Top 9 best practices to prevent IP conflict
Unresolved IP conflicts can quickly lead to downtime, connectivity issues, and frustrated users. The good news is that many of these conflicts can be avoided with the right IP address management practices.
From maintaining DHCP hygiene to segmenting networks with VLANs and documenting IP usage, proactive strategies go a long way in preventing duplicate IPs. Before we get into these best practices, let’s look at why IP conflicts happen in the first place and why preventing them is critical for reliable network performance.
On this page, you'll read:
- Why preventing IP address conflicts matters
- Why do IP conflicts occur in my network?
- The importance of preventing IP address conflicts
- 9 key ways to prevent IP address conflicts
- How to detect and resolve IP conflicts if they occur
- How OpUtils helps implement best practices
- FAQs on best practices to prevent IP conflicts
Why preventing IP address conflicts matters
As you might be aware, an IP address conflict occurs when the same IP is assigned to two devices. Such overlaps can cause connection drops, degraded performance, or even complete network outages. Preventing IP conflicts is essential to maintain smooth network operations and enhance overall network reliability and performance. By proactively managing IP assignments and maintaining proper IPAM hygiene, IT administrators can avoid unnecessary downtime, reduce troubleshooting efforts, and keep the network running efficiently.
Why do IP conflicts occur in my network?
IP address conflicts usually occur from a mix of human errors, system oversights, and network design gaps. Here are some of the most common causes of IP conflicts in networks:
- Overlapping static and dynamic assignments: IP conflicts often occur when manually assigned IP addresses collide with addresses automatically given out by the DHCP server. Without a systematic approach to IPAM, two devices may end up using the same IP, especially in larger networks.
- Expired or stale DHCP leases: When a DHCP lease isn’t properly released or renewed, the server might inadvertently assign the same IP to a different device.
- Manual configuration errors: Simple human mistakes, like entering the wrong IP address or duplicating a previously assigned one, can trigger conflicts.
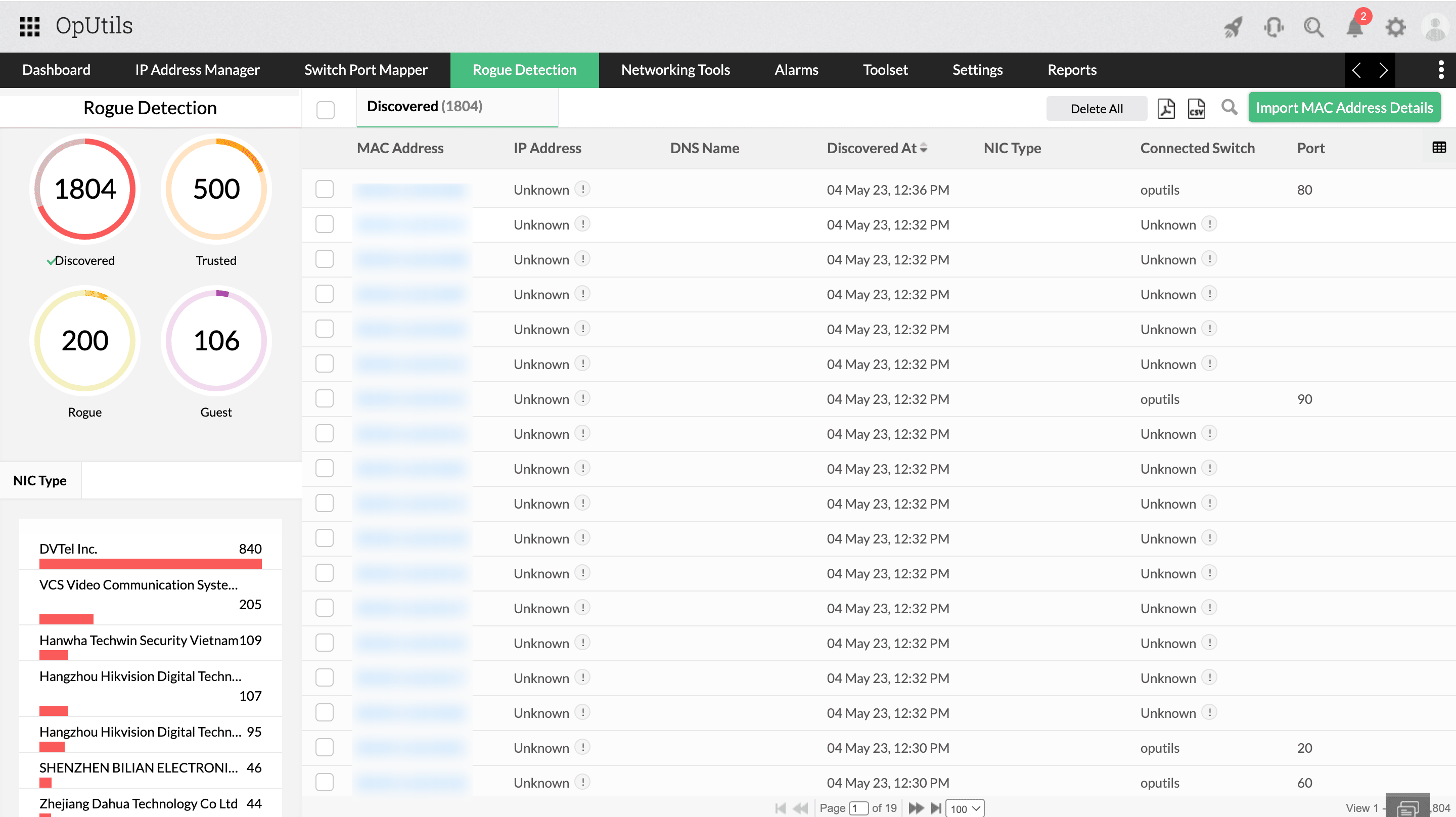
- Rogue or unauthorized DHCP servers: Rogue DHCP servers on the network can hand out IP addresses that clash with legitimate assignments, disrupting operations and creating unpredictable conflicts.
- Cloned devices or VM snapshots: Cloning physical devices or virtual machines without updating their network settings can result in multiple devices with identical IP addresses, causing conflicts and connectivity problems.
The importance of preventing IP address conflicts
IP address conflicts may seem minor, but their impact on network operations can be significant. When such conflicts are left unattended, IT teams are often forced to:
- Spend countless hours troubleshooting connectivity issues
- Deal with frustrated end-users
- Tackle breached service level agreements (SLAs)
- Face unnecessary resource drain
As networks scale with IoT devices, BYOD endpoints, and virtual environments, the risk of duplicate IP addresses grows, making proactive prevention even more essential. Addressing conflicts early also helps reduce potential security risks, as rogue DHCP servers or misconfigured devices can be exploited if left unattended.
By implementing structured IPAM and monitoring strategies, organizations can maintain stable network performance, optimize IT resources, and improve overall network reliability. This proactive approach reduces unexpected downtime, enhances SLA compliance, boosts IT efficiency, and ensures a smoother user experience across the network.
9 key ways to prevent IP address conflicts
Preventing duplicate IPs isn’t about a single fix, it requires consistent IP address management and structured network practices. Below are the key best practices IT teams can adopt to reduce conflicts, improve reliability, and optimize network performance.
- Adopt DHCP hygiene: A well-structured DHCP configuration is the foundation of IP address conflict prevention. Regularly maintaining DHCP scopes, avoiding overlapping pools, and ensuring proper lease management ensures addresses are allocated consistently and efficiently.
- Use IP reservations for critical devices: For servers, routers, and other critical devices, configure DHCP reservations. This ensures these devices always receive the same IP address, strengthening IPAM and preventing duplicates from disrupting essential services.
- Integrate DHCP and DNS services: When DHCP and DNS services are integrated, IP address records remain synchronized. This prevents outdated DNS entries from causing conflicts and ensures conflict prevention across both naming and addressing systems.
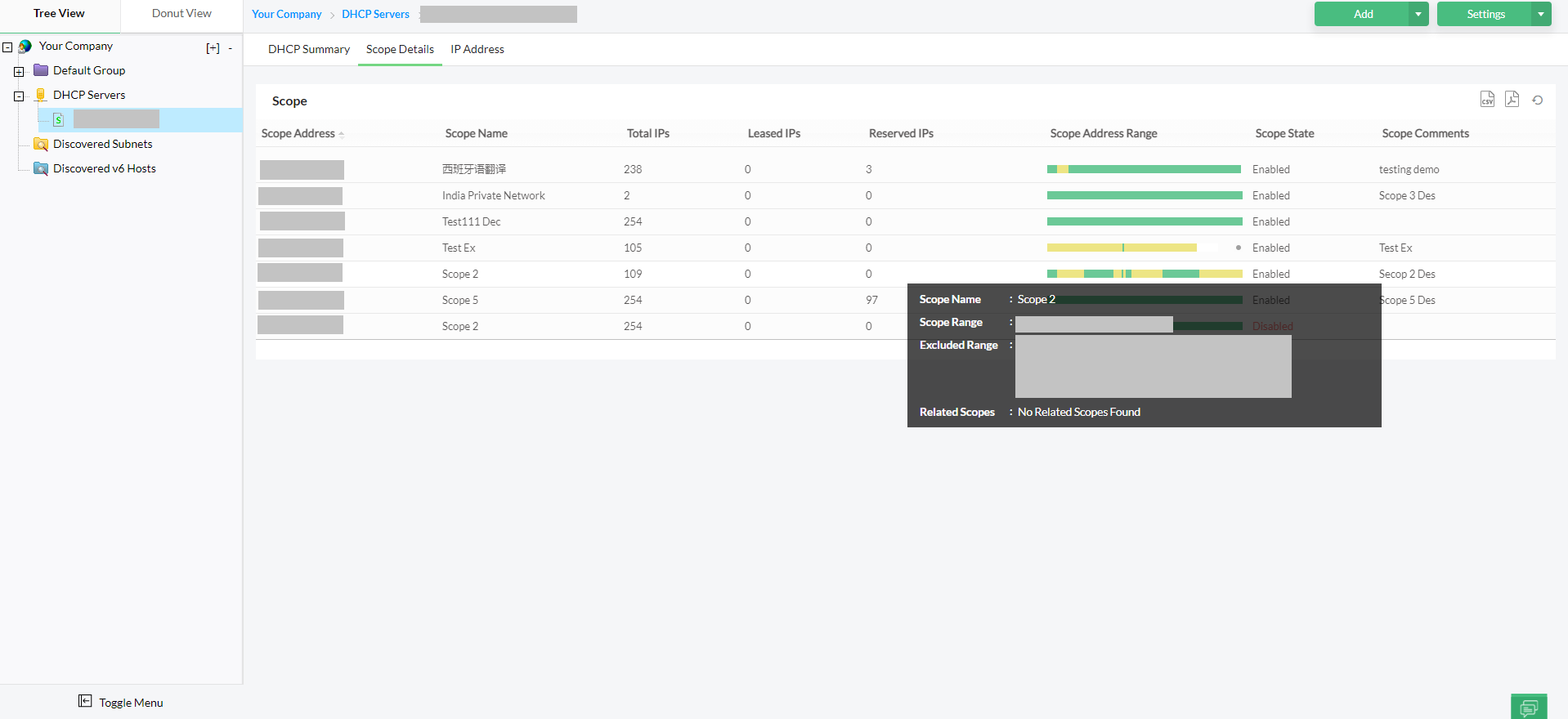
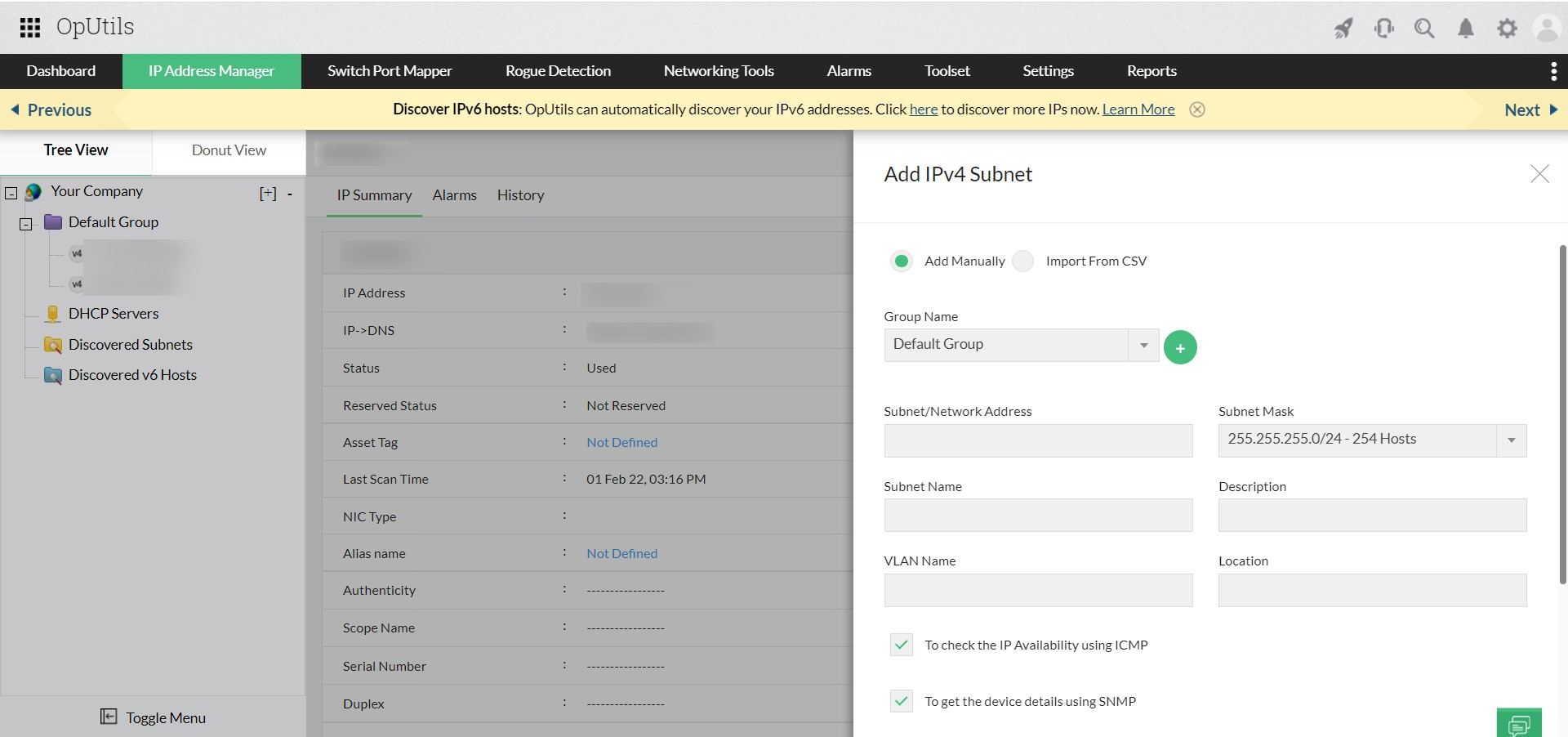
- Document subnets carefully: Thoughtful subnet planning and proper network segmentation reduce the risk of overlapping IP ranges. Documenting subnet allocations helps IT teams avoid unintentional conflicts and makes troubleshooting more efficient.
- Monitor with IPAM and network tools: Deploying IP address management software and network monitoring tools allows IT admins to quickly detect duplicate IPs, track allocation trends, and maintain visibility across large address spaces, strengthening overall IPAM.
- Audit stale or unused IPs regularly: Over time, stale or abandoned IP addresses may remain in DHCP or IPAM databases. Regularly auditing and cleaning up unused addresses helps prevent IP conflicts and improves network hygiene.
- Segment networks with VLANs or subnets: Breaking down large flat networks into VLANs or smaller subnets and supernets limits the scope of broadcast domains. This segmentation improves performance and minimizes the spread of IP conflicts when they do occur.
- Disable unused DHCP servers / enable rogue DHCP detection:Unauthorized DHCP servers can cause major IP allocation issues. Disable unused DHCP services and enable rogue DHCP detection to ensure only trusted servers issue addresses, preventing accidental or malicious conflicts.
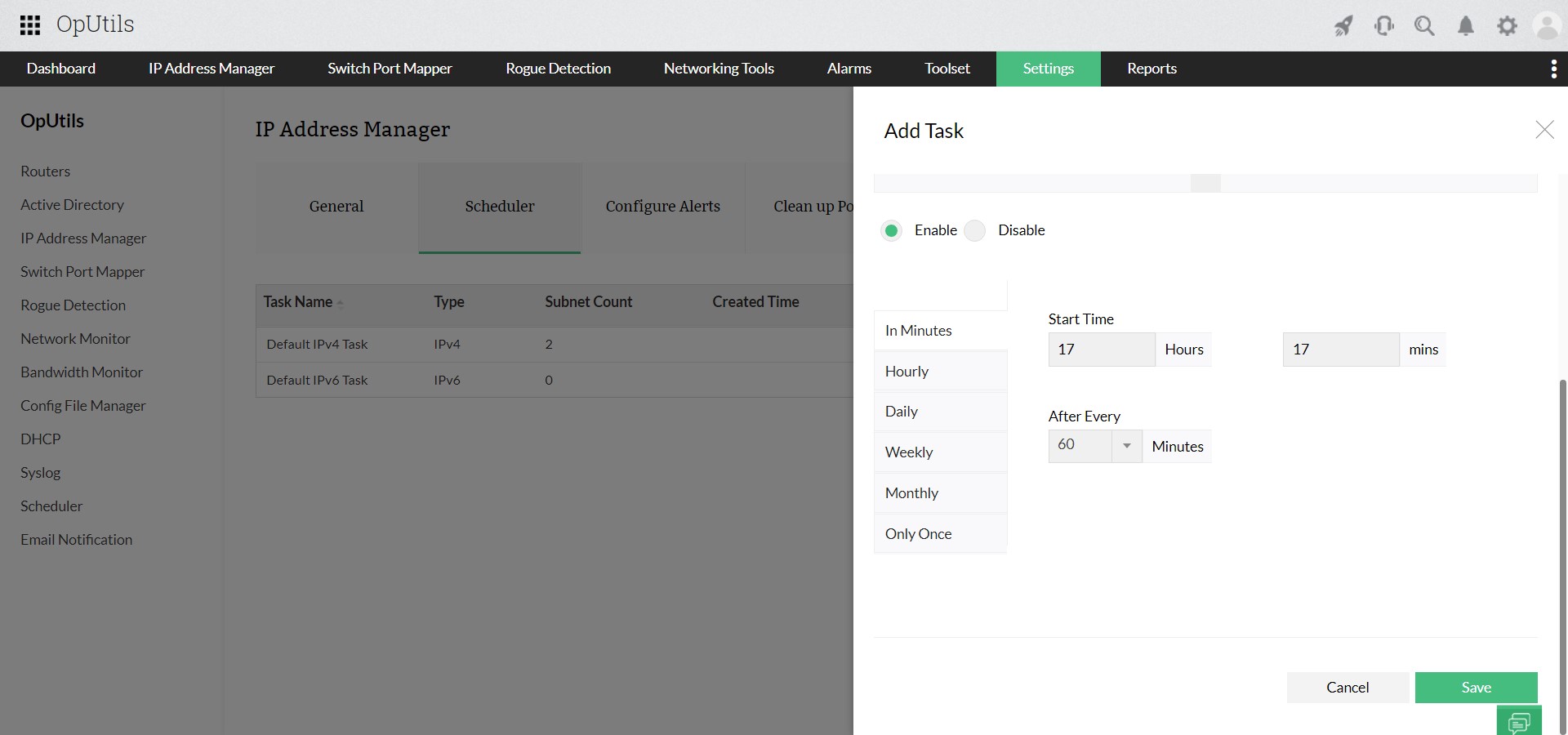
- Use shorter DHCP lease times in dynamic environments: In networks with frequent device churn such as BYOD, guest Wi-Fi, or IoT, shorter DHCP lease durations help free up addresses faster and reduce the chances of conflicts, enhancing network performance and smooth address allocation.
How to detect and resolve IP address conflicts if they occur after implementing the best practices
While the above best practices significantly reduce the probability of IP address conflicts in your network, no network is ever truly immune. Even with preventive measures, conflicts can still surface. When that happens, IT teams generally have two approaches: a manual method or a tool-based one.
Manual troubleshooting works for smaller networks, but at scale, relying on the right monitoring or IPAM tool makes conflict detection and resolution faster and more reliable.
Manual detection methods:
Operating systems often display alerts like “Windows has detected an IP address conflict” when duplicate IPs occur. Beyond OS prompts, admins can use commands such as ping, arp -a, or ipconfig to identify conflicting addresses and trace devices manually.
Automated detection with IPAM tools:
Monitoring solutions, IP scanners, and IPAM platforms make it easier to detect and resolve IP address conflicts in real time. These tools continuously scan the network, flag duplicate IPs, and provide visibility into device-to-IP mappings, removing guesswork and speeding up resolution. Bundled IPAM solutions provide extra efficiency and visibility.
Quick fixes to restore connectivity:
Once a conflict is identified, short-term fixes include renewing the DHCP lease, reassigning static IP addresses, or restarting network interfaces. These steps can restore connectivity quickly while a permanent solution is implemented.
Eliminating root causes:
To prevent recurring issues, IT teams must address the root cause of the conflict. This could mean tightening DHCP configuration, correcting overlapping subnets, or disabling unauthorized DHCP servers. By resolving the underlying issue, networks remain stable and less prone to repeat disruptions.
Ultimately, the real difference comes down to how you manage IP conflicts. While manual fixes may work temporarily, adopting a dedicated network management tool ensures scalability, visibility, and faster resolution when conflicts arise.
How OpUtils helps implement best practices to prevent IP conflicts
OpUtils empowers IT teams to put IP address conflict prevention best practices into action. Its comprehensive IP address manager ensures:
- DHCP hygiene and lease management: OpUtils ensures clean DHCP hygiene through accurate lease tracking and IP reservations, reducing the risk of conflicts and improving network reliability.
- MAC address mapping and rogue detection: By mapping device MAC addresses and detecting unauthorized devices, OpUtils safeguards your network from accidental or malicious IP conflicts.
- Real-time visibility with IP scanners and monitoring tools: Built-in IP scanners and monitoring tools provide instant insights into IP allocations, making it easy to detect duplicate IPs and audit stale or unused addresses.
- Simplified network segmentation and documentation: OpUtils enables IT teams to efficiently organize subnets, monitor segmented networks, reduce downtime, and maintain optimal network performance.
Take control of IP address conflicts and keep your network performing at its best. Get started with OpUtils today by trying it free for 30 days or book a personalized demo to see how it fits your network.
FAQs on best practices to prevent IP conflicts
What are the signs of an IP address conflict?
+What is the impact of IP conflicts on network performance?
+How do VLANs or subnet segmentation help prevent IP conflicts?
+Can multiple DHCP servers cause IP conflicts?
+What are the best practices for managing IP addresses in large networks?
+How quickly should IP conflicts be resolved to minimize impact?
+Proactively prevent and resolve IP conflicts in real time with OpUtils
Try OpUtils for free today