With the sophistication of security breaches increasing every day, relying only on usernames and passwords to secure users' accounts is no longer an option. It's essential to add additional layers of security to filter out unauthorized users. This is possible using two-factor authentication (2FA), a method in which users' identities are verified with additional authentication methods like biometrics, Google Authenticator, and YubiKey.
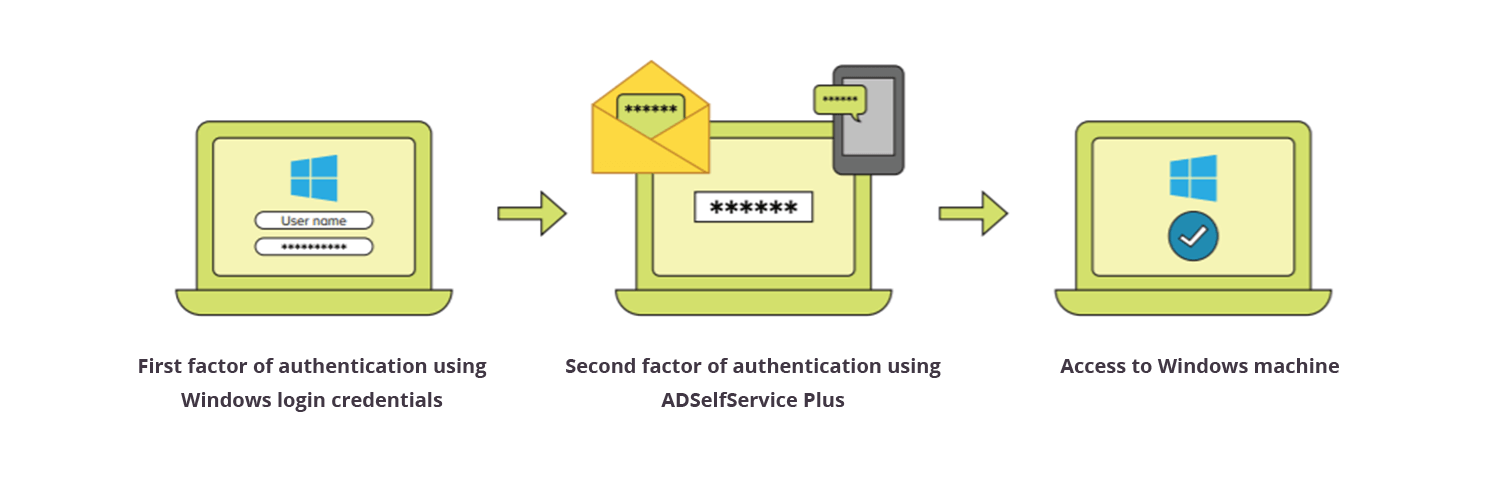
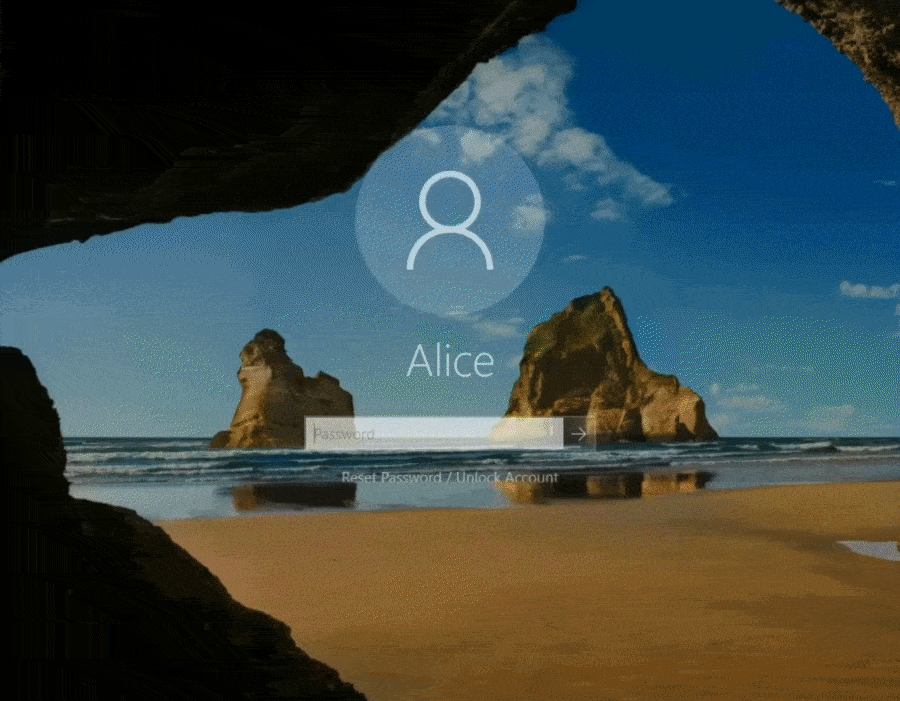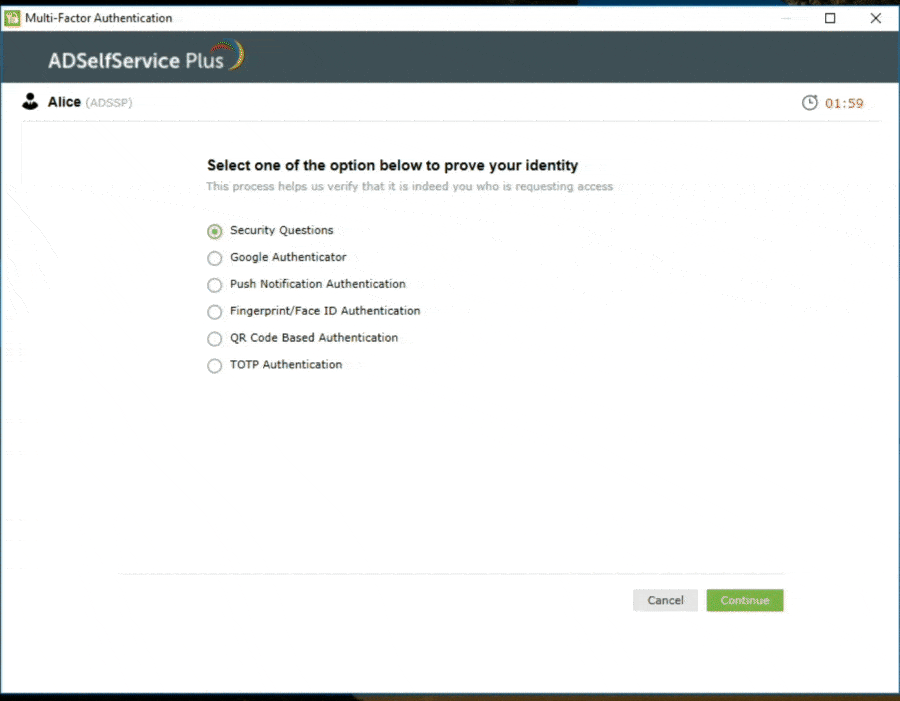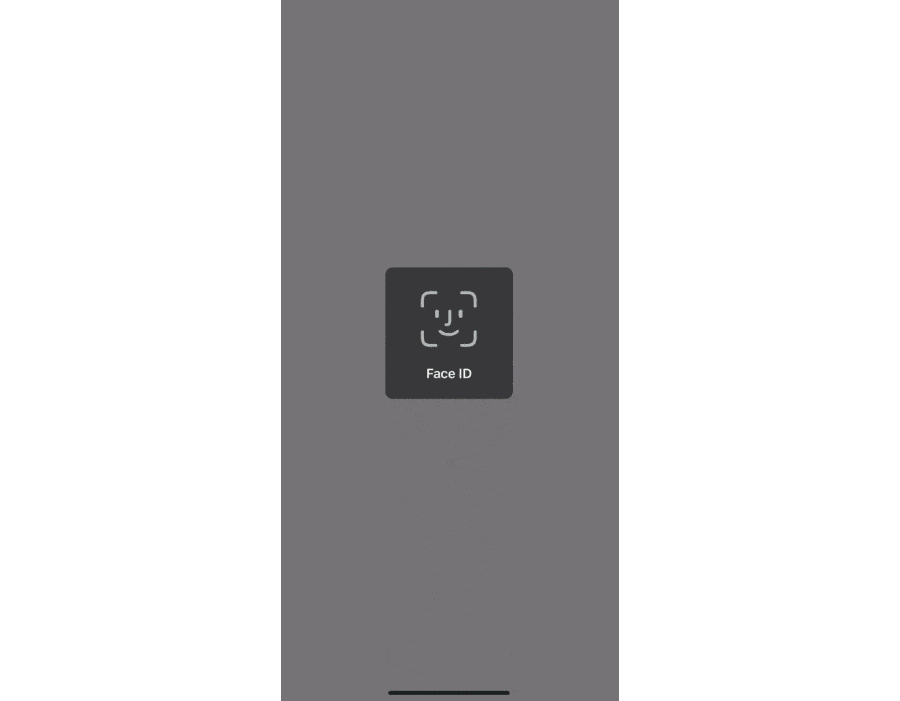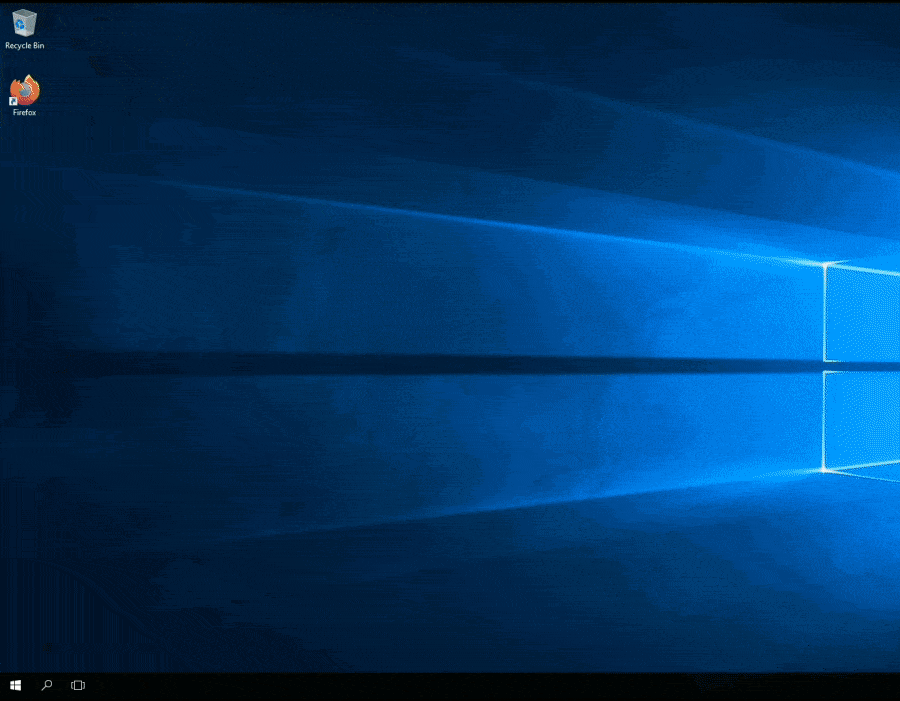
With ADSelfService Plus' 2FA for Windows logon feature enabled, users have to authenticate themselves in two successive stages to access their Windows machines. The first level of authentication happens using their usual Windows AD credentials. For the second level of authentication, admins can choose from the wide range of authentication factors that ADSelfService Plus offers, including the following:
Find the complete list of supported authenticators here.
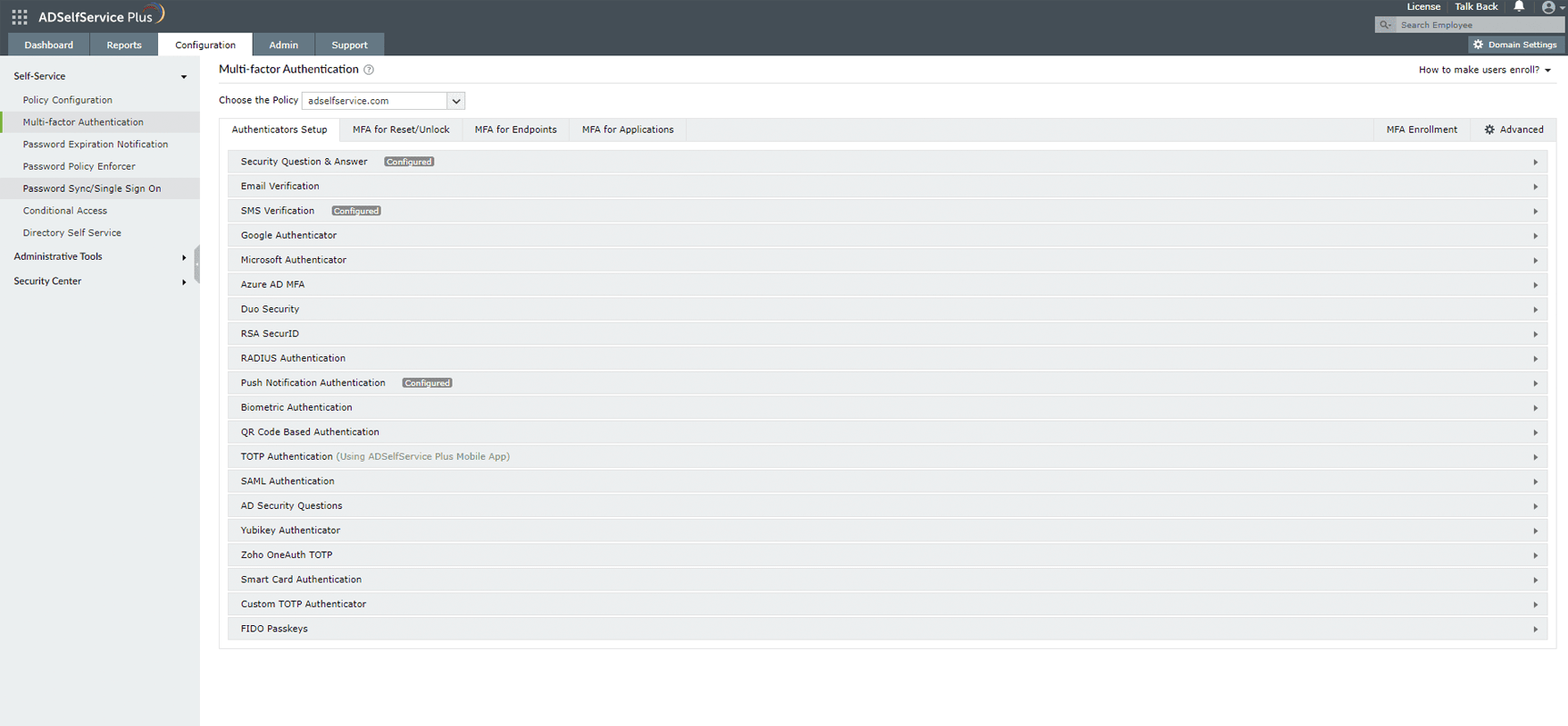
ADSelfService Plus offers 20 different authentication factors for admins to choose from. These ensure that even if an unauthorized user gains access to a user's credentials, they still cannot gain access to the user's machine.
Admins can customize ADSelfService Plus' Windows 2FA feature to suit their organization's needs as follows:
Machine-based 2FA is a feature that ADSelfService Plus offers in which 2FA is triggered during logon based on the device's policy settings and not the user's account settings. When this feature is enabled, all users logging on to a particular machine must prove their identities using 2FA. Admins can configure authentication methods for device-based 2FA from a range of authenticators similar to those available in ADSelfService Plus' Windows logon 2FA feature. Learn more
ADSelfService Plus provides 2FA for Windows User Account Control (UAC) to secure elevated system activities performed on standard user accounts. When this feature is enabled, 2FA will be prompted for all UAC credential prompts, and the user will be able to perform the administrative action only upon successful identity verification. ADSelfService Plus offers multiple authentication factors for Windows UAC 2FA. This feature is compatible with Windows 7 and later and Windows Server 2008 and later. Learn more
Offline 2FA is supported by ADSelfService Plus for Windows machines to ensure the security of remote workers and users who have no internet connectivity or when the ADSelfService Plus server is unreachable. Administrators can configure one or more 2FA factors that users can authenticate with during logon. Users are required to enroll in the appropriate authenticators while online, in order to access their machines when they are offline. Learn more
ADSelfService Plus provides 2FA for RDP, which secures remote Windows logons with additional authentication methods. It allows admins to prompt 2FA for RDP connections to the client machine (also known as the host machine) or the target machine. On enabling the RDP client-based 2FA, IP-based conditional access can be achieved for RDP logins. ADSelfService Plus allows admins to customize the authenticators to be prompted for RDP 2FA from the multiple authenticators it offers.
The following are the Windows operating system versions that the ADSelfService Plus login agent supports for Windows logon and RDP access.
Apart from the Windows operating system, ADSelfService Plus supports 2FA for macOS and Linux operating systems.
Windows 2FA ensures improved security, so that even if the passwords are compromised, unauthorized users will still need access to the email or phone of an authorized user to be able to log in to the Windows machines.
There are around twenty different authenticators in ADSelfService Plus, giving IT administrators a wide variety of options to choose from to set up an authentication mechanism for their users.
ADSelfService Plus also offers administrators the ability to configure 2FA based on users' OUs, groups, and domain memberships. So users with different privileges can have different levels of authentication.
With ADSelfService Plus, users can enable the trusted devices option to quickly log in to their machines without performing 2FA for a specified duration after initial identity verification.
Windows two-factor authentication (2FA) means securing logons to Windows machines using more than one factor of authentication to verify a user's identity before giving them network access.
Yes, by implementing 2FA for Windows logins, you can add extra layers of security to users' machines. Guarding machine logons using only a single factor—traditionally a username and password—leaves them vulnerable to attacks. However, incorporating additional authentication measures fortifies machines in your organization and safeguards them against breaches and attacks.
You can safeguard Windows machines in your organization by implementing ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus' Windows logon 2FA for local and remote logons. Apart from Windows machines, ADSelfService Plus provides 2FA for Linux and macOS machines as well. You can also enjoy other 2FA features of ADSelfService Plus, like:
To gain a better understanding of ADSelfService Plus' 2FA capability, please schedule a personalized web demo with our solution experts or download a free, 30-day trial to explore on your own.
ADSelfService Plus features 19 different authenticators for Windows logon 2FA. You can select from a range of authenticators, like YubiKey, biometrics, smart card, Microsoft Authenticator, and Duo Security, to provide additional security through Windows logon 2FA for your users.