Overview
Last updated on:
In this page
Risk posture describes an organization's overall ability to identify, assess, and respond to security risks. It requires a comprehensive review of the environment, including users, devices, network elements, configurations, and any stored information that could be exposed, along with an assessment of current security practices and software against known attack techniques.
Log360 currently supports risk posture assessments for the following sources:
- Active Directory
- SQL Server
Understanding the working of risk posture
Risk posture in Log360 is evaluated using pre-defined risk rules. These rules are derived from the CIS Benchmarks, which outline industry-accepted best practices for securing systems and applications. Each rule acts as a compliance criterion against which configurations of supported sources, such as Active Directory and SQL Server, are validated.
Each rule in risk posture is assigned a status that reflects whether the configuration complies with the defined baseline:
| Status | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Low/No Risk | This status informs that the selected source's configurations have met the recommended/user set compliance value as per their norms. | 
|
| High Risk | This status informs that the selected source's configurations have not met the recommended/pre-defined compliance standards set by the user or organization. | 
|
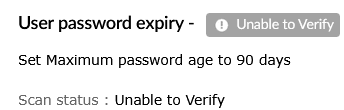
| Unable to Verify | This status informs that the Log360 server was unable to fetch the required data needed for analyzing the specific rule. It can be due to the following reasons.
|
|
Read also
This section explained how risk posture helps assess and monitor your organization's security configurations. To learn more about related capabilities, refer to the following articles: