- Free Edition
- Quick Links
- MFA
- Self-Service Password Management
- Single Sign-On
- Password Synchronizer
- Password Policy Enforcer
- Employee Self-Service
- Reporting and auditing
- Integrations
- Related Products
- ADManager Plus Active Directory Management & Reporting
- ADAudit Plus Real-time Active Directory Auditing and UBA
- Exchange Reporter Plus Exchange Server Auditing & Reporting
- EventLog Analyzer Real-time Log Analysis & Reporting
- M365 Manager Plus Microsoft 365 Management & Reporting Tool
- DataSecurity Plus File server auditing & data discovery
- RecoveryManager Plus Enterprise backup and recovery tool
- SharePoint Manager Plus SharePoint Reporting and Auditing
- AD360 Integrated Identity & Access Management
- Log360 (On-Premise | Cloud) Comprehensive SIEM and UEBA
- AD Free Tools Active Directory FREE Tools
Updating Windows cached credentials
Remote users often struggle to reset expiring passwords and update their machine's outdated cached credentials because they lack a connection to Active Directory. And in instances when they lose machine access due to an expired password, they are unable to reach out to the help desk for assistance and experience decreased productivity.
ADSelfService Plus, an identity security solution with multi-factor authentication, self service password reset, and password management capabilities, enables users to securely reset their Windows cached credentials even when they have no connection to Active Directory. It automatically updates the domain cached credentials on their Windows machines remotely using a VPN client. Cached credentials can also be updated without a VPN when an organization does not have VPN infrastructure or uses a VPN vendor not supported by ADSelfService Plus.
What are cached credentials?
When a user logs in to an Active Directory domain for the first time, the login credentials are stored, or cached, locally on their machine. These cached credentials are updated each time the machine is connected to Active Directory, i.e., to the corporate network, during login. When a remote user who is not connected to the corporate network logs in to their machine, their login information is verified locally against the cached credentials stored on their machine. If the verification succeeds, they can access the machine. In short, Active Directory cached credentials allow users to log in to their machines even when they have no way of reaching the domain controller for authentication.
Can cached credentials cause account lockouts?
Remote employees often encounter login problems because their cached credentials expired while working offline or without VPN. Mismatches in cached credentials and domain-stored credentials are likely to occur when users utilize more than one device for work. Let us consider an employee working in the hybrid model using two different devices—a desktop device at the office and a laptop at home. Say the employee recently changed their Active Directory password while working from the office on their domain-connected desktop device. Their laptop's cached credentials would still contain the old password since the device does not have a connection to the corporate network for an update. Forgetting this, the employee may try to log in with their new password on their laptop while working remotely, and they may get locked out after multiple attempts.
Alternatively, let us assume that after a couple of attempts, the employee realizes that their laptop still has the old password cached and continues to use it during login. However, in an unlikely circumstance, if the employee happens to bring their laptop to the office, it gets connected to the corporate network, and the cached credentials get updated without their knowledge. The employee now might habitually enter their old password during login and get locked out after multiple attempts.
How to update Windows passwords without connecting to a domain controller
After every password reset or change, ADSelfService Plus provides a cached credentials update for remote users either using a VPN client or without using a VPN client. It comes bundled with a GINA/Credential Provider client, also known as the Windows login agent, that allows remote users to perform a secure self-service password reset right from their login screens and forcefully updates their Windows machine's cached credentials afterwards.
How to update cached credentials with password reset
How to setup cached credentials update using ADSelfService Plus:
- Configure self-service password reset for Active Directory and enterprise applications.
- Setup MFA for password reset authentication using methods like biometrics, FIDO2 passkeys, and TOTPS.
- Enable cached credentials update and connect with the VPN server, if required.
Update cached credentials using a VPN client
Here's how ADSelfService Plus' cached credentials update via VPN works for remote Windows users.
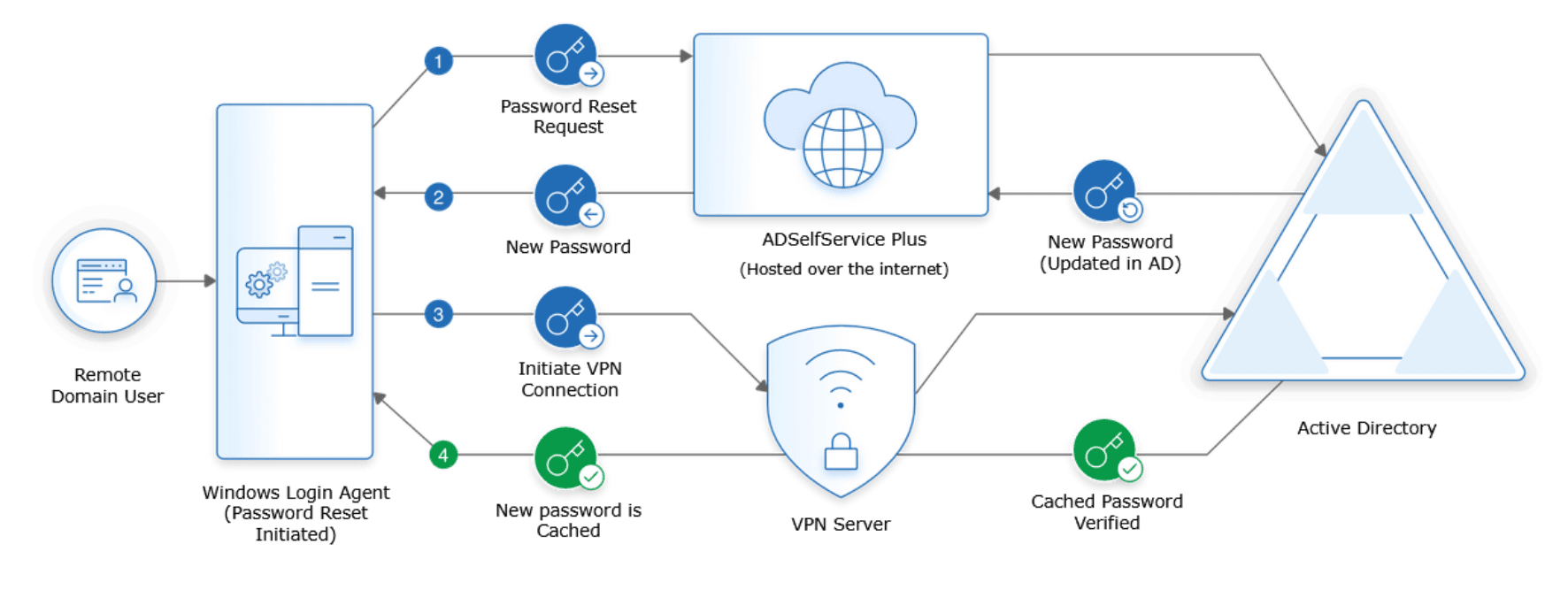
- When a remote user forgets their Active Directory password, they use ADSelfService Plus’ login agent to reset their password from their login screen.
- After users verify their identity through MFA and reset their password, ADSelfService Plus updates Active Directory with the new password.
- The new password is also sent to the login agent on the user's machine.
- The login agent automatically establishes a secure connection with Active Directory through VPN and initiates a request for updating the locally cached credentials.
- Once the request is successfully approved by Active Directory, the cached credentials on the user's machine are automatically updated.
Update cached credentials without using a VPN client
Here's how ADSelfService Plus' cached credentials update works for remote Windows users without using a VPN.
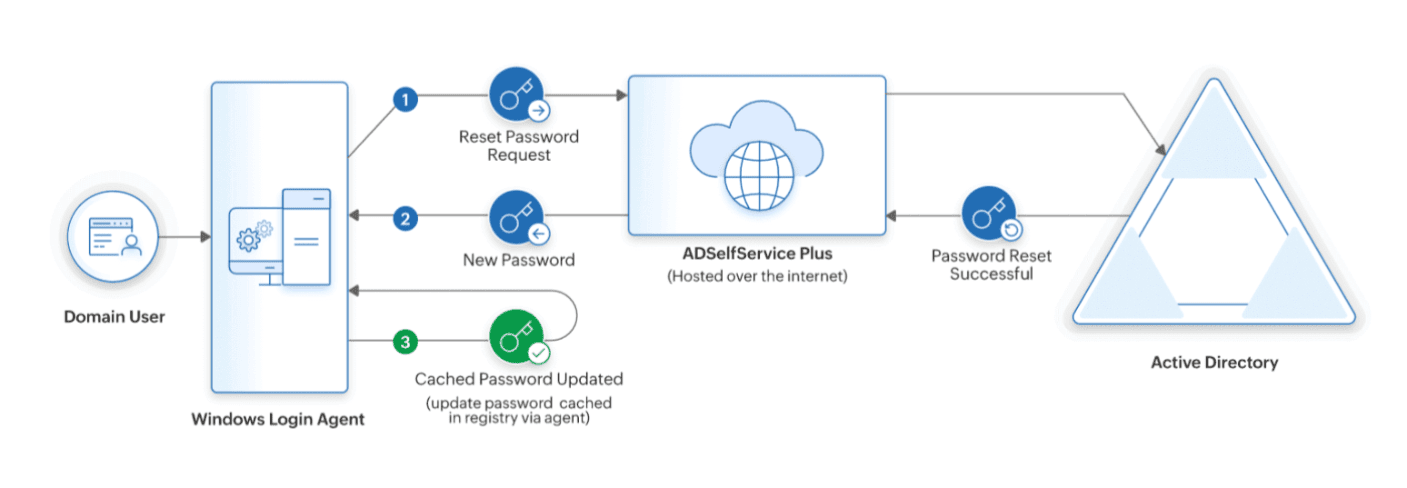
- When a remote user forgets their Active Directory password, they use ADSelfService Plus’ login agent to reset their password from their login screen.
- After users verify their identity through MFA and reset their password, ADSelfService Plus updates Active Directory with the new password.
- Once the new password is updated in Active Directory, the login agent automatically updates the local cache on users' machines with the new password.
Windows versions that support cached credentials update using ADSelfService Plus
Windows server versions: Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2, and Windows Server 2008
Windows client versions: Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista
VPN providers that ADSelfService Plus supports for Windows cached credentials update
- Fortinet
- Cisco IPSec
- Cisco AnyConnect
- Windows Native VPN
- SonicWall NetExtender
- Checkpoint EndPoint Connect
- SonicWall Global VPN
- OpenVPN
- Custom VPN
Benefits of updating Windows cached credentials using ADSelfService Plus
Improve identity security
Strengthen account protection by enforcing multi-factor authentication and applying strong password policies for cached password resets, which significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Improve employee productivity
Give remote users the ability to regain access to their machines quickly even if they forget their passwords, which helps avoid any major business interruptions.
Reduce password reset calls
Empower remote users with self-service password reset and cached credentials update features, and limit password-related help desk tickets.
Reduce costs
Resetting passwords through help desk assistance and connecting machines to the corporate network for a cached credentials update are both time-consuming and expensive processes, which can be easily eliminated using ADSelfService Plus.
FAQs
If cached credentials have expired, users may be locked out of their machines until they reconnect to the corporate network to refresh them. ADSelfService Plus solves this issue by allowing users to reset their passwords and update cached credentials remotely, preventing downtime.
Windows cached credentials cannot be accessed, they are securely stored as encrypted hashes in the local Security Account Manager (SAM) and accessed by the Local Security Authority (LSA), allowing users to log in offline without exposing plain-text passwords.
Highlights of ADSelfService Plus
Password self-service
Unburden Windows AD users from lengthy help desk calls by empowering them with self-service password reset and account unlock capabilities.
Multi-factor authentication
Enable context-based MFA with 20 different authentication factors for endpoint, application, VPN, OWA, and RDP logins.
One identity with single sign-on
Get seamless one-click access to more than 100 cloud applications. With enterprise single sign-on (SSO), users can access all their cloud applications using their Windows AD credentials.
Password and account expiry notifications
Notify Windows AD users of their impending password and account expiry via email and SMS notifications.
Password synchronization
Synchronize Windows AD user passwords and account changes across multiple systems automatically, including Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, IBM iSeries, and more.
Password policy enforcer
Strong passwords resist various hacking threats. Enforce Windows AD users to adhere to compliant passwords by displaying password complexity requirements.