Auto Logon Helpers for Remote Sessions
PAM360 securely stores passwords for remote systems and applications. Traditionally, organizations use remote desktop applications, PuTTY, or SecureCRT to connect to target systems. However, PAM360's Auto Logon Gateway feature enables seamless, password-free connections to remote systems and applications, eliminating the need to handle credentials in plain text. Key takeaways from this document are:
- How the Auto Logon Gateway Feature Works
- Setting Up Auto Logon Gateway
- Invoking Auto Logon Through Gateway
- Configuring Auto Logon Helpers for Specific Resource Types in PAM360
1. How the Auto Logon Gateway Feature Works
PAM360 includes built-in RDP, SSH, and SQL gateway engines that allow users to launch remote terminal sessions directly from their web browsers. These sessions, initiated from the Connections tab, are securely tunneled through the PAM360 server. This enables administrators to restrict RDP, SSH, and SQL permissions on end-user devices while still permitting controlled access through PAM360 tunneled remote sessions.
Remote sessions are emulated within the browser, eliminating the need for additional plugins or endpoint agents. The only prerequisite is an HTML5-compatible browser (e.g., Internet Explorer 9+, Firefox 3.5+, Safari 4+, or Chrome). When a resource supporting remote terminal sessions is added to PAM360, it will be automatically available for the authorized users. The Connections tab provides easy access to remote accounts, allowing users to launch sessions with a single click.
2. Setting Up Auto Logon Gateway for Resources
Auto Logon Gateway can be configured for three types of connections:
2.1 RDP and VNC Connections
PAM360 supports automatic RDP session initiation for all Windows-based systems. To configure access, a domain account or local account must be set up for authentication. Additionally, administrators can allow users to launch RDP sessions using their Active Directory (AD) credentials. Follow the below steps to configure Auto Logon for RDP:
- Navigate to the Resources tab and select the desired resource(s).
- Click Resource Actions >> Configure >> Auto Logon Helper.
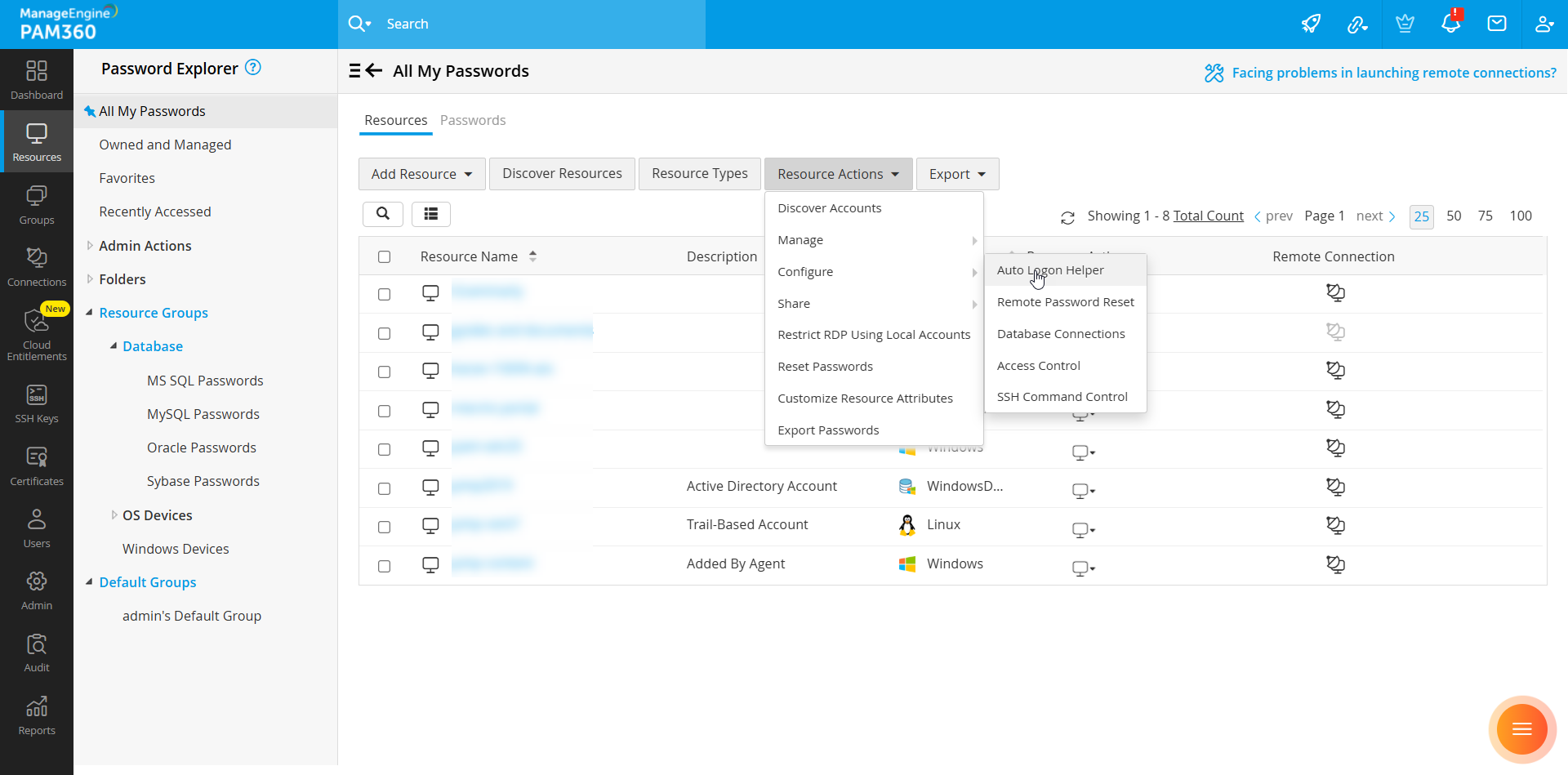
- In the Configure Auto Logon Helper window, select the required domain from the Domain Name dropdown.
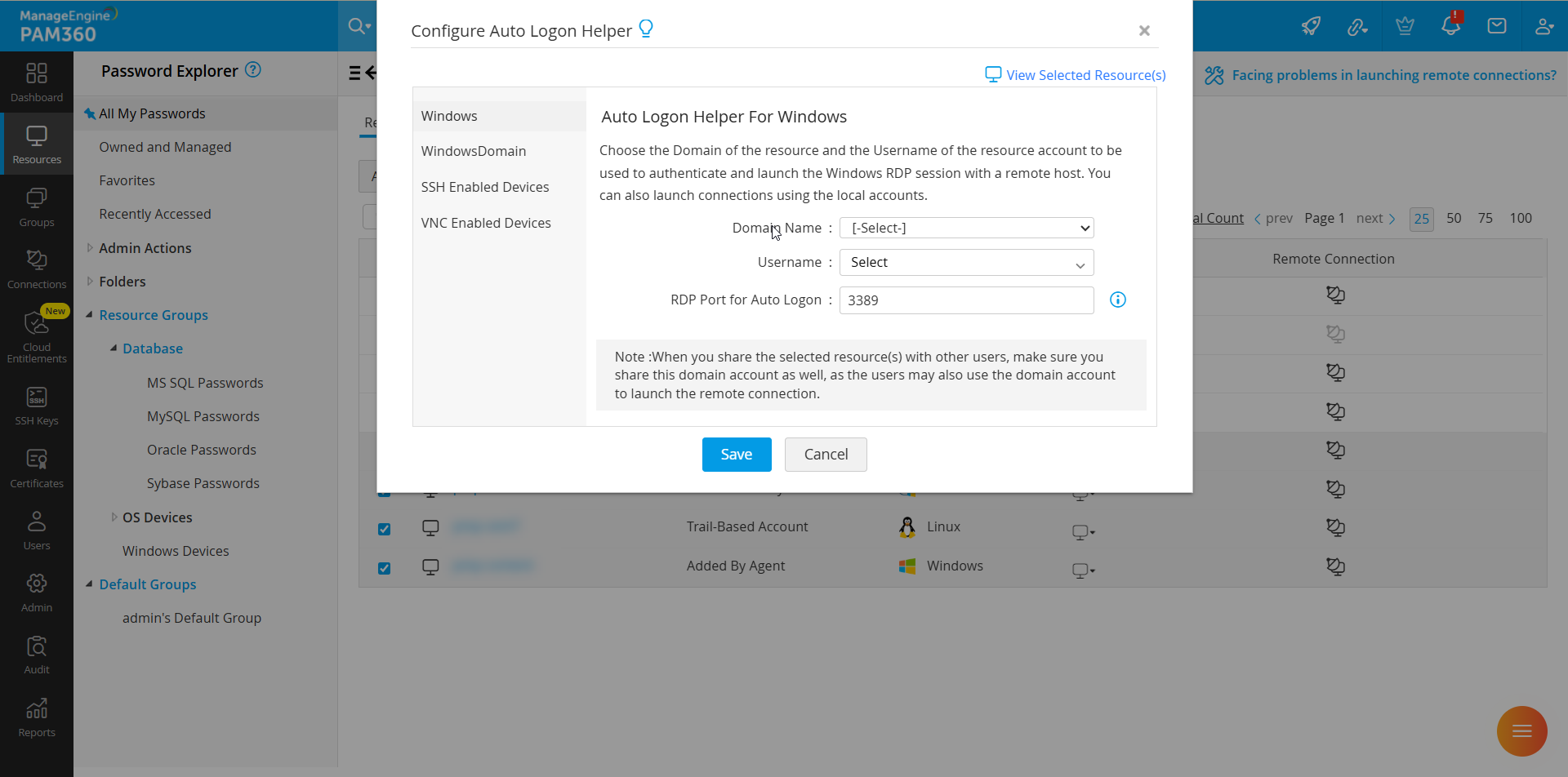
- Specify the Username and RDP Port.
- Click Save to apply the configuration.
The configured domain account will now appear under the Connections tab.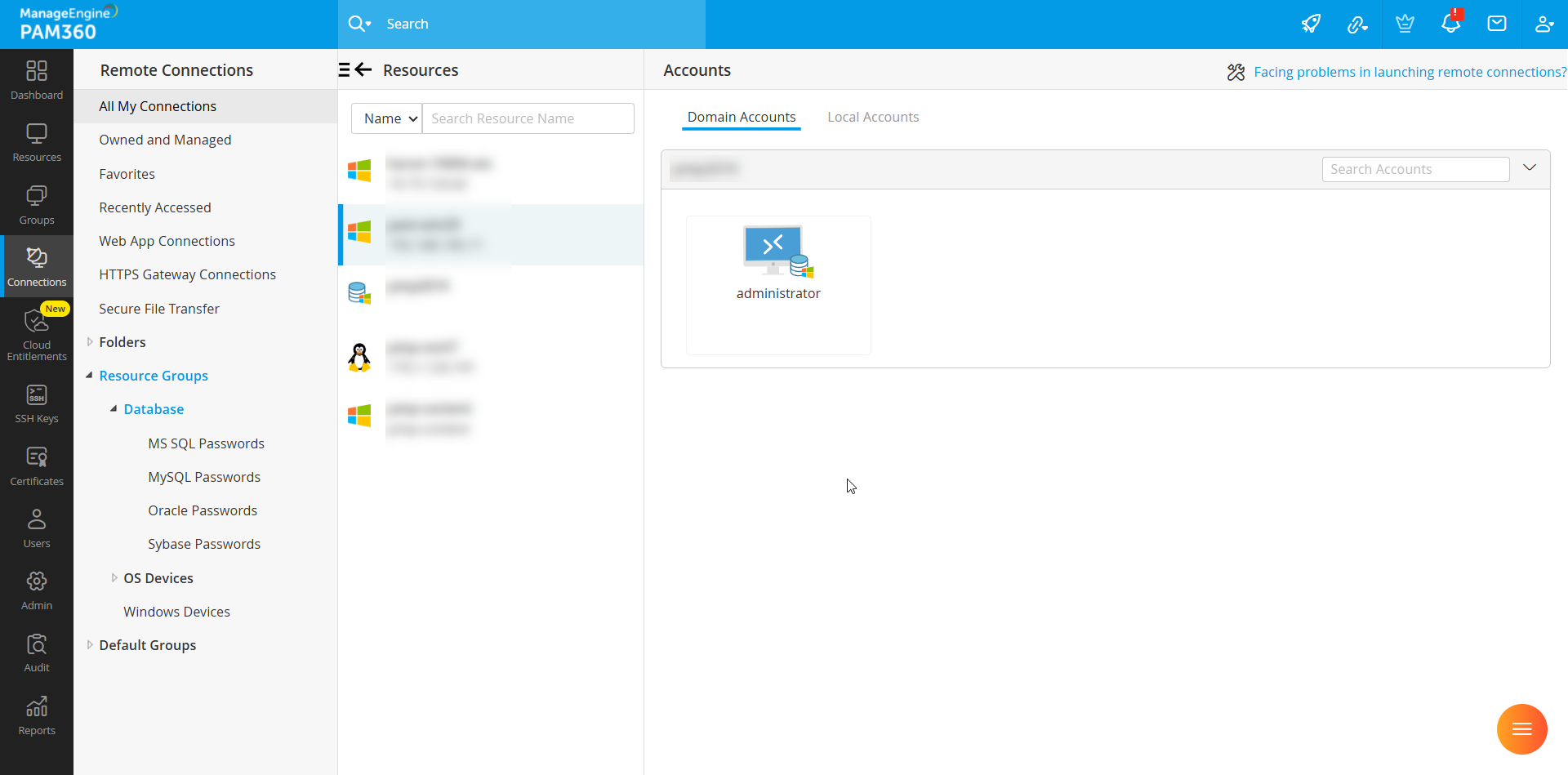
To customize the RDP and VNC Ports for individual resources, follow these steps:
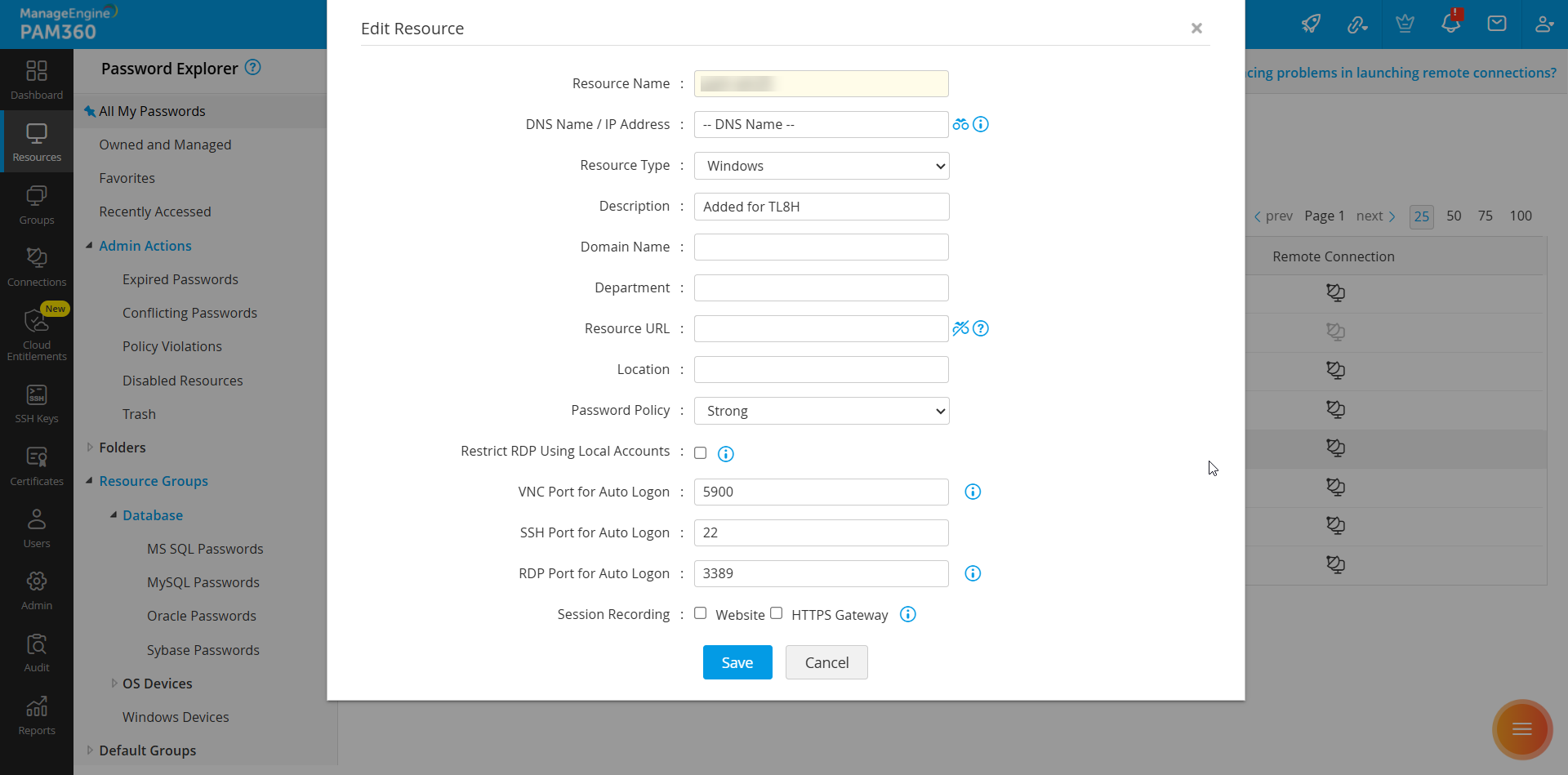
- Navigate to the Resources tab, select the target resource, and click Resource Actions >> Edit Resource.
- In the Edit Resource window, modify the RDP and VNC ports in the relevant fields as needed.
- Click Save to confirm the changes.
2.2 SSH Connections
PAM360 allows administrators to manage SSH-based devices, including Linux servers and network devices. SSH connections enable secure remote access using local SSH accounts shared with authorized users. Follow the below steps to configure Auto Logon for SSH-based devices for SSH sessions:
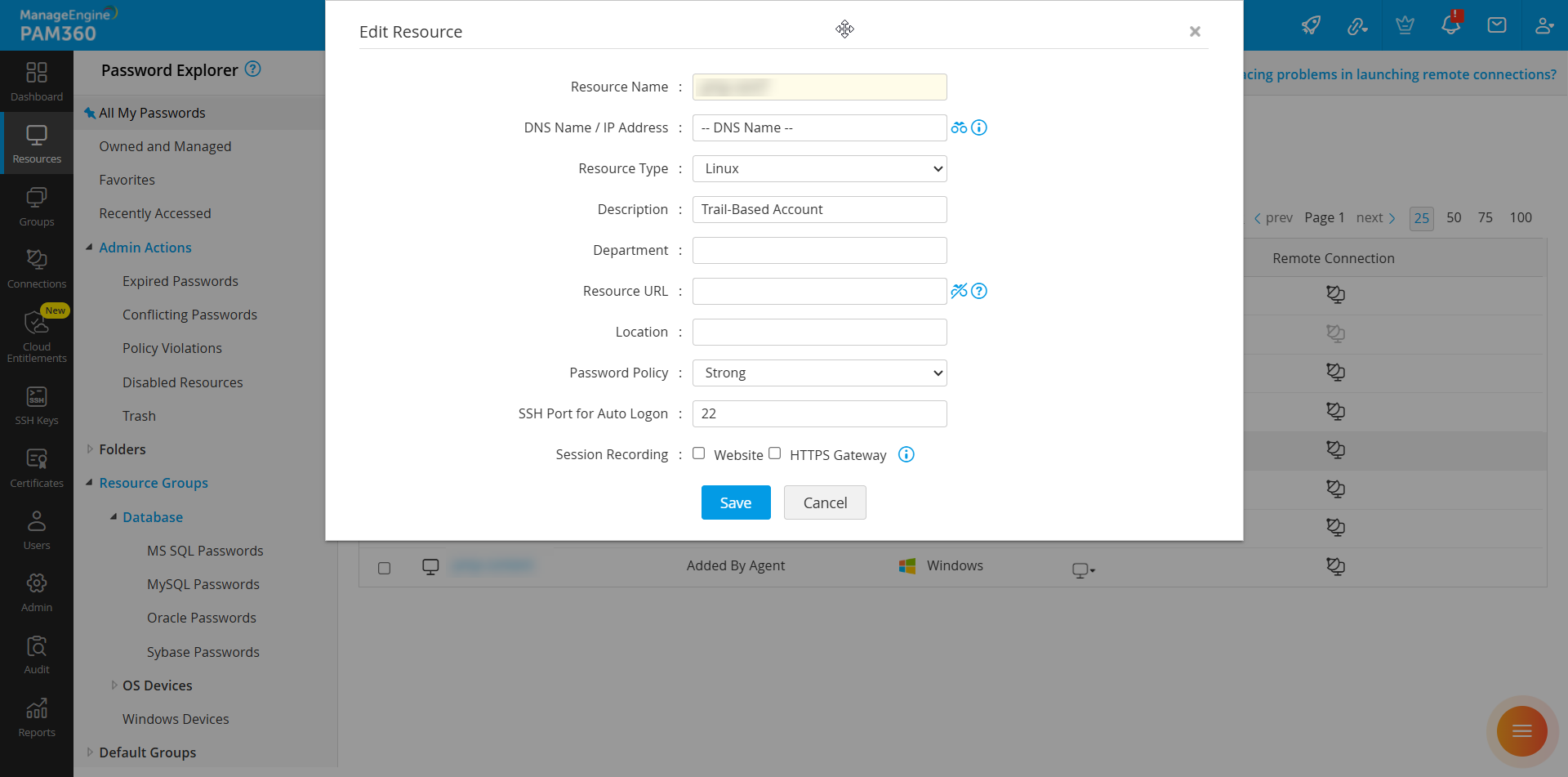
- Navigate to the Resources tab, select the target SSH-based resource, and click Edit Resource under Resource Actions.
- In the Edit Resource window that opens, enter the SSH port to be used for the connection in the SSH Port for Auto Logon field.
- Click Save to apply the changes.
2.3 SQL Connections
PAM360 supports remote PostgreSQL and MS-SQL database connections via command-line interfaces (CLI). Users can execute queries remotely through PAM360. Follow the below steps to configure Auto Logon for database resources:
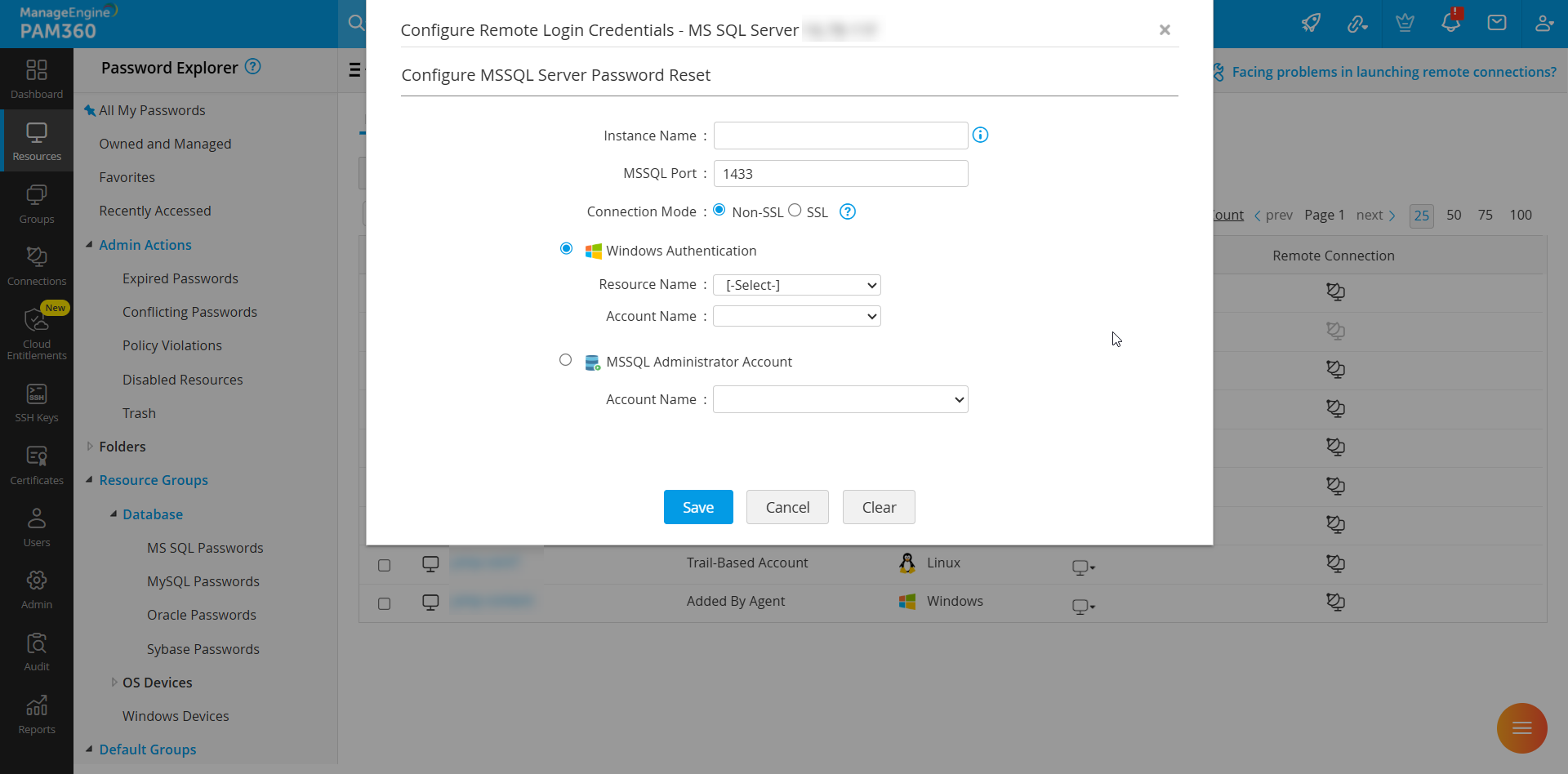
- Navigate to the Resources tab, select the target SQL resource, and click Resource Actions >> Configure Remote Password Reset.
- Specify the port number for the SQL connection.
- Click Save to enable SQL session access.
2.4 Port Requirements for Client Access
Windows RDP Auto Logon Gateway operates on port 8283 by default. This secure WebSocket (wss://) port must be open for client access. To change this port, navigate to Admin >> Server Settings >> PAM360 Server, then go to the Auto Logon tab and enter the desired port in the Remote Desktop Gateway Port field. SSH and Telnet Gateways do not require a separate port; they utilize the PAM360 web server port.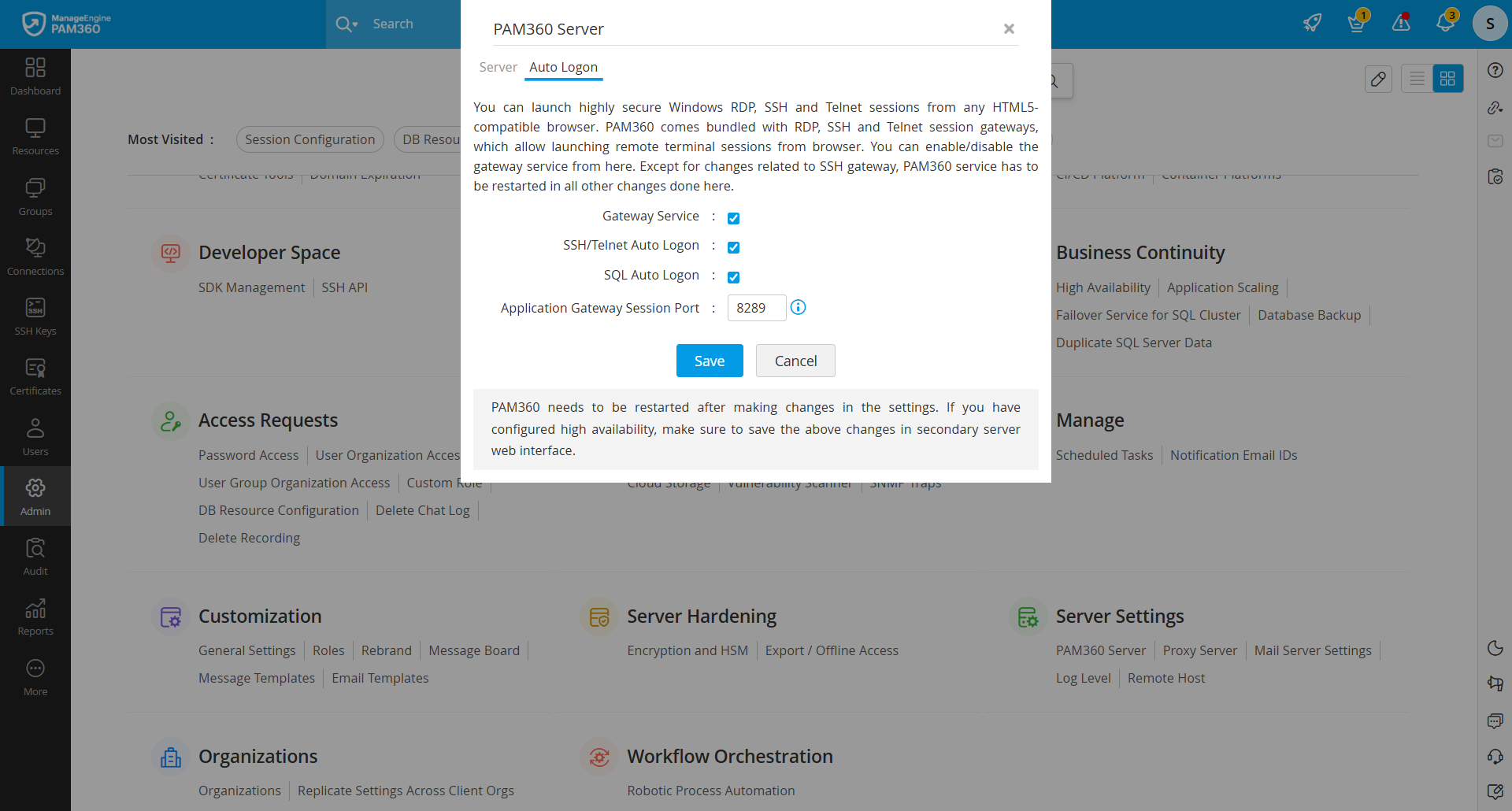
Security Recommendation
PAM360 generates a self-signed SSL certificate upon installation, which is also used by the Auto Logon Gateway to encrypt traffic. For enhanced security, apply a CA-signed certificate before enabling access for end users. If using a self-signed certificate, users must explicitly specify the gateway port in the URL, accept security warnings, and install the certificate. Refer to the Certificates Management section to generate unique SSL certificates directly from the PAM360 interface.
3. Invoking Auto Logon Through Gateway
Once an administrator adds a resource supporting RDP, SSH, or SQL sessions, Auto Logon Gateway is instantly available to authorized users. The Connections tab allows users to quickly locate remote accounts and initiate secure sessions with a single click.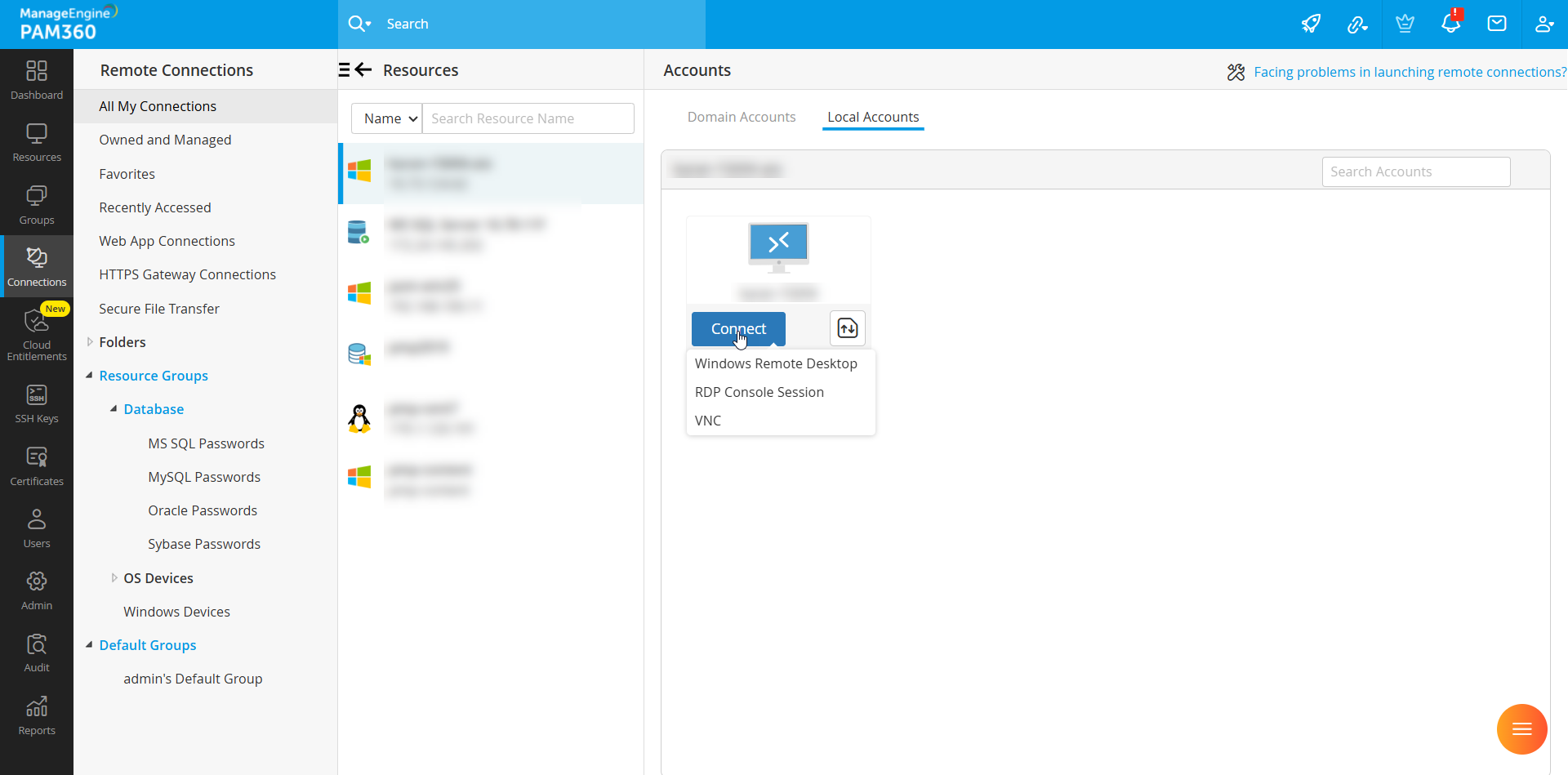
4. Configuring Auto Logon Helpers for Specific Resource Types in PAM360
By default, PAM360 assigns specific auto logon helpers to corresponding resource types for session initiation and remote connections. For instance, the Windows Remote Desktop helper (i.e., Remote Desktop Connection) is available for resource types such as Windows and Windows Domain. Similarly, other resource types are mapped to their respective auto logon helpers by default.
However, if you need to configure a specific helper for a different resource type while maintaining Auto Logon capability, you can manually modify the settings via the Auto Logon Helper page. Follow the below steps to configure a gateway engine for a specific resource type:
- Navigate to Admin >> Privileged Session >> Auto Logon Helper.
- On the Auto Logon Helper page, you will see a list of available Auto Logon Helpers along with their default resource type mappings for session initiation.
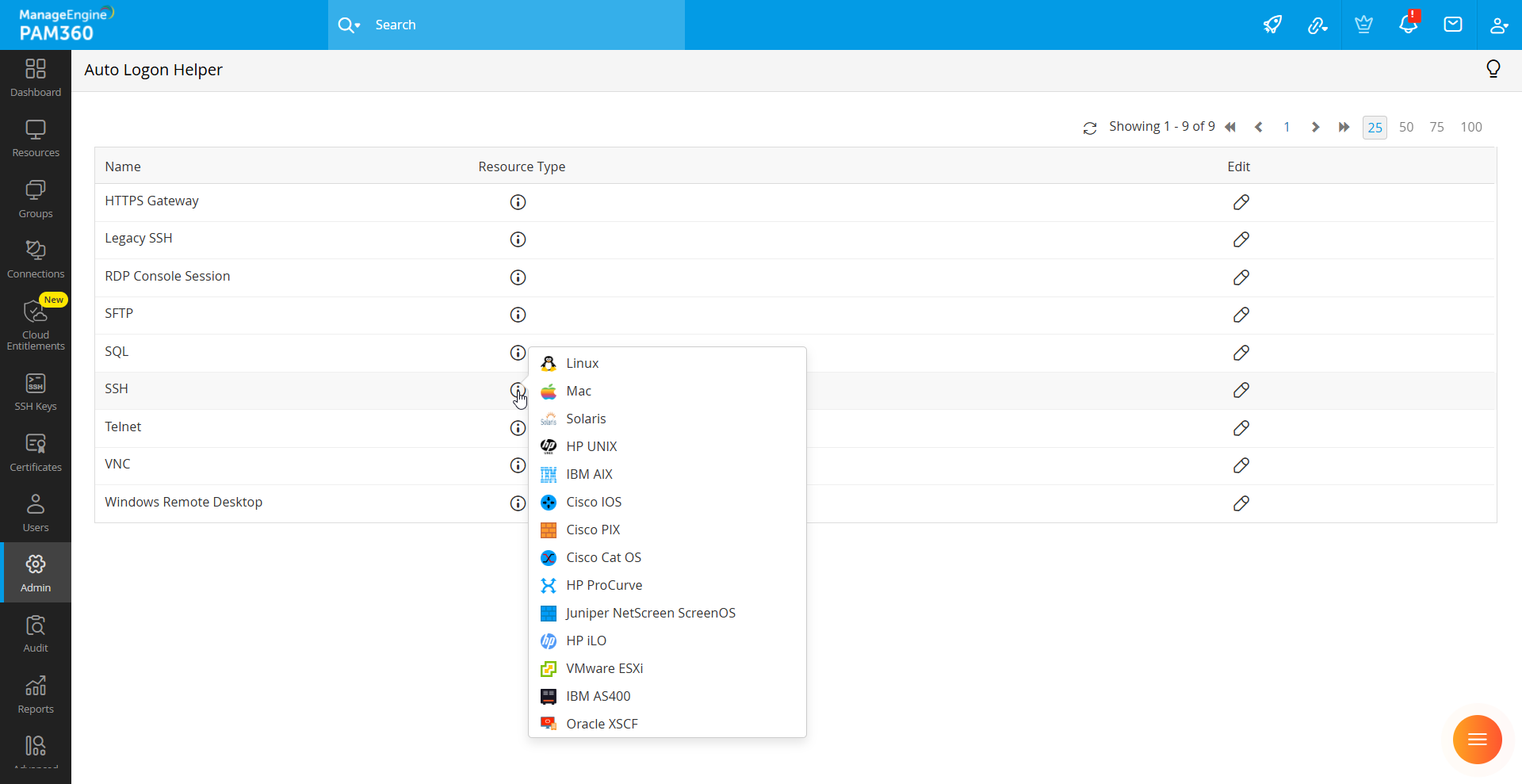
- Click the Edit icon next to the Auto Logon Helper you wish to modify.
- In the pop-up dialog that appears, select the desired resource type and move it to the right-side column using the arrow button and then, click Save.
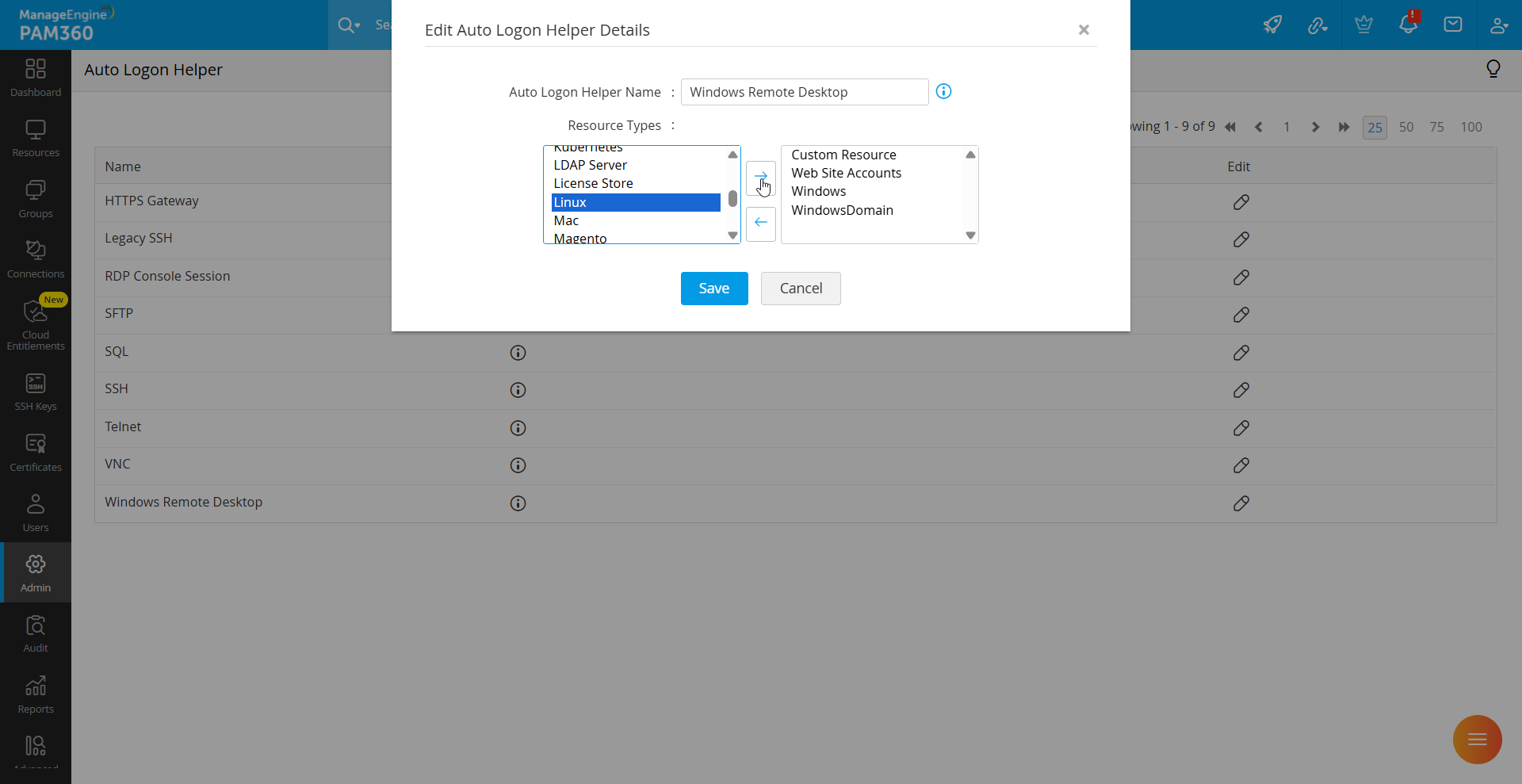
- Once saved, PAM360 will allow connections to the selected resource type using the configured auto logon helpers.
For example, if you want to enable Windows Remote Desktop (RDP) connections for Linux resources, follow these steps:
- Edit the Windows Remote Desktop gateway engine.
- Move the Linux resource type to the right-side column and click Save.
Now, the Windows Remote Desktop option will be available for Linux resources, enabling RDP-based connections.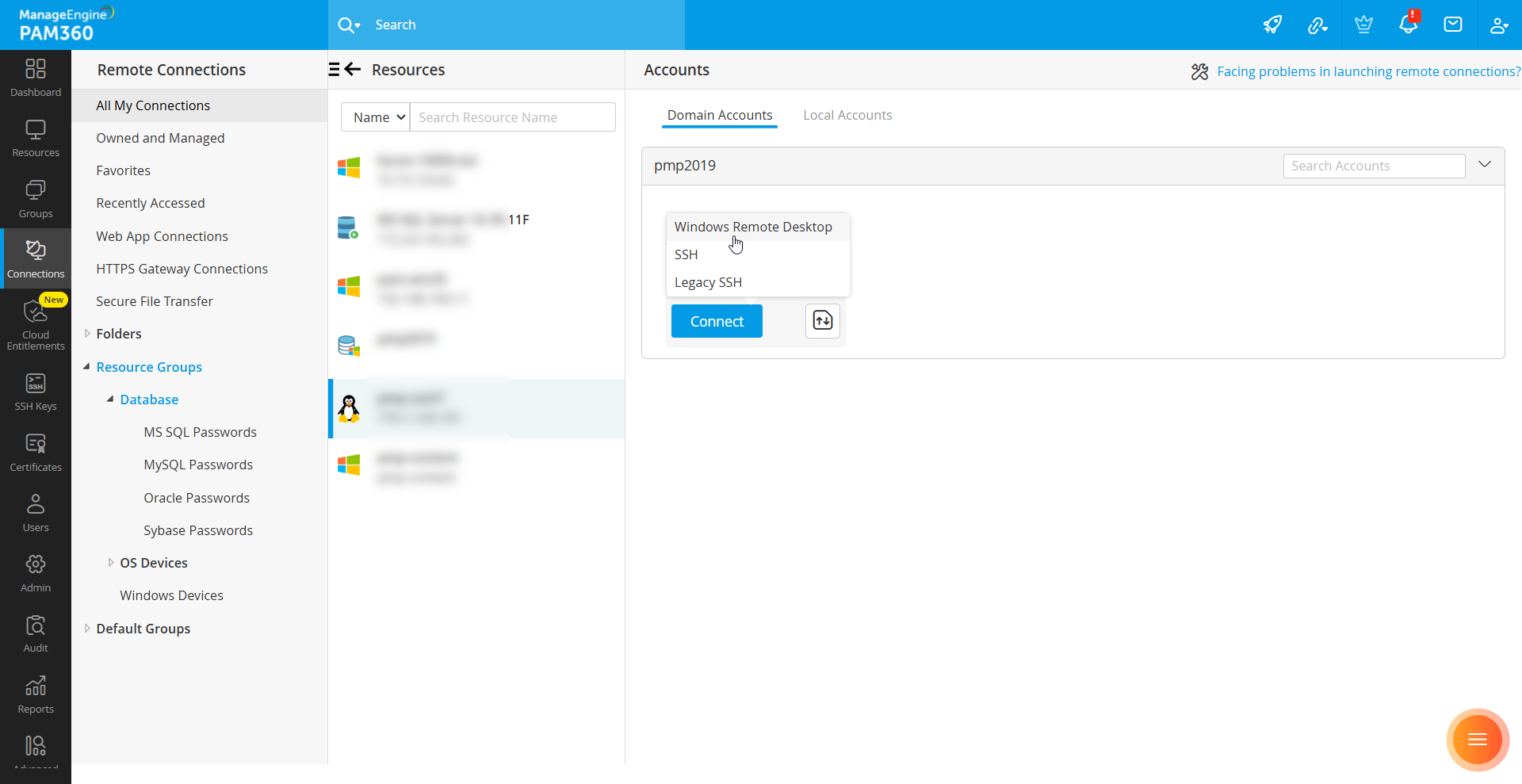
Caution
Ensure that the resource of the selected resource type supports the configured auto logon helpers for a successful connection. For example, SSH-based resources require RDP servers installed and configured to establish successful connections via Windows Remote Desktop.