What is vulnerability management?
Vulnerability management is a continuous process of discovering, assessing, prioritizing, remediating, and validating weaknesses across an organization's IT environment. Aimed at reducing the attack surface while keeping business operations running smoothly.
Generally, security teams employ vulnerability scanning software like ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus to identify security gaps and implement various methods to fix or address them.
Understanding the difference between a threat, a risk, and a vulnerability?
| Term | Definition | Nature | Control/Management | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Threat | Potential danger that can exploit vulnerabilities | Active, potential event | Can be blocked or mitigated | Malware (e.g., ransomware), phishing |
| Vulnerability | Weakness or flaw in a system that can be exploited | Static, weakness | Can be identified and fixed | Unpatched software, weak password |
| Risk | Likelihood and impact of a threat exploiting a vulnerability | Consequence, potential loss | Can be assessed and mitigated | Data breach, financial loss from attack |
How are vulnerabilities categorised and ranked ?
| Category Type | Examples | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| By weakness type | Buffer overflow, SQL injection, XSS, privilege escalation, misconfigurations | Helps map issues to CWE (Common Weakness Enumeration) for standardized tracking |
| By asset/surface | Endpoints (PCs, mobiles), Servers, Cloud workloads (containers, SaaS), Applications (web/API), Network/IO | Enables asset-based risk scoring and patch planning |
| By impact | Confidentiality breach, Integrity tampering, Availability disruption (DoS) | Directly ties vulnerability to business risk (data theft, downtime, fraud) |
CVSS-Based Vulnerability Ranking
What is CVSS?
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) gives a vulnerability a numerical score (0-10) that reflects its severity.
It uses three metric groups:
CVSS Metric Groups
| Metric Group | What It Measures | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Base | Intrinsic qualities of the vulnerability (constant over time) | Attack Vector (local vs remote), Complexity, Privileges Required, User Interaction, CIA Impact |
| Temporal | Changes over time (exploit availability, patch availability, maturity of exploit code) | PoC exploit released, vendor patch published |
| Environmental | Organization-specific context | Asset criticality, compensating controls, business impact |
CVSS Scoring Ranges
Table: CVSS Severity Ratings
| CVSS Score | Severity Level |
|---|---|
| 0.0 | None |
| 0.1-3.9 | Low |
| 4.0-6.9 | Medium |
| 7.0-8.9 | High |
| 9.0-10.0 | Critical |
A “CVSS 9.8” typically means a remote code execution flaw with no user interaction needed the worst-case scenario.
What is risk based vulnerability management ?
Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) shifts the focus from patching everything marked “critical” to addressing the vulnerabilities that truly endanger your business. Instead of relying only on CVSS severity, RBVM layers in threat intelligence, asset context, and business impact to drive smarter remediation decisions.
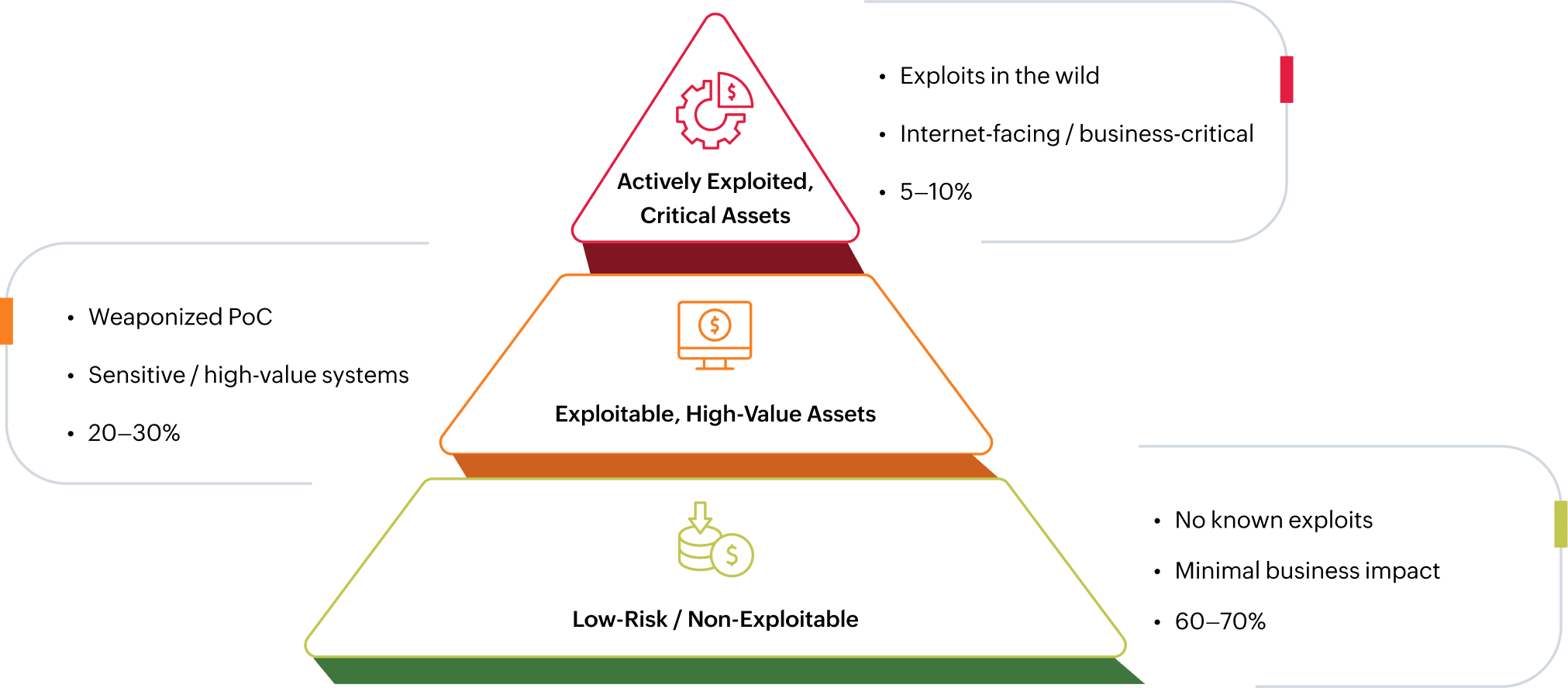
In essence, RBVM ensures security teams spend resources where they reduce the most real-world risk, not just the most theoretical severity.
Understanding the differences between Vulnerability Assessment and Vulnerability Management
Knowing how vulnerability assessment differs from vulnerability management
People often mix up vulnerability assessmentand vulnerability management , but they play distinct roles in cybersecurity.
- Vulnerability Assessment
It is a point-in-time scan that spots and lists weak points in systems, networks, or applications. It shows what vulnerabilities exist now ranked using systems like CVSS.
- Vulnerability Management
It is an continuous process that not finds vulnerabilities but also prioritizes, remediates, and validates fixes based on how they can be exploited how they affect the business, and how crucial the asset is. It makes sure risks decrease over time, not just get reported.
Strengthen your security posture with continuous vulnerability assessment and risk-based remediation. Start a free trial of ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus.

Assessment finds vulnerabilities, while management fixes and governs them over time.
Key Differences between vulnerability assessment and vulnerability management
| Aspect | Vulnerability Assessment (VA) | Vulnerability Management (VM) |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | One-time scan & report | Ongoing lifecycle process |
| Focus | Identify vulnerabilities | Reduce risk continuously |
| Output | Report with CVSS scores | Patched systems, compliance, dashboard |
Vulnerability management process
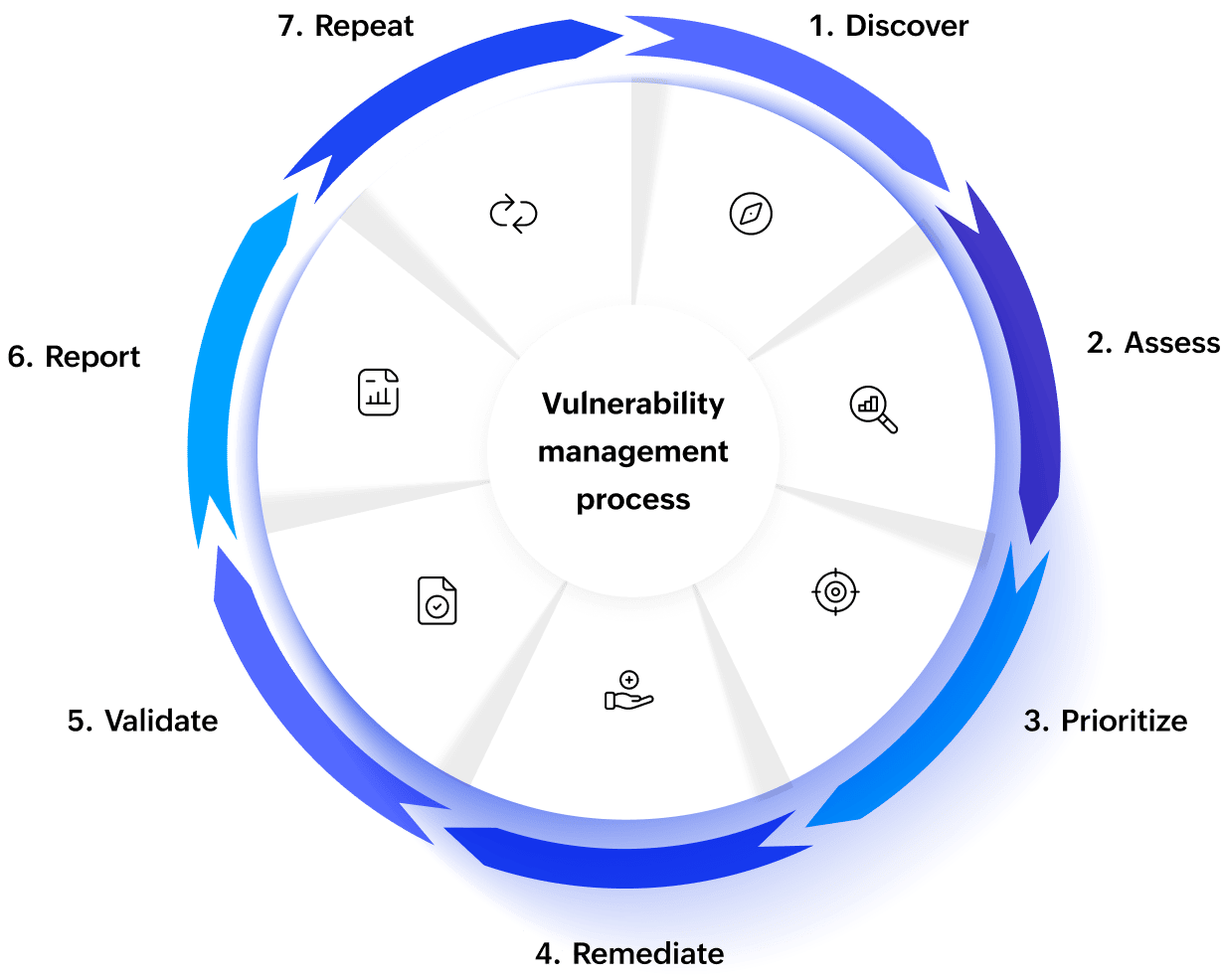
- Discovery
Identify and list assets across the environment (computers, servers cloud workloads, apps, databases, containers, and third-party parts).
Why it matters ? You can't guard what you don't know exists; seeing your assets forms the base of vulnerability management.
- Assessment
Vulnerability scanners and threat intelligence feeds help find misconfigurations missing patches outdated software, and known CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures).
Why it matters ? It gives a baseline of weaknesses and how severe they are.
- Prioritization
Experts rank vulnerabilities using systems like CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System), EPSS (Exploit Prediction Scoring System), and threat intelligence (KEV catalog, exploitability data) . They also consider how critical the asset is and its exposure (e.g., if it faces the internet)
Why it matters ? Not every "critical" vulnerability poses the same level of risk—setting priorities helps to use resources where the risk is highest.
- Remediation
Security teams deploy patches, change configurations, or add protective measures (like separating networks or creating virtual fixes) to solve vulnerabilities.
Why it matters ? It lowers the chance of attacks and makes the overall security stronger.
- Reporting & Continuous Improvement
Dashboards and reports keep tabs on key numbers like Mean Time to Remediate (MTTR) how many critical bugs get fixed on time, and how much of the system is checked. The team learns from past experiences to make the process better.
Why it matters ? This helps the company follow rules, gives bosses a clear picture, and shows how well the program is doing.
How ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus Helps
Effective vulnerability management isn’t just about finding CVEs it’s about closing the loop across discovery, prioritization, remediation, and compliance. ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus (VMP) brings all of this into a single platform:
- Agent-based scanning
Provides continuous visibility across on-premises and remote endpoints, ensuring even devices outside the corporate network are accounted for.
- Risk-based prioritization
Goes beyond CVSS scores by combining exploit intelligence (CISA KEV, EPSS), asset exposure, and business impact to rank vulnerabilities more effectively.
- Built-in patch management
Enables security teams to remediate OS and third-party application vulnerabilities directly, or apply configuration fixes when patches aren’t available.
- 75+ security configuration checks
Aligns with CIS benchmarks, helping IT teams harden systems and demonstrate compliance to auditors.
- Compliance-ready reporting
Provides detailed metrics on remediation timelines, SLA adherence, and security gap trends, making compliance reviews straightforward and transparent.
By consolidating vulnerability assessment, patching, and configuration management, Vulnerability Manager Plus ensures organizations not only reduce exploitable risk but also stay aligned with regulatory frameworks and industry standards.
