How to enable MFA for local admin accounts and user accounts?
In this article:
Objective:
This article explains how to configure local user MFA for local user and admin accounts on Windows. MFA can be enabled for local accounts in machines that are part of a workgroup or an Active Directory domain.
What this article help the user accomplish?
- Enable MFA for local admin and user accounts that don't belong to enterprise's AD environment. Protect the local user account during logins into workgroup-joined and domain-joined machines
- Configure offline MFA and device-based machine MFA to protect local user accounts and business-critical machines during vulnerable scenarios.
- Setup the authenticators preferred by the organization for local user MFA.
- Enroll users using CSV files for complete feature rollout.
Why is it important?
Local Windows accounts—particularly local administrators—are decentralized and independent of AD authentication policies. Often used in high privilege scenarios like recovery, testing, high-security isolation, and emergency access, these accounts are risky, vulnerable entry points for attackers. Enabling MFA adds an extra layer of security for local user accounts and protects access to critical machines and accounts that are not part of the AD environment.
Prerequisites:
General
- Download and install ADSelfService Plus, then apply the Professional edition Endpoint MFA license.
- SSL must be enabled: Log in to the ADSelfService Plus web console with admin credentials. Navigate to the Admin tab > Product Settings > Connection. Select the ADSelfService Plus Port [https] option. Refer to this guide to learn how to apply for a SSL certificate and enable HTTPS.
- Access URL must be set to HTTPS: Navigate to Admin > Product Settings > Connection > Connection Settings > Configure Access URL and set the Protocol option to HTTPS.
- Please make sure that the login agent installed on your machines meets the required version: version 6.12 or above for Windows. If not, update the agent to the latest version by following these steps.
- To avoid users being locked out of their machines, ensure that the SSL certificate (self-signed or CA-signed) uploaded in ADSelfService Plus' connection settings is installed in the Trusted Root store on all relevant Windows workstations.
Prerequisites for offline MFA
- Offline MFA support requires the Professional Edition of ADSelfService Plus with Endpoint MFA.
- Offline MFA is supported only for Windows machines (except Windows 10 version 1803) and macOS logins. For remote logins, offline MFA is not supported for Windows RDP-client authentication.
- Please make sure that the login agent installed on your machines meets the required version: version 6.3 or above for Windows, and version 3.0 or above for macOS. If not, update the agent to the latest version by following these steps. If you have not installed the login agent yet, please configure offline MFA before doing so to ensure that the changes are updated.
Steps to enable MFA for local accounts
Step 1: Enable local user MFA
- Launch ADSelfService Plus and log in as an admin.
- Log into the ADSelfService Plus portal. Go to Configuration.
- Click Local User MFA settings and check the Enable Local User MFA option.
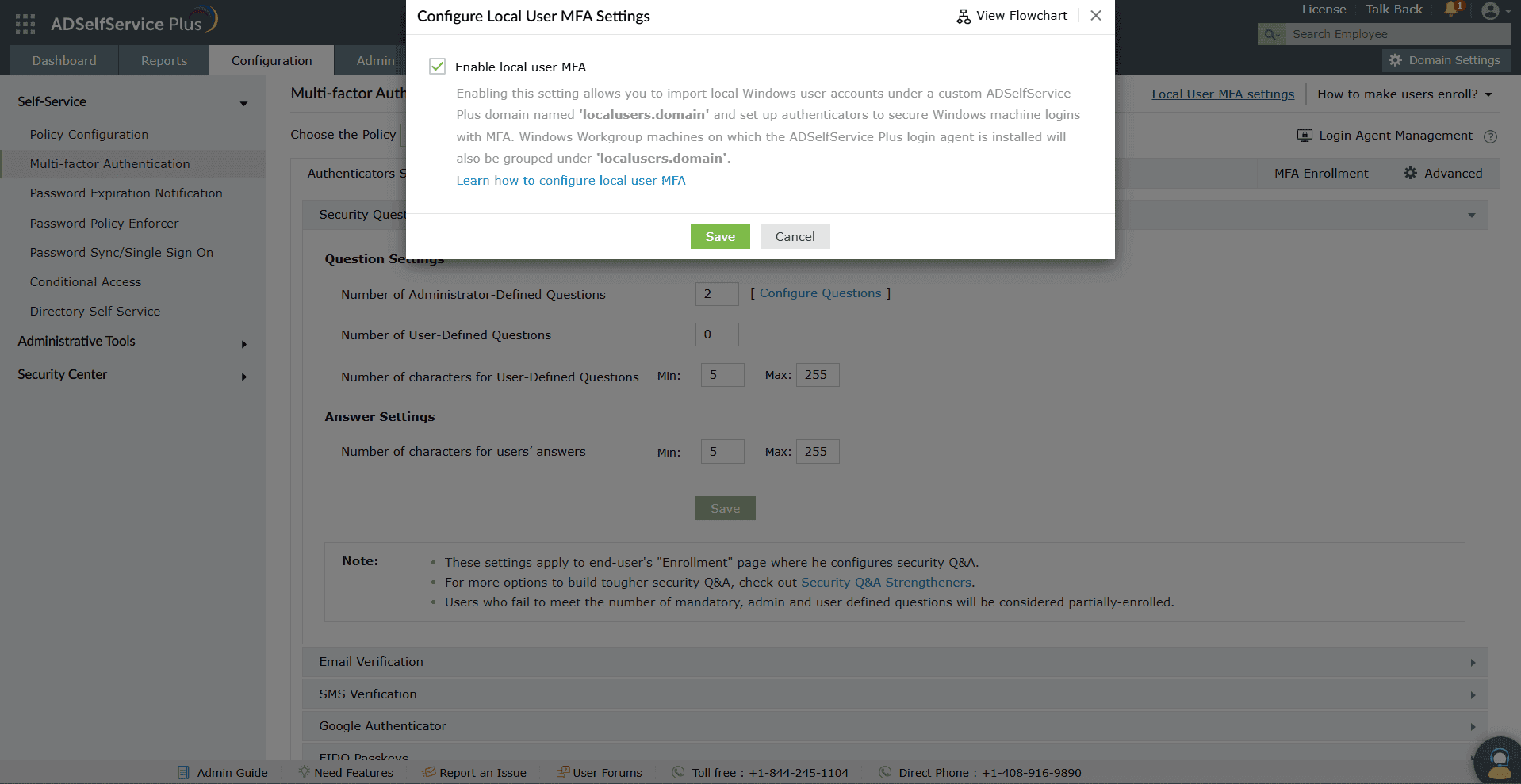
Figure 1. Local user MFA configuration
Step 2: Authenticator configuration
The required authenticators must be enabled based on their organizational policies and user device configuration. To do so:
- Go to Configuration > Multi-factor Authentication > Authenticators Setup.
- Click on the Choose the Policy drop-down. Choose localusers.domain.
- Go to the Authenticators tab and enable the required authenticators.
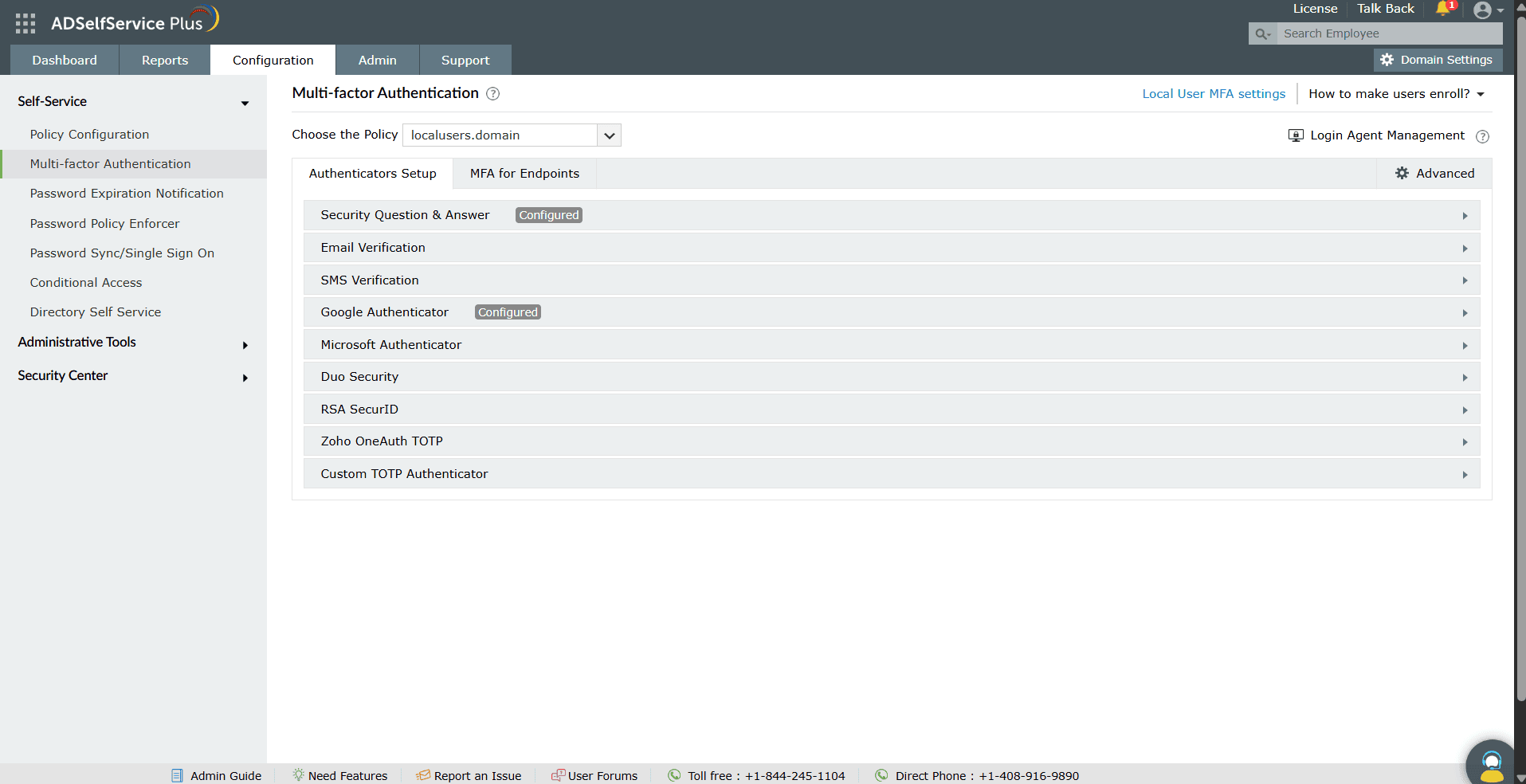
Figure 2. Authenticators setup for local user MFA
ADSelfService Plus supports the following authenticators for local user MFA:
- Security Questions and Answers
- Email Verification
- SMS Verification
- Google Authenticator
- Microsoft Authenticator
- Duo Security
- RSA SecurID
- Zoho OneAuth TOTP
- Custom TOTP Authenticator
For offline local user MFA:
- Google Authenticator
- Microsoft Authenticator
- Zoho OneAuth TOTP
- Custom TOTP Authenticator
For steps on enabling the authentication methods, refer to the Authenticators section.
Step 3: MFA configuration
Next, enable MFA for Windows accounts in the ADSelfService Plus portal by following these steps:
- Go to Configuration > Multi-factor Authentication.
- Click on the Choose the Policy drop-down. Choose localusers.domain.
- Go to the MFA for Endpoints tab.
- In the MFA for Machines section, select the Enable _ authentication factor(s) for machine logins checkbox. Use the drop-down provided to select the number of authentication factors to be prompted during logins.
- Use the Choose Authenticators for Machine logins drop-down to select the required authenticators configured in step 1.
- If you want to enable offline local user MFA, select the Choose authenticators for offline MFA checkbox and select the required authenticators from the drop-down.
- Click Save Settings.
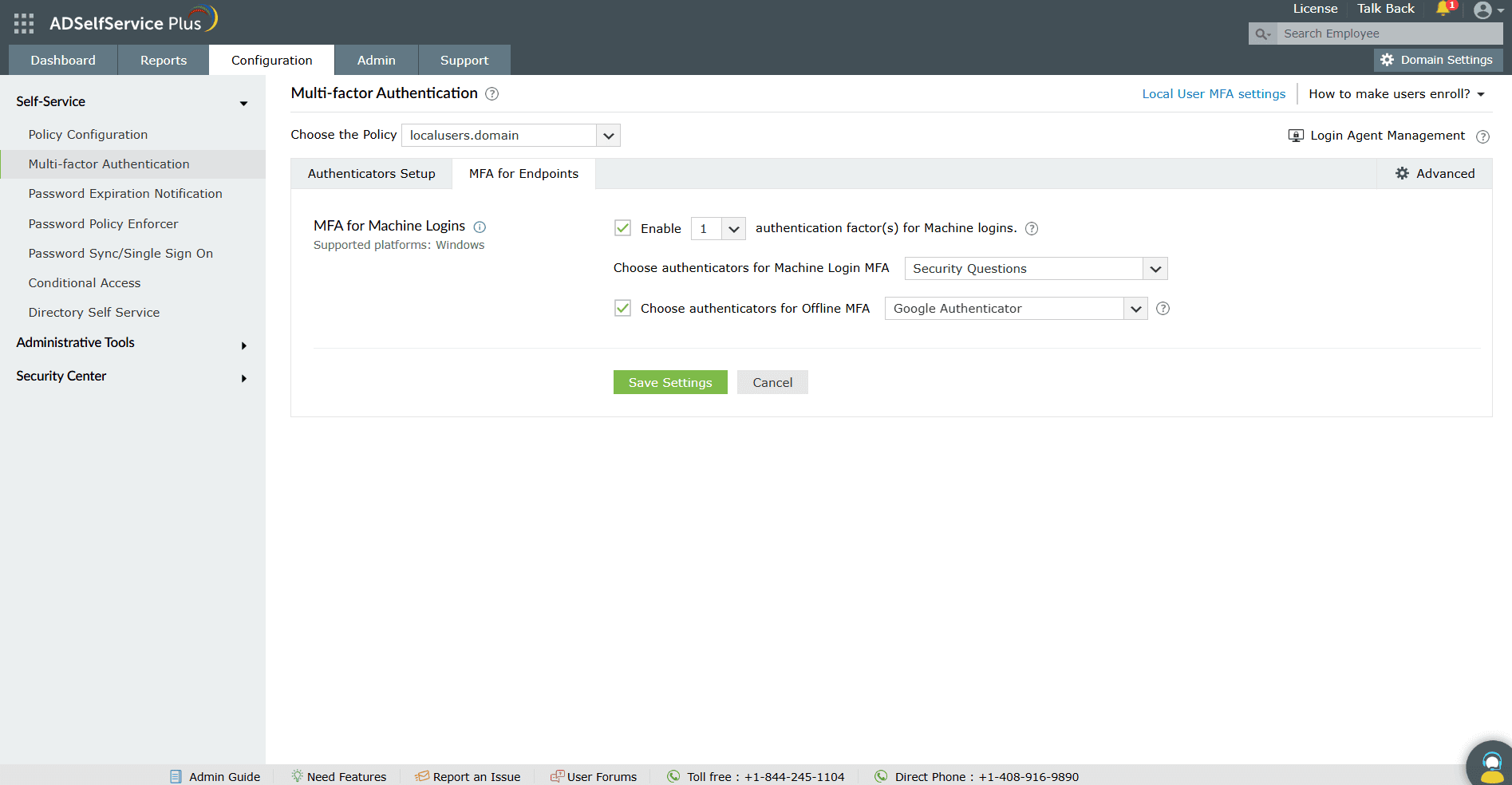
Figure 3. Selecting authenticators for local user MFA and offline local user MFA.
To configure MFA for local users during UAC prompts, RDP logins, and system unlocks:
- Click Advanced. Go to the Endpoint MFA tab.
- Use the drop-down provided for the Enable MFA for _ checkbox to select User Account Control and System unlocks.
- Select the Enable MFA for Remote Desktop access during RDP server authentication checkbox.
- Click Save.
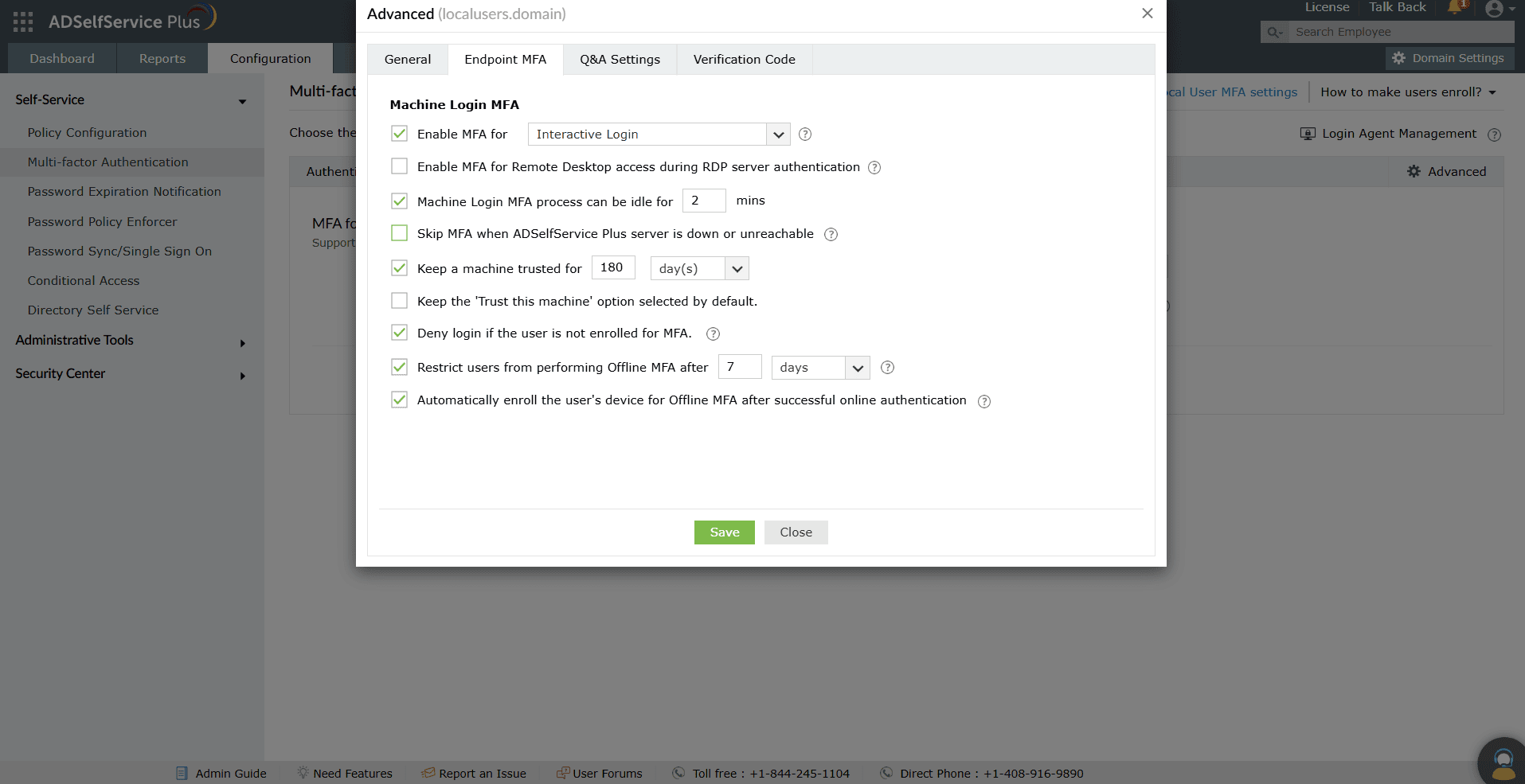
Figure 4. Policy-based RDP, UAC, and system unlocks MFA configuration for local user MFA.
To configure device-based local user MFA for machines:
- Navigate to Configuration > Administrative Tools > GINA/Mac/Linux (Ctrl+Alt+Del) > GINA/Mac/Linux Installation > Installed Machines.
- From the Select Domain drop-down, select Workgroup.
- Click Advanced Machine MFA Settings at the bottom-right of the page.
- Under Advanced Machine MFA Settings, select the Windows endpoints you wish to secure with MFA.
- Click Save to apply the new configuration.
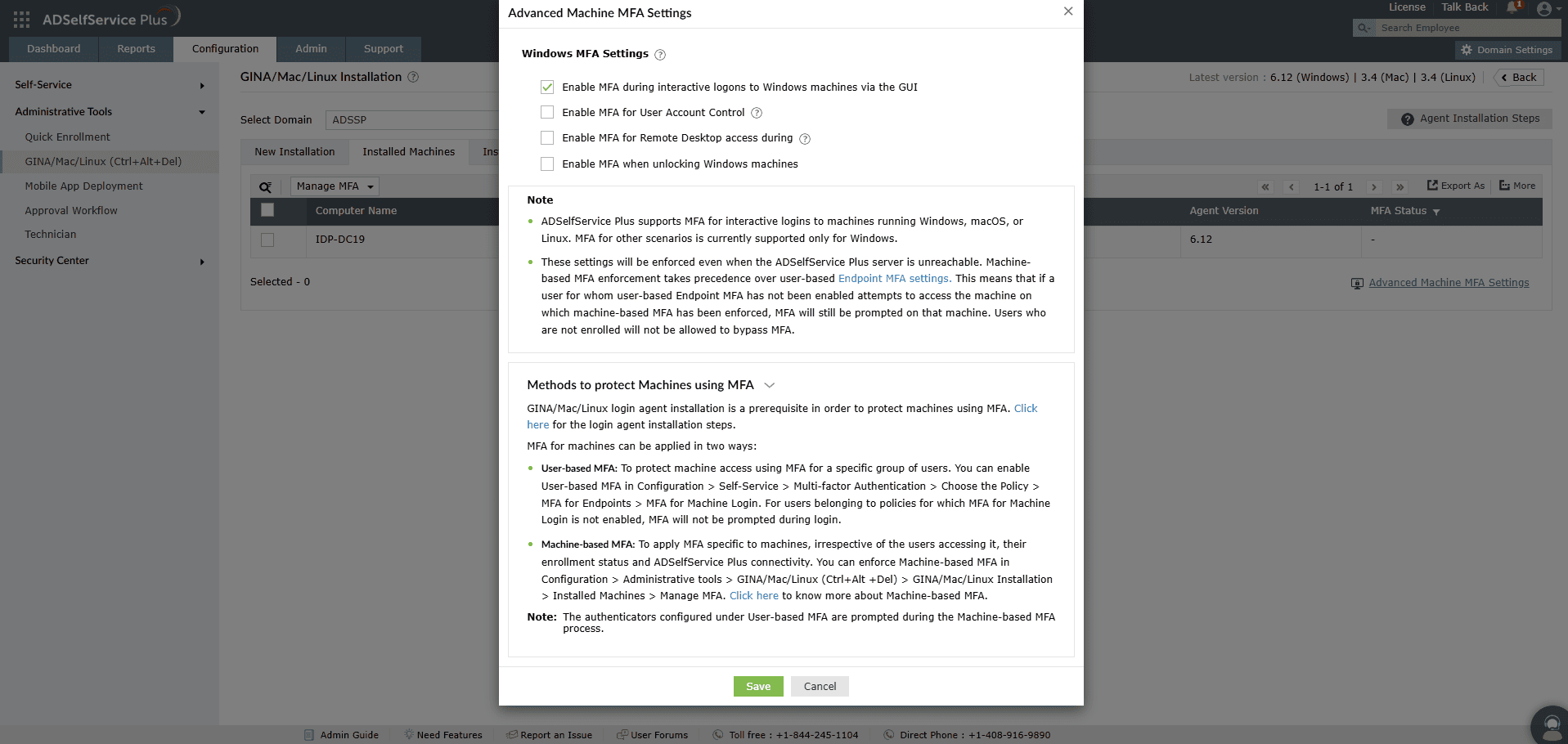
Fig 5. Enabling device-based local user MFA
Step 4. Local user enrollment
End-users must be enrolled with ADSelfService Plus to perform MFA during local user account access. Admins need to enroll the local users requiring MFA by uploading a CSV file with the list of users and their authentication information. Unlike domain users, local users cannot self-enroll with ADSelfService Plus.
Prerequisite: Ensure each local user enrolled under localuser.domain has a unique username.
- Log in to the ADSelfService Plus web console as an admin.
- Navigate to Configuration > Administrative Tools > Quick Enrollment, and click Import Enrollment Data from CSV File.
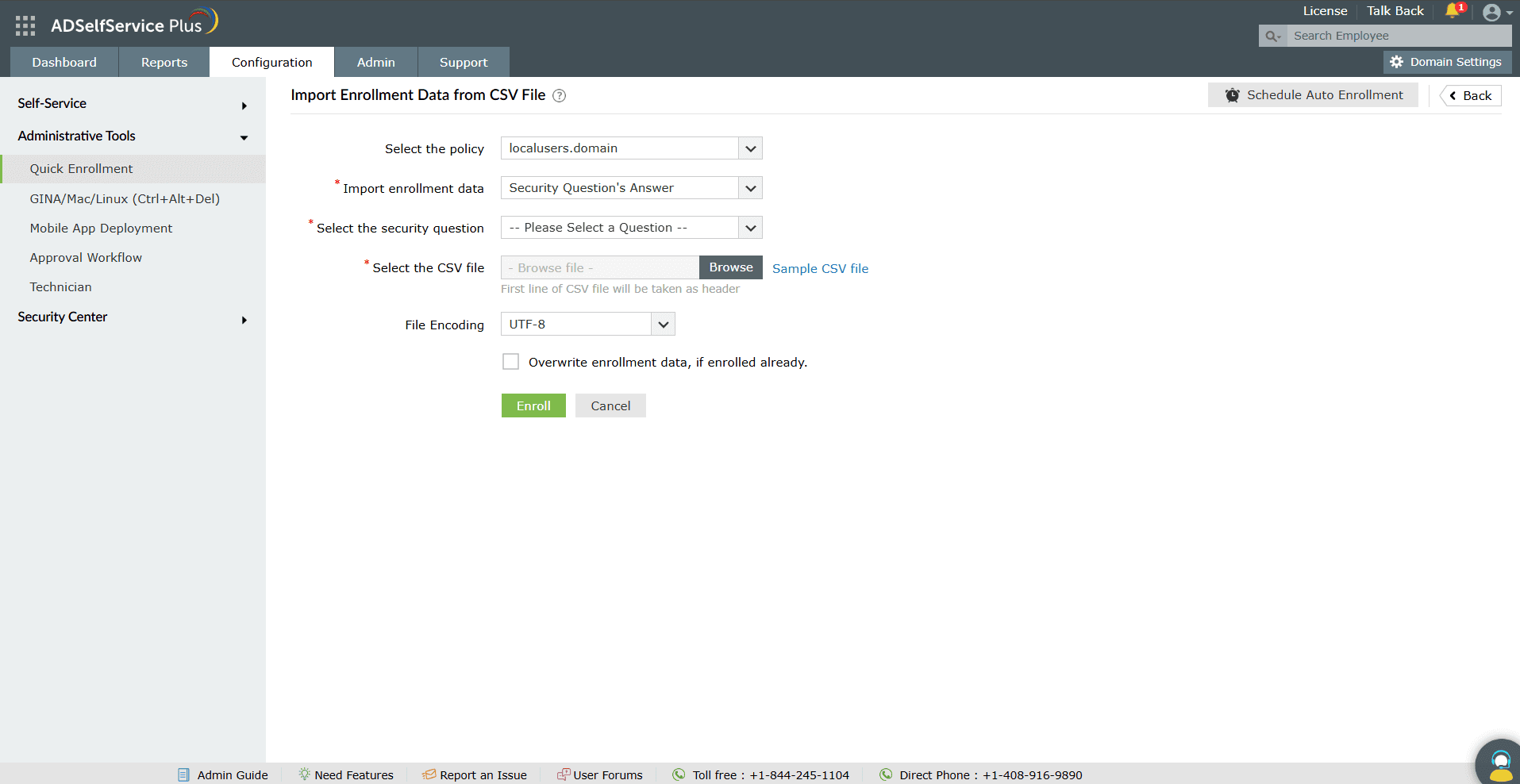
Figure 6. User enrollment for local user MFA by importing CSV file.
- Select the localusers.domain policy from the Select Policy drop-down.
Note: You can configure OU and group-based policies by going to Configuration > Self-Service > Policy Configuration. Using policies, you can enable forced enrollment for a specific group of users.
- Select the enrollment data you want to import from the Import drop-down. Please note that each authentication method requires different kinds of enrollment data.
Note: If the import data includes Email ID or Mobile Number, ensure that the number of secondary email addresses or secondary mobile numbers does not exceed the allowed limit. You will also need to ensure that the email addresses and mobile numbers are in the permitted formats.
Learn more.
- Select the security question if you have chosen to import only the answer.
- Click Choose File, and select the CSV file containing the enrollment data.
- Select the encoding standard supported by the CSV file from the File Encoding drop-down.
- Check the Overwrite enrollment data if enrolled already box if you want to overwrite users’ enrollment data.
- Click Enroll.
Step 5: Login agent installation
ADSelfService Plus' Windows login agent must be installed on the required end-user machines to configure local user MFA.
Login agent installation in workgroup machines
The Windows login agent can only be installed manually in workgroup machines. To view the complete installation steps:
- Launch ADSelfService Plus and log in as an admin.
- Navigate to Configuration > Administrative Tools > GINA/Mac/Linux (Ctrl+Alt+Del).
- Click Manual Installation Steps (GINA/MAC/Linux) to open the Manual Installation Steps pop-up.
- Follow the steps provided in the pop-up.
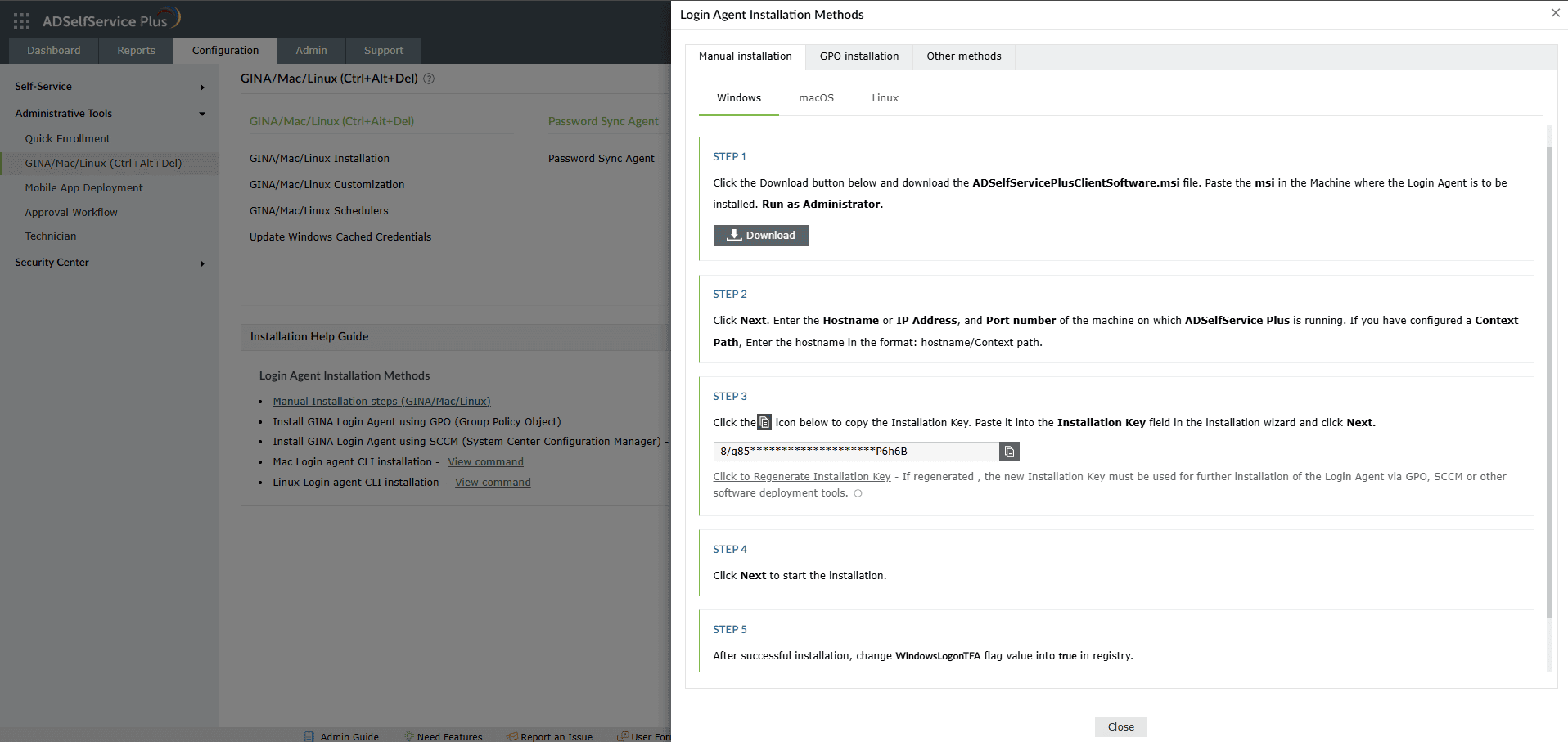
Figure 7. Manual login agent installation steps displayed in the GINA/Mac/Linux (Ctrl+Alt+Del) section.
Login agent installation in domain-joined machines
The Windows login agent can be installed by five methods in domain-joined machines:
- Installation from the ADSelfService Plus admin portal
- Manual installation
- Using GPO
- Using SCCM
- Using ManageEngine Endpoint Central
Validation and confirmation
To ensure that the local user MFA feature is properly configured:
- Generate the MFA Enrolled Users Report (Reports > MFA Reports > MFA Enrolled Users Report) for the domain localusers.domain and make sure all the enrolled users appear.
- View the Installed Machines report (Configuration > Administrative Tools > GINA/mac/Linux (Ctrl+Alt+Del) > GINA/mac/Linux Installation > Installed Machines)) and check the following:
- When localusers.domain is selected, the login agent-installed workgroup machines are listed with relevant details.
- When a configured domain is selected, the login agent-installed machines part of the domain are listed with relevant details.
- Access a login-agent installed machine to check whether the MFA process is triggered:
- If user-centric local user MFA is enabled, MFA is prompted when an enrolled user attempts to access the machine.
- If machine-centric local user MFA is enabled, MFA is prompted when any user, enrolled or not-enrolled, attempts an access the machine.
Best practices
To seamlessly and securely confgure local user MFA:
- Enroll all standalone user accounts for local user MFA to prevent any security gaps.
- Ensure your users can access the enabled authenticators.
- Safeguard the login agent installation key and prevent it from getting compromised. In case of a leak, regenerate the installation key and reinstall the login agent in the machines with the new key.
Related topics and articles
How to enable MFA for privileged users?
How to enable multi-factor authentication for RDP?
How to reach support
For any queries regarding setting up local user MFA for your enterprise, reach out to support@adselfserviceplus.com
Highlights of ADSelfService Plus
Allow Active Directory users to self-service their password resets and account unlock tasks, freeing them from lengthy help desk calls.
Get seamless one-click access to 100+ cloud applications. With enterprise single sign-on, users can access all their cloud applications using their Active Directory credentials.
Intimate Active Directory users of their impending password and account expiry via email and SMS notifications.
Synchronize Windows Active Directory user passwords and account changes across multiple systems automatically, including Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, IBM iSeries, and more.
Strong passwords resist various hacking threats. Enforce Active Directory users to adhere to compliant passwords by displaying password complexity requirements.
Enable Active Directory users to update their latest information themselves. Quick search features help admins scout for information using search keys like contact numbers.