Ryuk is a type of ransomware that first emerged in 2018 and was operated by a Russian hacker group called Wizard Spider. Ryuk ransomware enters a network through various vectors such as phishing emails, malware spam, Trojans, and downloadable malware. It then encrypts sensitive files in the network and demands a ransom payment in bitcoins for releasing the decryption keys.
Although it primarily targets enterprise environments, Ryuk has evolved to be one of the greatest threats to the healthcare sector. In October 2020, Ryuk was responsible for 75% of attacks on the United States healthcare sector, and Wizard Spider became one of the most notorious RaaS operators.
History of Ryuk
Ryuk ransomware was initially based on the source code of Hermes ransomware, which emerged in 2017. Some considered Ryuk to be another name for Hermes 2.1, a variant of Hermes. However, during Ryuk's evolution over the years, Wizard Spider made various alterations to the source code, making Ryuk more advanced than and markedly different from Hermes.
Unlike Hermes, which operated as a commodity ransomware kit sold to hackers for launching their own ransomware campaigns, Ryuk operates based on the Download as a Service (DaaS) distribution model. In the DaaS model, the operator seeks affiliates to distribute the malware through various vectors, but the execution of the attack is solely carried out by the operator.
How Ryuk ransomware works
The following are the various stages of a Ryuk ransomware attack.
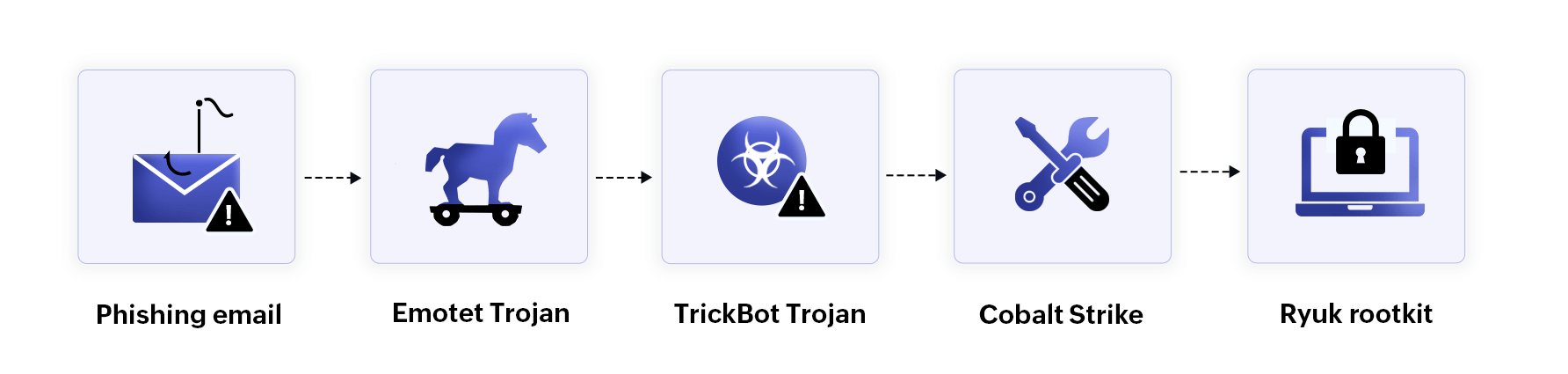
Figure 1: How Ryuk ransomware works
Initial access
Ryuk gains initial access to a network through phishing emails where users unknowingly click malicious attachments or links. These emails often contain harmful files disguised as Word documents. Once opened, the attachments execute malicious scripts, compromising the device and connecting it to the Emotet botnet, a large network of infected devices that are compromised by the Emotet Trojan.
Execution
Ryuk ransomware is deployed by the TrickBot Trojan, which spreads via the Emotet botnet. TrickBot, a sophisticated Trojan used by the Wizard Spider group, facilitates the deployment of the Ryuk rootkit. Once TrickBot infiltrates the network, attackers typically execute PowerShell scripts or exploit RDP to establish a connection between the compromised device and the command-and-control (C2) server. Following this, the Ryuk rootkit is downloaded and activated using Cobalt Strike.
Persistence and defense evasion
Ryuk establishes persistence within the network by leveraging proxy tools such as SystemBC. It then evades detection by disabling antivirus solutions and endpoint detection and response software.
Privilege escalation and lateral movement
Using AD enumeration tools, Ryuk identifies domains within the network and extracts domain credentials. With these valid user accounts and credentials, it escalates its privileges and moves laterally across the network, ultimately gaining access to sensitive files and folders.
Encryption and exfiltration
Ryuk utilizes RSA-2048, a type of asymmetric encryption, to encrypt sensitive files. Asymmetric encryption involves a public key for encrypting plaintext and a private key for decrypting ciphertext. In a Ryuk attack, Wizard Spider encrypts the files using the public key and withholds the private key to prevent the victim from decrypting the files.
The encrypted files are appended with the RYUK extension. The files are then exfiltrated and transferred to the C2 server using AES-256 encryption, which is a symmetric encryption method that involves a single key for both encryption and decryption.
Extortion
Ryuk ransomware attackers demand a ransom payment for releasing the decryption key. Unlike other ransomware operators, Wizard Spider does not maintain a dedicated ransomware site for negotiations and payments. Instead, victims are contacted directly via email and provided with a Bitcoin wallet address for the ransom payment.
External tools leveraged by Ryuk
| Tool name | Usage |
| Cobalt Strike | A penetration testing tool used to launch the ransomware payload |
| SharpHound | An AD enumeration tool used to exfiltrate domain credentials |
| Rubeus | A command-line tool used to exploit Kerberos authentication and extract domain credentials |
| Kerbrute | A command-line tool used for AD enumeration |
| AdFind | A command-line tool used to query AD |
| vsftpd | FTP server software that serves as a backdoor for exfiltrating data |
| SystemBC | A proxy remote access Trojan used to evade detection and maintain persistence |
| GMER | A tool that terminates security tools |
A development in Ryuk attacks
In September 2020, Ryuk attacks took a major turn. TrickBot was replaced by a Windows-based Trojan called BazarLoader. BazarLoader created a backdoor for attackers, enabling them to execute malicious processes alongside legitimate Windows processes, which made Ryuk attacks harder to detect. As a result, Ryuk became even more notorious, and the IoCs became even more difficult for security tools to identify.
How to protect against Ryuk ransomware
Here are 10 best practices for detecting and mitigating Ryuk ransomware attacks:
- Email filtering: Email filtering tools flag suspicious phishing emails and block them from reaching a user's inbox.
- Static file analysis: Static file analysis tools detect malicious executables and attachments by scanning files for known ransomware IoCs and signatures.
- User and entity behavior monitoring: Implement tools that monitor user and entity behavior to detect anomalies such as unauthorized access, privilege escalation, and lateral movement within the network.
- Security information and event management (SIEM): Deploy a SIEM solution to gain comprehensive visibility across the entire network, enabling the identification of threats and facilitating faster incident response.
- Vulnerability assessments: Conduct vulnerability scans, regularly patch and update all endpoints and network devices, and continuously audit them for vulnerabilities.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Enforce MFA for all user accounts to add an additional layer of security, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Strong password policies and the principle of least privilege: Enforce strong password policies and adhere to the principle of least privilege, limiting user permissions to only what is necessary.
- File integrity monitoring: Use file integrity monitoring solutions to track changes to sensitive files and folders, alerting administrators to any unauthorized modifications.
- Data backups and encryption: Regularly back up files containing sensitive data and protect both the original files and backups with robust encryption techniques to prevent unauthorized access.
- Employee awareness training: Regularly conduct employee awareness training programs to educate users on how to identify phishing emails, suspicious processes, and malicious executables, reducing the risk of human error.
Related solutions
ManageEngine Log360 is a comprehensive SIEM solution with advanced ransomware detection and mitigation capabilities. Log360 stands out as one of the best ransomware protection solutions with these powerful features:
- 360-degree network visibility: Log360 provides complete visibility into the network through out-of-the-box audit reports and interactive dashboards on a single console.
- Ransomware detection: Predefined correlation rules and alert profiles for ransomware detection help you identify potential ransomware activities in real time.
- User and entity behavior analytics: With its ML-based behavior monitoring capabilities, Log360 detects anomalous activities in the network to identify potential signs of a ransomware attack.
- File monitoring: Log360's file integrity monitoring feature monitors unauthorized file access attempts, creations, deletions, and modifications to protect sensitive data from ransomware.
- Cloud app security: Log360's CASB capabilities block suspicious websites and ban malicious applications to secure sensitive cloud data from ransomware threats.
- Ransomware incident response: The ransomware detection alert profiles include built-in incident response workflows that, when enabled, prevent the propagation of ransomware attacks.
To explore more, sign up for a personalized demo of Log360. Or, you can discover its powerful capabilities with a fully functional, 30-day, free trial.