- Free Edition
- Quick Links
- MFA
- Self-Service Password Management
- Single Sign-On
- Password Synchronizer
- Password Policy Enforcer
- Employee Self-Service
- Reporting and auditing
- Integrations
- Related Products
- ADManager Plus Active Directory Management & Reporting
- ADAudit Plus Real-time Active Directory Auditing and UBA
- Exchange Reporter Plus Exchange Server Auditing & Reporting
- EventLog Analyzer Real-time Log Analysis & Reporting
- M365 Manager Plus Microsoft 365 Management & Reporting Tool
- DataSecurity Plus File server auditing & data discovery
- RecoveryManager Plus Enterprise backup and recovery tool
- SharePoint Manager Plus SharePoint Reporting and Auditing
- AD360 Integrated Identity & Access Management
- Log360 (On-Premise | Cloud) Comprehensive SIEM and UEBA
- AD Free Tools Active Directory FREE Tools
Why is 2FA required?
In today’s digital landscape, securing organizational access demands more than just strong passwords. Solutions like Active Directory two-factor authentication (also known as dual factor authentication or 2FA)—a key capability within multi-factor authentication (MFA)—are now essential for organizations of all sizes. As cyber-threats grow more sophisticated, relying on passwords alone is no longer enough to protect sensitive data and critical systems. By adding an extra layer of security through dual factor authentication or two step verification, organizations force an intruder to compromise not just one, but two elements before gaining access.
Passwords can no longer be considered the only reliable factor for authentication. Consider the following statistics:
- Verizon states that 82% of data breaches involve human vulnerabilities, like social engineering, errors, and misuse.[1]
- According to password statistics put forth by Dataprot, 51% of people use the same password for work and personal accounts. Moreover, 57% of people who have already been victims of phishing attacks still haven't changed their passwords.[2]
- Many infamous cyberattacks on large-scale industries, such as the Colonial Pipeline and Ireland’s Health Service Executive, started with one exposed password.[3]
Without two factor or two step verification, a single weak password creates a major vulnerability. Dual factor authentication addresses this by enforcing a second validation—such as an OTP, push notification, or biometric scan—alongside the password, greatly minimizing risk and reinforcing your organization's security.
What is 2FA fatigue?
2FA fatigue refers to a user’s tendency to become desensitized by frequent two-factor authentication requests. This fatigue is especially common with methods that trigger push notifications or require repeated code entries throughout the day. The security risk: users experiencing 2FA fatigue may start approving authentication prompts without scrutiny or try to bypass the system for convenience, which attackers can exploit—known as push fatigue attacks, where threat actors bombard users with approval requests until one of them gets accepted.
Best practice: Educate users to carefully scrutinize every request, and offer diverse authentication methods such as biometrics or hardware keys to ensure security without compromising user convenience.
Types of 2FA
There are various types of 2FA methods today, each with its own balance of security and convenience. ADSelfService Plus supports a wide range of dual factor authentication methods—including both basic and advanced options—to fit diverse enterprise needs.
Here are the commonly used types of 2FA:
- SMS 2FA (SMS two-factor authentication): A unique OTP is sent to a user’s registered mobile device via SMS during login.
- Time-based OTP (TOTP): Generated via apps like Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Zoho OneAuth.
- Push notification authentication: Upon login attempt, a notification is sent to the user’s mobile app for one-tap approval.
- Email-based verification: A security code is emailed to the user for identity confirmation.
- Biometric authentication: Involves fingerprint or facial recognition as a second factor.
- Hardware authenticators: Includes YubiKey, RSA SecurID, or smart cards for secure physical authentication.
- Security questions: Users answer pre-configured questions to verify identity.
SMS 2FA (SMS two-Factor authentication)
SMS 2FA is a simple, widely adopted authentication method that adds a second identity verification step via mobile text message. Here's how it works with ADSelfService Plus:
- A user signs in with their password.
- ADSelfService Plus triggers a secure OTP to the user’s registered phone number via SMS.
- The user enters the OTP to complete logon.
SMS 2FA vulnerabilities
SMS 2FA offers basic convenience, but it’s important to acknowledge its vulnerabilities:
- SIM swapping: Attackers social-engineer mobile carriers to transfer a victim’s number to their own SIM, intercepting the SMS code.
- SMS interception: Malware or rogue apps may capture incoming messages.
- Phishing risk: Users may be tricked into entering recent SMS codes on fraudulent sites, allowing attackers real-time access.
- Network weaknesses: SMS is unencrypted end-to-end, potentially exposing data over insecure networks.
Best practice: Combine SMS 2FA with stronger alternatives (like authenticator apps or hardware tokens) for critical systems and educate the users regarding threats like phishing and SIM swapping.
Common 2FA bypass techniques
Attackers continuously seek new ways to bypass two-factor authentication. The most prevalent 2FA bypass techniques include:
- Phishing proxies: Fake websites intercept real passwords and 2FA codes, relaying them to the legitimate site in real time.
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks: Compromised browsers or networks are used to capture and reuse authentication tokens.
- SIM swapping and social engineering: As mentioned, enable attackers to receive SMS or call-based 2FA codes.
- Malware: Compromised devices can read or intercept authentication codes delivered via SMS, email, or even app notifications.
- Exploiting 2FA fatigue: Attackers may abuse push notification exhaustion, sending multiple requests until a user accidentally or carelessly approves one.
Best practice: Educate users to spot phishing attempts, enforce strong authentication using app-based or hardware tokens for sensitive accounts, and implement adaptive risk policies that trigger additional verification for anomalous sign-in behavior.
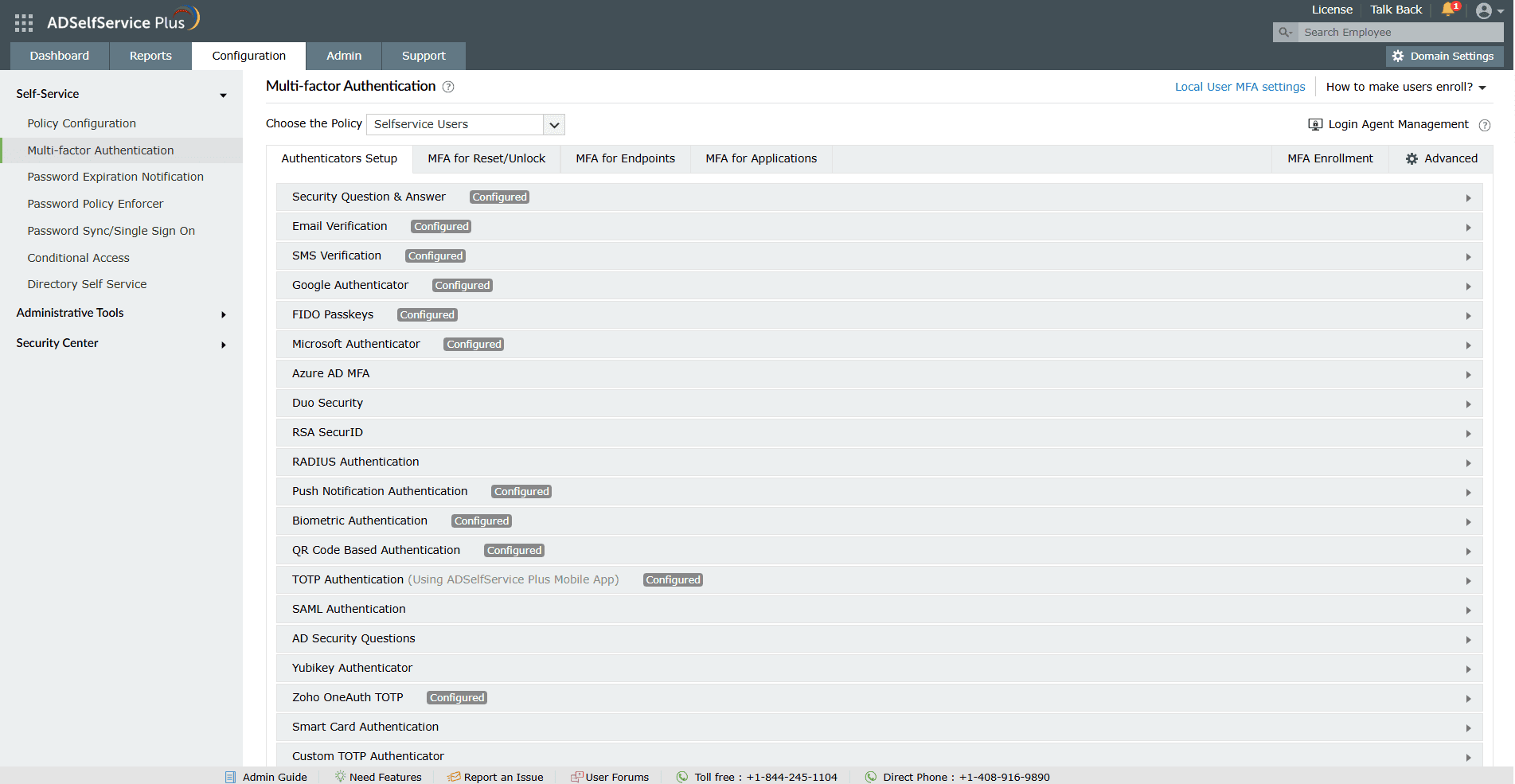
Native AD tools vs. ADSelfService Plus for 2FA
Native Active Directory tools provide either limited or no built-in two-factor authentication, while ADSelfService Plus offers a feature-rich, centralized, and easy-to-manage two-factor authentication solutions for broad enterprise needs.
| Feature | Native AD tools | ADSelfService Plus |
|---|---|---|
| 2FA/MFA for Windows/macOS/Linux logons | Not natively supported | Yes, multi-method |
| 2FA for VPN, OWA, RDP, SSPR, Offline | No (requires add-ons) | Yes, out of the box |
| Variety of authentication methods | Limited (mainly smart card) | 20+ options (biometric, TOTP, etc.) |
| Centralized policy management | No | Yes, via the unified admin console |
| User self-service enrollment | No | Yes |
| Regulatory compliance support | Partial | Full, with audit trails |
Native tools do not provide built-in dual factor authentication for most scenarios. For organizations seeking the best 2FA solution, a dedicated platform like ADSelfService Plus offers advanced, easy-to-manage, and highly configurable multi-method coverage.
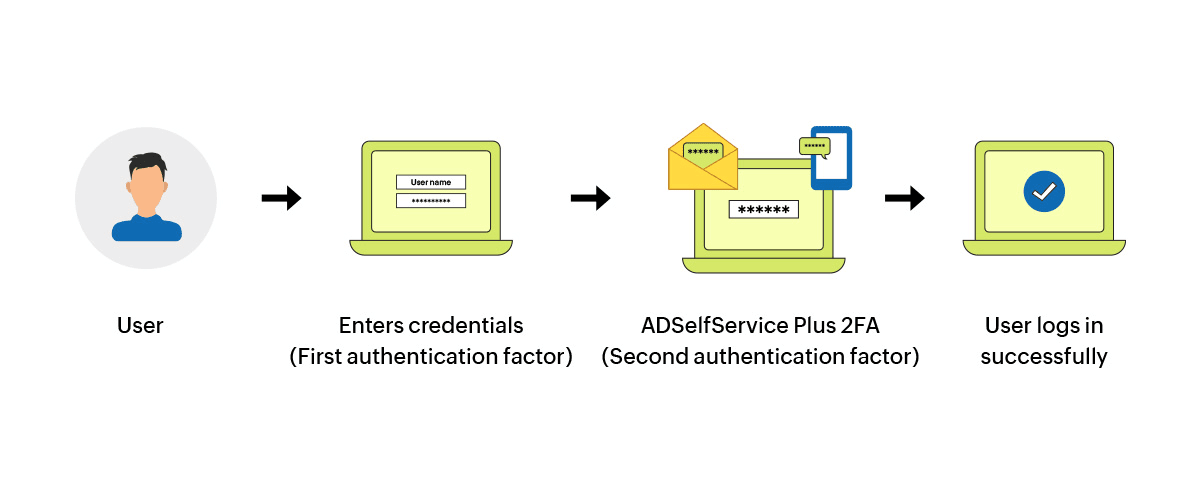
How does dual factor authentication work with ADSelfService Plus?
ADSelfService Plus two-factor authentication process works similarly for both application and endpoint logons. Each time a user requests access to a particular resource, they first have to verify their identity using a primary factor of authentication, which is typically—but not always—a password. Once primary authentication is completed, the user is prompted to perform secondary authentication. After completion of the secondary authentication, users are granted access to the respective resource.
Below is an illustration of how the two-factor authentication method works in ADSelfService Plus.
Comprehensive 2FA solution
ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus offers comprehensive, context-aware Endpoint MFA to secure all points of contact in your enterprise with advanced authentication methods such a biometrics, hardware tokens, and TOTPs.
2FA for machine access
Ensure secure access to Windows, macOS, and Linux machines using Active Directory two-factor authentication for user logins
2FA for machine access
Allow users to securely access IT resources through a VPN after a stringent authentication flow with advanced enterprise authentication methods.
2FA for OWA
Ensure secure access to OWA accounts by deploying Active Directory two-factor authentication with strong factors during OWA logins.
Offline 2FA
Secure your offline remote users by enabling Active Directory two-factor authentication for offline Windows and macOS machine logons.
Machine-centric 2FA
Enforce 2FA at the machine level so that every user logging into a specific machine must verify their identity, regardless of individual user policies or enrollment status.
2FA for enterprise applications
Regulate enterprise application access via SSO using strong authenticators such as FIDO passkeys, YubiKey, and biometric authentication for Active Directory users.
2FA for SSPR
Enable users to perform Active Directory self-service password reset (SSPR) and self-service account unlock only after user identity verification using the two-factor authentication types supported by SSPR.
Apply specific authentication methods to different user policies.
Below are some of the two-factor authentication methods that ADSelfService Plus offers:
- FIDO passkeys
- Biometric authentication (fingerprint or facial recognition)
- Push notification authentication
- Duo Security
- Microsoft Authenticator
- Google Authenticator
- YubiKey authentication
- RSA SecurID
- Push notification
- Smart card authentication
- Entra ID MFA
- RADIUS
- Time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs)
- Custom TOTP authenticators
- Zoho OneAuth TOTPs
- QR-code-based authentication
- Security questions and answers
- SMS verification
- Email verification
- SAML authentication
What makes the best 2FA solution?
The best 2FA solution balances robust security, user convenience, and flexibility. Key features include:
Wide range of authentication methods: Support for SMS, authentication apps, biometrics, hardware tokens, and more controls.
Seamless integration: Works across endpoints (Windows, macOS, Linux), VPNs, web applications, and self-service workflows.
Centralized management: Unified policy and enrollment for all users.
User self-service: Easy enrollment and troubleshooting reduce IT workload.
Strong compliance features: Audit logs and reporting help meet standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and NIST.
ADSelfService Plus exemplifies the best 2FA solution by offering over 20 authentication methods, granular policy controls, and comprehensive support for enterprise requirements.
Key benefits of implementing 2FA using ADSelfService Plus
Enabling two-factor authentication with ADSelfService Plus brings numerous advantages for your organization, directly addressing common IT security challenges:
- Unrivaled security: Drastically reduces the risk of all password-based attacks, including phishing, brute-force, and credential stuffing, by making compromised credentials useless without the second factor.
- Mitigate insider threats: Provides an essential layer of security against compromised internal accounts, accidental misconfigurations, or malicious insiders seeking to elevate privileges.
- Protect critical resources: Safeguards sensitive data, business-critical applications, and systems that are integrated with and reliant on your AD infrastructure.
- Flexible authentication methods: Offers support for a wide range of factors including biometrics, push notifications, Time-based One-Time Passwords (TOTP), security keys (e.g., YubiKey), and more.
- Adaptive security policies: Implement conditional access policies based on user location, device trustworthiness, or time of access, adding an intelligent layer of defense.
Incorporating dual factor authentication with the right mix of technology is widely recognized as the gold standard for identity security. By leveraging the best 2FA solution, you ensure not just compliance, but lasting peace of mind for your business and users.
Citations:
- Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, 2023
- Dataprot: Password Statistics, 2022
- Public reporting on Colonial Pipeline and Ireland’s HSE cyber incidents
FAQs
Yes, implementing two-factor authentication with strong authentication factors like biometrics and smart cards can defend better against modern-day cyberattacks when compared to the traditional username and password method.
ADSelfService Plus simplifies 2 factor authentication configuration for admins by providing an enriched, user-friendly console. It enables you to set up different 2FA flows for different groups or departments in your organization, i.e., you can configure specific methods of 2FA for privileged accounts in Windows Active Directory. You can choose the number of authenticators that end users must verify with for each activity, like self-service, application logons, and endpoint logons. ADSelfService Plus also makes the 2FA enrollment process a breeze for both users and admins.
No, Active Directory two-factor authentication requires additional tools like NPS extension, or other third-party solutions.
Yes, using ADSelfService Plus, Active Directory two-factor authentication can be enabled for on-premise and remote logins.
Yes, ADSelfService Plus integrates with on-premises Active Directory for 2FA.
Yes. Both terms refer to adding additional authentication layers to Active Directory logins. While Active Directory two-factor authentication is a subset of AD MFA requiring an extra layer of authentication apart from username and password, AD MFA can involve two or more layers of authentication.
Highlights of ADSelfService Plus
Password self-service
Eliminate lengthy help desk calls for Windows Active Directory users by empowering them with self-service password reset and account unlock capabilities.
MFA
Enable context-based MFA with 20 different authentication factors for endpoint, application, VPN, OWA, and RDP logins.
One identity with single sign-on
Get seamless one-click access to more than 100 cloud applications. With enterprise single sign-on, users can access all their cloud applications using their Windows Active Directory credentials.
Password and account expiry notifications
Notify Windows Active Directory users of their impending password and account expiration via email and SMS notifications.
Password synchronization
Synchronize Windows Active Directory user passwords and account changes across multiple systems automatically, including Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, IBM iSeries, and more.
Password policy enforcer
Enforce strong passwords to resist hacking threats. Require Windows Active Directory users to choose compliant passwords by displaying password complexity requirements.