The Patch Management Architecture consists of the following components:
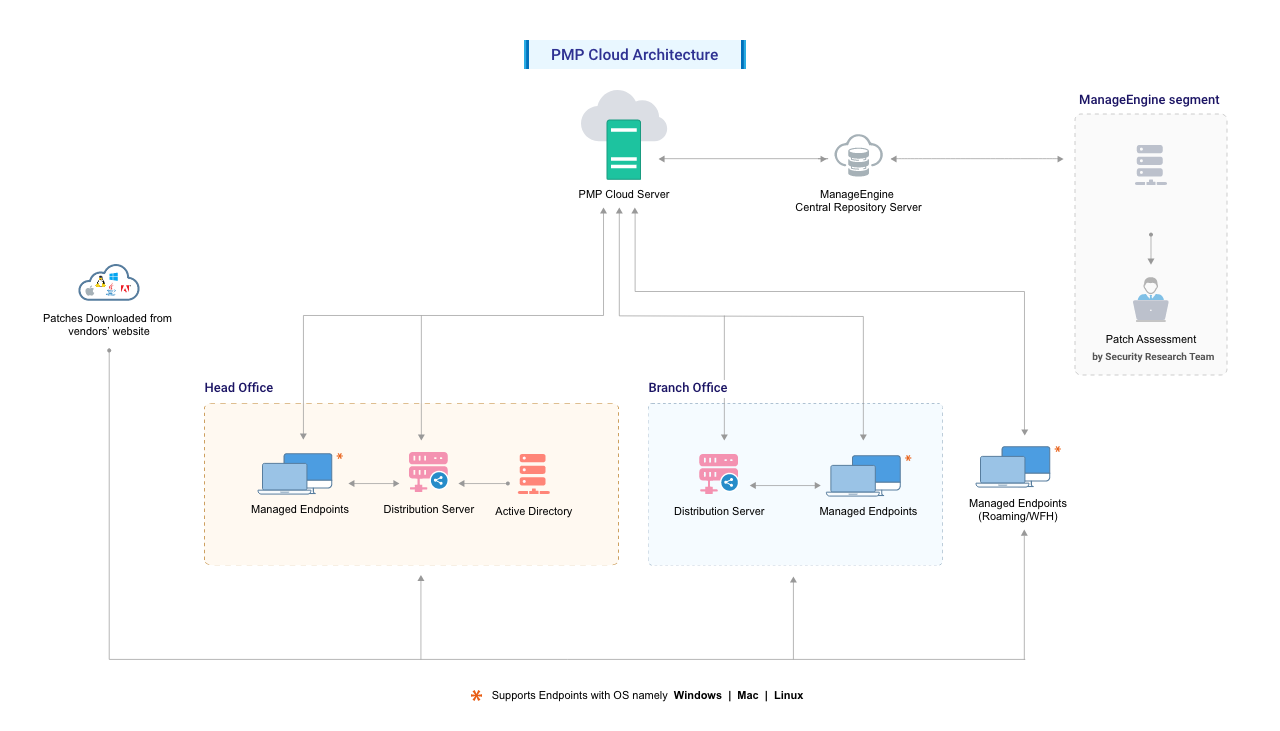
Fig: Patch Management Architecture
The Security Research Team at Zoho Corp. plays a vital role in maintaining cybersecurity. They continuously monitor the internet and vendor websites, such as those of Microsoft, Apple, Linux distributions, and other third-party applications, to gather vulnerability information.
Patch download, assessment for patch authenticity and testing for functional correctness is also carried out by our team. The final analysis and data are correlated to obtain a consolidated vulnerability database which serves as a baseline for vulnerability assessment in the enterprise. The modified vulnerability database is then published to the Central Patch Repository for further use.
The process of managing this data involves several key steps such as:
Only Windows and Mac patches will be tested before release to the central repository. It is recommended that Linux patches be tested in a des environment before deployment.
The entire process, from information gathering to patch analysis and publishing, is conducted periodically, ensuring that updates are incorporated into the Central Patch Repository promptly.
Once the updates are supported the corresponding patch details will be available in the Central Patch Repository.
Once supported, the updates will be available in the product after the sync between the Central Patch Repository and the Patch Manager Plus server has occurred. as per the configured time (once every day at the time you have configured in the Patch Database settings). You can also manually initiate this sync for the patches to show up after they have been supported.
The Central Repository Server is a portal in the Zoho Corp. site, which hosts the latest vulnerability database that has been published after a thorough analysis. This database contains all the patch information, which will be passed to the central server at regular intervals. For users working from home, the agent installed on their machine will pull the patch information from this database directly and download and install the patches from the vendor websites.
The Patch Manager Plus Cloud is a secure, scalable patch management solution hosted in ManageEngine’s global data centers. IT teams can access the cloud server remotely to deploy patches, automate tasks, and manage endpoint security with ease. All activity data—such as patch status, scan results, and user actions—is stored securely and can be exported for auditing and compliance. Unlike on-premises setups, the Patch Manager Plus server is not located at the end-user’s site, offering a fully cloud-hosted, maintenance-free experience. With Patch Manager Plus Cloud, you get:
The Distribution Server of Patch Manager Plus Cloud primarily acts as an AD Connector for your network. In addition, this can be used as a distribution point to streamline the bandwidth rates through your network. Distribution Server can be setup in any one of your remote/branch offices. IT administrators can setup the distribution server with replication policy rules (the data will be replicated from central server to distribution server based on this rule). In addition, the distribution server synchronizes with the Patch Manager Plus Cloud server for missing patch details. These patches are then downloaded directly from the respective vendor's website and distributed across the branch office agents depending on the status of the missing patches on each computer.
Patch Manager Plus, being a domain based approach to your endpoint solution, will sync resources information from active directory or workgroup. In cloud hosted setup, business can populate the resource information using AD Connector.
Patch Management is a two-stage process:
Patch Assessment or Scanning
The systems in the network are periodically scanned to assess the patch needs. Using a comprehensive database consolidated from Microsoft's and other bulletins, the scanning mechanism checks for the existence and state of the patches by performing file version checks, registry checks and checksums. The vulnerability database is periodically updated with the latest information on patches, from the Central Patch Repository. The scanning logic automatically determines which updates are needed on each client system, taking into account the operating system, application, and update dependencies.
On successful completion of an assessment, the results of each assessment are returned and stored in the server database. The scan results can be viewed from the web console.
Patch Download and Deployment
Upon selecting the patches to be deployed, the delivery process varies based on the endpoint's network location.
Under a Distribution Server (DS) setup, both patch metadata and patch binaries are provided to endpoints by the DS. The DS periodically downloads patch information from the Central Patch Repository and retrieves the required binaries directly from vendor websites.
For remote endpoints, such as those used by employees working from home, the agent directly accesses the vulnerability database and downloads patches from the respective vendor websites.
In both cases, all patch URLs and binaries are validated using checksums during both download and installation to ensure integrity.
Note: All Linux agents (including the ones under the Distribution Server) will directly download patches from the vendor websites.
Ports used by Patch Manager Plus Cloud are 443 for server-agent communication and 8384 for communication between (remote) agent and distribution server.