In this article:
This article explains how to prevent brute-force attacks by using ADSelfService Plus' comprehensive security measures, including MFA, CAPTCHA implementation, strong password policies, and advanced monitoring capabilities. Learning how to prevent brute-force attacks is crucial for protecting your Active Directory environment from automated credential-based attacks that systematically attempt to crack user passwords.
Brute-force attack prevention involves implementing multiple security layers to detect, block, and stop brute force attack attempts. With ADSelfService Plus, you can prevent brute-force attacks through various security mechanisms that work together to create a robust defense against credential-based threats.
By implementing effective brute-force attack prevention strategies, you can:
Implementing MFA for identity verification is crucial to prevent brute-force attacks. Even if attackers successfully crack passwords, MFA provides an additional security layer.
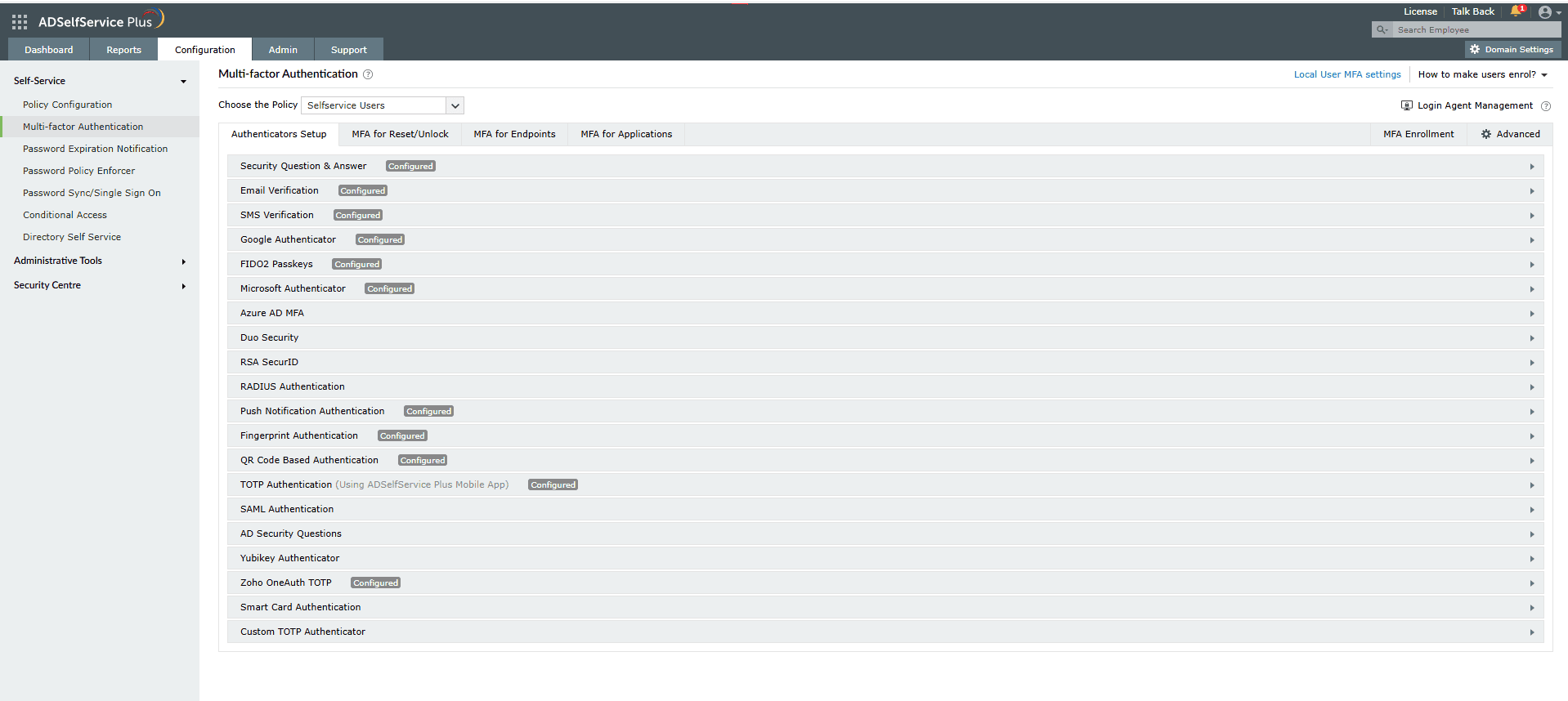
Figure 1. The MFA Authenticators Setup interface displaying a plethora of authentication methods to keep brute-force attacks at bay.
CAPTCHA is one of the most effective methods to stop brute force attack attempts as it prevents automated bots from making repeated login tries. To prevent brute-force attacks using CAPTCHA:
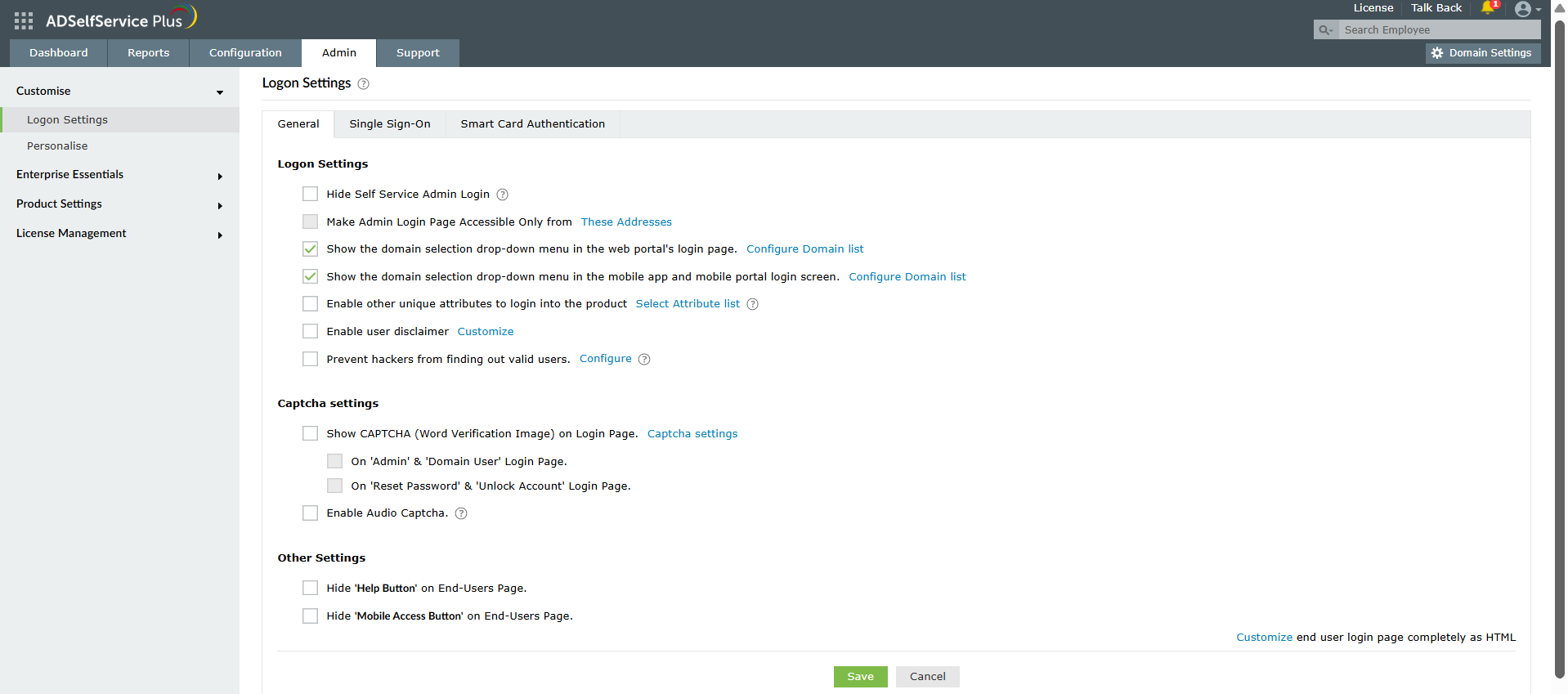
Figure 2. CAPTCHA configuration settings on ADSelfService Plus' Login Settings page to stop brute-force attacks in their tracks.
ADSelfService Plus allows you to block users who fail at the identity verification step, which helps prevent brute-force attacks on security questions and verification codes.
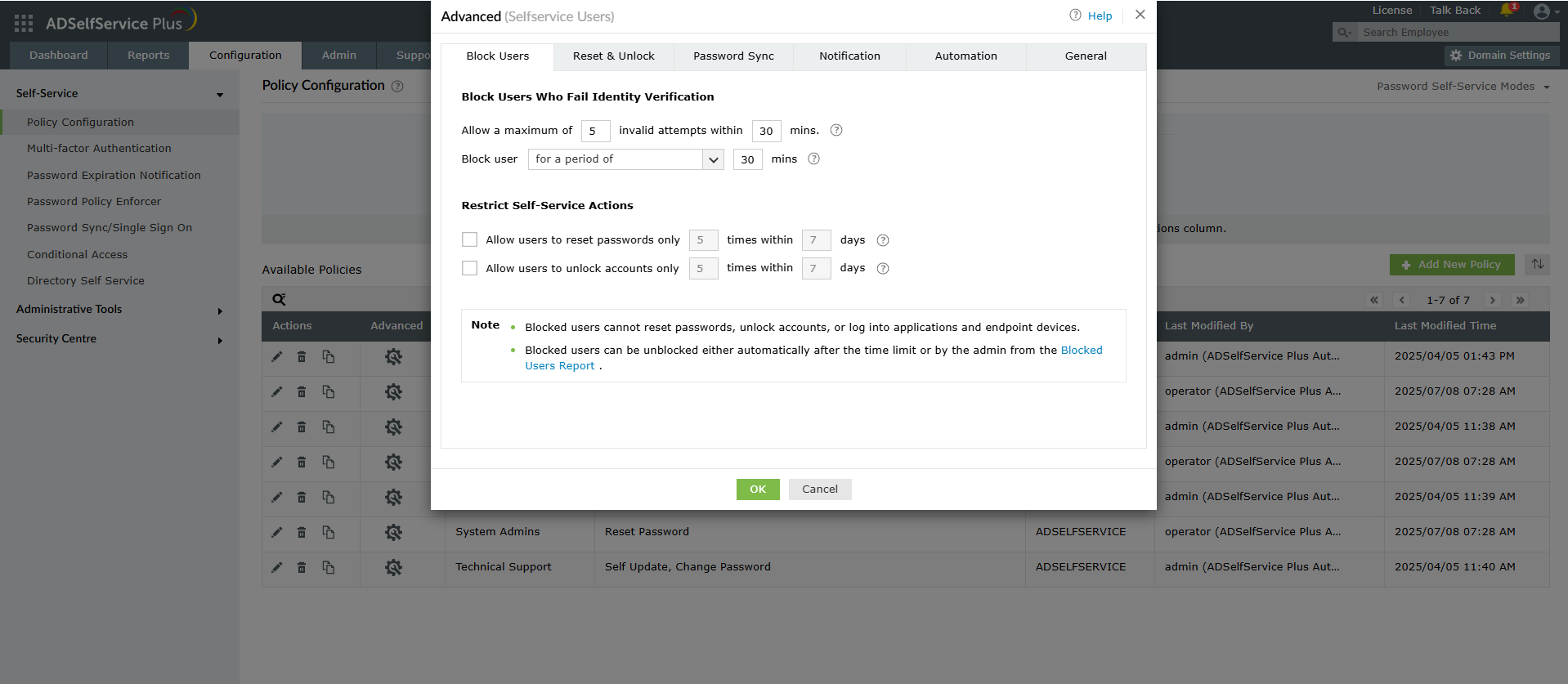
Figure 3. The user blocking configuration interface showing how to prevent brute-force attacks on identity verification.
Strong password policies are crucial when learning how to prevent brute-force attacks as weak passwords are the primary target of these automated attacks. The Password Policy Enforcer feature helps prevent brute-force attacks by ensuring users create strong, unique passwords that resist automated cracking attempts.
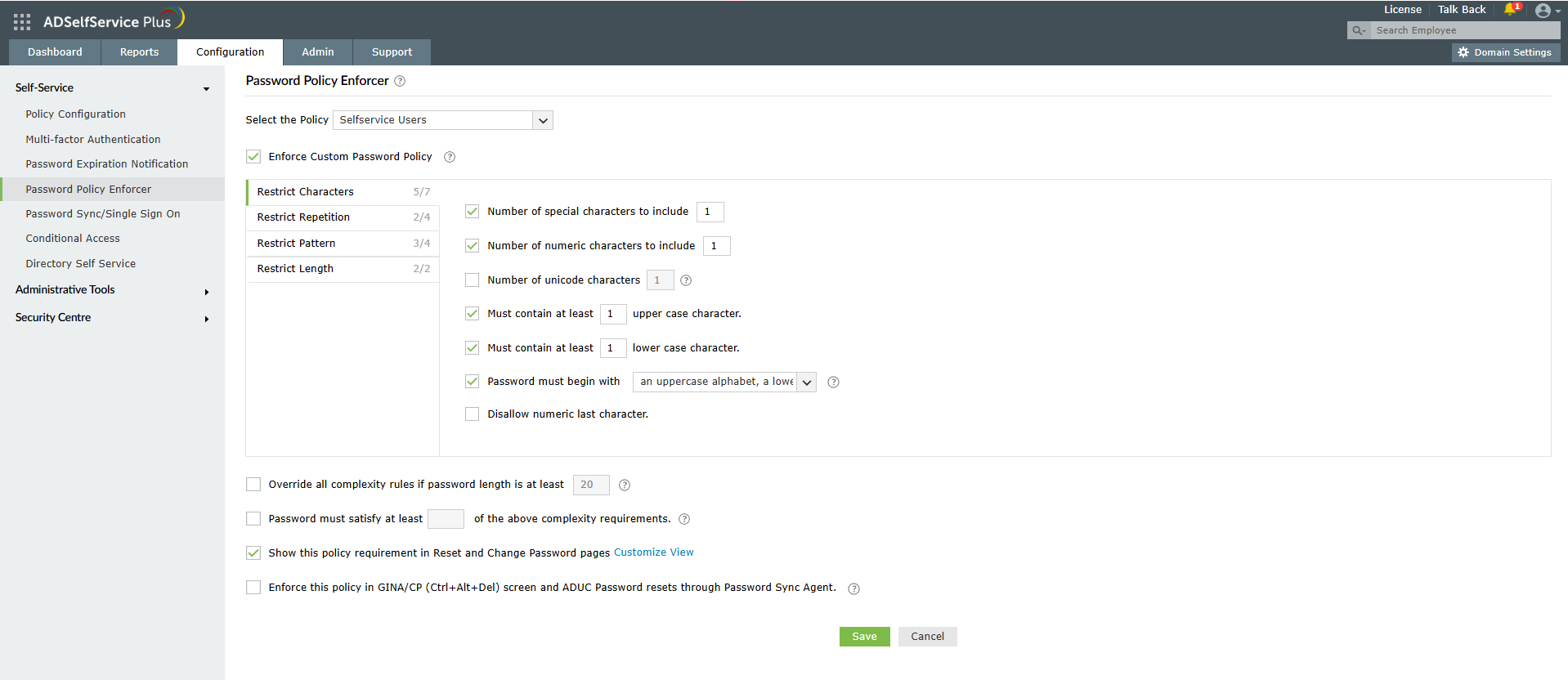
Figure 4. Password Policy Enforcer configuration helps you thwart brute-force attacks by enforcing strong password requirements.
Risk-based policies are an advanced technique for administrators who want to know how to prevent brute-force attacks based on contextual factors. Conditional access helps prevent brute-force attacks by implementing risk-based authentication policies.
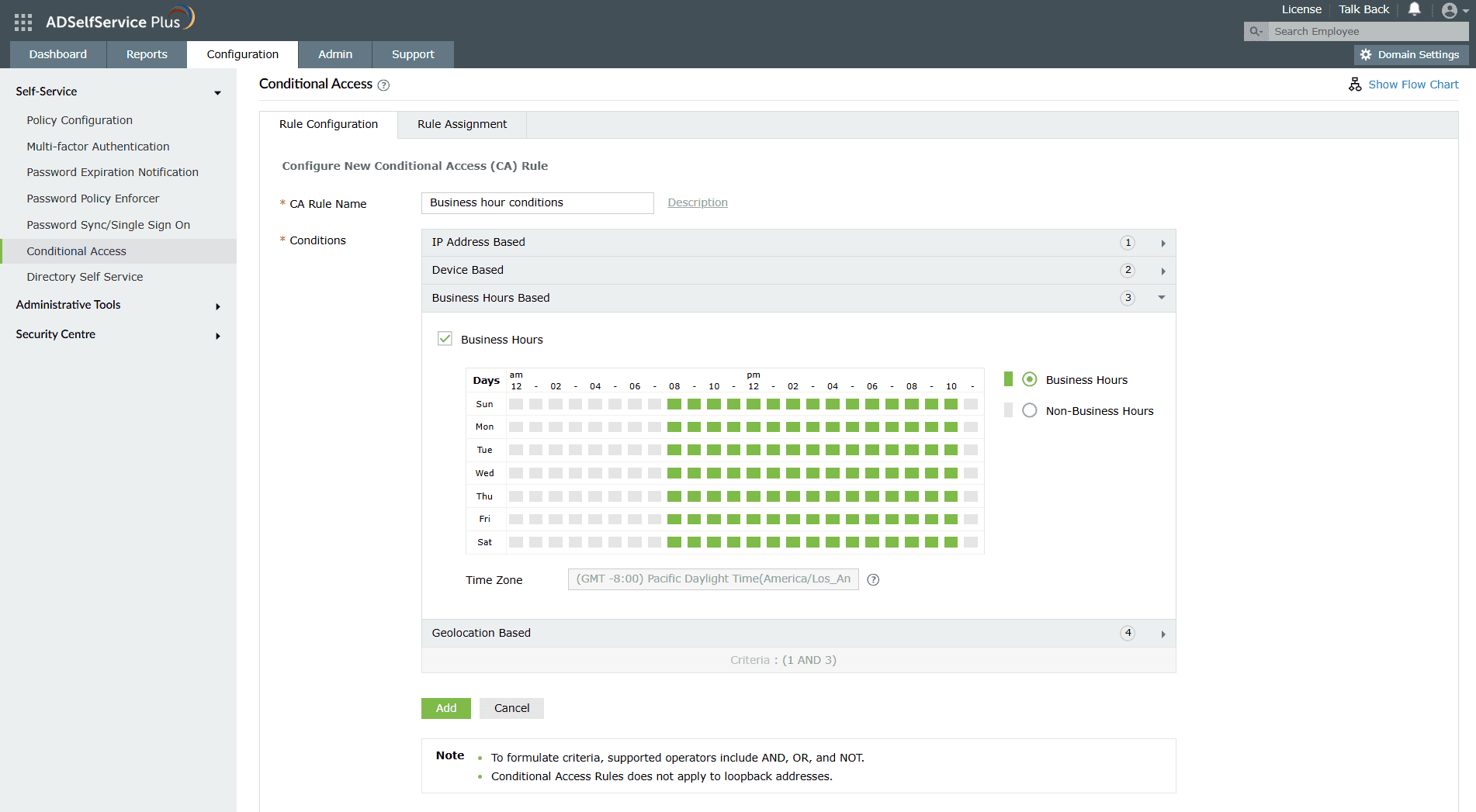
Figure 5. Conditional Access settings help in preventing brute-force attacks by implementing risk-based authentication policies.
Knowing how to prevent brute-force attacks includes implementing effective monitoring, which requires continuous observation of login activities.
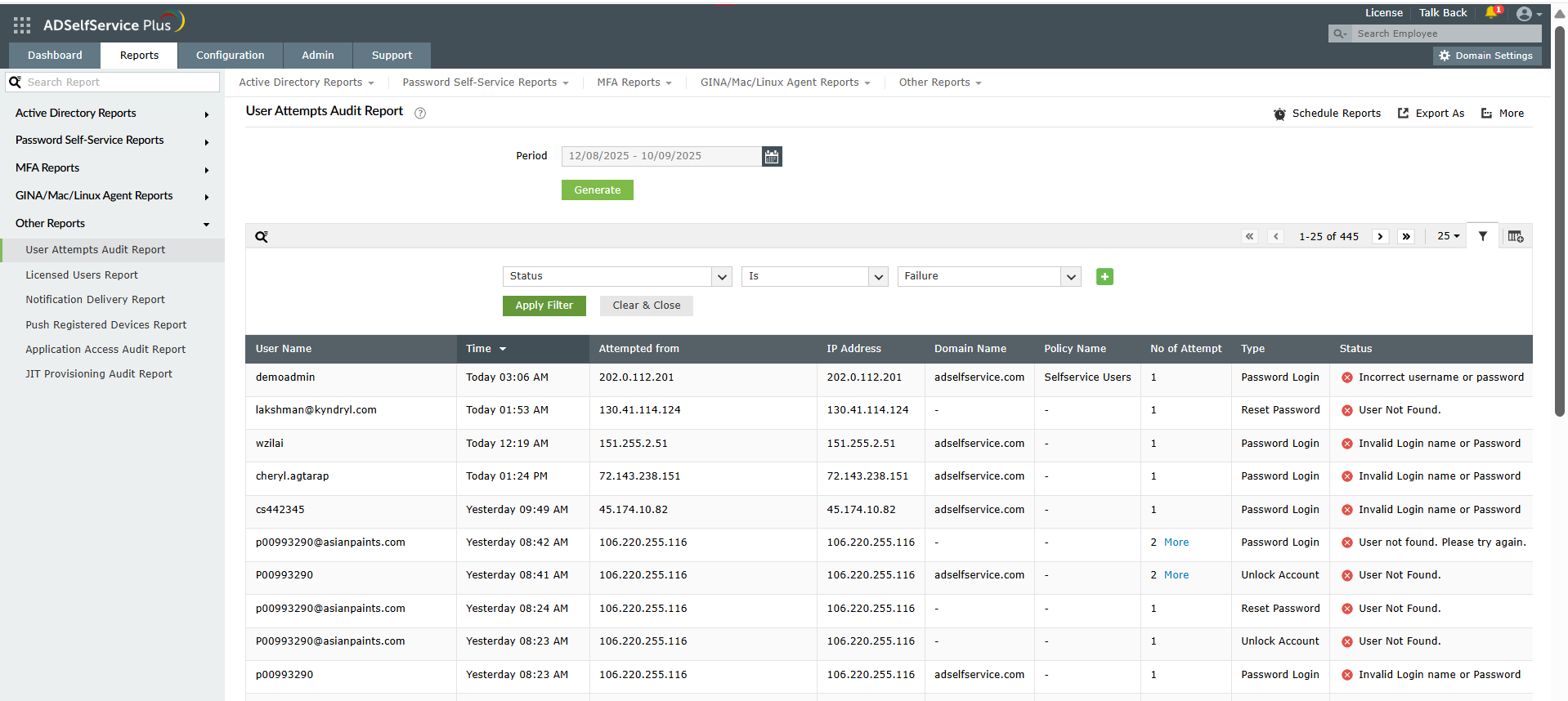
Figure 6. The User Attempts Audit Report helps prevent a brute-force attack through monitoring and analysis of failed login attempts.
Effective session management is another crucial aspect when you want to know how to prevent brute-force attacks. To configure session security settings:
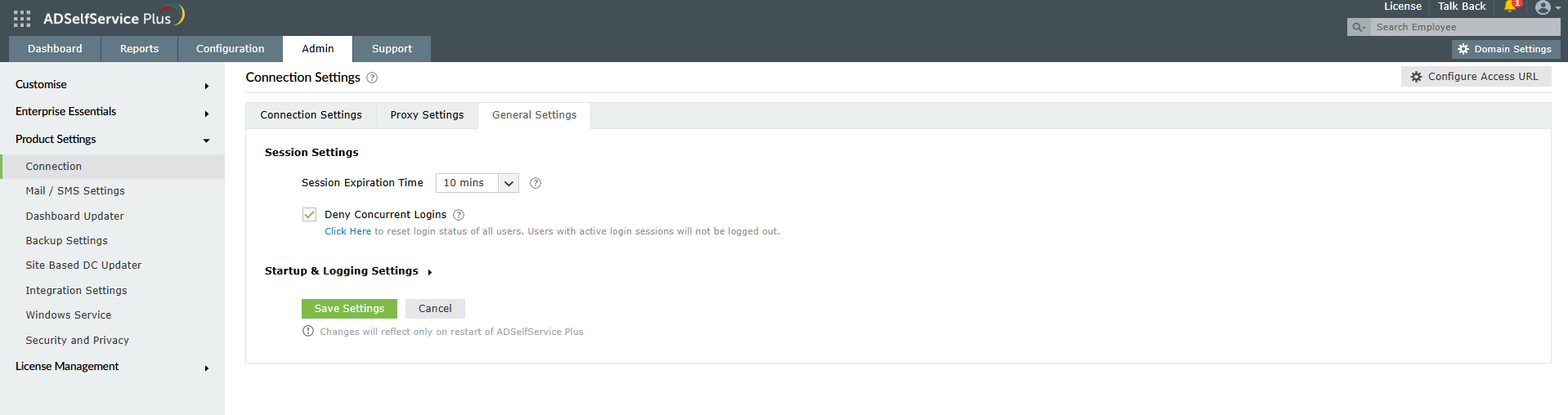
Figure 7. Session Settings configuration helps prevent a brute-force attack through concurrent login restrictions and session timeouts.
How to prevent password spray attacks
How to secure RDP against brute-force attacks
MFA for Active Directory accounts
Need further assistance? Fill this form, and we'll contact you rightaway.
Allow Active Directory users to self-service their password resets and account unlock tasks, freeing them from lengthy help desk calls.
Get seamless one-click access to 100+ cloud applications. With enterprise single sign-on, users can access all their cloud applications using their Active Directory credentials.
Intimate Active Directory users of their impending password and account expiry via email and SMS notifications.
Synchronize Windows Active Directory user passwords and account changes across multiple systems automatically, including Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, IBM iSeries, and more.
Strong passwords resist various hacking threats. Enforce Active Directory users to adhere to compliant passwords by displaying password complexity requirements.
Enable Active Directory users to update their latest information themselves. Quick search features help admins scout for information using search keys like contact numbers.