flexibility to sign CSRs using a custom root CA certificate, empowering organizations to maintain full control over their certificate issuance process.
If you do not already have a root CA certificate, you can create one directly within PAM360. To do this, enable the Generate root certificate checkbox while creating a new certificate, as outlined in Section 1 of the documentation.
If you already have a certificate in PAM360 and wish to designate it as a root certificate for signing CSRs, follow these steps:
- Navigate to Certificates >> Certificates.
- Select the desired certificate.
- Click More from the top menu and choose Mark as Root.
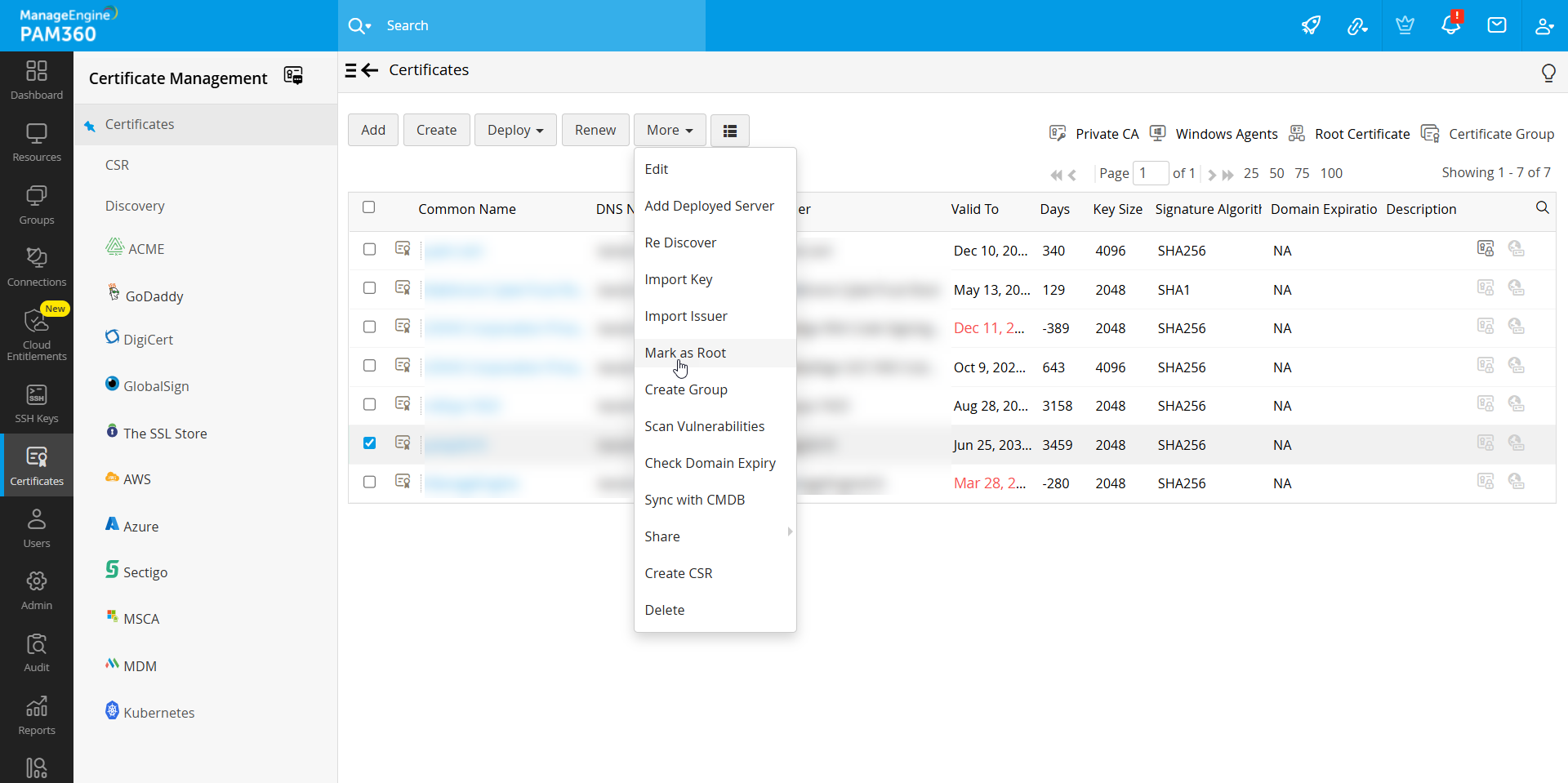
This streamlined process allows you to effortlessly configure and manage your root CA certificates within PAM360, ensuring robust control over your organization's certificate infrastructure.
Follow these steps to sign certificates using the custom root certificate:
- Select the CSR and click Sign from the top menu.
- In the pop-up that opens, select the Sign Type as Sign with Root.
- Select the trusted root CA certificate in the Select Certificate field.
- Specify the certificate Validity period in days.
- Select checkbox to Sign intermediate certificate. This allows users to sign the certificate on behalf of root CA.
- To add optional properties to the new certificate, click Advanced Options to expand the menu. Here, there are two categories of options, Key Usage and Extended Key Usage. Select the required options to set the preferred flags for the certificate to denote the purpose for which the new certificate may be used. The Key Usage options include Non Repudiation, Digital Signature, Data or Key Encipherment, Server/Client Authentication etc. You can choose the properties and mark them as critical by selecting the Critical checkbox.
- Click Sign to issue the certificate.
- View the signed certificate under Certificates >> Certificates.

You can also use the root CA certificate to simultaneously generate and sign certificates to user groups in bulk directly from PAM360.
- Navigate to Certificate and click Root Certificate on top right corner of the window.
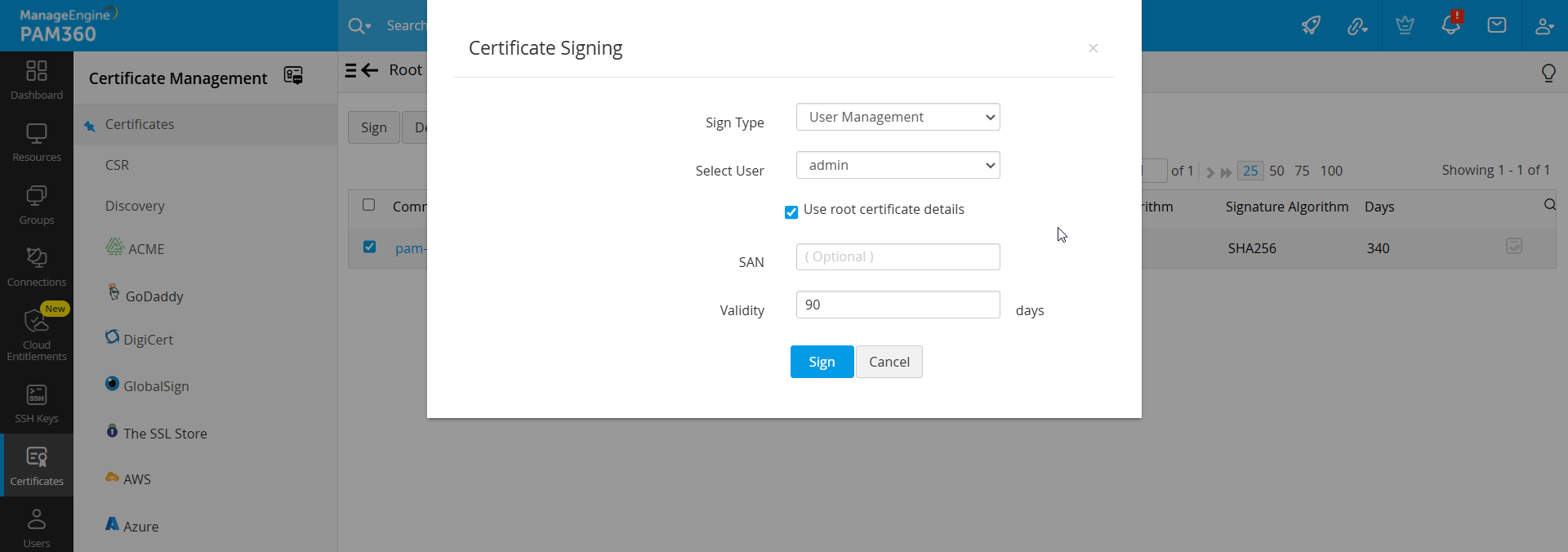
- Select the required root CA certificate and click Sign. In the pop-up that opens, choose the Sign Type, User or User Groups to which certificates have to be created and deployed, mention the SAN and validity (in days).
- The User Management sign type allows you to generate and sign certificates for user accounts in PAM360.
- Select the user account for which you need to generate a certificate.
- By default, the user certificates inherit the same parameters as that of the root certificate. You can change it by disabling the Use root certificate details option.
- After filling in the details, click Sign.
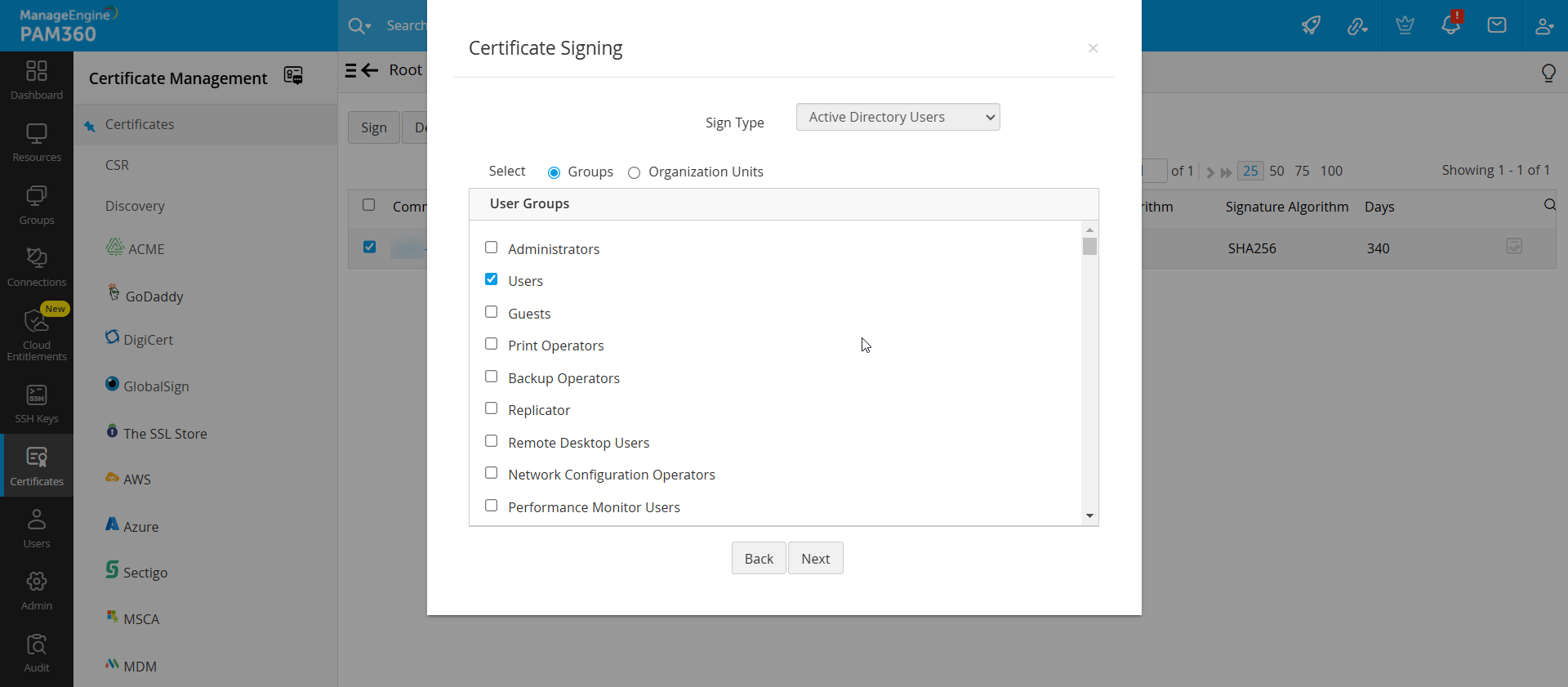
- The Active Directory Users sign type allows you to generate and sign certificates to user accounts mapped to the Active Directory within your network environment.
- Select the Domain Name and provide the Primary Domain Controller and Secondary Domain Controller address, Username and Password.
- Choose the Import Type as Single and specify the User to Import or User Group to Import.
- Choose the Import Type as Groups/OU tree to choose the users or user groups in bulk for which certificates need to be created.
- After selecting the users, enter the certificate validity in days. By default, the user certificates inherit the same parameters as that of the root certificate. You can change it by disabling the Use root certificate details option.
- Adjust parameters as required, then click Sign.
- The generated certificates are listed in PAM360's certificate repository.
After signing the certificate requests and obtaining the certificates, deploy them to the necessary end-servers. Refer to the detailed Certificate Deployment section for step-by-step guidance.
Caution
When signing certificates with a custom root CA for web applications, ensure all browsers in the network trust the root CA certificate to avoid security warnings.