Executing Program
You can configure Applications Manager to automatically trigger scripts/programs/server commands when an alarm is generated. This will help minimize manual intervention in resolving system/application issues.
This document covers:
Configuring Execute Program Action
To execute a program, follow these steps:
- Select the New Action link from the top menu.
- Click Execute Program from the Actions in the left frame and specify the following details:
- Enter the Display Name for the action.
- Choose whether the program to be executed is from the local server or from a remote server.
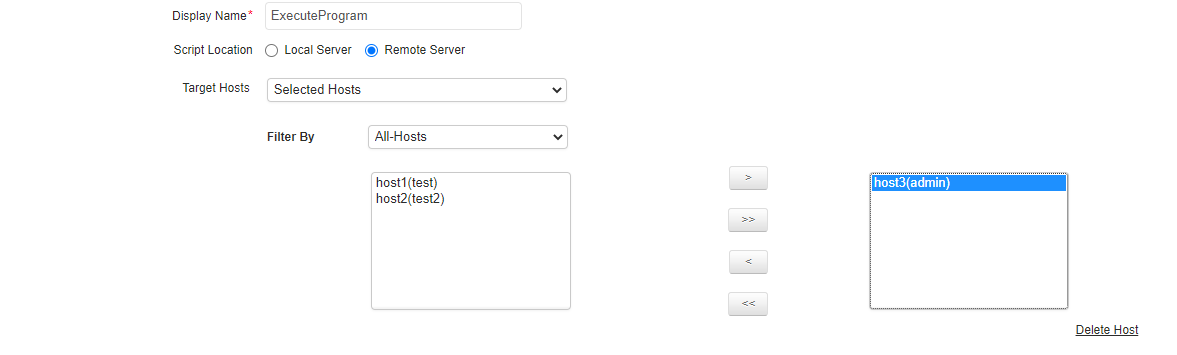
- If the program is in a remote server, specify the Target Hosts on which these actions are to be executed. There are three options available here:
- Auto-select Hosts: This option will automatically detect and trigger Execute Program action based on the associated monitor. For example, if the action is associated with a host, the action will be triggered for that particular host. If the action is associated with a Tomcat monitor, this action will be triggered for the host of the Tomcat server.
- Selected Hosts: This option lets you specify the exact hosts on which the action will be triggered. You can select the hosts from the ones listed.
- All Hosts in the selected Monitor Group: This option lets the action to be triggered on the server monitor's hosts present in the Monitor Groups. You can select the Monitor Group from the ones listed.
Additionally, you can also choose to add a new host. For configuring a new host, enter the following details - Host Name / IP Address, Execution Mode (Telnet/SSH/Powershell), User Name and Password of the host, port number (Default Telnet port no: 23, SSH port no: 22) and then specify the command prompt value (for Telnet/SSH), which is the last character in your command prompt. Default value is $ and possible values are >, #, etc.
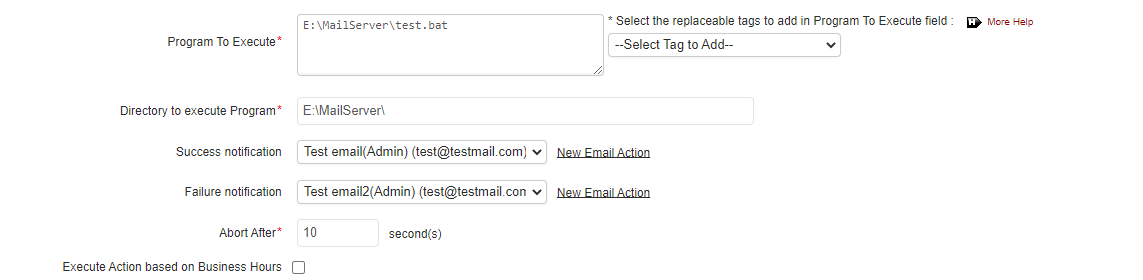
- Specify the program to be executed either as a command or as a script file. Make sure to implement the following methods if the program is to be executed as a script file:
- If the script file to be executed is located in a directory, then specify the script file name along with the absolute directory path.
- If the script file is to be executed from a remote Applications Manager server, it can be done easily by uploading the script file via Upload Files/Binaries option.
You can also make use of Replaceable Tags to provide additional arguments to the program specified in this field.
- Enter the directory path from which the script should be executed in the Directory to execute Program field.
- You can use the success and failure notification fields to receive response for both success or failure conditions of an action either by selecting an existing email address or by defining a new email address using the New Action link.
- The Abort after field is used to specify the timeout value for the program. Specify the time after which the program should be terminated.
Note: It is important to provide the required time for aborting the command execution since the alarm processing is held up by the program execution. That is, while executing the program, the command runs synchronously in the mail alarm processing thread. This will delay all the alarms, following the alarms being processed, until the program execution is completed or terminated.
- If you want to execute the action during specific time periods, enable the Execute Action based on Business Hours option and select the Business Hour during which the action has to be executed. The action can be configured such that it is executed during or outside the selected Business Hours. Use the drop-down menu to select your time window or click on 'Add New Business Hour' to create a new time window.
- Click Create Action to finish. This will list the Execute Program action name and its details along with the other actions configured.
View/Edit Execute Program Action
You can view and edit an existing Execute Program or execute that action from Admin tab > Actions page.
- To edit the action, click the Edit [
 ] icon.
] icon.
- You can also have a trial execution of the action. To do so, click the Execute icon [
 ] of that action.
] of that action.
Execute Program Usage
Pointers to where you can use Execute Program action
- Integrate a .vbs script to be executed by writing a simple .bat file. With this you can restart a remote service, reboot a machine etc.
- Execute custom actions like calling a python script or Java class etc.
- Invoke a .wav file to make some alarm noise on the server.
- Execute a script on a remote server.
- Trigger actions like cleaning up a hard disk when the usage exceeds some threshold limit.
Note: Passing arguments to custom scripts can be further enhanced by using Replaceable Tags.
Securing Execute Program Action
The Execute Program action option is designed to help users handle application problems and perform automated recovery actions with minimal manual intervention. While it enables quick response to alarms, its usage should be controlled to maintain system security.
Execute Program Action has the integrated ability to run scripts (including PowerShell scripts) and server commands based on the user privileges that run Applications Manager. Caution must be exercised with its usage. Some additional security and access control features include:
- Only users with Administrator or Delegated Administrator privileges are allowed to create or use Execute Program actions.
- Any Execute Program Action created by an Administrator or Delegated Administrator will remain disabled and in Pending Approval status until approved by a Super Administrator.
- Create, Edit, or Delete operations on Execute Program actions are audited, and details are available under Settings → Audit Logs.
- You can blacklist specific commands that are considered unsafe by adding them to the BlackListCommands.properties file located under <Applications Manager Home>\conf\. Learn more.
- Script uploads can be disabled under Settings → Server Settings → Enable file upload.
- Always verify scripts before running them and ensure they come from trusted sources to prevent unintended or malicious execution.
Local Server Execution
On performing Local execution in Applications Manager, the program or script runs on the same server as the service, inheriting its administrative privileges. This enables it to perform tasks with elevated access but also requires caution, as any unauthorized changes to the script could pose security risks.
Note: Running scripts with elevated privileges can pose security risks if unauthorized users modify them to perform malicious actions.
Remote Server Execution
When a script is executed on a remote server in Applications Manager, it operates with the privileges of the configured user account. This setup allows for controlled execution by limiting the script’s actions to those allowed by the assigned user permissions. By using this model, security risks are minimized, as scripts can only perform actions within the specific access rights of the user account, preventing unauthorized or potentially harmful actions from taking place outside the user’s designated privilege level.
Note: Running scripts with user-specific permissions on remote servers reduces security risks, as scripts cannot perform actions beyond the user’s authorized level.
Best Practices for Secure Script Execution
- Secure Script Execution: Apply security measures like access controls and regular audits to safeguard scripts.
- Monitor Script Execution: Consistently review execution logs for any suspicious activity.
- Secure Remote Configuration: Set up secure configurations, including access controls and firewall rules, on remote servers.
- User Account Permissions: Assign only the necessary permissions to the user account used for remote script execution.
- Monitor Remote Server Activity: Regularly inspect remote server logs to detect any unusual or unauthorized actions.
Note: Implement a privilege-based access control for scripts, ensuring they operate under the principle of least privilege. Scripts should execute with either administrative or specific user permissions, depending on the chosen execution mode, to enhance security and minimize potential risks.
Thank you for your feedback!

