SOC 2 compliance
- Home page
- Compliance
- What is SOC 2 compliance?
What is SOC 2 compliance?
Service Organization Control Type 2 (SOC 2), is a framework developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) to ensure organizations have cybersecurity measures in place to protect their customers' sensitive data. It is generally implemented by technology and cloud computing organizations, helping them to demonstrate their commitment to maintaining a secure data environment.
Types of SOC 2 reports
SOC 2 compliance is classified into two types of reports, each serving a distinct purpose.
SOC 2 Type I: The main goal of the Type I report is to evaluate a company's design of controls at a specific point in time. For example, if a company undergoes a SOC 2 Type I audit, the report will gauge whether the security controls were appropriately designed as of a particular date.
SOC 2 Type II: In Type II reports, auditors not only assess the design of controls but also their operational effectiveness over a specific period of time (typically three to 12 months).
Who must comply with SOC 2?
SOC 2 compliance is relevant for organizations that deal with sensitive information and provide services such as data hosting, processing, and storage for their clients. Organizations that must comply with SOC 2 are technology and cloud service providers, data centers, third-party vendors and contractors, and companies in financial, healthcare, and education. Complying with SOC 2 ensures confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and reduces the likelihood of data breaches.
Consequences of non-compliance
Though SOC 2 compliance is not a mandatory regulatory standard, it is important to comply, and not doing so can impact the organization's reputation, relationships with clients, legal standing, and overall business operations. Let's take a closer look at some of the consequences.
Loss of customer trust
Without an SOC 2 report, customers might perceive that a company is not fully committed to protecting their information. This perception can affect their trust and influence their business decisions. To meet SOC 2 compliance, organizations should effectively implement controls in areas such as:
- Access control.
- Password management.
- Change management.
- Incident response.
- Logging and monitoring.
- Other critical areas of data protection.
Increased cybersecurity risks
The absence of SOC 2 compliance may highlight potential weaknesses in an organization's security posture. Addressing SOC 2 standards helps strengthen the information security infrastructure, thereby enhancing the organization’s ability to prevent security incidents like data breaches.
Loss of competitive advantage
Adherence to SOC 2 compliance is increasingly becoming a competitive differentiator. Organizations lacking an SOC 2 report might find themselves at a competitive disadvantage compared to those practicing and demonstrating robust security practices, as SOC 2 compliance reassures clients and partners of an organization's commitment to security.
Legal consequences
Failure to comply with SOC 2 standards may lead to legal repercussions, especially if the non-compliance results in a data breach or if contractual obligations are violated. This could result in lawsuits, fines, and other legal actions.
SOC 2 requirements for compliance
The AICPA has established five Trust Services Categories (TSCs), formerly known as the Trust Services Principles, upon which the SOC 2 framework is based. These standards are focused on data encryption and physical security. To achieve and maintain SOC 2 compliance, organizations need to implement and demonstrate their adherence to these criteria.
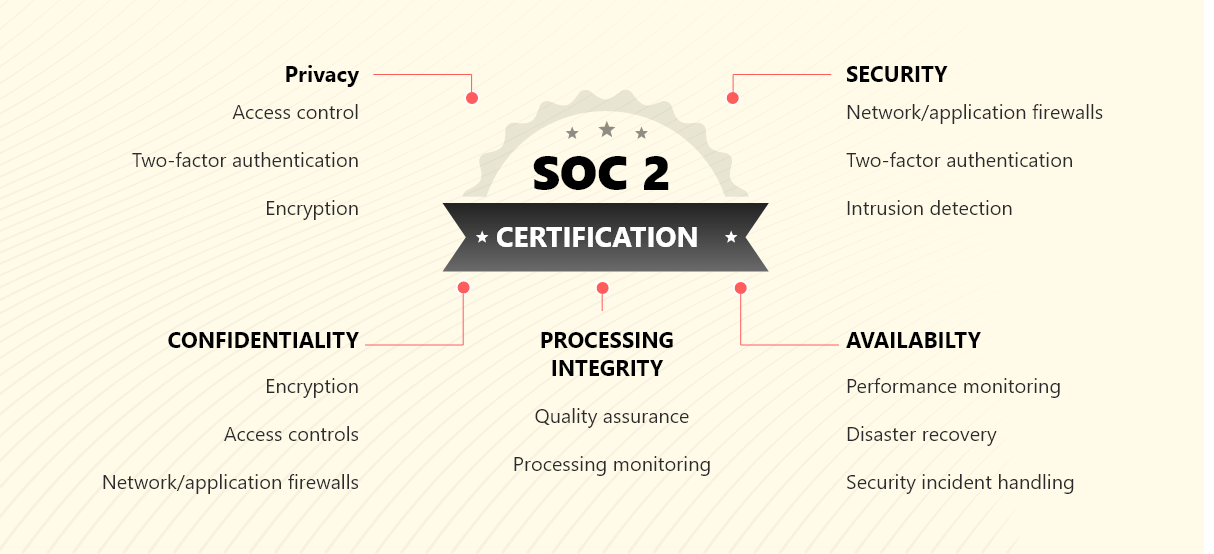 Figure 1: SOC 2 trust service principles
Figure 1: SOC 2 trust service principles
Security
The security principle involves the protection of data and systems against unauthorized access. To achieve this, organizations need to have firewalls, intrusion detection and recovery systems, and two-factor authentication. This principle helps the organizations establish access controls and also assesses whether they are protected against potential security breaches and incidents. Under the security principle, there are nine criteria listed:
- The control environment (CC1.0)
- Communication and information (CC2.0)
- Risk assessment (CC3.0)
- Monitoring of controls (CC4.0)
- Design and implementation of controls (CC5.0)
- Logical and physical access (CC6.0)
- System operations (CC7.0)
- Change management (CC8.0)
- Risk mitigation (CC9.0)
Availability
The availability principle is relevant to businesses offering data center or hosting services to clients. It guarantees that the system offered to clients remain operational and accessible as mutually agreed upon. It also assesses whether the services align with the expected level of availability specified by clients. Organizations should establish incident response and recovery plans to minimize the impact of service interruptions. This principle has three criteria:
- Managing processing capacity (A1.1)
- Protecting data and infrastructure (A1.2)
- Having a recovery plan (A1.3)
Processing integrity
The processing integrity principle ensures that the services are provided in a complete, accurate, authorized, and timely manner. It makes sure any errors are investigated and corrected without compromising services. To avoid data tampering, organizations should implement data validation, data reconciliation procedures, and data quality assessments.
- Using reliable information (PI1.1)
- Implementing policies for input (PI1.2)
- Implementing policies for processing (PI1.3)
- Ensuring accurate and timely outputs (PI1.4)
- Securely storing information (PI1.5)
Confidentiality
The confidentiality principle focuses on the agreements established with clients regarding the utilization, access, and protection of their information. It assesses adherence to contractual obligations in ensuring the proper safeguarding of client information. This category has two main criteria:
- Identifying and maintaining confidential information (C1.1)
- Proper disposal of confidential information (C1.2)
Privacy
The privacy principle is mainly focused on the collection, retention, disclosure, and disposal of customer information. This can be done by regular risk and privacy impact assessments. There are five criteria listed under this principle:
- Privacy criteria related to notice and communication of objectives related to privacy (P1.0)
- Privacy criteria related to choice and consent (P2.0)
- Privacy criteria related to collection (P3.0)
- Privacy criteria related to use, retention, and disposal (P4.0)
- Privacy criteria related to access (P5.0)
- Privacy criteria related to disclosure and notification (P6.0)
- Privacy criteria related to quality (P7.0)
- Privacy criteria related to monitoring and enforcement (P8.0)
The SOC 2 roadmap
Achieving SOC 2 compliance involves a structured approach, and here are some key steps.
Choose your TSCs
After learning about the five TSCs, your organization needs to understand which one applies and emphasize it on your audit. The TSCs are generally selected based on the type of data stored or transmitted.
Review security controls
After choosing the criteria, your organization needs to focus on its security controls and check if any changes need to be made. You should also make sure that all documents and standards are up to date and SOC 2 compliant.
Risk assessment
After updating your security controls, you'll need to conduct a risk assessment procedure. This step will verify the updated controls and make sure your company is ready for a SOC 2 audit. The risk assessment (internal audit) should take place every year. This is an important step, as it detects any risks associated with changes in growth or location.
Complete the SOC 2 audit
Companies that plan to get SOC 2 compliance must undergo two types of audits; internal and external. For an external audit, you can reach out to external auditing firms. The auditing firm creates a report where they share their opinion on how well the information is presented, if the control measures are appropriate, and whether they actually work.
Maintain compliance
After attaining SOC 2 compliance, it will need to be renewed every year, with the next audit occurring 12 months from the date the report was initially issued. Maintaining compliance will help safeguard your customers' sensitive information and also help you stay competitive in an industry that is becoming more regulated.
SOC 2 best practices
Consistent monitoring
It is necessary to monitor your security controls continuously, especially for SOC 2 Type II audits. This monitoring will act as proof that will be shared with auditors. This can be achieved by implementing a tool that can automate the monitoring and evidence collection process.
Perform gap analysis
Before the actual SOC 2 audit, perform a gap analysis to find out if there are any weaknesses in your systems. Fix any problems by modifying workflows, implementing or adjusting security controls, etc.
Execute awareness training
It's important to conduct a security awareness program for all employees, detailing their roles in complying with certain security controls and creating and maintaining a secure environment.
Conduct pen tests
Penetration testing, also called ethical hacking, is a cybersecurity practice that is designed to assess the security of systems or networks in an organization. It is usually done by a skilled third-party, known as a penetration tester or ethical hacker, who attempts to exploit vulnerabilities in the system's defenses. This is a mandatory requirement for a SOC 2 audit as it will help to identify any security vulnerability present in your network.
Detailed reports of security events
Maintain detailed reports on all the security events or incidents that take place in your network, including how a particular event or incident was made known, steps taken to resolve it, and how much damage it caused to the organization. This will display your transparency and will benefit you during the SOC 2 audit.
Incident response and alerts
To achieve SOC 2 compliance, organizations must promptly identify and address security threats. This requires alert systems for incidents like unauthorized file transfers and account logins, along with a robust incident response and recovery plan. Automated cybersecurity solutions aid in monitoring such events. When alerted, your organization should follow its incident response plan, which will include containment, investigation, remediation, and communication steps.
Comply with SOC 2 using EventLog Analyzer
EventLog Analyzer is a valuable tool for achieving and maintaining SOC 2 compliance. It simplifies compliance auditing and enhances network security through effective log management, threat analytics, and real-time event correlation.
The real-time event correlation engine plays a pivotal role in ensuring system and communication protection by correlating data from different log sources to detect threats like unauthorized access, data breaches, and system vulnerabilities. Additionally, its integrated compliance management feature simplifies IT compliance auditing with ready-made reports, helping you meet regulatory requirements like SOC 2.