File upload protection with DataSecurity Plus
ManageEngine DataSecurity Plus is a unified data security posture management platform, that helps secure you data across network servers, endpoint devices, and the cloud. DataSecurity Plus' Cloud Protection module focuses on enforcing strict control measures over file transfers across the cloud, managing the use of cloud applications, and monitoring your organization's web traffic.
Ensuring file upload security is not just about protecting your IT infrastructure from cyberattacks and data loss, it's also about achieving compliance with various data protection laws like the GDPR and CIPA. With DataSecurity Plus's file upload control feature, you can do both.
-
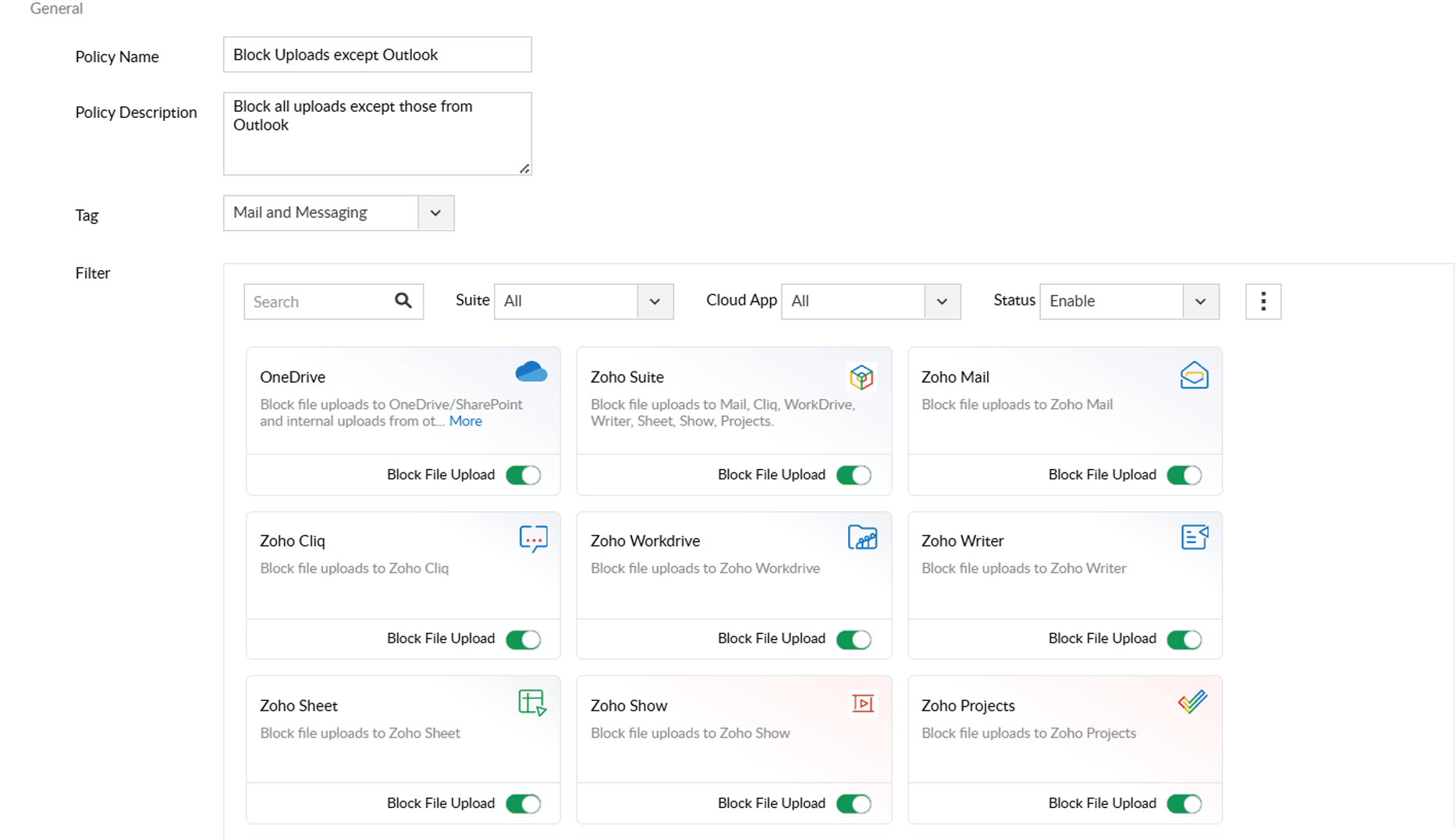
Allow file uploads only from trusted cloud applications and block uploads from all other sources.
-
Control file uploads granularly with criteria such as content type, content length, etc.