What is Amazon VPC?
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a commercial cloud computing service that enables users to create a logically isolated section within the AWS Cloud. Within this isolated section, users can launch AWS resources in a self-defined virtual network. It essentially allows users to create resources like EC2 instances, databases, and other Amazon Web Services (AWS) inside a private, isolated section of the AWS Cloud.
AWS provides VPC to enterprises as a solution for better cloud security. With this solution, organizations can launch their resources into a virtual cloud space that can be privately accessed, adding layers of security to their cloud resources.
Each Amazon account created after 2013 comes with a preconfigured default VPC. Therefore, users can launch instances straight away without having to configure anything. The default VPC is preconfigured with:
- A size /16 IPv4 CIDR block that provides up to 65,536 IPv4 addresses.
- A size /20 subnet in each availability zone that offers 4,096 addresses per subnet.
- An internet gateway connected to the VPC.
- A default security group and a default NACL.
Architecture and working of VPCs
The architecture of VPC consists of:
- Foundation and framework: The AWS Cloud's core infrastructure serves as the basis for Amazon VPC. An organization's cloud resources require network isolation and segmentation, which the VPC provides as the framework.
- Subnets: You can segregate your resources logically in Amazon VPC by creating subnets. Each subnet has a distinct function. For example, you might have a subnet for web servers, another for application servers, and a third for databases.
- Access control: The security groups and network access control lists (NACLs) are used in Amazon VPC to manage access control. These act as virtual gates, controlling traffic flow in and out of subnets and instances, based on defined rules.
- Utilities and services: Internet gateways for internet connectivity, NAT gateways for outbound internet access, VPN connections for secure communication, and direct connect for dedicated network connections to your on-premises infrastructure are just a few of the services and tools that AWS offers with Amazon VPC to support your virtual infrastructure. For example, you can use an internet gateway to set up internet access with VPC, allowing resources inside your VPC to connect to the internet privately or exchange data.
- Security and monitoring: Network firewalls, encryption, monitoring tools, and logging capabilities are some of the security features in Amazon VPC that guard your virtual environment from unauthorized access and malicious activities.
- Extension and renovation: You can scale and modify the network infrastructure with Amazon VPC as needed in order to adapt security policies, integrate new AWS services, and add or delete subnets with ease to meet evolving business needs.
Prior to delving deeper into the way it works, let's understand the key concepts that are necessary for Amazon VPC to operate correctly.
Default VPC
Every region has a default VPC set up when you register an AWS account. With this ready-to-use environment, you can begin deploying instances immediately. Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is the Amazon Web Service you use to create and run virtual machines in the cloud. Each EC2 instance you deploy in the default VPC has a private and public IP address, facilitating communication between the instances and the internet with the help of AWS's infrastructure.
Generating extra VPCs
You can divide your network into different segments by creating more VPCs. For example, you can keep distinct VPCs for development and production environments. The isolation and security of your different environments are guaranteed by the complete independence of these extra VPCs from any other VPC in your network.
A new VPC is launched with an IP address range, router, NACL, default security groups, and route table of its own. Moreover, you can increase the number of subnets, security groups, network ACLs, etc. based on the needs of your project.
While the default VPC is great for launching new instances, IAM policies do not apply to it. Creating a VPC allows users to define and customize their virtual network so it abides by the organization's IAM policies, thereby making it more secure and reliable.
Configuring the subnet
Subnets are a range of IP addresses in the VPC. You can establish one or more subnets inside your VPC. Subnets are not allowed to navigate availability zones; they must all reside fully within one availability zone. Subnets can be defined for various uses. For example, private subnets for resources that shouldn't be directly available from the internet and public-facing subnets for resources that are accessible from the internet.
Defining route tables
Route Tables are the backbone of network traffic flow. They are a collection of rules, or routes, that specify the direction in which network traffic is to be sent. A route table, which manages the subnet's routing, needs to be connected to each subnet in your VPC. Although you can link more than one subnet to a single route table, each subnet can only have one connected route table at a time.
Internet gateway
An essential element that gives network traffic a route between your Amazon VPC and the internet is an internet gateway. It's an AWS-managed component designed to be highly available and scalable, ensuring reliability and performance.
The internet gateway plays two critical roles. First, it serves as a route through which your VPC can communicate with the internet. Second, it performs network address translation (NAT) for instances that have been assigned public IPv4 addresses.
The internet gateway is essential in two ways:
- It acts as a conduit for communication between your VPC and the internet.
- It handles NAT for instances that have public IPv4 addresses assigned to them.
An internet gateway must be attached to your VPC in order to enable internet access within it. Also, you must make sure that instances have publicly routed IP addresses (public or elastic IPs) and change your subnet's route table to direct traffic to the internet gateway.
VPN Connection
Secure internet communication between your on-premises network and your virtual private network (VPN) is made possible by a VPN connection. By securely extending your current network infrastructure to the AWS cloud, you can seamlessly integrate AWS-hosted resources and applications with those in your on-premises data center or office.
VPC peering
VPC peering is a networking connection that allows you to privately route traffic between two VPCs, either inside the same region or across separate AWS regions. Peer VPC instances are able to communicate with one another much like they would if they were on the same network.
Transitive peering connections are not supported by VPC peering. If suppose, there is a VPC peering connections between VPC A and VPC B as well as between VPC A and VPC C. But you cannot route traffic from VPC B to VPC C through VPC A. You need to establish a VPC peering connection between VPC B and VPC C in order to transport traffic between them.
Refer to figure 1 below, which depicts the way the components mentioned above work together.
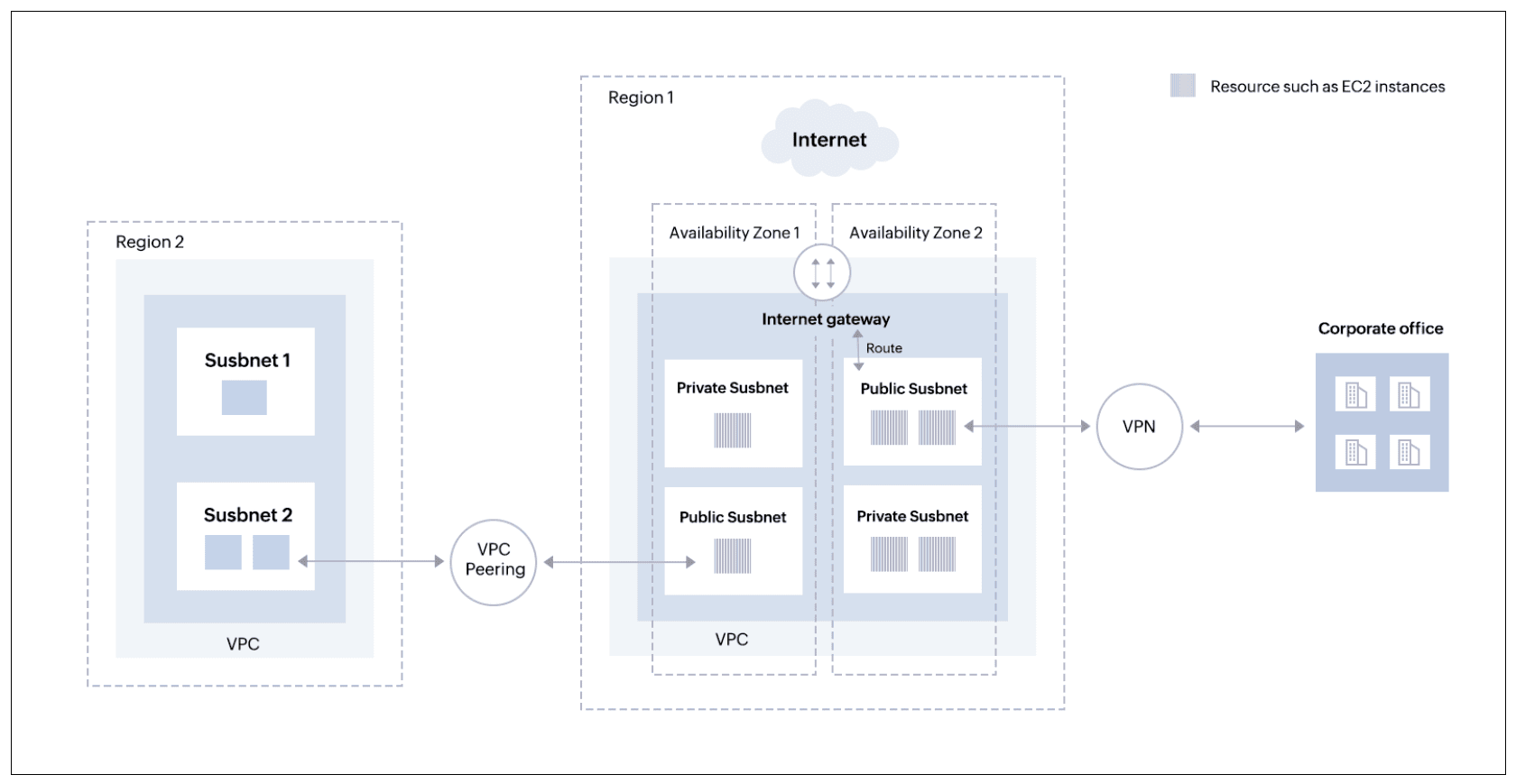
Figure 1: Amazon VPC architecture and working
- This VPC is fully self-contained and isolated. It is a logical constraint that establishes a shared networking and security boundary for your applications and services.
- The instances will only be able to communicate with each other inside the VPC. You have complete control over how the instances access resources outside of the VPCs.
- In this case, a public IP address is assigned to the instance and an internet gateway is attached to the VPC to provide internet connectivity.
- The public subnet will always have a route to get out to the internet. Here, for example, you can put servers that would host public facing webpages.
- On the other side, the private subnet doesn't have the route. For example, you can put your critical databases here. This will provide an extra layer of security protection from the outside world.
- You can also connect the VPC to our own corporate data center using the site-to-site VPN connection, making the AWS cloud an extension of your data center.
- A VPC peering connection must be established to route traffic discreetly between two VPCs and enable instances in either VPC to communicate with one another as though they were on the same network.
- Since each VPC spans a single area, we can be certain that all of the instances within it are physically located there and that there is no connection outside of the region between them.
However, do you wonder how the private subnet gets to the internet without the route?
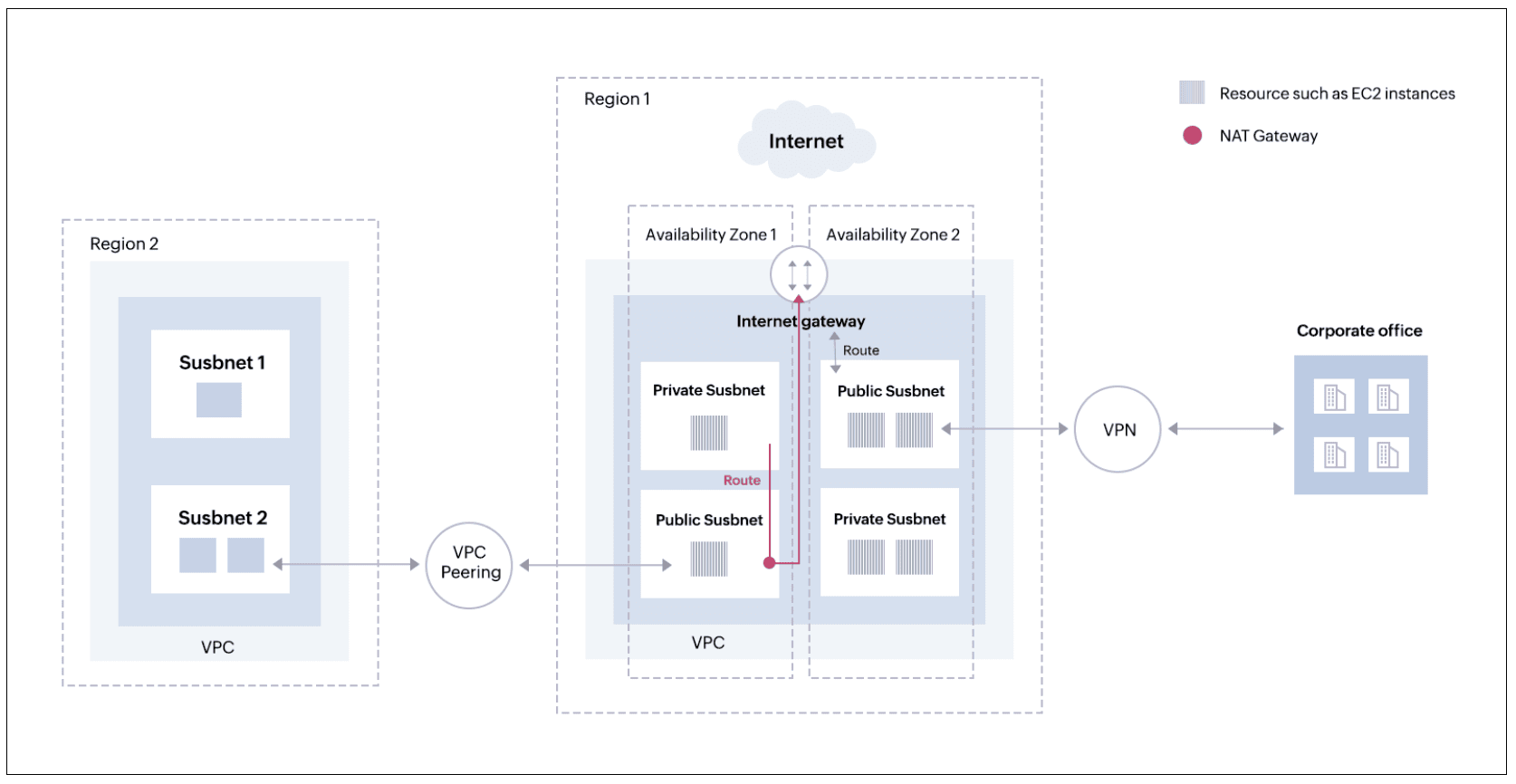
Figure 2: NAT Gateways in Amzon VPCs
In these situations, you add a route from your private instance to a NAT gateway that has been established in the public subnet. Next, we add a NAT gateway to the internet gateway. Your resources in the private subnet are now able to access the internet (refer to Figure 2).
The two ways that you can control the flow of traffic are as follows:
- NACLs: Stateless firewalls that regulate traffic at the subnet level are called NACLs. They are optional but NACLs are useful for creating rules that allow or deny communication to and from subnets inside your VPC. These rules can only be used with IP addresses to either allow or deny the IP address.
- Security group: Security groups manage traffic for one or more instances by functioning as a virtual firewall. Rules that permit traffic (only allow) to and from instances can be defined depending on parameters like the protocol, port, and source and destination IP addresses.
Benefits of using Amazon VPC:
- Added security through isolation: Users can create multiple virtual networks with Amazon VPC and each is separated from the others. Resources in one VPC are protected from direct communication with resources in another VPC because of this isolation unless specifically allowed to do so.
- Achieve business requirements through customized configurations: Users have full control over the IP address range, subnets, route tables, and network gateways within their VPC. This makes it possible to create unique network configurations to satisfy certain needs.
- Effective access controls through security capabilities: In order to regulate incoming and outgoing traffic to and from instances, VPC offers security capabilities including security groups and network access control lists (ACLs). This facilitates the VPC's implementation of security policies and access controls.
- Connectivity options: There are multiple ways to link an Amazon VPC to the internet, on-premise data centers, or other VPCs. These choices include: AWS Direct Connect, VPN connections, internet gateways, and virtual private gateways.
- Improved performance with subnetting: It is possible for users to split up their VPC into subnets, each residing in a specific availability zone within a particular AWS region. Improved fault tolerance, scalability, and resource management are made possible via subnetting.
- Cost effectiveness: By only paying for the resources you use, VPC allows you to optimize costs. You can also consolidate your networking infrastructure with VPC, which eliminates the need for separate networking hardware and streamlines management.
What type of organizations need Amazon VPCs?
Many different types of organizations can benefit from Amazon VPC, but those with complex networking requirements or strict security and compliance requirements stand to gain the most. Using Amazon VPC can be advantageous for the following kinds of organizations:
- Enterprises: With Amazon VPC, big enterprises with a variety of IT infrastructure needs can create scalable and secure networks for their services and apps. VPC can handle the various networking needs that enterprises have, including multiple data centers, hybrid cloud configurations, and regulatory requirements.
- Startups and small businesses: Amazon VPC is advantageous even for small organizations and startups, especially if they anticipate rapid growth or have specific security and compliance needs. They can create safe, scalable networks with VPC without having to make an expensive upfront investment in physical infrastructure.
- E-commerce companies: Amazon VPC helps e-commerce enterprises that depend on AWS for hosting their online stores ensure both the reliability and security of their e-commerce apps. VPC allows them to isolate their e-commerce infrastructure from other parts of their IT environment and implement advanced security measures to protect customer data.
- Financial institutions: The sensitive nature of financial data means that financial institutions, such banks, insurance companies, and investment businesses, must adhere to strict security and compliance standards. Their financial applications and services can be hosted on highly secure and compliant networks, via the Amazon VPC. To know more on how Amazon VPC can help enhance the security posture of the financial sector, check out this page.
- Healthcare organizations: HIPAA and other requirements must be followed by healthcare institutions that handle sensitive PHI. Amazon VPC provides the necessary security controls and compliance features to build HIPAA-compliant environments for hosting electronic health records (EHR) systems and healthcare applications. To know more on how Amazon VPC can help enhance the security posture of the Healthcare sector, check out this page.
- Government agencies: Using Amazon VPC, government agencies and public-sector organizations can create environments that are secure and compliant for hosting government applications and services, even in the face of stringent security and compliance regulations. With VPC, they can take advantage of the AWS Cloud's scalability and flexibility while still meeting regulatory standards.
- Media and entertainment companies: Using Amazon VPC, media and entertainment organizations can create scalable and resilient networks for content delivery, including streaming services, content distribution networks (CDNs), and digital media platforms. They may ensure great performance and availability for their media distribution infrastructure through VPC.
- Educational sector: To securely store and manage sensitive student data and academic resources in a private, isolated environment and to ensure compliance with data security rules, the educational sector needs Amazon VPC. It offers scalable infrastructure that facilitates seamless access and performance for online learning platforms and educational apps. Furthermore, it enhances security by allowing institutions to control network configurations, including traffic flow and access permissions, safeguarding against cyberthreats. To know more on how Amazon VPC can help enhance the security posture of the educational sector, check out this page.
Use cases of Amazon VPC
Consider the use case of a software development company that must maintain strict access restrictions and network isolation while safely hosting their database infrastructure and web applications in the cloud. This company wishes to migrate its database and web application infrastructure to the cloud. They want a system that provides high security, scalability, and flexibility because they have sensitive client data that needs to be protected.
The software development company decides to use Amazon VPC to host their web application and database infrastructure securely in the AWS Cloud. Here are the use cases they can cater to:
- Network isolation: A new VPC with private and public subnets is created. To communicate with the internet, the web servers are placed in public subnets, and for further protection, the database servers are placed in private subnet.
- Security groups and network ACLs: The security group is set up to manage incoming and outgoing traffic to their EC2 instances. For instance, direct access to the database servers is prohibited, but HTTP/HTTPS traffic to web servers from the internet is permitted. To provide even more security, network ACLs are set up to regulate traffic at the subnet level.
- Database hosting: Amazon RDS is selected for MySQL as their database infrastructure because it makes it simple for them to set up, scale, and maintain a relational database in the cloud. Security groups are also set up, so that only web servers are permitted access, and they install their RDS instance within the private subnet.
- VPN connectivity: To safely link the office network with the cloud resources, VPN connection is established between the on-premises network and the VPC. This makes it possible for their development team to safely use VPC resources.
- Monitoring and logging: To monitor their RDS databases, EC2 instances, and other VPC resources, Amazon CloudWatch is enabled. VPC Flow Logs are also enabled to capture information about the IP traffic going to and from network interfaces in their VPC for security analysis and troubleshooting.
- Backup and recovery: Amazon RDS automatic backups and snapshots is used to setup automated backups for their RDS databases, ensuring data durability and recovery.
The software development company successfully moves its database and web application architecture to the cloud while upholding strict security and compliance standards by utilizing Amazon VPC. Due to the flexibility and scalability of AWS services, they can concentrate on creating and refining their software rather than worrying about infrastructure maintenance.
Importance of securing and monitoring Amazon VPC
Security is the primary reason to use Amazon VPC. VPC is an isolated division of the AWS public cloud that allows you to deploy AWS resources in a secure manner. Similar to many provisions of AWS, Amazon VPC also helps you reduce the costs associated with a private cloud. VPC is one of the tools you should learn immediately if you want to start using AWS for your business. Even though using Amazon VPC gives added security over traditional networks, it still needs to be monitored and secured itself. Numerous cyberattackers do target Amazon VPC.
An unsecured VPC might be subject to cyber threats. Monitoring Amazon VPC allows you to proactively identify and resolve issues, optimize resource use, and ensure compliance with security and regulatory standards. Here are some other reasons why maintaining VPC security is critical for strengthening your network infrastructure:
- Enhancing performance: Monitoring the essential components of your Amazon VPC allows you to obtain insights into the performance of your network infrastructure, identify and address any issues early on, and optimize the utilization of resources for improved performance. The components that need to be monitored include network traffic, load balancers, NAT Gateway, VPN flow logs, VPN connection performance and subnet performance.
- Resource utilization: Tracking the resource usage within the VPC, including EC2 instances, databases, and other services aids in resource allocation optimization and the identification of cost-saving opportunities.
- Security and compliance: Identifying potential security breaches, unauthorized access attempts or unusual activities by monitoring the network traffic and access patterns are necessary to maintain the security and compliance of your infrastructure.
- Troubleshooting: Monitoring the network throughput, latency and error rates will help you quickly troubleshoot and resolve the issues before they impact the performance or availability of your applications.
- Cost management: Identifying the unused resources by gaining visibility into the resource usage will help you optimize the infrastructure to cut down unwanted expenses spent within VPC.
To learn more about the need for monitoring and securing Amazon VPC, check this page.
Ready for the next step?
Explore how you can protect your organization's sensitive information from being misused. Sign up for a personalized demo of ManageEngine Log360, a comprehensive SIEM solution that can help you detect, prioritize, investigate, and respond to security threats.
You can also explore on your own with a free, fully functional, 30-day trial of Log360.