If you want to move an AD user to another OU using PowerShell, the easiest way is through the Move-ADUser cmdlet. It helps IT administrators move users to a different OU based on the needs of the organization (like department shifts) or for compliance reasons (such as applying targeted Group Policies or security controls). This article covers practical examples of moving single and multiple users efficiently while maintaining security and accountability.
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
Get-ADUser -Identity "username" | Move-ADObject -TargetPath "OU=TargetOU,DC=domain,DC=com"
$users = Get-ADUser -Filter * -SearchBase "OU=SourceOU,DC=contoso,DC=com" | Select-Object -Property DistinguishedName
foreach ($user in $users) {
Move-ADObject -Identity $user.DistinguishedName -TargetPath "OU=DestinationOU,DC=contoso,DC=com"
}
This moves the user's account to a target OU within the same domain:
Get-ADUser -Identity <sAMAccountName> | Move-ADObject -TargetPath "OU=<TargetOU>,DC=<domain>,DC=<tld>"
This directly moves the user from the source OU to the target OU using their distinguished name:
Move-ADObject -Identity "CN=<UserCN>,OU=<SourceOU>,DC=<domain>,DC=<tld>" -TargetPath "OU=<TargetOU>,DC=<domain>,DC=<tld>"
This moves multiple users to a new finance OU by importing their usernames from a CSV file:
Import-Csv "C:\UsersList.csv" | ForEach-Object {
Get-ADUser -Identity $_.SamAccountName | Move-ADObject -TargetPath "OU=Finance,DC=domain,DC=com"
}
This moves every user from the source OU to the target OU:
Get-ADUser -SearchBase "OU=<SourceOU>,DC=<domain>,DC=<tld>" -Filter * | ForEach-Object {
Move-ADObject -Identity $_.DistinguishedName -TargetPath "OU=<TargetOU>,DC=<domain>,DC=<tld>"
}
This moves the user to the nested OU inside the main OU:
Get-ADUser -Identity <sAMAccountName> | Move-ADObject -TargetPath "OU=<ChildOU>,OU=<ParentOU>,DC=<domain>,DC=<tld>"
The following are a few parameters commonly used with the Move-ADUser cmdlet:
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| -Identity | Specifies the AD object (the user, computer, group, etc.) to be moved; you can use the object’s distinguished name or globally unique identifier (GUID) |
| -TargetPath | Defines the destination OU or container where the object should be moved to |
| -Server | Specifies the domain controller (DC) or AD Domain Services instance to connect to for executing the move operation |
| -Credential | Runs the command using alternate user credentials instead of those of the account that is currently logged in |
| -Partition | Identifies the AD partition that contains the object to be moved (for example, DC=domain,DC=com) |
| -PassThru | Returns the moved object after the command runs, allowing you to verify it or use it in subsequent commands |
| -Confirm | Prompts you for confirmation before executing the move, which is useful for avoiding accidental changes |
| -WhatIf | Simulates the command without making any changes, letting you review the outcome beforehand |
Solution: This means the $user or identity variable is empty or not correctly retrieved. Make sure you pass a valid object or distinguished name. For instance, use Get-ADUser $username to fetch the user and confirm the variable contains the expected object before using it in Move-ADUser.
Solution: This occurs when the target OU doesn't exist, is misspelled, or was recently removed. Check the distinguished name carefully and verify the OU exists using Get-ADOrganizationalUnit.
Solution: This happens when the current security context lacks required permissions, especially during cross-domain moves. Ensure you have the correct rights and consider specifying the -Credential parameter or reauthenticating with an account that has adequate privileges.
Solution: When moving objects across domains, ensure that both the source and target DCs are relative identifier (RID) Masters. Connect to the appropriate DC or perform the move on a DC holding the RID Master role for both domains. Verify roles using netdom query fsmo.
Solution: Users in domain local groups cannot be moved across domains directly. Remove them from incompatible groups first, perform the move, then reassign group memberships afterward.
Solution: The account running the command lacks sufficient permissions. Execute PowerShell with an account that has the necessary rights: ideally Domain Admins or delegated permissions for the relevant OUs.
Solution: This happens if the source and target OUs are the same. Verify that the source and destination distinguished names are different before attempting the move.
AD Users and Computers (ADUC) is a common method of moving AD users.
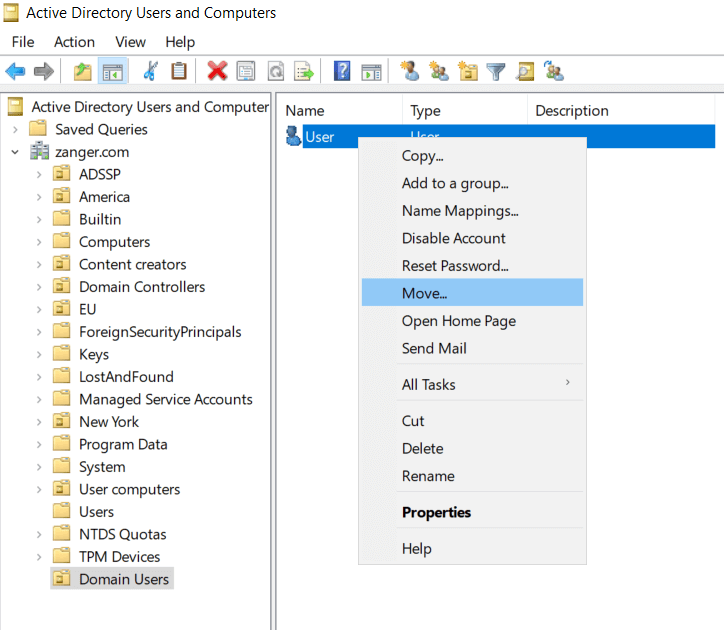
You can easily move user accounts, either individually or in bulk, between OUs using ADManager Plus.
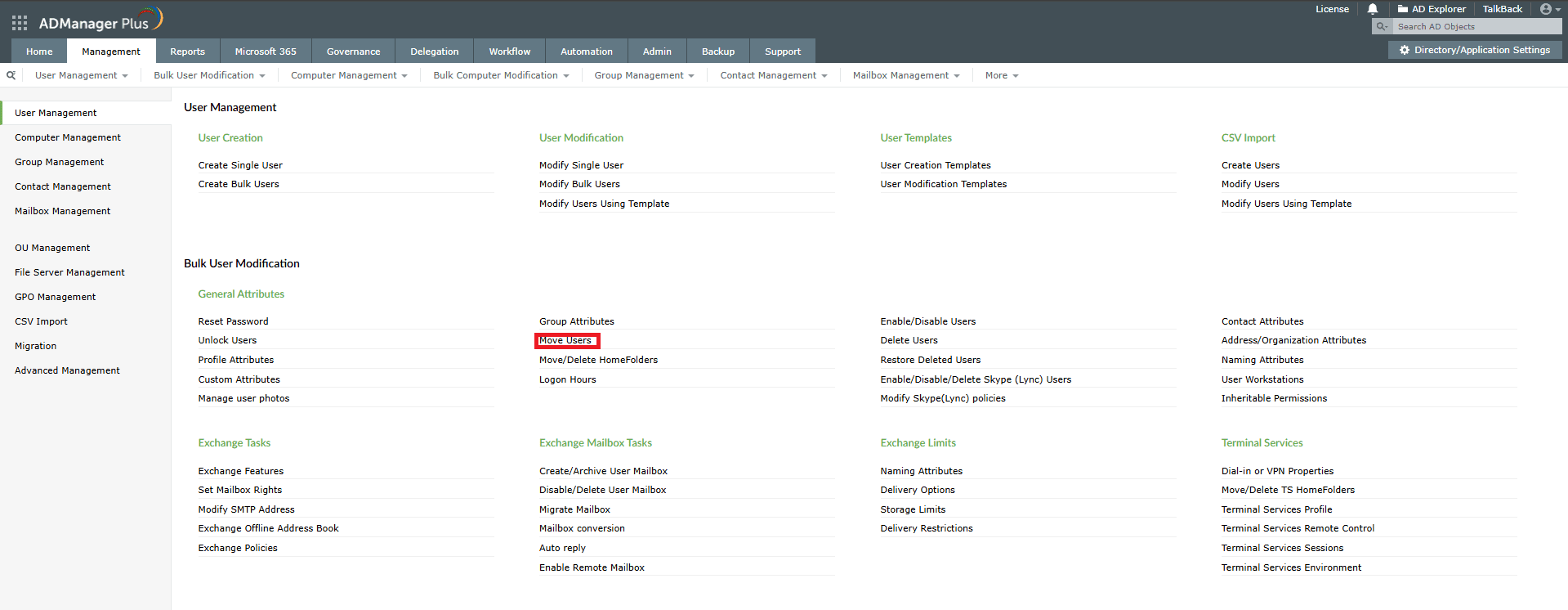
Although moving AD users from one OU to another with native tools like PowerShell looks simple, it comes with a few limitations:
ADManager Plus makes AD management easier and faster through a single, intuitive console. Here’s why it’s a better choice for IT teams:
Using ADUC
Moving a computer object between OUs in ADUC doesn't involve just a single permission; it requires create rights on computer objects in the source OU and delete rights on computer objects in the target OU. However, this is considered highly privileged access.
To minimize risk, delegate these rights to a dedicated security group and review its membership regularly:
Using PowerShell
Run the same script for both the source and target OUs:
# Replace values
$OU = 'OU=SourceOU,DC=yourdomain,DC=com'
$group = 'YOURDOMAIN\DelegatedGroup'
$groupSID = (New-Object System.Security.Principal.NTAccount($group)).Translate([System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier]).Value
$ComputerObjectGUID = 'bf967a86-0de6-11d0-a285-00aa003049e2'
$rights = [System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectoryRights]::CreateChild -bor [System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectoryRights]::Delete
$rule = New-Object System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectoryAccessRule($groupSID, $rights, 'Allow', $ComputerObjectGUID, 'All')
$acl = Get-ACL "AD:\$OU"
$acl.AddAccessRule($rule)
Set-ACL "AD:\$OU" $acl
Using ADManager Plus
Alternatively, script-free tools like ADManager Plus can be used to do the same with just a few clicks:
Moving users across domains requires trust and migration tools (such as AD Migration Tool (ADMT) or PowerShell) or click-and-go interface tools (like ADManager Plus) as ADUC alone cannot handle password, security identifier (SID ) history, or domain-specific attribute replication.
Using ADMT
Using PowerShell
For cross-domain or cross-forest migration, you can use an export and import approach.
Get-ADUser -Filter * -Properties * | Export-Csv C:\Temp\Users.csv -NoTypeInformation
Import-Csv C:\Temp\Users.csv | ForEach-Object {
New-ADUser -Name $_.Name -SamAccountName $_.SamAccountName -UserPrincipalName $_.UserPrincipalName -Path $_.OU -GivenName $_.GivenName -Surname $_.Surname -AccountPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString $_.Password -AsPlainText -Force) -Enabled $true
}
Using ADManager Plus
For a script-free, user-friendly option: