Connection Settings
PAM360 offers advanced configuration settings for remote connections, allowing administrators to customize the RDP, SSH, and VNC connections based on their requirements, improving the user experience. Administrators can modify various connection options, such as the SSH terminal type, desktop composition for RDP connections, encoding type for VNC connections, etc. Administrators can modify the connection settings for RDP, SSH, and VNC connections from a centralized window, and these changes are applied only for the remote connections launched from the PAM360 interface and are not saved in the remote device.
This help document covers the following topics in detail:
1. Glossary of Terms
Understanding encoding methods is essential for optimizing the remote connection performance based on the network conditions. Explore the following table to learn about the different encoding techniques used in remote connections.
| Terminology | Explanation |
|---|---|
ZRLE | ZRLE (Zlib Run-Length Encoding) is a compression algorithm used in VNC protocols to efficiently transmit graphical data over remote connections. It combines Zlib compression with run-length encoding (RLE) to reduce repetitive pixel patterns, making it ideal for low-bandwidth environments. |
Raw | Raw is a basic encoding method where the length * height pixel data is transmitted without any compression or encoding, thereby offering minimal processing overhead. It sends the exact pixel values of the screen, making it suitable for local connections or high-speed networks but inefficient for low-bandwidth environments due to the large data volume. |
Tight | Tight encoding is a VNC compression method optimized for low-bandwidth environments, such as slow modem connections. It uses the Zlib library to compress raw pixel data and applies pre-processing techniques to maximize compression efficiency while reducing CPU usage. For color-rich screen areas, optional JPEG compression is used to reduce bandwidth consumption further. |
Hextile | Hextile encoding is a VNC compression method suited for medium- to high-speed networks, such as LANs. It divides the screen into small rectangular tiles (typically 16×16 pixels) and compresses each tile separately. For solid-colored areas, it uses run-length encoding (RLE), while more complex tiles are encoded using raw pixel data. |
CopyRect | CopyRect (Copy Rectangle) encoding optimizes data transfer by referencing existing screen areas instead of resending unchanged pixel data. When data is moved, only the coordinates of the source and destination rectangles are transmitted, significantly reducing bandwidth usage for repetitive or static screen content. |
2. Configuring Connection Settings
PAM360 allows administrators to configure connection settings for RDP, SSH, and VNC connection types. You can configure connection settings using any of the following methods:
- Navigate to the Resources tab and switch to the Passwords tab. On the Passwords pane, click the Account Actions icon beside the desired account whose connection settings you wish to configure and select Connection Settings from the displayed options.
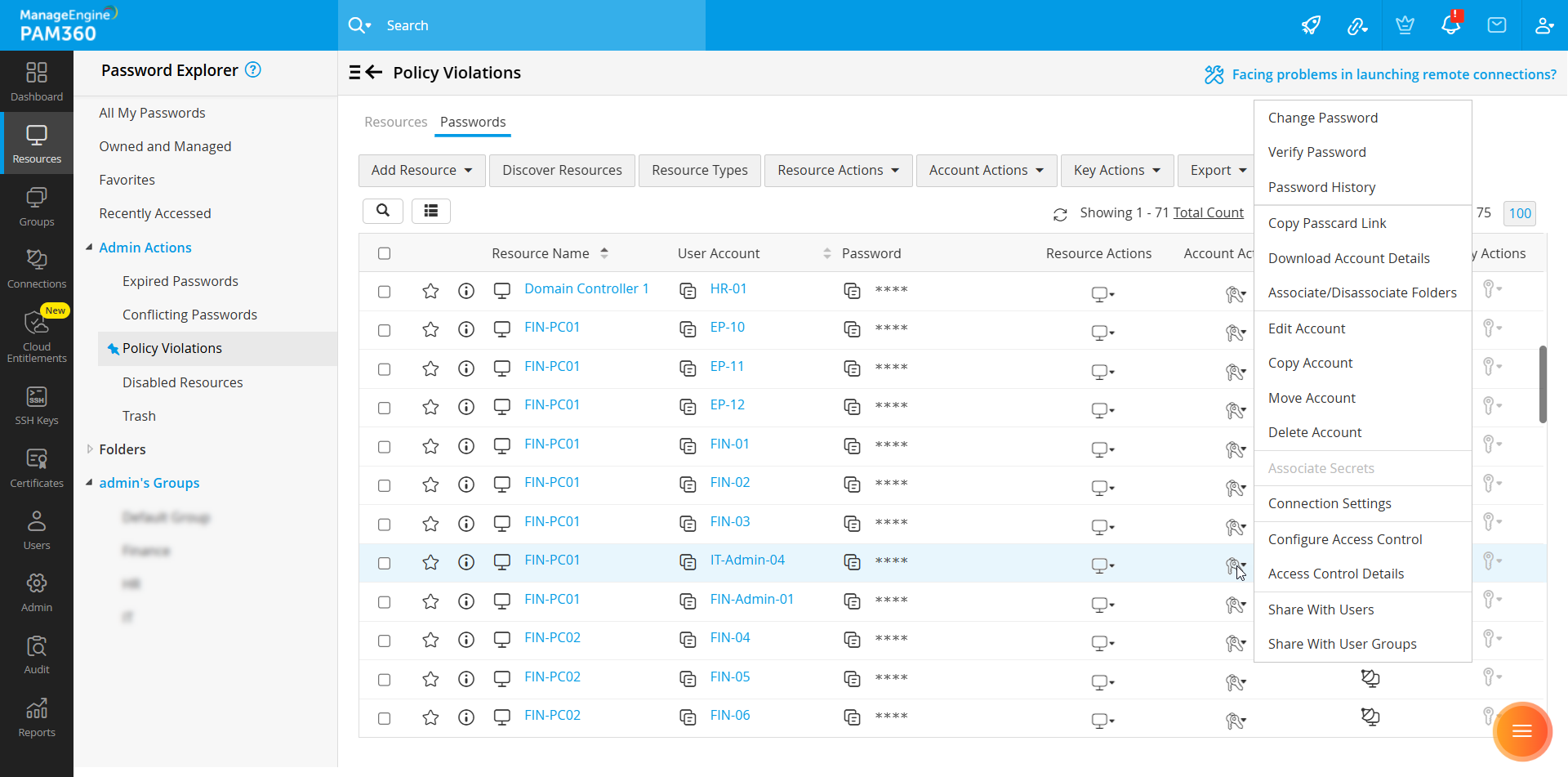
- To configure connection settings for multiple accounts in bulk, select the desired accounts on the Passwords tab, click the Account Actions button on the top pane, and select Connection Settings from the displayed options.
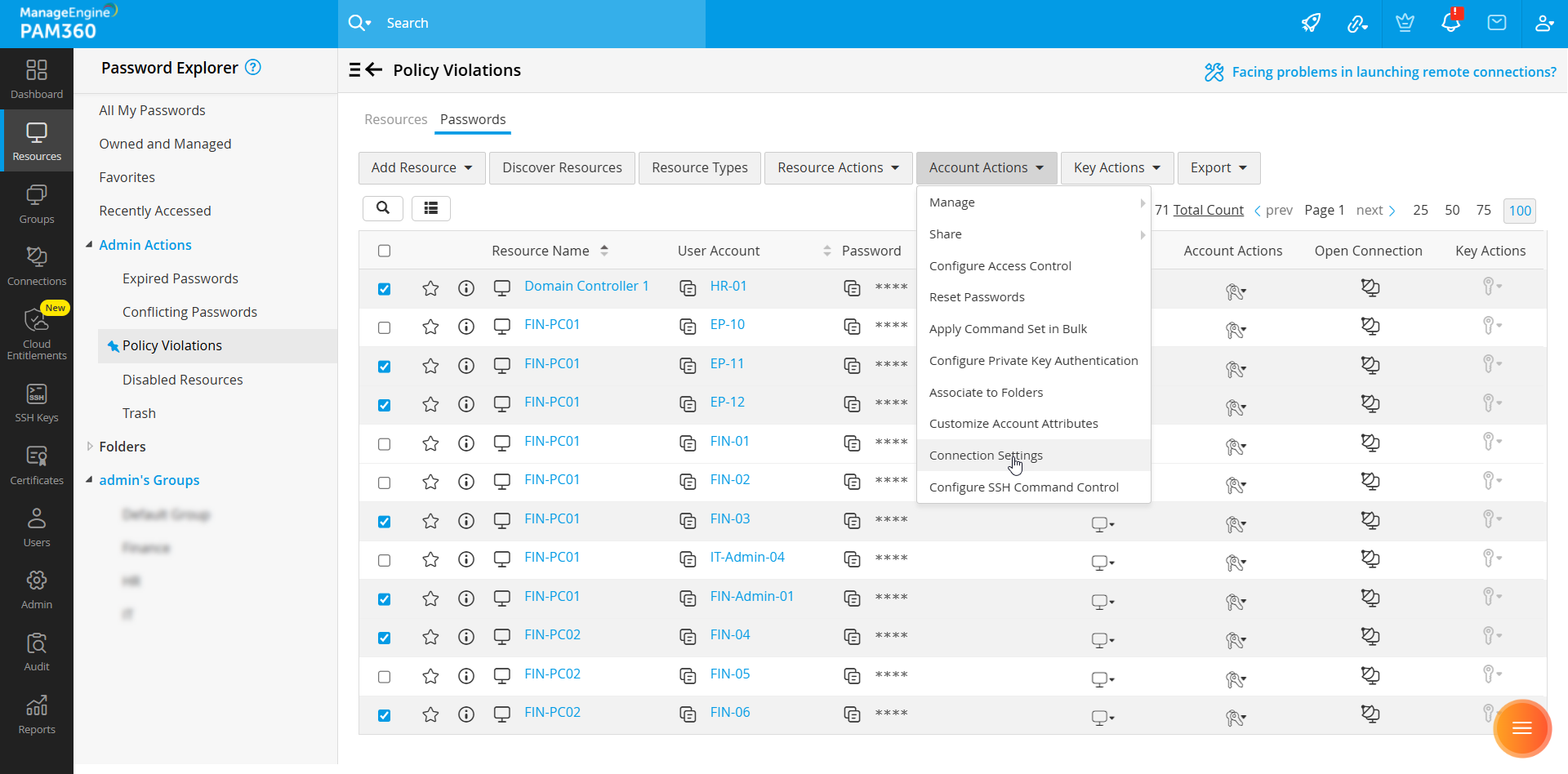
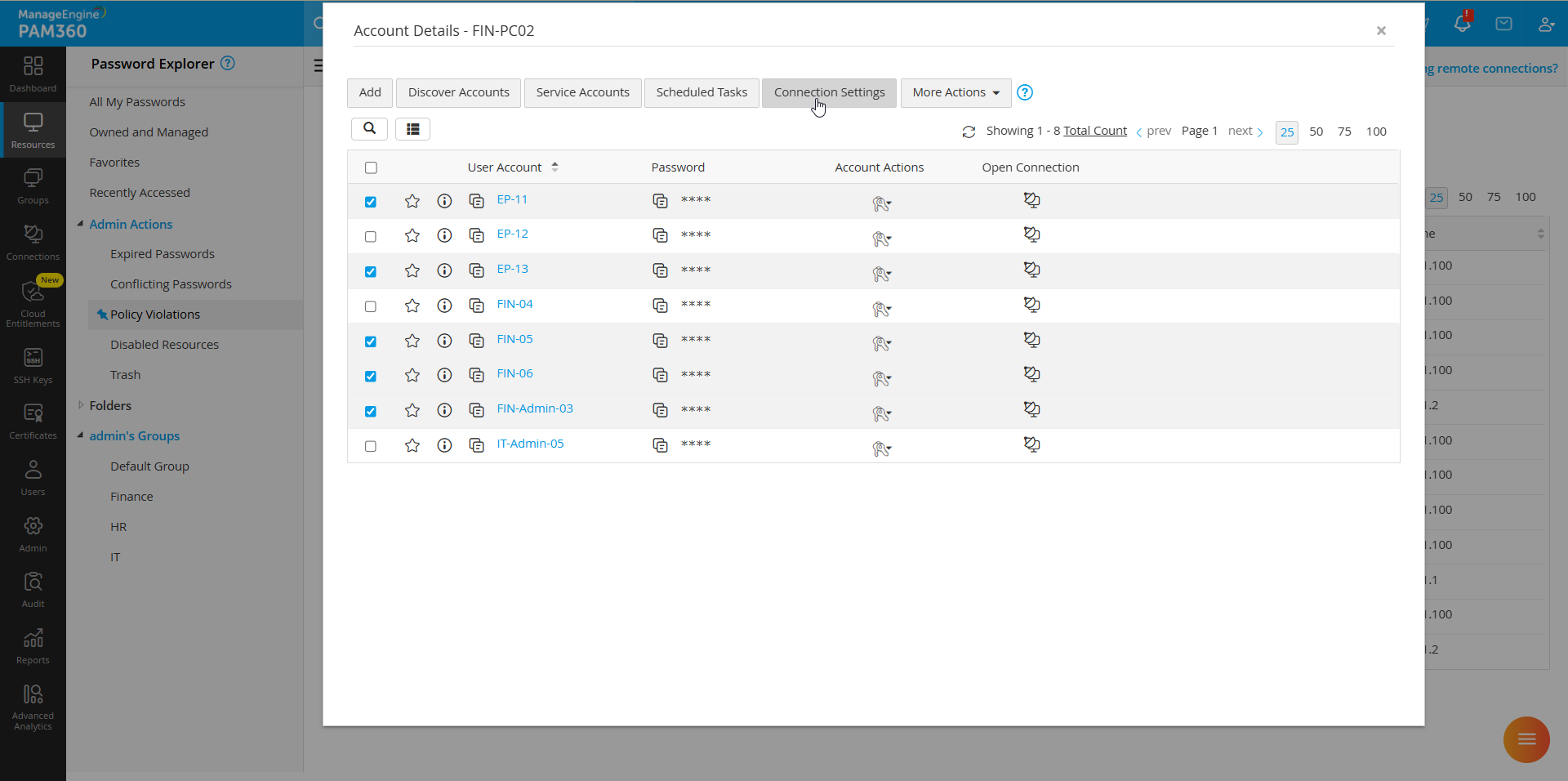
- Alternatively, if you wish to configure connection settings in bulk for multiple accounts within a resource, go to the Resources tab and click on the resource whose accounts you wish to modify. In the Account Details window, select the desired accounts from the list, and click the Connections Settings button on the top pane.
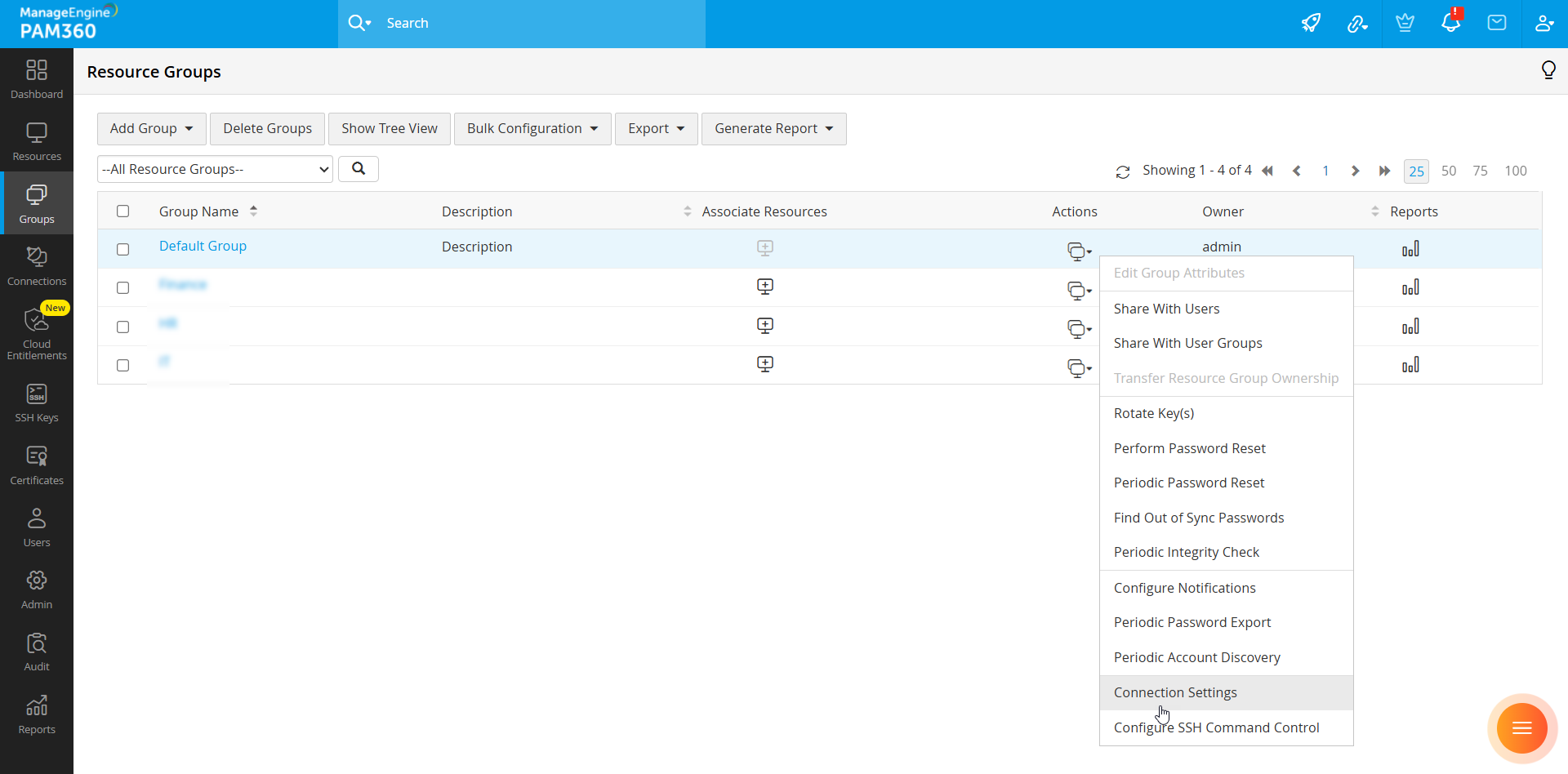
- To configure connection settings for a group of resources, navigate to the Groups tab, click the Actions icon beside the desired resource group, and select Connection Settings from the displayed options.
- On the Configure Connection Settings window that appears, modify the necessary connection settings and click Save to save the configured changes.
Depending on the selected account, you will see the connection settings for one or all of the following connection types on the Configure Connection Settings window.
2.1 RDP Connections
As shown below, the connection settings for remote sessions launched using RDP are organized into four sections: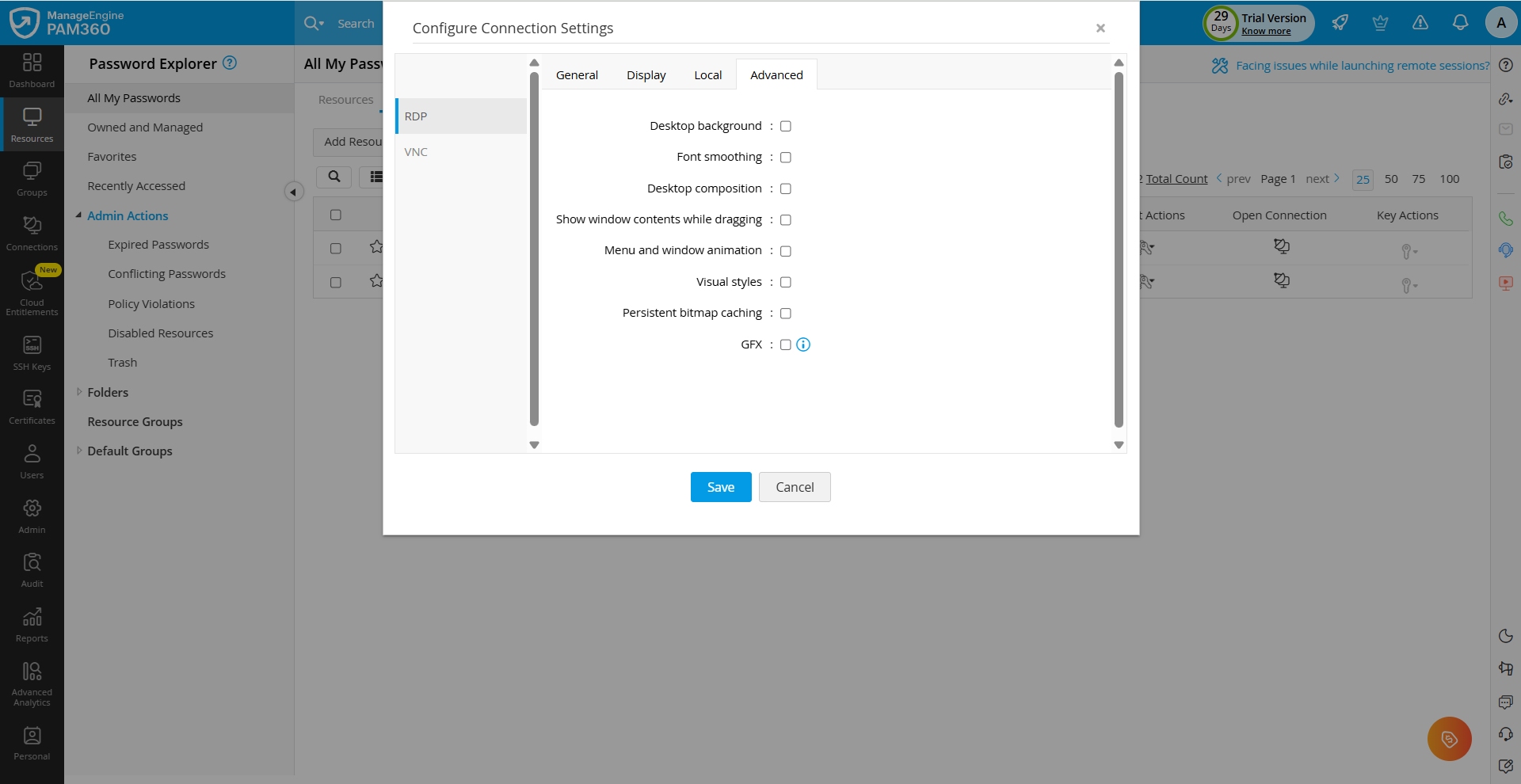
- General
- Connect to console session - Enable this checkbox to initiate a console session to the remote machine.
- If a regular remote session is active on a target machine (Windows Client Edition), starting a console session will disconnect the existing user session and start a new console session.
- If the target machine is a Windows Server, the console session will get initiated with the regular remote session using a CAL (Client Access License) without disrupting other user sessions.
Additional Details
- Display
- Color depth - Choose the desired color depth from the displayed options.
Caution
Higher color depths result in vibrant output but at the cost of increased bandwidth, which can impact network performance on slower connections.
- Disable remote cursor - Enable this checkbox to hide the remote computer's mouse cursor from your screen during the RDP session.
- Color depth - Choose the desired color depth from the displayed options.
- Local
- Remote audio playback - Select how audio from the remote machine should be played during the RDP session playback.
- Quality - Adjust the visual quality of the remote session to balance performance and display clarity.
- Clipboard - Enable this checkbox to share data between the local and remote machines through clipboard redirection.
- Printer - Enable this option to allow printing from applications running on the remote computer to your physical printers, redirecting your local printers.
- Printer Name - Specify the name of the local printer to be used for printing from within the remote session if local printer redirection is enabled.
- Drives - Enable this checkbox to facilitate secure file transfer between your local machine and the target machine.
- Text Only - Enable this checkbox to disable the graphical elements on the remote session and improve session performance over low-bandwidth connections.
- Advanced - These are settings related to visual enhancements and performance optimizations. Click here to view Microsoft's documentation for detailed information about the various options displayed in this section.
- When the GFX option under the Advanced tab is enabled, the visual experience of remote sessions are enhanced by offloading graphics processing to the GPU on the remote host or by optimizing the bandwidth and image quality using advanced codecs, resulting in smoother visuals, improved performance, and support for high-quality remote desktop experiences.
Caution
When the GFX option is enabled, for proper rendering of the RDP session, ensure the Prioritize H.264/AVC 444 graphics mode for Remote Desktop Connections and Enable H.264/AVC 444 hardware encoding for Remote Desktop Connections policies are enabled under the RDP group policy settings. If these policies are disabled, the connection will be established, but the screen will appear blank.
To configure the keyboard layout for remote sessions, navigate to General Settings >> Remote Session Management and choose a language from the Keyboard Language dropdown. The selected language applies to all the users in the PAM360 environment. The default language settings will be applied if a keyboard language is not configured.
Additional Details
Users can select their preferred keyboard language for remote sessions in the Remote Session Settings window, which can be accessed by clicking the My Profile icon. The selected keyboard language will apply only to remote sessions initiated after the configuration.
2.2 SSH Connections
Typically, terminal types and the corresponding sets of commands that can be executed during the SSH connections vary from one SSH device to another. For example, if the SSH device added to PAM360 is IBM AS400 and the terminal type selected is a Linux terminal type, say xterm, then a few commands will not work as expected, reducing efficiency considerably. Therefore, it is essential to define the exact terminal type for each SSH device added to PAM360 so that PAM360 can emulate the terminal and process the commands used on that particular terminal. Enter the terminal name in the Terminal Type field for the selected SSH device and click Save. Click here for a brief list of terminal emulators.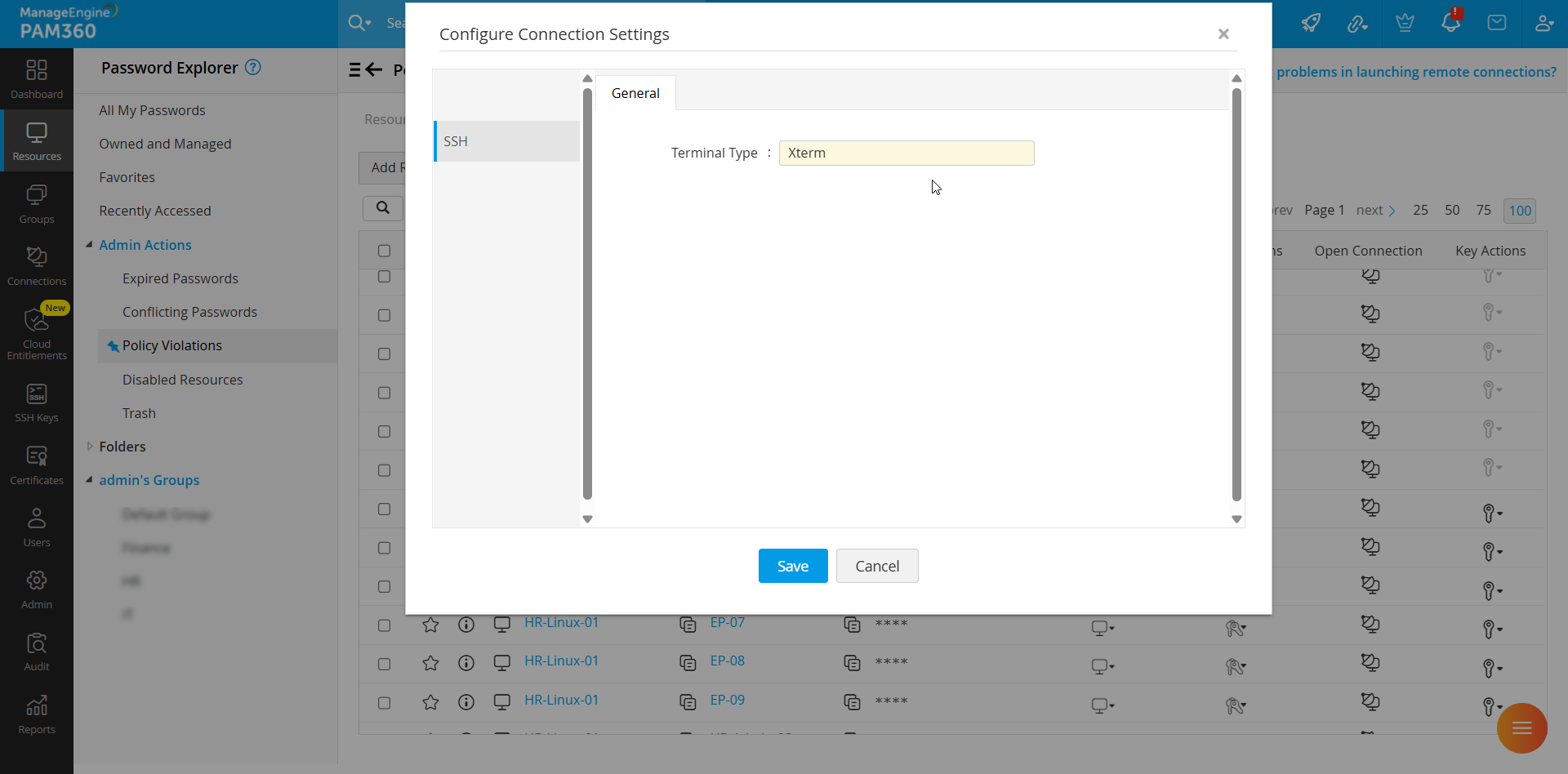
2.3 VNC Connections
PAM360 allows you to configure the following connection settings to improve the user experience and enforce control over the remote connections established using VNC protocol.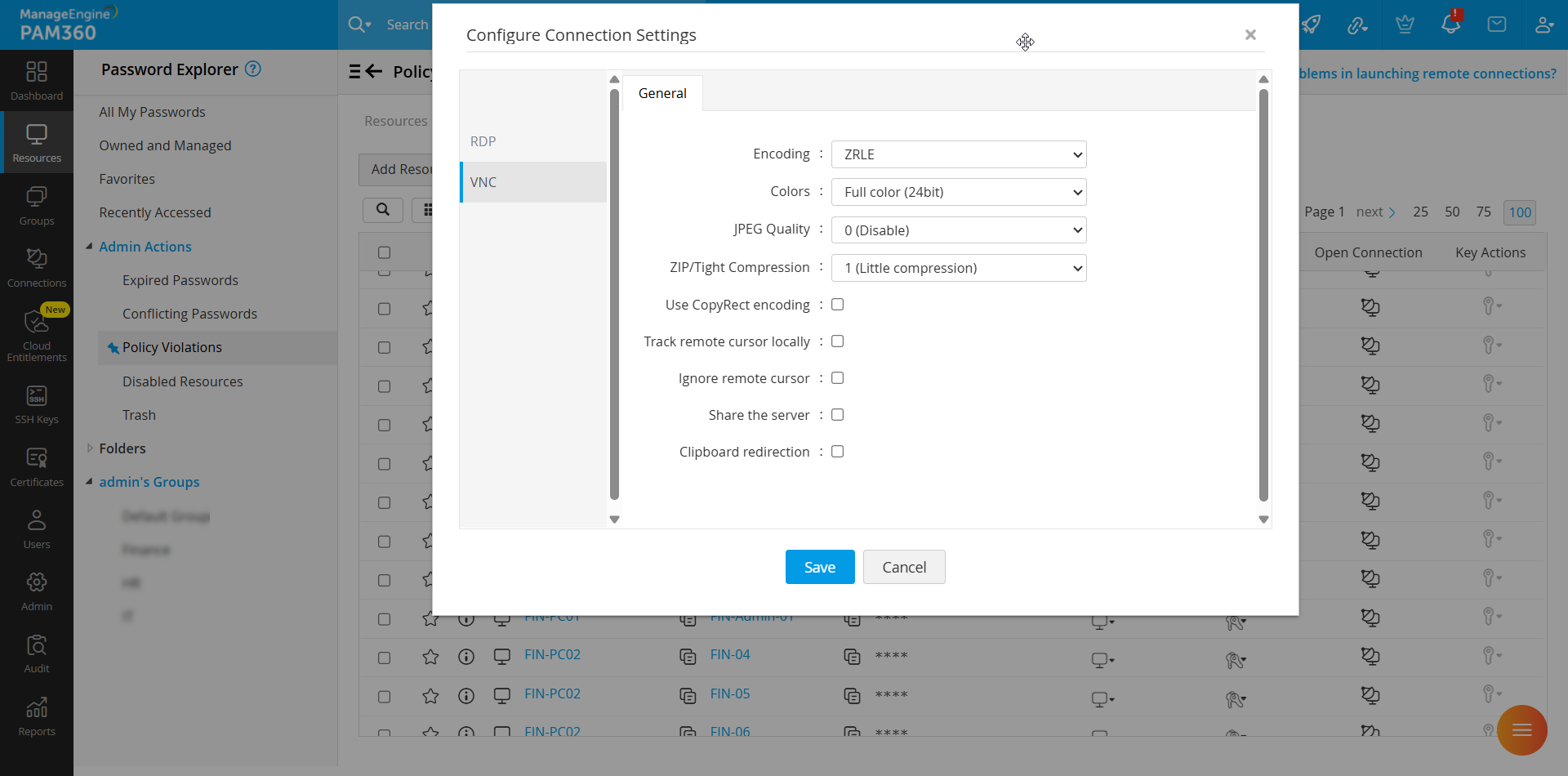
- Encoding - Select the desired encoding method from the displayed options to optimize performance and bandwidth usage during VNC sessions.
- Colors - Choose the color depth for the remote session to balance visual quality and connection speed.
- JPEG Quality - Adjust the quality of JPEG compression to optimize the trade-off between image clarity and bandwidth consumption.
- ZIP/Tight Compression - Select a compression level between 1 and 9 to reduce the size of transmitted data, enhancing session performance.
- Use CopyRect encoding - Enable this checkbox to improve efficiency by only transmitting the rectangle location when moving data, rather than resending the entire image.
- Track remote cursor locally - Enable this checkbox to display a local cursor that tracks the remote cursor’s movement.
- Ignore remote cursor - Enable this checkbox to hide the remote machine's cursor during the VNC sessions.
- Share the server - Allow multiple users to simultaneously connect to the same VNC session for collaborative access.
- Clipboard redirection - Tick this checkbox to enable the sharing of clipboard content between the local and remote machines during VNC sessions.