- Free Edition
- Quick Links
- MFA
- Self-Service Password Management
- Single Sign-On
- Password Synchronizer
- Password Policy Enforcer
- Employee Self-Service
- Reporting and auditing
- Integrations
- Related Products
- ADManager Plus Active Directory Management & Reporting
- ADAudit Plus Real-time Active Directory Auditing and UBA
- Exchange Reporter Plus Exchange Server Auditing & Reporting
- EventLog Analyzer Real-time Log Analysis & Reporting
- M365 Manager Plus Microsoft 365 Management & Reporting Tool
- DataSecurity Plus File server auditing & data discovery
- RecoveryManager Plus Enterprise backup and recovery tool
- SharePoint Manager Plus SharePoint Reporting and Auditing
- AD360 Integrated Identity & Access Management
- Log360 (On-Premise | Cloud) Comprehensive SIEM and UEBA
- AD Free Tools Active Directory FREE Tools
NIST password guidelines
The NIST password guidelines, as outlined in Special Publication (SP) 800-63B by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), are designed to enhance password strength. Since 2014, NIST password standards have been revised almost every year, taking insights from password cracking experts, vulnerable password practices, hacker behavior, and previous password breaches. This makes the NIST standards the most influential, recommended standard for password creation. A NIST-compliant password is tough to crack yet simple to use.
What are the latest NIST password guidelines?
NIST SP 800-63B extends beyond password best practices, also providing brief guidelines for the authentication and management of digital identities. The following table lists NIST's authenticator and verifier requirements found in SP 800-63B and how ADSelfService Plus can aid your organization in achieving compliance with these requirements.
| NIST requirement | Requirement description | How ADSelfService Plus helps satisfy the requirement |
| Section 5.1.1.1 | A memorized secret, i.e., a password, passphrase, or PIN, must have a minimum of eight characters, with a recommended minimum of 15 characters for enhanced security. Maximum password length should support up to 64 characters. | With ADSelfService Plus' Password Policy Enforcer, you can customize the minimum password length to be eight characters or the recommended 15 characters, depending on your organization's requirement. You can also customize the maximum password length to support up to 64 characters. |
| Section 5.1.1.1 | All American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) characters, including the space character, and Unicode characters should be accepted by verifiers in memorized secrets. | ADSelfService Plus allows you to configure the number of special, Unicode, numeric, uppercase, and lowercase characters that users must include in their passwords. You can also configure the character type with which a password must begin. |
| Section 5.1.1.1 | Users should not be given hints by verifiers to assist them in recalling their memorized secret. | ADSelfService Plus does not provide password hints for users during identity verification. |
| Section 5.1.1.1 | Users' memorized secrets should not contain previously breached secrets; dictionary words; repetitive or sequential characters (e.g., aaaaaa or 1234abcd); or context-specific words, such as the name of the service, the username, and derivatives thereof. Verifiers must prompt users to choose a different secret if any of these conditions is satisfied. | ADSelfService Plus allows you to restrict users from utilizing dictionary words, palindromes, predictable patterns, repeated characters, and consecutive characters from usernames and old passwords while setting new passwords. By integrating with Have I Been Pwned?, a breached password database, it ensures that your users do not set weak or compromised passwords during password resets and changes. |
| Section 5.1.1.1 | Verifiers should offer a password strength meter to assist users in choosing strong memorized secrets. | ADSelfService Plus provides a Password Strength Analyzer that offers instant visual feedback on password strength when users change or reset their passwords. |
| Section 5.1.1.1 | Memorized secrets should not be changed periodically unless there is evidence of a compromise of the secret. | ADSelfService Plus does not encourage frequent or periodic end-user password changes. However, admins can trigger an automatic password reset action for users with potentially compromised passwords. |
| Section 5.1.1.1 | Users should be permitted to utilize the paste functionality while entering a memorized secret, which facilitates the use of password managers, increasing the likelihood that users will choose stronger memorized secrets. | With ADSelfService Plus, you can allow or prevent users from using copy and paste functions in the password fields. |
| Section 5.1.1.1 | To assist users in successfully entering a memorized secret, verifiers should offer an option to display the secret—rather than a series of dots or asterisks—until it is entered. | ADSelfService Plus gives users the option to view their password while it is being entered. |
| Section 5.2.2 | To protect against online guessing attacks, consecutive failed authentication attempts on a single account should be limited to no more than 100. | ADSelfService Plus allows you to configure the number of failed logon attempts that are allowed for a user within a specified time and the lockout duration. |
| Section 5.2.2 | To reduce the likelihood that an attacker will lock a legitimate user out of their account, a CAPTCHA should be completed before attempting authentication. | ADSelfService Plus allows you to show or hide a CAPTCHA before a user attempts authentication. |
| Section 5.2.2 | To reduce the likelihood that an attacker will lock a legitimate user out of their account, risk-based or adaptive authentication techniques should be employed, which include the use of IP address, geolocation, timing of request patterns, or browser metadata. | ADSelfService Plus provides conditional access policies that automatically provide additional MFA methods as configured for suspicious access requests based on users' IPs, geolocations, times of access, and devices used. |
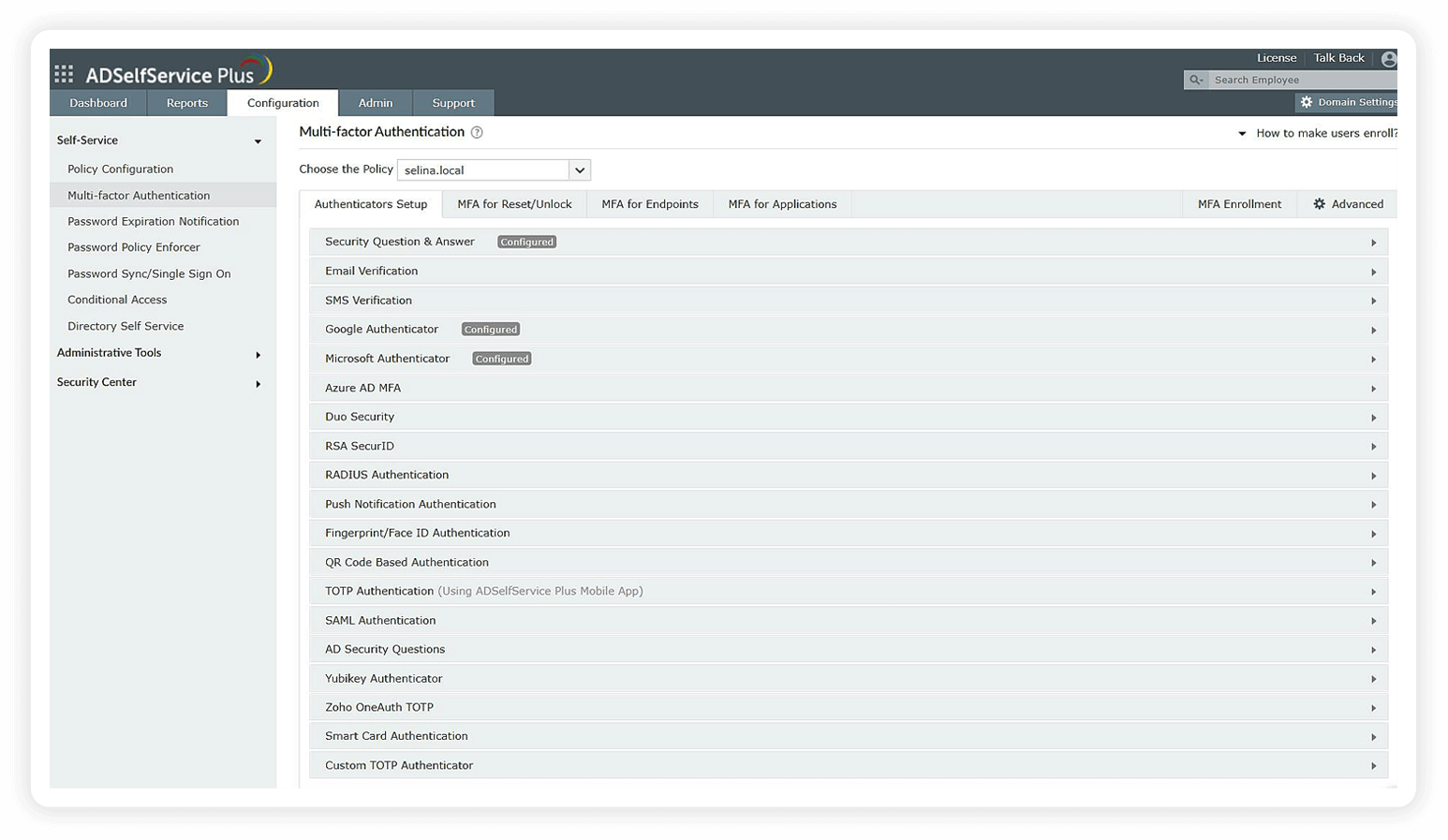
| Section 5.2.3 | For certain security limitations identified and mentioned in this section, biometrics should be used only as part of MFA alongside a physical authenticator (something you have) and not as a stand-alone authenticator. | ADSelfService Plus allows you to configure a biometric authenticator alongside other authenticators, including YubiKey, TOTPs, and smart cards. |
| Section 5.2.3 | No more than five consecutive failed authentication attempts should be allowed for the biometric authenticator. | ADSelfService Plus allows you to configure the number of failed logon attempts that are allowed for a user within a specified time. |
| Section 5.2.3 | In case of five consecutive failed biometric authentication attempts, a delay of at least 30 seconds before the next attempt should be imposed or the biometric authenticator should be disabled entirely. | ADSelfService Plus allows you to configure the account lockout duration in case of a failed biometric authentication attempt. |
| Section 5.2.5 | To resist phishing and manipulator-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, verifier impersonation-resistant authentication mechanisms should be deployed. | ADSelfService Plus provides a FIDO passkey authenticator that resists phishing and MITM attacks with its public key cryptography technology. |
| Section 5.2.8 | To resist replay attacks, replay-resistant authentication mechanisms should be deployed. | ADSelfService Plus provides the FIDO passkey authenticator, which resists replay attacks with its public key cryptography technology. |
Furthermore, NIST classifies authentication mechanisms into three categories and calls them Authenticator Assurance Levels (AALs): AAL1, AAL2, and AAL3. Click here to learn more about AALs and how they differ from each other.
NIST password guidance and tips
Successfully implementing a NIST password policy requires understanding both the technical requirements and practical considerations for your organization. The latest NIST password recommendations emphasize a user-centric approach that balances security with usability. Here are key tips for effective implementation:
Tip #1: Prioritize password length over complexity
When configuring NIST password length settings, organizations should prioritize the recommended 15-character minimum over the absolute eight-character requirement. This approach to NIST password length standards provides significantly stronger protection against modern attack methods while remaining manageable for users. Supporting up to 64 characters accommodates users who prefer passphrases, which often provide better security and memorability than shorter, complex passwords.
Tip #2: Embrace modern complexity standards
Modern NIST password complexity guidelines have evolved beyond traditional character type requirements. Instead of forcing users to include specific combinations of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols, current NIST password complexity standards focus on screening against known vulnerabilities and encouraging natural password creation patterns that users can remember and maintain securely.
Tip #3: Implement effective password history controls
Effective NIST password history management prevents password cycling, where users alternate between a small set of known passwords. Implementing proper NIST password history controls through ADSelfService Plus ensures users cannot simply revert to recently used passwords, maintaining the integrity of your authentication system over time.
Tip #4: Adopt a comprehensive security framework
Organizations following NIST password requirements should consider the broader context of authentication security. These NIST password rules work most effectively when combined with complementary security measures such as MFA, breach monitoring, and user education. The goal is creating a comprehensive security framework that implements current NIST password standards while supporting practical business operations and user productivity. For detailed implementation strategies and best practices, explore our comprehensive guide to NIST password standards.
Comply with NIST password and authentication standards using ADSelfService Plus
ADSelfService Plus offers the Password Policy Enforcer, access policies, and MFA capabilities to help your organization meet NIST password requirements and authentication standards.
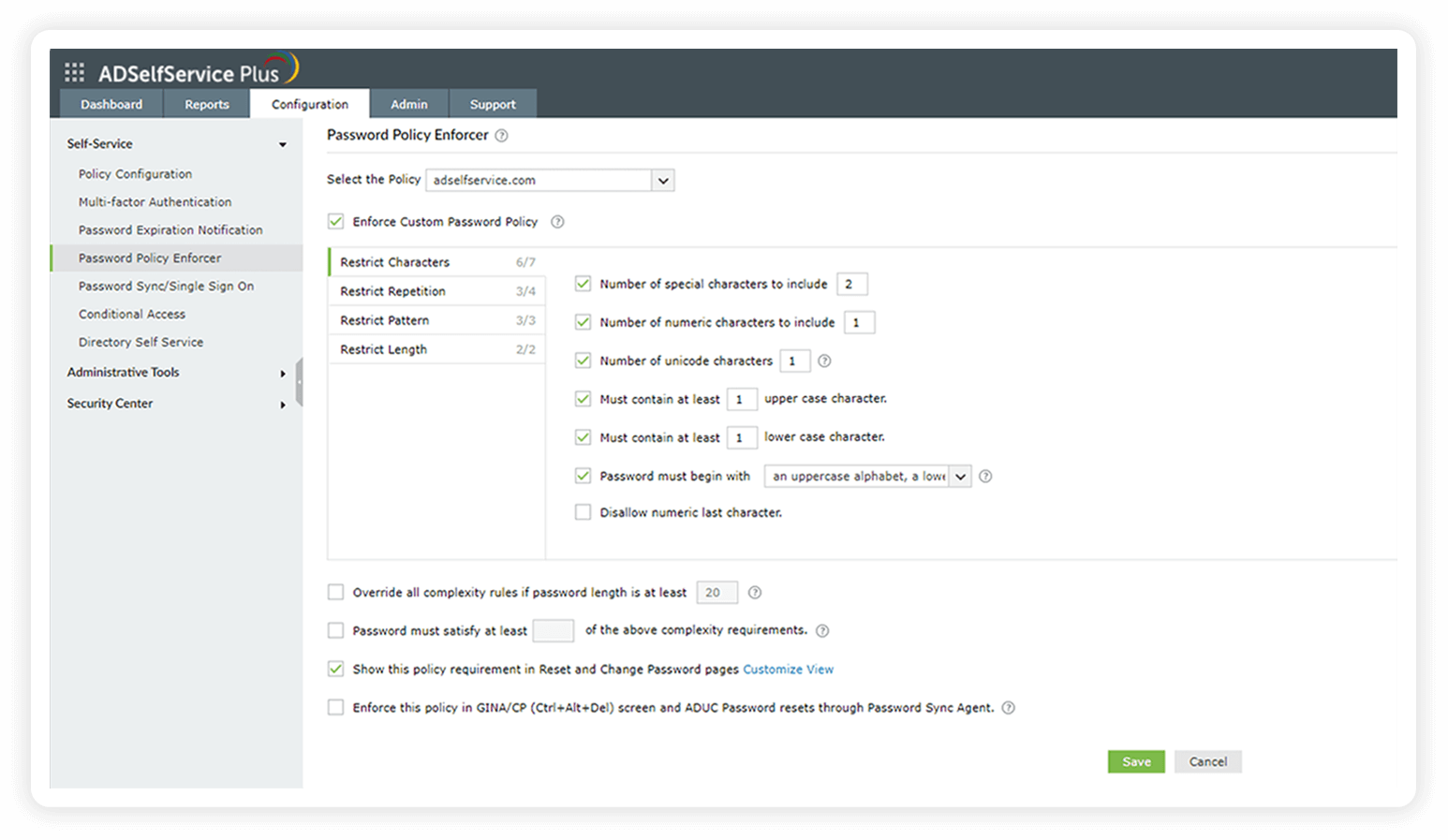
Password Policy Enforcer
The Password Policy Enforcer allows you to enforce a custom password policy that seamlessly integrates with the built-in AD password policies, providing more granular control. ADSelfService Plus' password policies can be set to enforce the following requirements:
- Restrict Characters
- Restrict Repetition
- Restrict Pattern
- Restrict Length
These settings include mandating the number of special, numeric, and Unicode characters. You can also set the type of character with which the password must begin.
Restrict users from reusing any of their previous passwords during password creation.
Restrict users from reusing any of their previous passwords during password creation.
These settings help restrict the use of consecutive characters from usernames or previous passwords. Consecutive repetition of the same character can also be restricted.
Restrict users from reusing any of their previous passwords during password creation.
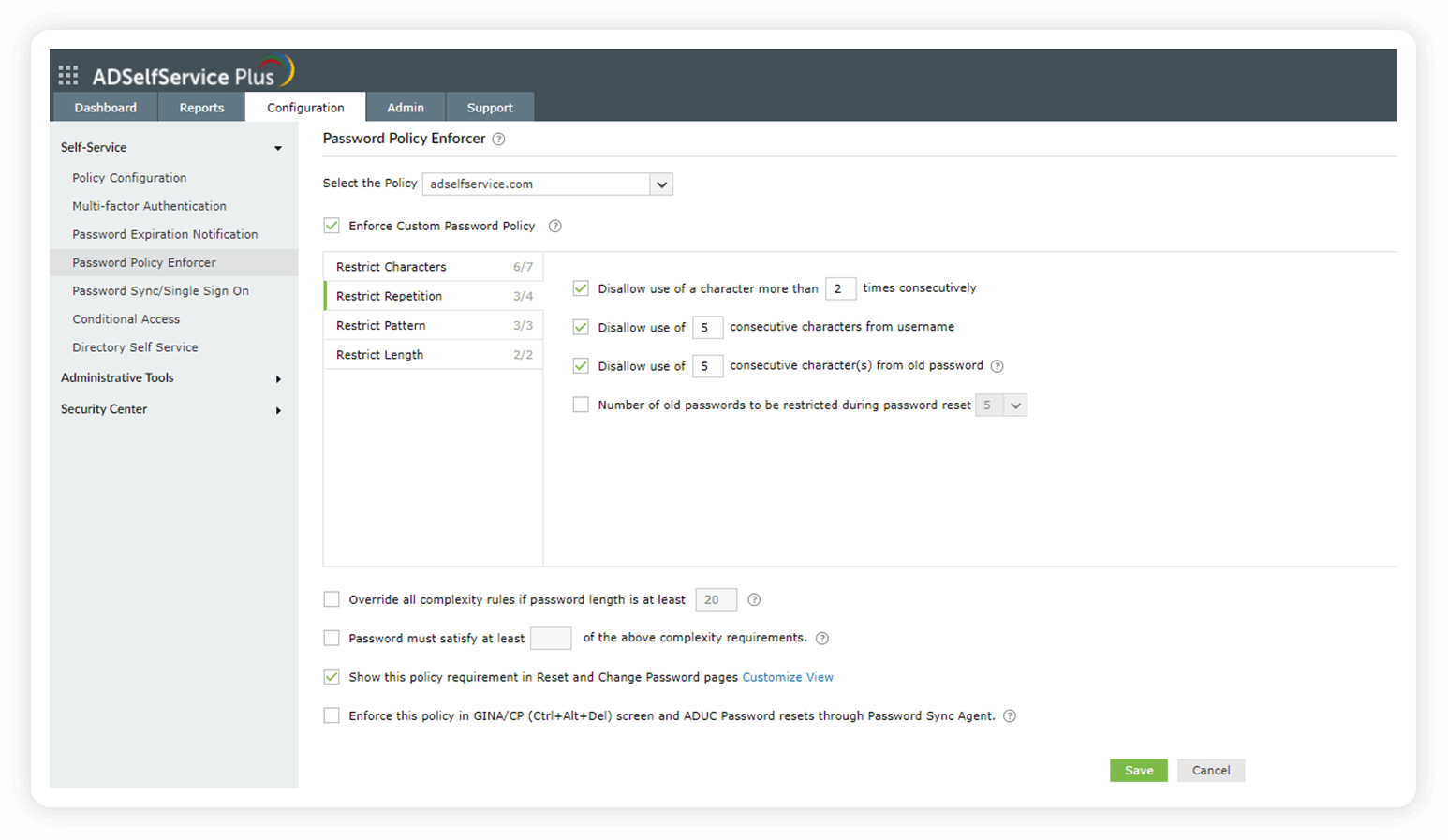
Restrict users from reusing any of their previous passwords during password creation.
The settings under this tab help restrict custom dictionary words, patterns, and palindromes that might be commonly used.
Restrict users from using common patterns, dictionary words, and palindromes in their passwords.

Restrict users from using common patterns, dictionary words, and palindromes in their passwords.
These rules let you set both a minimum and maximum number of characters for the password.
Configure the minimum and maximum password length to satisfy the NIST password guidelines.
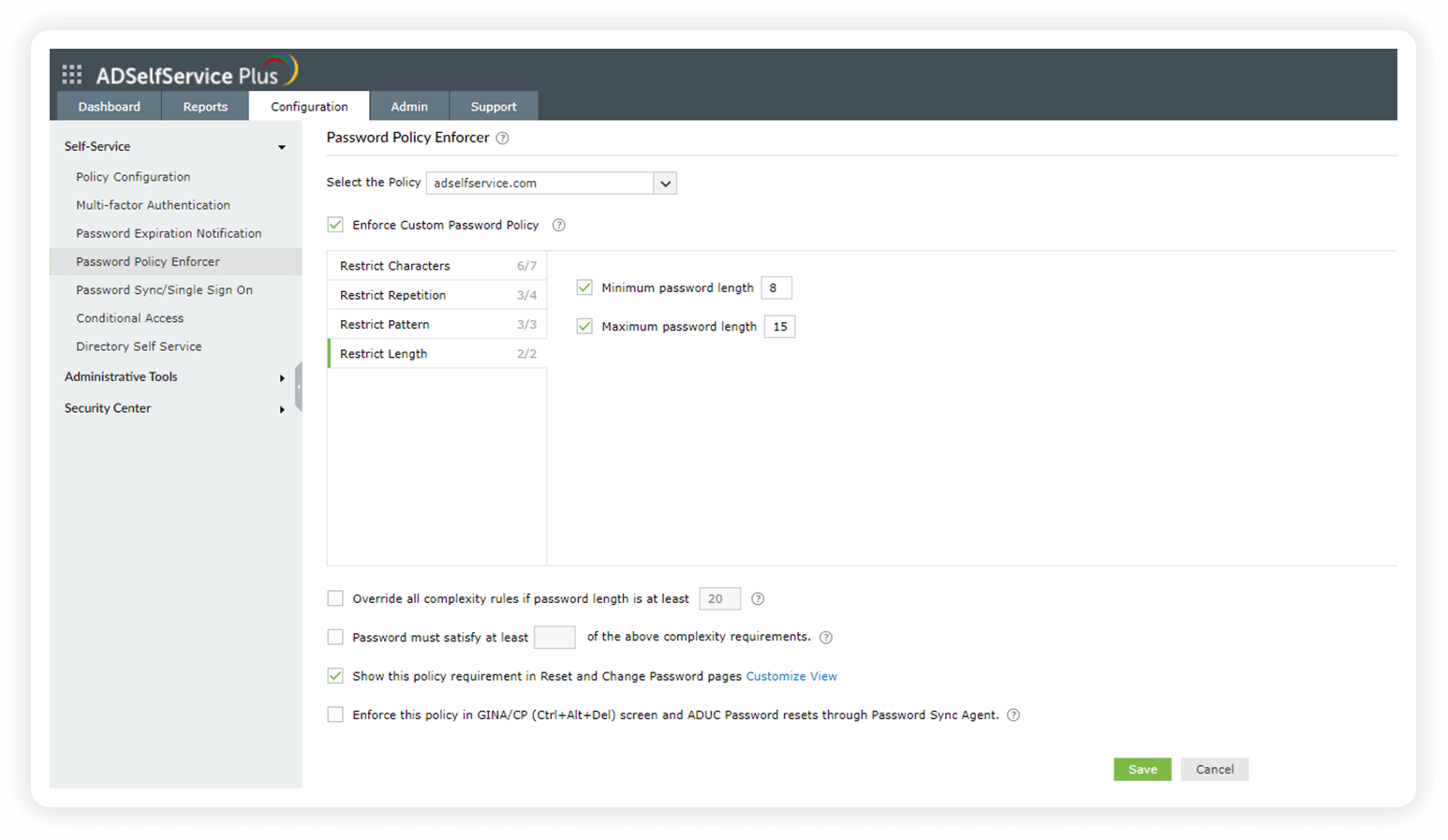
Configure the minimum and maximum password length to satisfy the NIST password guidelines.
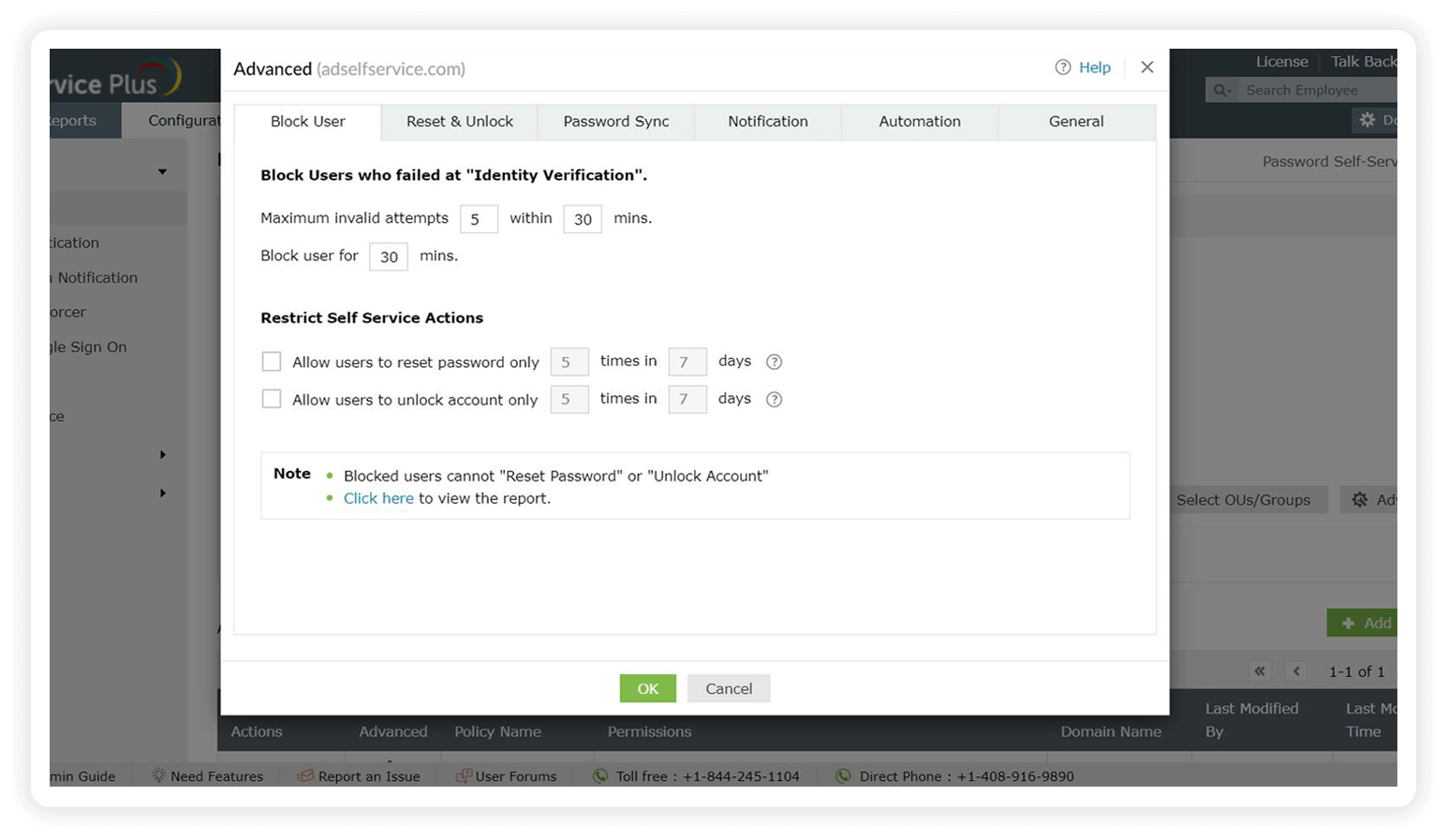
Access policies
ADSelfService Plus allows you to define any number of self-service policies in a given domain. These policies can be configured as shown below so that your organization meets NIST password requirements and NIST password standards for enhanced password security.
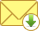
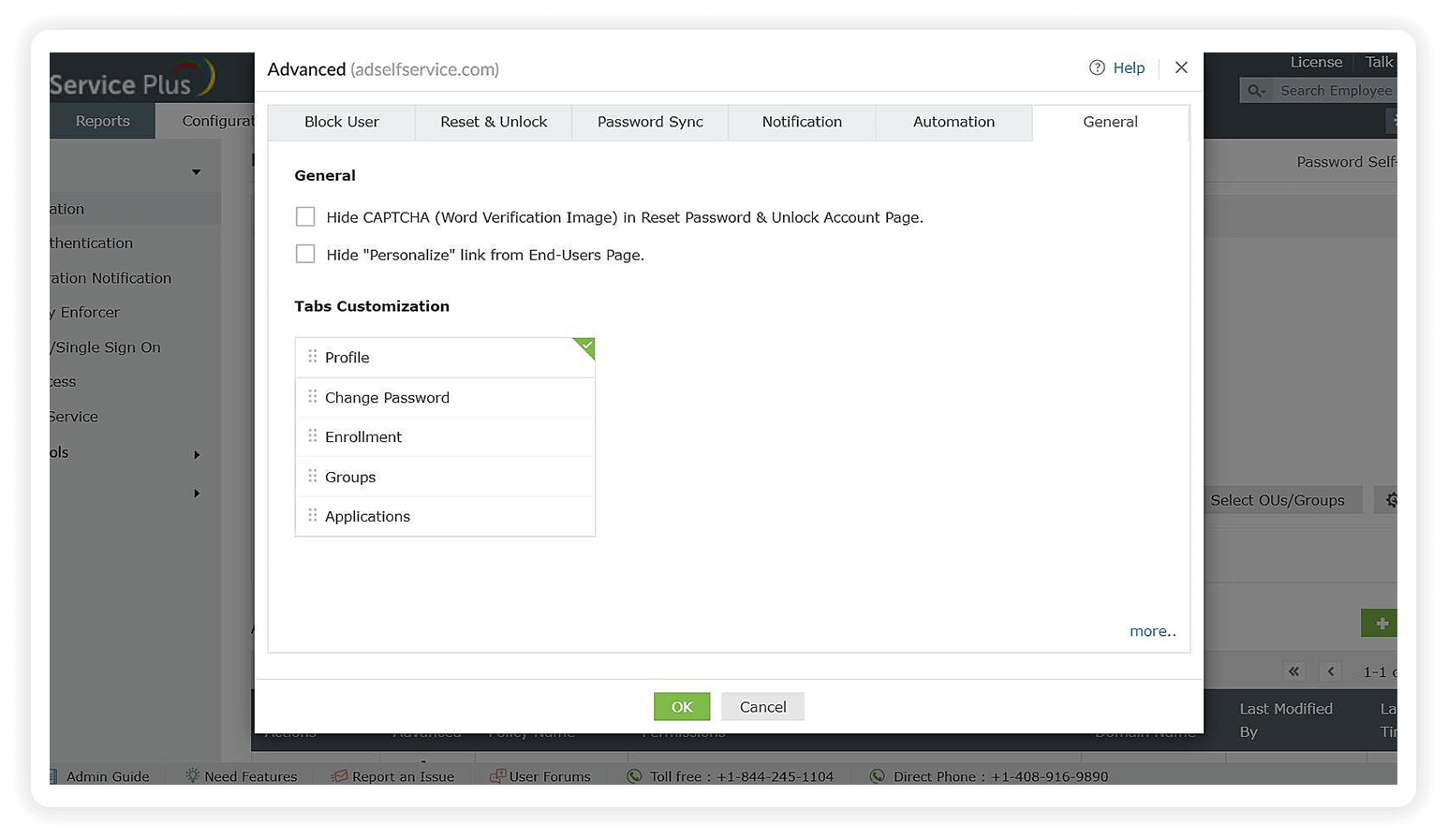
- Set the maximum number of times users can fail at identity verification, after which they get blocked automatically.
- Restrict the number of times users can reset their passwords using self-service.
- Allow or prevent copy and paste actions in password fields to comply with NIST password policy guidelines.
- Enforce AD password history settings during password resets to restrict the repetition of passwords per NIST password rules.
- Enable the Password Strength Analyzer to help users with password creation by displaying the strength of the password.
- Provide CAPTCHA code verification for user logins to provide added security.
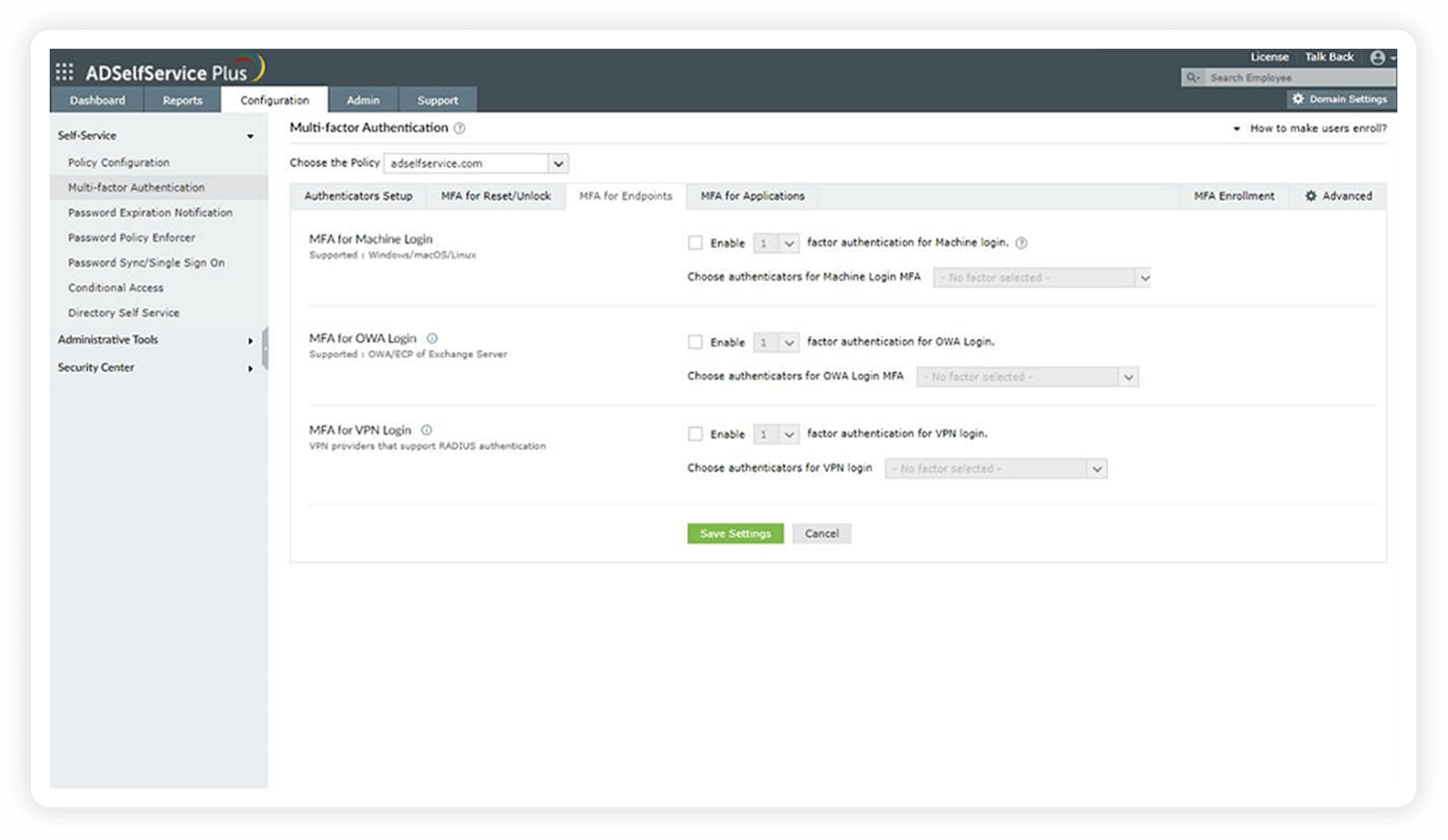
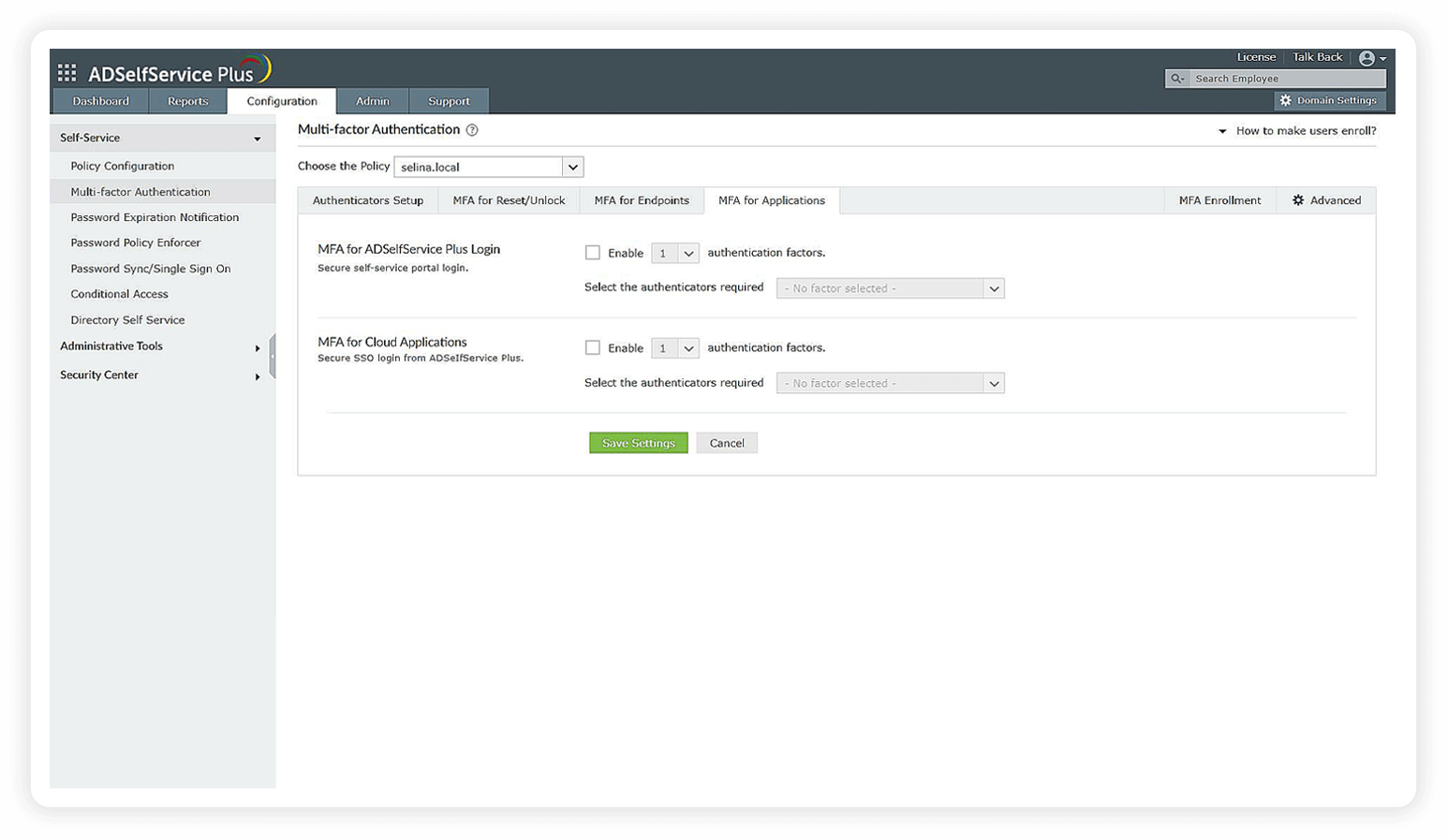
MFA
ADSelfService Plus offers MFA for applications, both cloud-based and on-premises, and endpoints. It helps you reduce surface attacks and protects your business by mandating a higher level of identity assurance.
Reasons why your organization needs ADSelfService Plus' MFA support:
- Authenticates users with adaptive MFA techniques apart from their default username and password.
- Offers 20 different authenticators to choose from, including biometrics, FIDO passkeys, Duo Security, TOTPs, YubiKey, and smart cards.
- Allows the configuration of workflows to customize authenticators for users of different OUs, domains, or groups.
- Secures both local and remote login attempts on servers and workstations.
- Tackles all credential-based cyberattacks, including phishing, brute-force, password spray, and dictionary attacks.
- Helps your organization meet the GDPR, the PCI DSS, and HIPAA compliance mandates, in addition to the NIST SP 800-63B.
Benefits of using ADSelfService Plus to comply with NIST password requirements
- Fine-grained flexibility
Tailor NIST password policy configurations for various user roles within the organization based on their access levels to sensitive data.
- Integration with Have I Been Pwned?
Integrate with Have I Been Pwned?, a breached password database, and ensure users avoid weak or compromised passwords during resets and changes, helping organizations meet NIST password recommendations.
- Conditional access policies
Automatically intensify MFA methods for suspicious access requests using conditional access policies based on a user's IP, location, and time of access.
- Compliance with other regulations
Align with PCI DSS, HIPAA, Essential Eight, CJIS, SOX, and GDPR standards.
Strengthen your business’s cyberdefenses with ADSelfService Plus, a one-size-fits-all solution that helps your employees adopt NIST password guidelines and best practices for a secure authentication process.
Highlights of ADSelfService Plus
Password self-service
Eliminate lengthy help desk calls for Windows AD users by empowering them with self-service password reset and account unlock capabilities.
One identity with a single sign-on
Gain seamless one-click access to more than 100 cloud applications. With enterprise single sign-on, users can access all their cloud applications using their Windows AD credentials.
Password synchronization
Synchronize Windows AD user passwords and account changes across multiple systems automatically, including Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and IBM iSeries.
MFA
Enable context-based MFA with 20 different authentication factors for endpoint, application, VPN, Outlook on the web, and RDP logins.
Password and account expiration notifications
Notify Windows AD users of their impending password and account expiration via email and SMS notifications.
Password Policy Enforcer
Strong passwords resist various hacking threats. Require Windows AD users to adhere to compliant passwords by displaying password complexity requirements.