What is SaaS change management?
SaaS change management refers to the structured approach organizations take to implement, monitor, and manage changes in their SaaS applications. These changes could include updates, feature rollouts, integrations, or transitions between SaaS tools.
The goal of SaaS change management is to ensure that any modifications to the SaaS environment occur smoothly, with minimal impact on daily operations, while maximizing user adoption and reducing risks. Unlike traditional software changes, SaaS applications are often updated frequently, making it essential to have a streamlined process for managing these changes effectively.
Why is change management crucial for SaaS applications?
Organizations depend on multiple SaaS applications to manage their operations, from communication tools like Slack to CRM solutions like Salesforce. However, these applications are dynamic and subject to frequent changes, including:
- Feature updates: SaaS providers regularly release updates or new features.
- System integrations: Changes in APIs or third-party integrations can affect workflows.
- User access modifications: Role-based permissions may change as teams evolve.
- Vendor updates: Transitioning to new SaaS vendors or services should be carefully monitored to maintain consistency within your SaaS ecosystem.
Without a structured SaaS change management process, organizations face the risk of operational disruptions, security vulnerabilities, and decreased productivity. Key reasons why SaaS change management is critical include:
- Ensuring business continuity
Change management ensures smooth transitions with minimal interruptions. When SaaS applications undergo updates, planned rollouts and structured communication prevent sudden downtime or workflow disruptions. By managing changes strategically, teams can continue operating seamlessly while adapting to new updates without compromising business activities.
- Minimizing risk
SaaS changes, if unplanned, can introduce errors, misconfigurations, or security gaps. A robust change management strategy anticipates these challenges, mitigates potential risks, and ensures all updates are tested and validated before deployment. This reduces the likelihood of data loss, security vulnerabilities, or application failures.
- Enhancing user adoption
Change can cause resistance among employees, especially when new features or tools are introduced without adequate preparation. Effective change management includes training, communication, and support, which help users understand and adapt to changes quickly. This accelerates user adoption and ensures employees can make the most of the updated tools.
- Maintaining compliance
SaaS changes must adhere to organizational policies and regulatory standards. A structured change management process involves monitoring and documenting all modifications, ensuring compliance with internal and external requirements. Proper tracking reduces the risk of audit failures and regulatory penalties.
- Optimizing ROI
SaaS investments are significant, and effective change management ensures maximum value. By minimizing disruptions, encouraging user adoption, and eliminating redundancies, organizations can optimize workflows and resources. This leads to better ROI and ensures that SaaS tools deliver their intended benefits.
How to identify if your organization needs SaaS change management
If your organization struggles with unplanned disruptions, inefficient processes, or adoption issues, it's a clear sign that you need a robust SaaS change management process. Here are some symptoms and issues faced:
Symptoms of poor SaaS change management:
- Frequent service disruptions after software updates or changes: Without proper planning or testing, updates can disrupt workflows or cause tools to malfunction. Teams may face unexpected downtime, leading to missed deadlines and frustration.
- Decreased productivity due to unclear processes or lack of user training: If employees are not informed or trained on new features or updates, their productivity suffers. They may waste time figuring out changes on their own, leading to inefficiency and errors.
- Confusion among employees regarding new tools or features: Employees often struggle to adapt when changes are not communicated clearly. This confusion impacts their confidence and results in inconsistent usage of tools, reducing overall efficiency.
- Repeated security breaches or data loss from unmonitored changes: Unauthorized or untested changes can create security loopholes. Unmonitored updates may lead to accidental data breaches, data loss, or misconfigurations that compromise system integrity.
- Increased shadow IT usage due to dissatisfaction with managed SaaS tools: When organizations fail to manage changes effectively, employees may turn to unauthorized tools to meet their needs. Shadow IT not only increases security risks but also leads to fragmented workflows.
- Difficulty in tracking and managing changes across multiple SaaS tools: As SaaS ecosystems grow, organizations struggle to keep track of changes, updates, and usage across all applications. Without centralized oversight, critical updates or risks can go unnoticed.
Common issues organizations face:
- Lack of visibility
Organizations that rely on multiple SaaS tools often lack centralized visibility. Updates, feature rollouts, or user access changes may occur without the knowledge of IT or leadership teams. This leads to unmonitored changes that can disrupt workflows or introduce risks. Without a single view of all SaaS applications, it becomes nearly impossible to track changes or assess their impact.
- Resistance to change
Employees often resist change, particularly when it is sudden, poorly communicated, or not aligned with their workflows. Lack of training or support further exacerbates this issue, as employees may feel overwhelmed and frustrated. This resistance prevents teams from leveraging new tools or features effectively, stalling adoption and reducing the ROI of SaaS investments.
- Overlapping tools
Organizations sometimes adopt multiple SaaS tools that serve similar purposes, leading to redundancies. For instance, teams may use two project management tools or overlapping communication platforms. Poor change management exacerbates this problem by making it harder to identify redundant tools, increasing costs and creating confusion among users.
- Security risks
Without proper change management, unauthorized or untested changes can compromise security. For example, poorly managed updates may result in misconfigurations that expose sensitive data or grant unauthorized access. Additionally, shadow IT usage increases security vulnerabilities, as IT teams lose control over tools employees are using.
- Missed opportunities
SaaS providers frequently release updates, enhancements, or new features that can improve workflows or productivity. However, without a change management process, organizations may fail to recognize or adopt these improvements. This means they miss opportunities to optimize operations, enhance user experiences, or gain a competitive edge.
If any of these symptoms sound familiar, it's time to adopt a structured SaaS change management strategy. By addressing these challenges, organizations can improve visibility, ensure smooth transitions, and enhance their SaaS ecosystem's overall effectiveness.
SaaS change management process
A well-defined SaaS change management process ensures organizations can plan, implement, and monitor changes systematically. Below are the essential steps to follow:
- Assess the change
- Understand the scope and impact of the change: Start with analyzing the nature and extent of the proposed change. Determine whether the change is a minor update, a feature addition, or a significant workflow alteration. Understanding the scope ensures that no element is overlooked during implementation.
- Identify which SaaS tools, users, or workflows will be affected: Changes often have ripple effects across tools and teams. Clearly outline which applications, departments, or users will experience the impact to anticipate their needs and challenges.
- Define the objectives of the change and align them with business goals: Clearly articulate why the change is necessary. Ensure that the change contributes to organizational objectives, such as improving efficiency, reducing costs, enhancing security, or optimizing workflows. Setting measurable goals ensures success can be evaluated later.
- Plan the change
- Develop a detailed plan, including timelines, resources, and roles: Create a comprehensive roadmap that outlines what needs to be done, by whom, and within what timeframe. Assign clear responsibilities to stakeholders, allocate resources (e.g., budget, personnel, and tools), and prepare a realistic schedule for implementation.
- Prioritize changes based on urgency and impact: Not all changes have the same level of importance. Use prioritization frameworks (e.g., high-impact or low-impact matrices) to focus on the most critical updates first. Urgent security fixes or high ROI changes should take precedence.
- Communicate the plan to relevant stakeholders to ensure transparency: Stakeholders—including managers, IT teams, and end users—must be informed about the changes in advance. Share key details such as objectives, timelines, and benefits. Proactive communication reduces confusion and builds trust.
- Implement the change
- Execute the changes while minimizing disruptions to operations: Implement changes in a controlled environment to avoid sudden disruptions. Schedule updates during off-peak hours, or use maintenance windows to reduce the impact on day-to-day operations.
- Roll out updates in phases, if possible, to test impacts on smaller teams: Adopt a phased rollout strategy by starting with a smaller group of users or a single department. Monitor how the change affects their workflows and gather early feedback before deploying it organization-wide.
- Provide training or documentation to help users adapt to the changes: Prepare training sessions, user manuals, a FAQ sheet, or video tutorials to educate employees about new tools, features, or workflows. Training ensures smooth adoption and minimizes resistance or confusion.
- Monitor and review
- Track the outcomes of the change using performance metrics: Measure the success of the implemented change by tracking KPIs. Metrics such as user adoption rates, tool performance, or downtime reduction help evaluate the effectiveness of the change.
- Gather user feedback to assess adoption and satisfaction: Solicit input from employees and stakeholders to identify any challenges they face. Conduct surveys, host Q&A sessions, or set up help desks to resolve concerns quickly.
- Identify and resolve any issues or bottlenecks that arise: Monitor for unexpected issues such as workflow disruptions, technical errors, or resistance to change. Address these bottlenecks proactively to prevent further disruptions.
- Document and optimize
- Maintain documentation of all changes for compliance and future reference: Record all details of the change, including timelines, affected tools, implementation steps, outcomes, and lessons learned. Documentation ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and serves as a reference for future changes.
- Continuously refine the change management process based on lessons learned: Use insights from past experiences to improve your change management strategy. Identify what worked well and what can be enhanced to make the process more efficient and effective.
By following these steps, organizations can manage SaaS changes in a structured and proactive manner, ensuring smoother transitions and maximum value realization.
Benefits of timely SaaS change management
Reduced disruptions
Effective planning and implementation ensure that changes are executed with minimal downtime or workflow interruptions. By scheduling changes during low-usage periods and testing updates before full rollout, organizations can maintain operational continuity and avoid unexpected issues.
Increased user adoption
Well-managed changes include comprehensive training, documentation, and proactive communication. Employees are better equipped to understand and use new tools or features, leading to higher adoption rates. This reduces resistance to change and maximizes the benefits of the updates.
Improved productivity
When changes are rolled out systematically, employees experience fewer disruptions and less confusion. Clear communication, training, and support allow teams to adapt quickly, maintain workflows, and continue working efficiently without productivity dips.
Better visibility and control
A structured change management process provides centralized oversight of all SaaS changes. Organizations can track updates, assess their impact, and ensure no changes go unnoticed. This visibility enhances decision-making and ensures accountability.
Enhanced ROI
Timely and well-executed SaaS changes allow organizations to maximize the value of their tools. By reducing disruptions, increasing adoption, and eliminating redundancies, companies can optimize resource usage and generate higher returns on their SaaS investments.
Stronger security
Changes are monitored and tested to ensure that no misconfigurations, unauthorized access, or vulnerabilities are introduced. A robust change management process minimizes security risks and protects sensitive data.
Optimized workflows
By aligning SaaS updates with business objectives, organizations can streamline processes, automate tasks, and eliminate inefficiencies. Optimized workflows lead to improved overall efficiency and business performance. Timely SaaS change management empowers organizations to stay agile, adapt to evolving needs, and maintain business continuity in a fast-paced digital environment.
Risks associated with poor SaaS change management
Neglecting SaaS change management can have severe consequences for organizations, including:
Operational disruptions
Poorly managed changes can lead to unexpected downtime, workflow interruptions, or system outages. This halts critical business processes, resulting in delays, customer dissatisfaction, and financial losses.
Security vulnerabilities
Unmonitored changes increase the risk of security gaps, misconfigurations, or unauthorized access. Without oversight, sensitive data may be exposed to cyberattacks, leading to breaches, compliance violations, and reputational damage.
Loss of productivity
Confusion and a lack of training during SaaS changes can disrupt employee workflows. Resistance to change, unclear processes, or technical issues affect morale and output, slowing down productivity across teams.
Increased costs
Mismanaged changes often result in redundancies, unused tools, or resource wastage. Fixing errors or mitigating disruptions adds extra costs, negatively impacting the organization's budget and ROI.
Compliance risks
Failure to document changes or align with organizational policies can result in audit failures and regulatory penalties. Poor change management increases the risk of non-compliance with legal and industry-specific standards.
Poor user adoption
When users are not informed or trained, they may struggle to adapt to new tools or features. This leads to frustration, reduced adoption rates, and missed opportunities to leverage SaaS improvements.
Data loss
Unplanned or untested changes can result in errors during data migrations, updates, or integrations. This may cause permanent loss of critical information, disrupting operations and harming business continuity.
To avoid these risks, organizations must adopt a structured and proactive SaaS change management process. By doing so, they can ensure smoother transitions, protect their operations, and maximize the value of their SaaS investments.
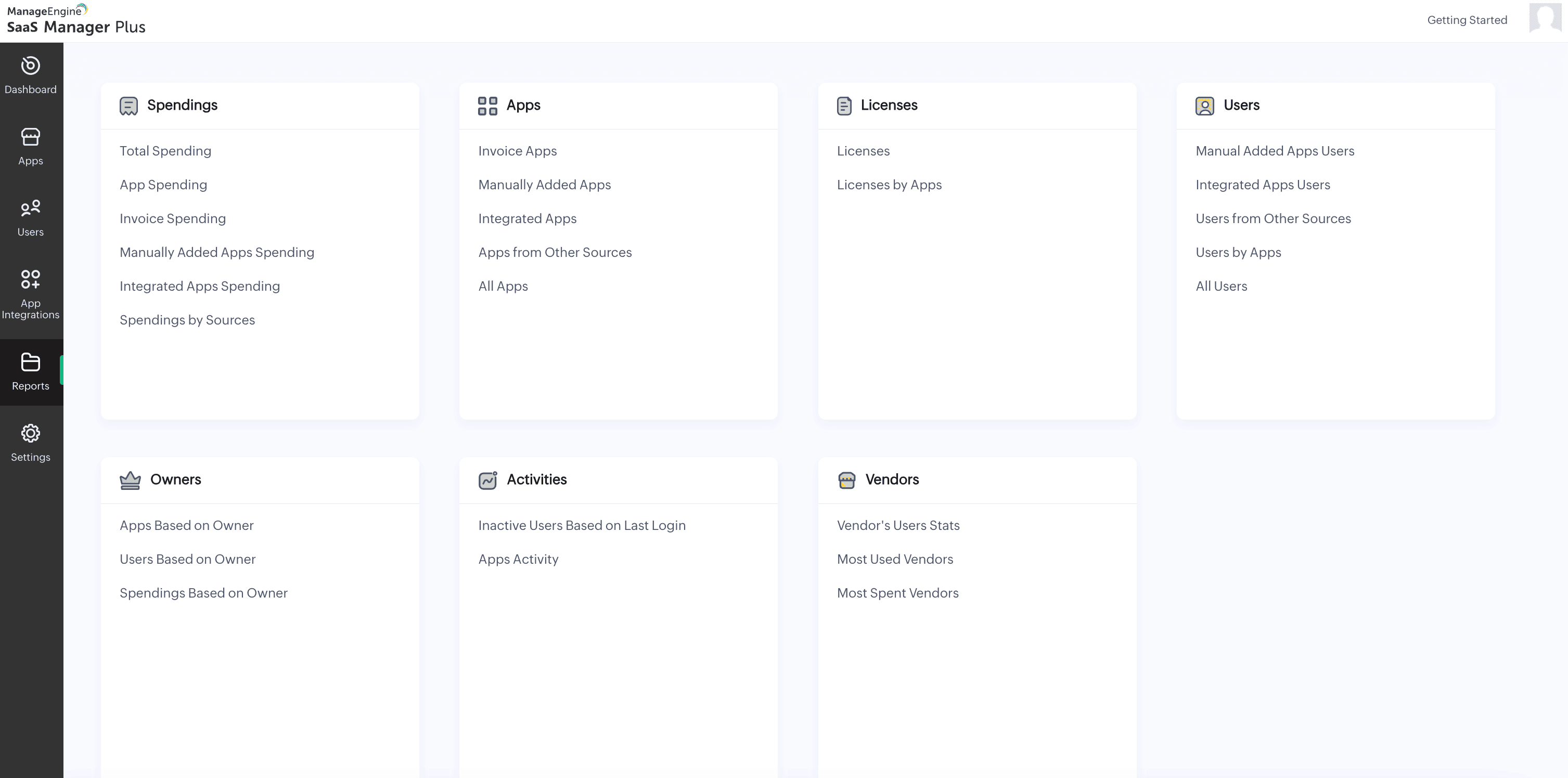
How SaaS Manager Plus helps in the SaaS change management process
ManageEngine SaaS Manager Plus is a powerful tool designed to simplify and streamline the SaaS change management process. With its advanced features, organizations can manage changes efficiently while minimizing risks and disruptions.
Centralized visibility into SaaS tools
SaaS Manager Plus provides a comprehensive inventory of all SaaS applications in use. This ensures organizations can identify which tools are undergoing changes, track their usage, and assess their impact on operations.
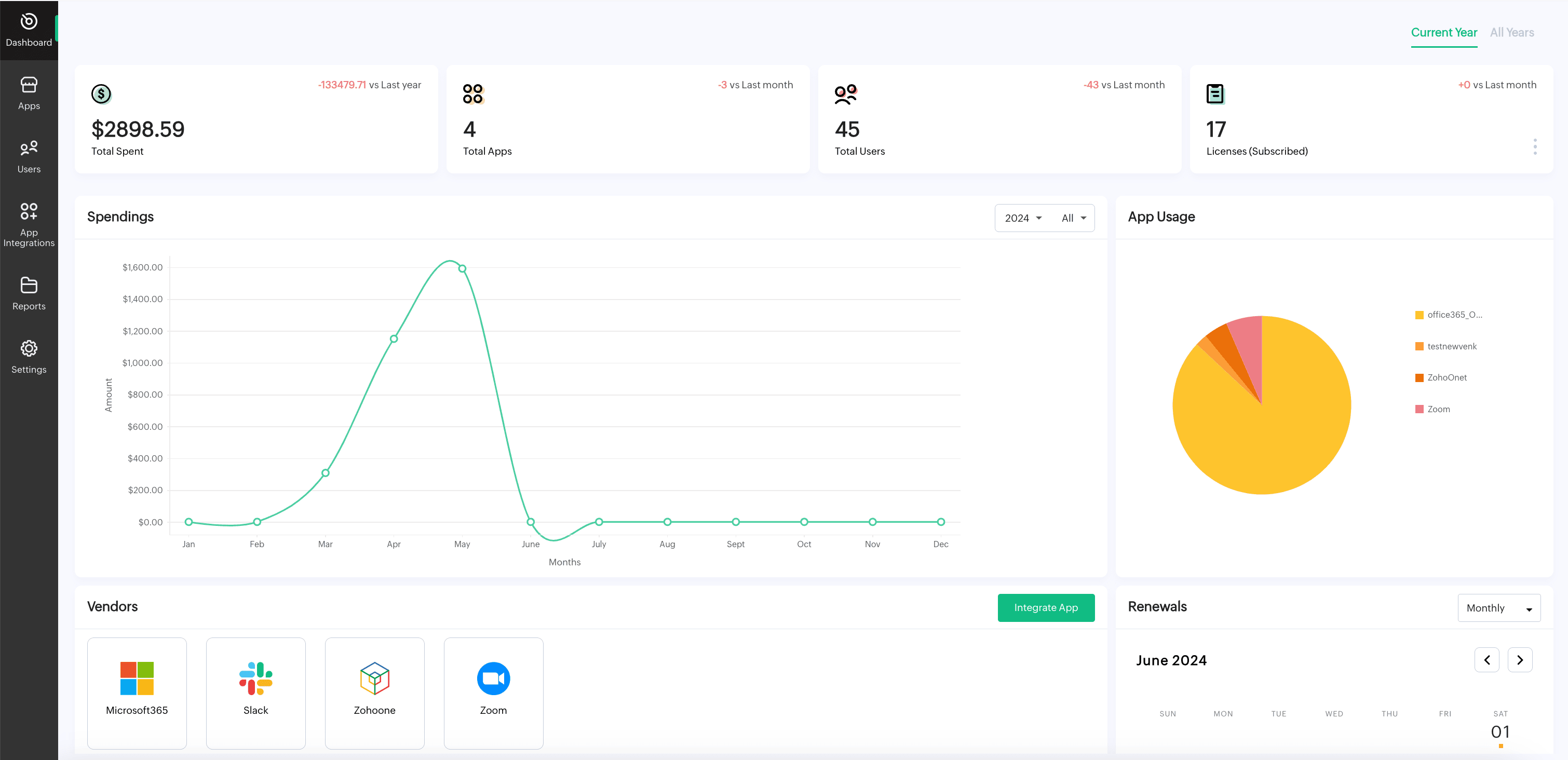
Proactive change tracking and reporting
The platform tracks changes to SaaS tools in real time, offering detailed reports on updates, user access modifications, and configuration changes. This helps organizations stay informed and make data-driven decisions.
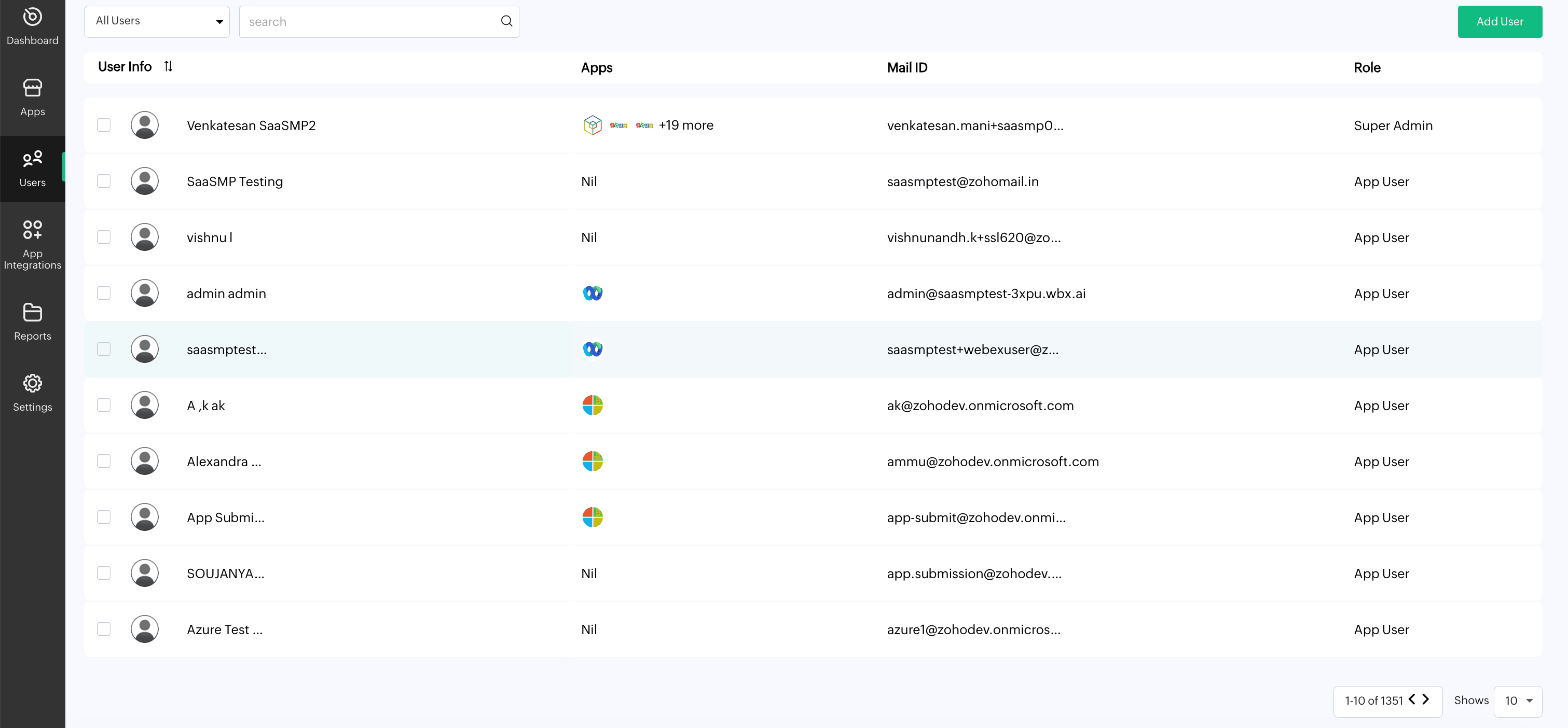
Streamlined user management
SaaS Manager Plus simplifies user life cycle management, including onboarding and role-based access control. This ensures that changes in user access align with organizational policies and security requirements.
Cost optimization tools
The platform identifies underutilized or redundant SaaS subscriptions, helping organizations consolidate tools and reduce unnecessary spending. This makes it easier to plan for changes and maximize ROI.
Enhanced security and compliance
SaaS Manager Plus monitors data access, ensuring that changes do not expose organizations to security vulnerabilities. It also maintains an audit trail of all changes for compliance purposes.
Automation for efficient workflows
By automating critical tasks such as license tracking, renewal management, and user provisioning, SaaS Manager Plus reduces manual effort and speeds up the change management process.


